Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1340-1348.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250521
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
Improvement effect of short-chain fatty acids on inflammation-induced autophagic damage in ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovary syndrome and its mechanism
- Department of Reproductive Medicine,Second Affiliated Hospital,Hainan Medical University,Haikou 570100,China
-
Received:2024-09-18Accepted:2024-12-14Online:2025-09-28Published:2025-11-05 -
Contact:Ying HU E-mail:zhe446@sina.com
CLC Number:
- R711.75
Cite this article
Ying HU,Yong HUANG. Improvement effect of short-chain fatty acids on inflammation-induced autophagic damage in ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovary syndrome and its mechanism[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(5): 1340-1348.
share this article
Tab.1
Primer sequences of RT-qPCR"
| Primer | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| TNF-α | F:CCTCTCTCTAATCAGCCCTCTGR:GAGGACCTGGGAGTAGATGAG |
| IFN-γ | F:GAGTGTGGAGACCATCAAGGAAGR:TGCTTTGCGTTGGACATTCAAGTC |
| IL-6 | F:ACTCACCTCTTCAGAACGAATTGR:CCATCTTTGGAAGGTTCAGGTTG |
| IL-18 | F:TGGCTGCTGAACCAGTAGAAR:ATAGAGGCCGATTTCCTTGG |
| GAPDH | F:CCAGGTGGTCTCCTCTGAR:GCTGTAGCCAAATCGTTGT |
Tab.3
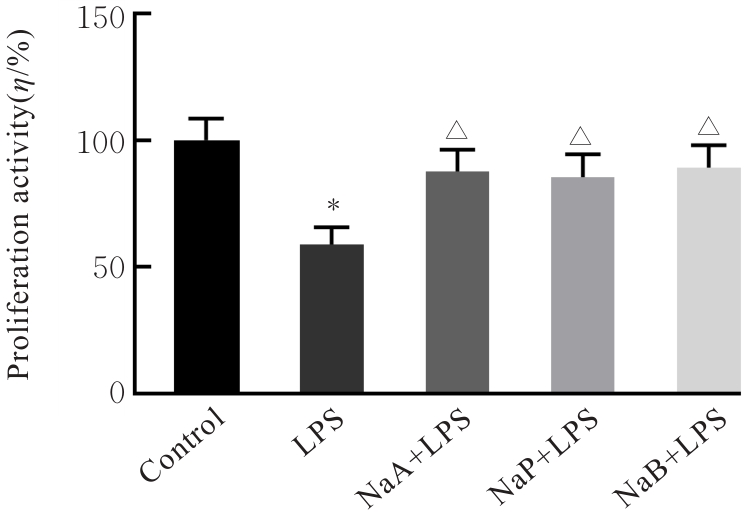
Proliferation activities of KGN cells after treated with different concentrations of NaA,NaP and NaB"
| Group | Proliferation activity |
|---|---|
| NaA (mmol·L-1) | |
| 0 | 100.00±11.07 |
| 6 | 99.61±10.25 |
| 12 | 99.02±9.53 |
| 24 | 98.86±10.85 |
| 48 | 98.57±10.32 |
| NaP (mmol·L-1) | |
| 0 | 100.00±10.55 |
| 6 | 99.86±10.14 |
| 12 | 99.25±10.19 |
| 24 | 98.73±9.96 |
| 48 | 98.49±9.87 |
| NaB (mmol·L-1) | |
| 0 | 100.00±10.81 |
| 6 | 99.75±10.22 |
| 12 | 99.46±10.10 |
| 24 | 98.60±9.88 |
| 48 | 98.51±10.03 |
Tab.5
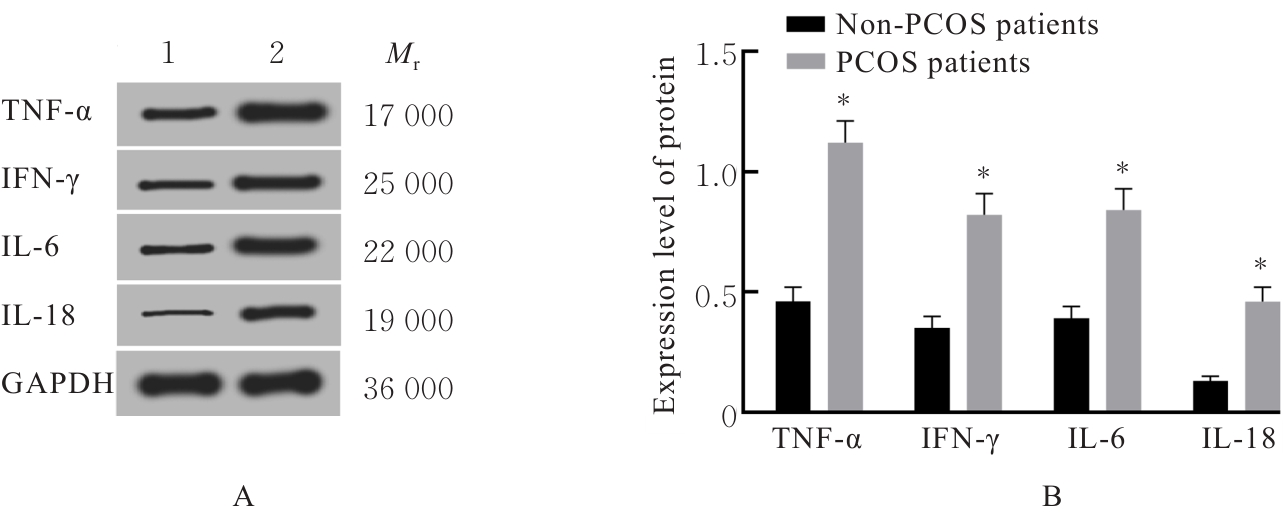
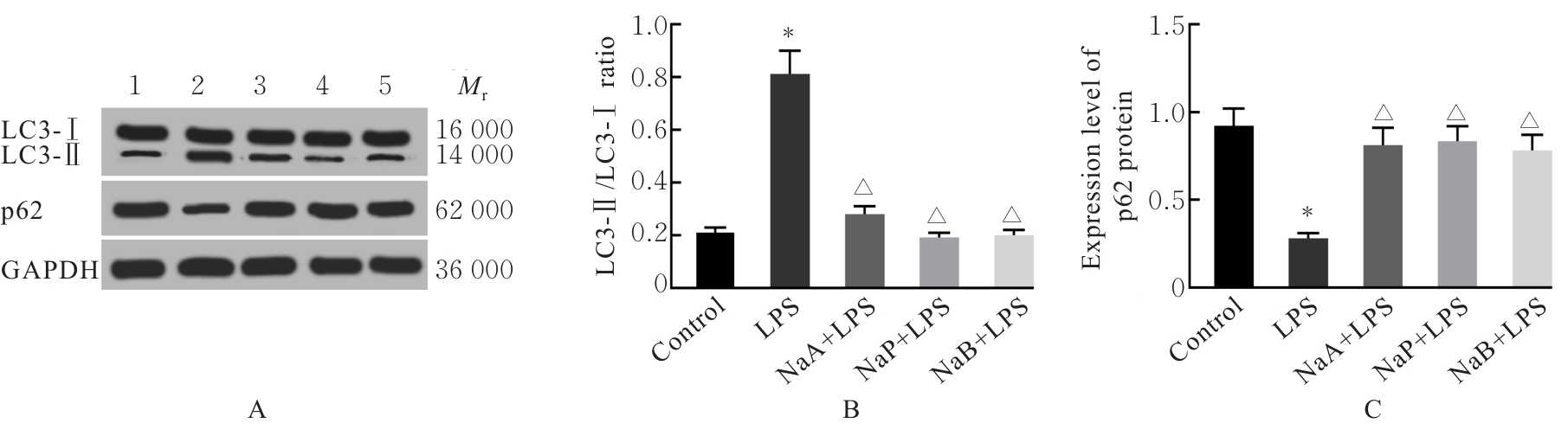
Expression levels of TNF-α,IFN-γ,IL-6 and IL-18 mRNA in KGN cells in various groups"
| Group | TNF-α | IFN-γ | IL-6 | IL-18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.06 | 1.00±0.07 | 1.00±0.04 |
| LPS | 2.26±0.25* | 1.89±0.21* | 1.69±0.18* | 1.88±0.20* |
| NaA+LPS | 1.36±0.15△ | 1.29±0.14△ | 1.19±0.13△ | 1.34±0.15△ |
| NaP+LPS | 1.28±0.13△ | 1.44±0.15△ | 1.10±0.12△ | 1.39±0.16△ |
| NaB+LPS | 1.33±0.14△ | 1.40±0.16△ | 1.23±0.13△ | 1.22±0.14△ |
| [1] | SHRIVASTAVA S, CONIGLIARO R L. Polycystic ovarian syndrome[J]. Med Clin N Am, 2023, 107(2): 227-234. |
| [2] | XIE Q, HONG W L, LI Y, et al. Chitosan oligosaccharide improves ovarian granulosa cells inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1086232. |
| [3] | 朱瑞可, 孙 婧, 史 昊, 等. 血清基础黄体生成素水平对多囊卵巢综合征患者卵泡期长效长方案助孕结局的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2024,59(6): 859-862. |
| [4] | ZHANG Q, REN J, WANG F F, et al. Mitochondrial and glucose metabolic dysfunctions in granulosa cells induce impaired oocytes of polycystic ovary syndrome through Sirtuin 3[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 187: 1-16. |
