吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 1381-1389.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210850
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
RET/胶粉复合改性沥青制备及其混合料性能评价
- 长安大学 材料科学与工程学院,西安 710064
Preparation and evaluation of RET/rubber composite modified asphalt and asphalt mixture
Sui-ning ZHENG( ),Rui HE(
),Rui HE( ),Tian-yu LU,Zi-yi XU,Hua-xin CHEN
),Tian-yu LU,Zi-yi XU,Hua-xin CHEN
- School of Materials Science and Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
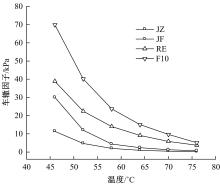
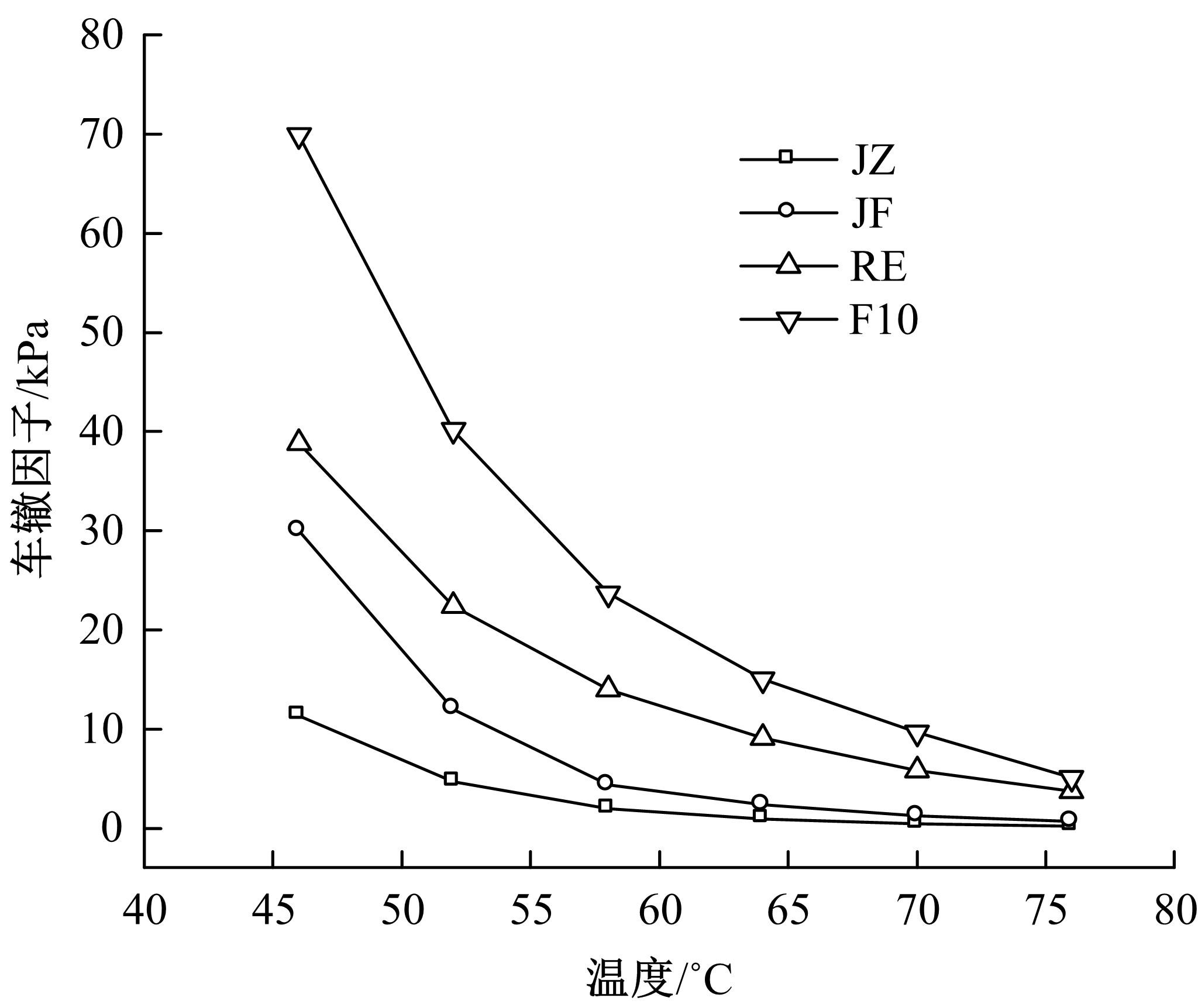
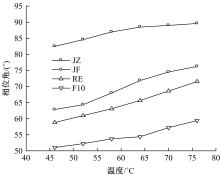