| [5] | JOZKOWIAK M, PIOTROWSKA-KEMPISTY H, KOBYLAREK D, et al. Endocrine disrupting chemicals in polycystic ovary syndrome: the relevant role of the theca and granulosa cells in the pathogenesis of the ovarian dysfunction[J]. Cells, 2022, 12(1): 174. |
| [6] | BARREA L, MARZULLO P, MUSCOGIURI G, et al. Source and amount of carbohydrate in the diet and inflammation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Nutr Res Rev, 2018, 31(2): 291-301. |
| [7] | LIU Y S, LIU H, LI Z T, et al. The release of peripheral immune inflammatory cytokines promote an inflammatory cascade in PCOS patients via altering the follicular microenvironment[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 685724. |
| [8] | TONG C, WU Y, ZHANG L L, et al. Insulin resistance, autophagy and apoptosis in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: Association with PI3K signaling pathway[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 1091147. |
| [9] | LUO X D, GONG Y Y, CAI L Y, et al. Chemerin regulates autophagy to participate in polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49(11): 3000605211058376. |
| [10] | HE J, ZHANG P W, SHEN L Y, et al. Short-chain fatty acids and their association with signalling pathways in inflammation, glucose and lipid metabolism[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(17): 6356. |
| [11] | 王 怡, 杨宏毅, 杨焕焕. 短链脂肪酸在多囊卵巢综合征发生发展中的作用[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2021, 12(4): 163-165. |
| [12] | 赵元元, 路军涛, 吴小华. 人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体miR-100对多囊卵巢综合征患者颗粒细胞炎症的影响[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版), 2023, 61(5): 51-58. |
| [13] | PATEL S. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), an inflammatory, systemic, lifestyle endocrinopathy[J]. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, 2018, 182: 27-36. |
| [14] | VELEZ L M, SELDIN M, MOTTA A B. Inflammation and reproductive function in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Biol Reprod, 2021, 104(6): 1205-1217. |
| [15] | RUDNICKA E, SUCHTA K, GRYMOWICZ M, et al. Chronic low grade inflammation in pathogenesis of PCOS[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(7): 3789. |
| [16] | 张梦蝶, 张欢欢, 肖成炜. 多囊卵巢综合征患者血清TNF-α改变和糖脂代谢异常关系的临床研究[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2023, 39(7): 1141-1144. |
| [17] | PENG Z, SUN Y F, LV X L, et al. Interleukin-6 levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(2): e0148531. |
| [18] | LI L S, ZHU J, YE F J, et al. Upregulation of the lncRNA SRLR in polycystic ovary syndrome regulates cell apoptosis and IL-6 expression[J]. Cell Biochem Funct, 2020, 38(7): 880-885. |
| [19] | ZHANG H Y, ZHU F F, ZHU Y J, et al. Effects of IL-18 on the proliferation and steroidogenesis of bovine theca cells: Possible roles in the pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2021, 25(2): 1128-1139. |
| [20] | 张丽娜, 王 娟, 姚 雪, 等. IFN-γ在多囊卵巢综合征中的表达及对卵巢颗粒细胞的影响[J]. 江苏大学学报(医学版), 2020, 30(6): 480-485. |
| [21] | BHARDWAJ J K, PALIWAL A, SARAF P, et al. Role of autophagy in follicular development and maintenance of primordial follicular pool in the ovary[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(2): 1157-1170. |
| [22] | ZHAO Y, ZHAO X X, JIANG T Y, et al. A retrospective review on dysregulated autophagy in polycystic ovary syndrome: from pathogenesis to therapeutic strategies[J]. Horm Metab Res, 2024, 56(8): 547-558. |
| [23] | POPELKA H, KLIONSKY D J. Structural basis for extremely strong binding affinity of giant ankyrins to LC3/GABARAP and its application in the inhibition of autophagy[J]. Autophagy, 2018, 14(11): 1847-1849. |
| [24] | LAMARK T, SVENNING S, JOHANSEN T. Regulation of selective autophagy: the p62/SQSTM1 paradigm[J]. Essays Biochem, 2017, 61(6): 609-624. |
| [25] | ZHANG M M, HU R N, HUANG Y J, et al. Present and future: crosstalks between polycystic ovary syndrome and gut metabolites relating to gut microbiota[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 933110. |
| [26] | ZHANG J C, SUN Z H, JIANG S M, et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis V9 regulates the secretion of sex hormones in polycystic ovary syndrome patients through the gut-brain axis[J]. mSystems, 2019, 4(2): e00017-19. |
| [27] | LIU K L, HE X, HUANG J Y, et al. Short-chain fatty acid-butyric acid ameliorates granulosa cells inflammation through regulating METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification of FOSL2 in polycystic ovarian syndrome[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2023, 15(1): 86. |
| [28] | OLANIYI K S, BASHIR A M, ARELOEGBE S E, et al. Short chain fatty acid, acetate restores ovarian function in experimentally induced PCOS rat model[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(7): e0272124. |
| [29] | ZHANG H L, WANG W, ZHAO J M, et al. Relationship between body composition, insulin resistance, and hormonal profiles in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023, 13: 1085656. |
| [30] | BULLETTI C, BULLETTI F M, SCIORIO R, et al. Progesterone: the key factor of the beginning of life[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(22): 14138. |
| [31] | FERREIRA S R, MOTTA A B. Uterine function: from normal to polycystic ovarian syndrome alterations[J]. Curr Med Chem, 2018, 25(15): 1792-1804. |
| [1] | Lulu FU,Yinggang ZOU,Xiaoyu ZHENG,Xueying ZHANG,Jingshun ZHANG,Min WANG,Qiang ZHANG,Lianwen ZHENG. Expression of placenta expressed transcription factor 1 in ovarian tissue of polycystic ovary syndrome rats and its effect on proliferation of rat ovarian granulosa cells [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(5): 1177-1184. |
| [2] | Xing YUE,Xuemei LI,Hanxiao ZHANG,Chuanyi ZUO,Lijuan ZHU,Jing LYU,Chengshun ZHANG,Xin CAO. Role of serum total bile acid level in development of arrhythmia in ApoE-/- mice [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(4): 879-886. |
| [3] | Xiaoxia HU,Yalong LI,Dongliang YANG,Bazeren LA,Xinyue LIU. Effect of high glucose on polarization of Raw264.7 macrophages in vitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 403-411. |