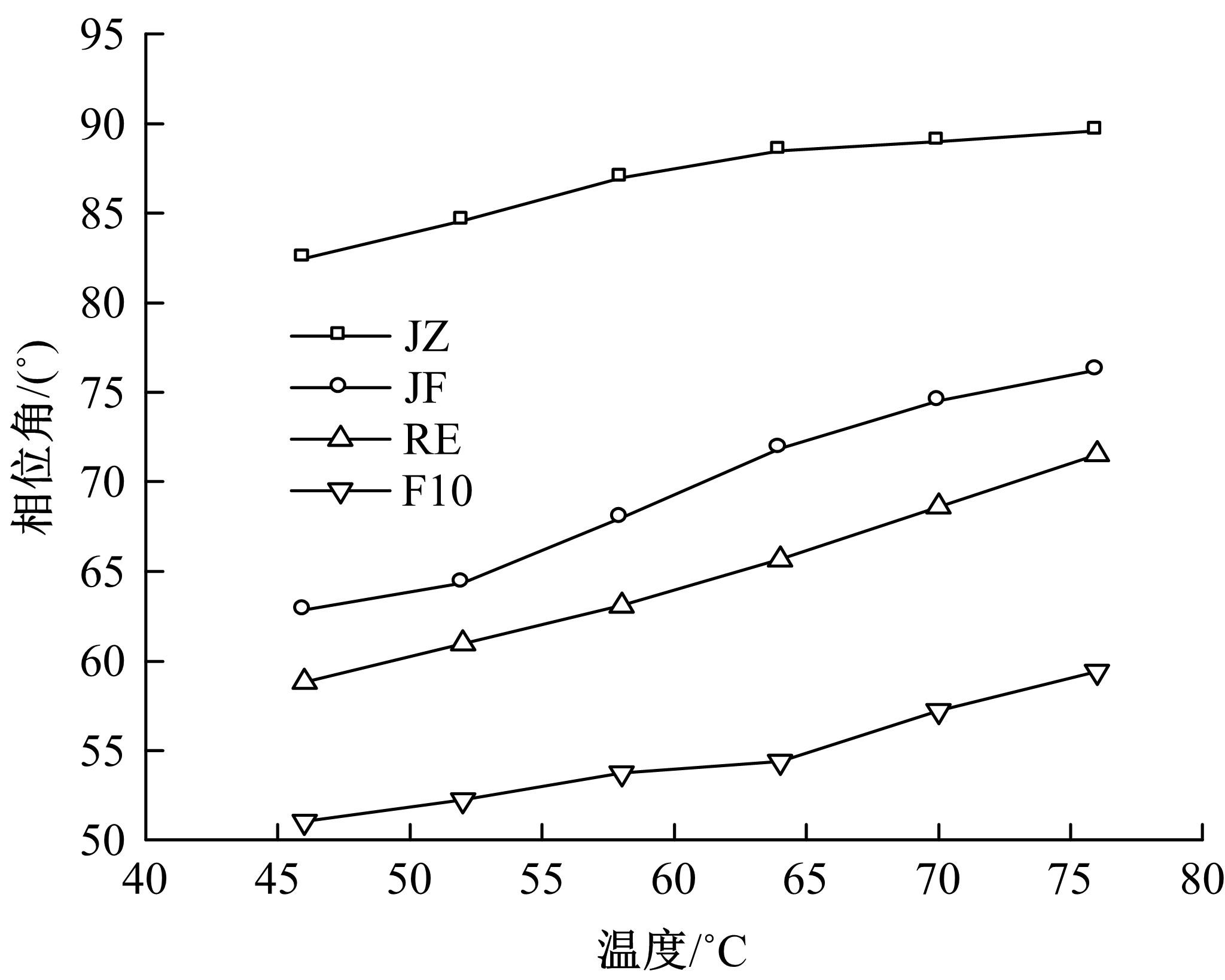
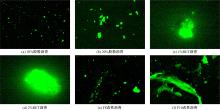
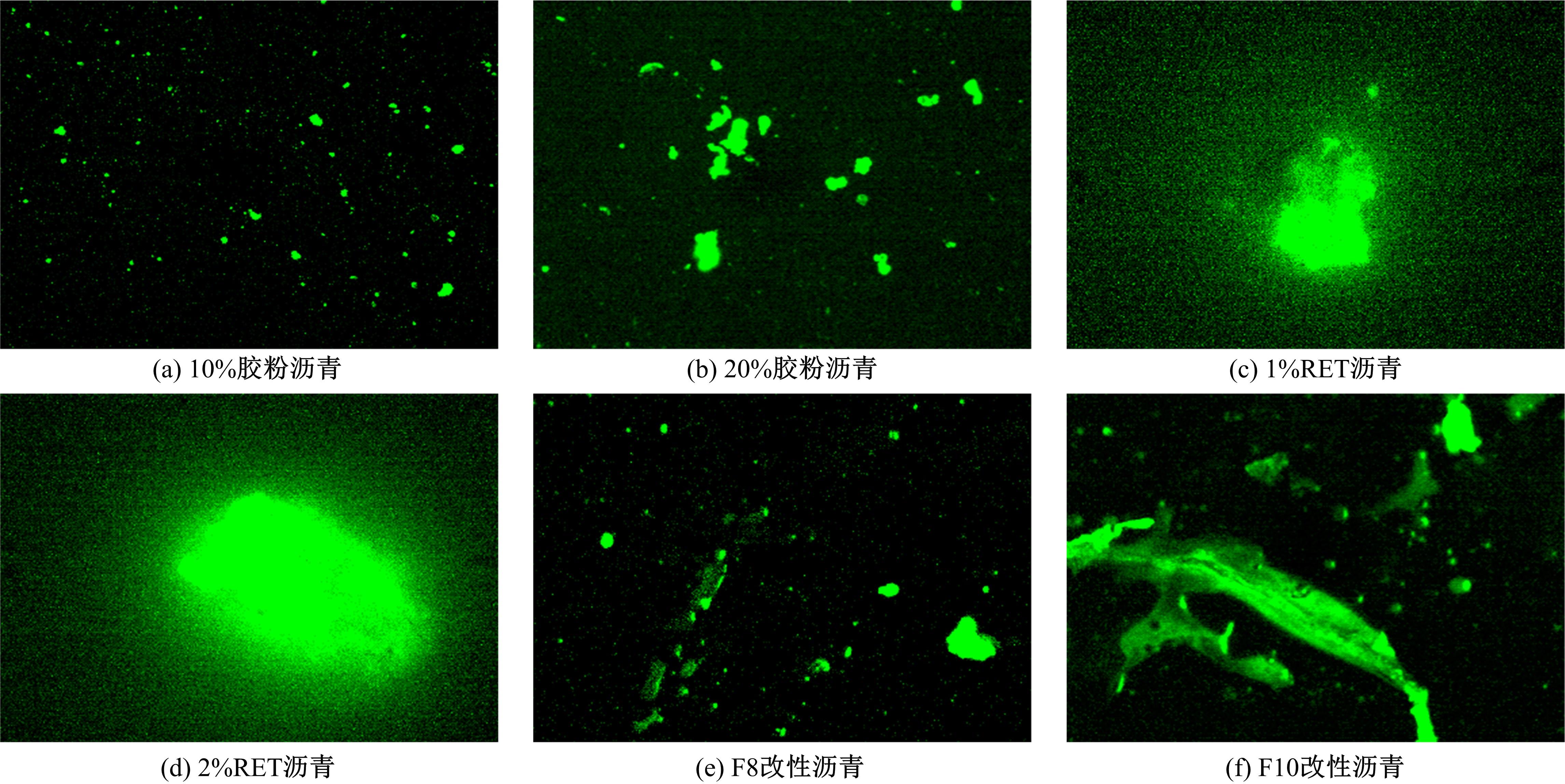
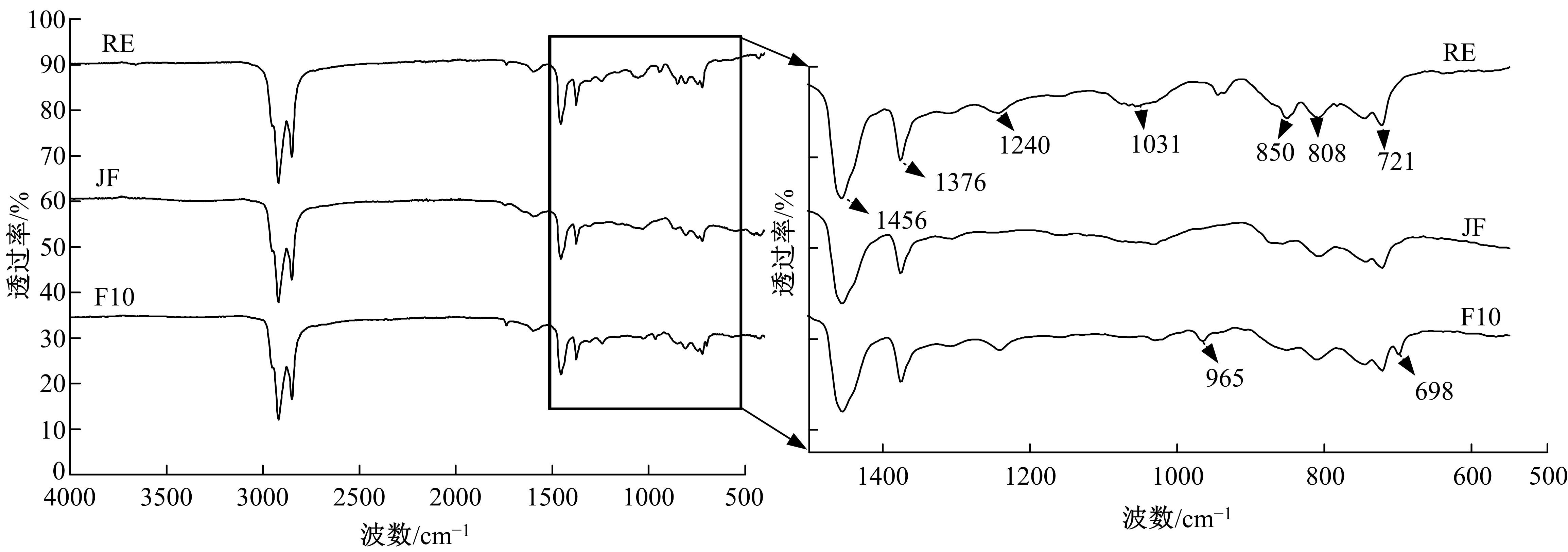
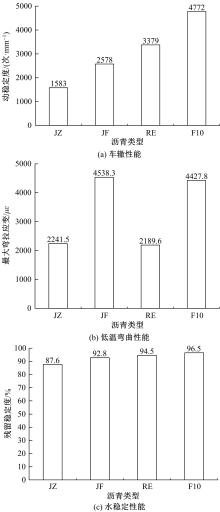
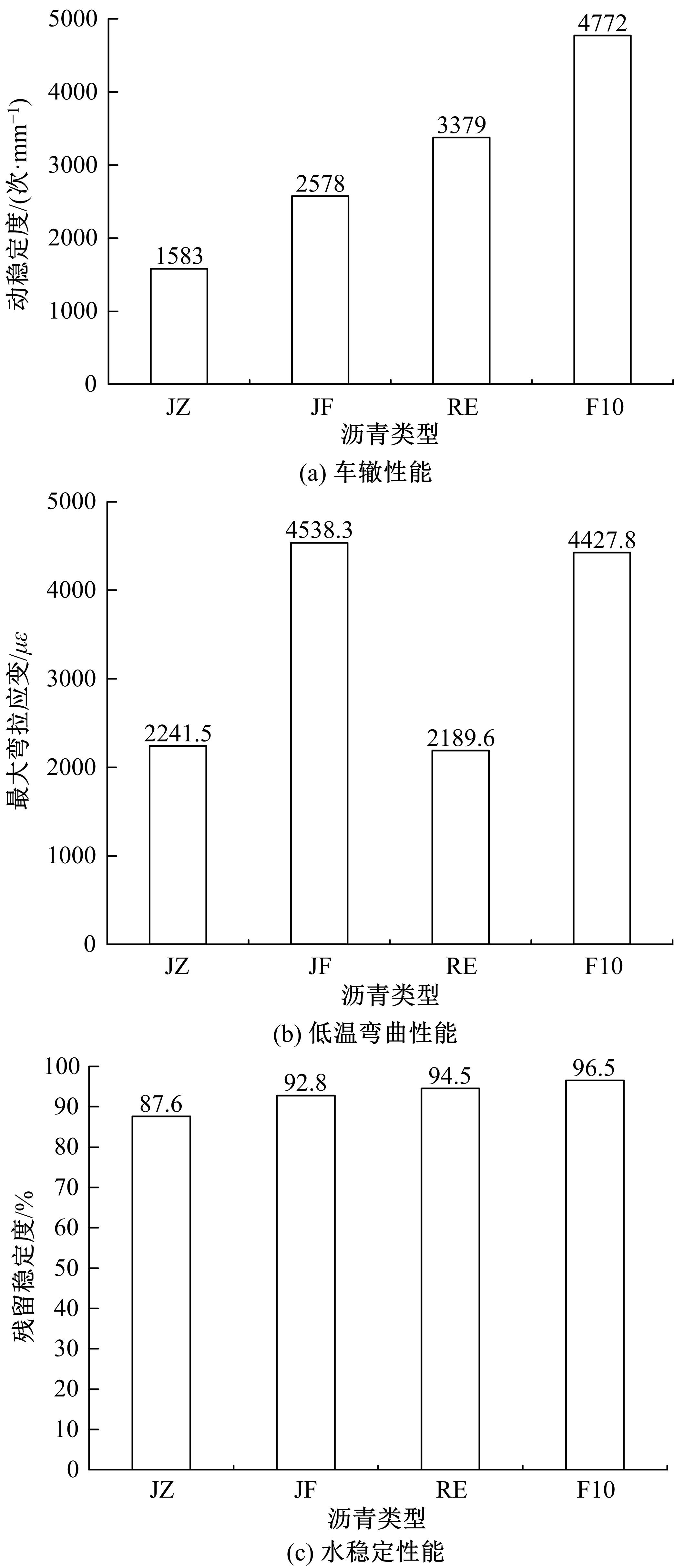
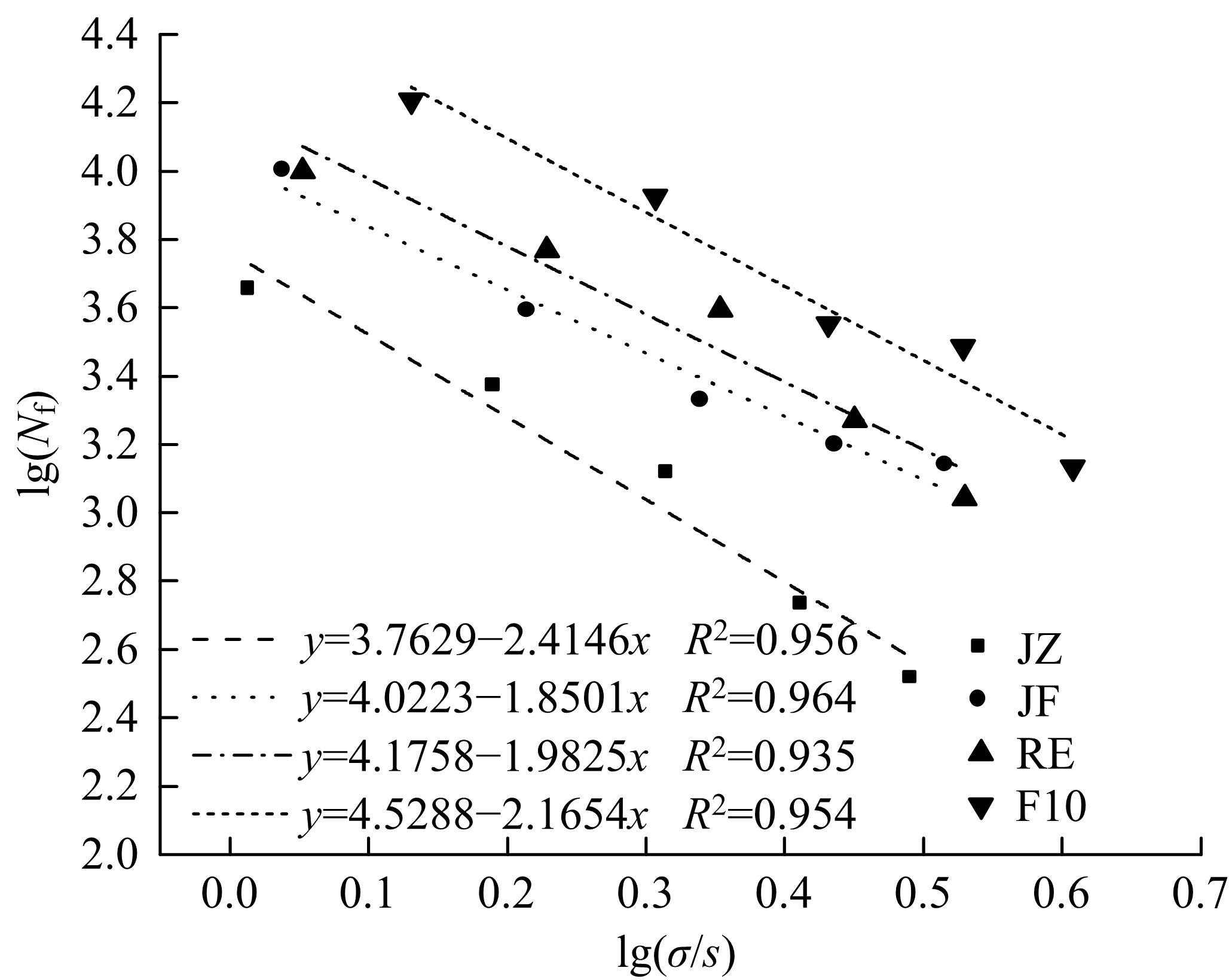
为确定反应性弹性体三元共聚物(RET)/胶粉复合改性沥青最佳组成配比,借助Design-Expert分析了RET、胶粉和油分掺量与沥青性能之间的定量关系,采用动态剪切流变仪、红外光谱仪和荧光显微镜探究了复合改性机理,并对复合改性沥青路用性能和疲劳性能进行了验证评价。结果表明:RET和胶粉掺量与改性沥青性能存在非线性函数关系,RET、胶粉和油分最佳掺量分别为沥青质量的1.69%、16.52%和1.83%;RET/胶粉复合体系可与沥青发生化学反应生成新的吸收峰,使改性剂与沥青之间的边界减弱,改善胶粉与沥青的相容性,提升RET沥青的低温性能,从而提高沥青混合料的路用性能。
中图分类号:
- U414