| [4] | Junjie JIANG,Hao WU,Kang HE,Zhiqiang SAN,Qing YANG,Hui LI,Na LI. Repair effect of ginseng polypeptide thermosensitive hydrogel on heat-induced skin injury in rats and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(2): 360-369. |
| [5] | Yanyan BAI,Yutong ZHOU,Haijuan SUI,Zhuo LIU. Improvement effect of asiatic acid on damage of lipopolysaccharide-induced hippocampum neuron in rats through Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 85-95. |
| [6] | Yinxia TAI,Han ZHANG,Lei YU,Xianchun ZHU. Changes in levels of inflammatory factors in gingival crevicular fluid of patients with periodontal disease before and after invisible appliance:A Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 182-190. |
| [7] | Jianfeng YAO,Peiya WU,Liying CHEN,Yanting WANG,Youxia LING,Xiaoyan CHEN,Wanzhen CHEN,Ping TAO,Rongfu HUANG,Youzhu LI. Effect of PTEN mRNA expression level in granulosa cells on follicular fluid hormone secretion in infertile patients with polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 164-171. |
| [8] | Xingqi SU,Lingmin ZHAO,Di MA,Jiulin YOU,Ying CHEN,Liangshu FENG,Jing WANG,Jiachun FENG,Chuan WANG. Analysis on correlation of cerebral infarct area with cytokines and immune status in patients with acute ischemic stroke [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(1): 124-132. |
| [9] | Haixia CHEN,Hongru LI,Jingyi LIU,Zhifang XU,Shuwen LIU,Yuan YANG,Yang CHEN,Yu LUO,Yinjie CUI. Research progress in changes of intestinal flora after spinal cord injury and their effects on spinal neuroinflammation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(6): 1751-1756. |
| [10] | Haoyu WANG,Yuqi WANG,Bingqian WANG,Jinhan NIE,Jiaqing YAN,Min HU. Inhibitory effect of mesalazine on pro-inflammatory factors and peroxides in RAW264.7 cells and its therapeutic effect on periodontitis model rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1250-1258. |
| [11] | Wenhui LIU,Miao YU,Ying GUO,Yupeng LIU,Yang XING,Xinyu HONG,Jiale CUI. Research progress in effect of CXC chemokine receptor 3 on occurrence and development of nervous system diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(5): 1474-1480. |
| [12] | Xiaoyu WANG,Bing LI,Guohui LIU. Research progress in application of inflammatory markers in diagnosis and treatment of coronary heart disease [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1173-1181. |
| [13] | Yiyan YU,Zhimin ZHANG,Jiawen CHEN,Xin LIU,Yan LI,Hongyan ZHAO. Research progress in relationship between macrophage polarization and oral diseases [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 864-871. |
| [14] | Shuang YANG,Na XU,Jianxu ZHANG,Chengbiao SUN,Yan WANG,Mingxin DONG,Wensen LIU. Improvement effect of rubusoside on motor dysfunction and neuroinflammation in mice with spinal cord injury and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(2): 326-335. |
| [15] | Yajie GE,Wen XU,Shimin GUAN,Lina WANG. Research progress in etiology and pathogenesis of polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 288-294. |
|
||