| 1 | Gama D A, Yan Y, Rodrigues J K G, et al. Optimizing the use of reactive terpolymer, polyphosphoric acid and high-density polyethylene to achieve asphalt binders with superior performance[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 169: 522-529. |
| 2 | Geckil T, Seloglu M. Performance properties of asphalt modified with reactive terpolymer[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 173: 262-271. |
| 3 | Singh D, Ashish P K, Changder R S, et al. Effect of warm-mix additives and lime on intermediate-temperature fracture property of RET-and PPA-modified asphalt binder[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2019, 31(7): 04019112. |
| 4 | 郝培文,常睿,刘红瑛,等. 反应性弹性体三元共聚物改性沥青及其混合料性能与机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7): 1952-1962. |
| Hao Pei-wen, Chang Rui, Liu Hong-ying, et al. Mechanism and performance of reactive elastomeric terpolymer modified asphalt and asphalt mixture[J]. Acta Materiae Composite Sinica, 2018, 35(7): 1952-1962. | |
| 5 | Keyf S, Ismail O, Corbacioglu B D. Polymer-modified bitumen using ethylene terpolymers[J].Petroleum Science and Technology, 2007, 25(7): 915-923. |
| 6 | 王大伟. RET改性沥青及其混合料的技术特性试验研究[D]. 重庆:重庆交通大学土木工程学院, 2013. |
| Wang Da-wei. Experimental research on technical characteristics of RET modified asphalt and asphalt mixture[D]. Chongqing: School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2013. | |
| 7 | Xu C, Zhang Z, Liu F. Improving the low-temperature performance of RET modified asphalt mixture with different modifiers[J]. Coatings, 2020, 10(11): 10111070. |
| 8 | 雷宁静. 废胶粉复合改性高黏沥青制备及其关键指标研究[D]. 西安:长安大学材料科学与工程学院, 2020. |
| Lei Ning-jing. Reserch on preparation and key evaluation index of high viscosity asphalt modified by crumb rubber[D]. Xi'an: School of Material Science and Engineering, Chang'an University, 2020. | |
| 9 | 刘耀辉,陈乔旭,宋雨来,等. 火山灰-SBS、胶粉-SBS和SBS改性沥青压缩变形行为及机理[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(6): 1861-1867. |
| Liu Yao-hui, Chen Qiao-xu, Song Yu-lai,et al.Compressive behavior and mechanism of volcanic ash-SBS, rubber powder-SBS and SBS modified asphalt[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(6): 1861-1867. | |
| 10 | Ren S, Liu X, Xu J, et al. Investigating the role of swelling-degradation degree of crumb rubber on CR/SBS modified porous asphalt binder and mixture[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 300: 124048. |
| 11 | Zheng W, Wang H, Chen Y,et al.A review on compatibility between crumb rubber and asphalt binder[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 297: 123820. |
| 12 | 曹支才,张宏亮.双螺杆挤出胶粉与RET复合改性沥青及其混合料性能研究[J].公路工程,2020,45(2): 156-162. |
| Cao Zhi-cai, Zhang Hong-liang. Study on properties of twin-screw extrusion crumb rubber powder and RET composite modified asphalt and asphalt mixture[J]. Highway Engineering, 2020, 45(2): 156-162. | |
| 13 | Ahmedzade P. The investigation and comparison effects of SBS and SBS with new reactive terpolymer on the rheological properties of bitumen[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 38: 285-291. |
| 14 | 常睿,郝培文. RET复配胶粉改性沥青流变特性与改性机理研究[J].材料导报, 2016, 30(24): 130-136. |
| Chang Rui, Hao Pei-wen. Rheological properties and modified mechanism of RET compound rubber modified asphalt[J]. Materials Review, 2016, 30(24): 130-136. | |
| 15 | 田迎春, 韩森. RET复配胶粉改性沥青混合料路用性能与耐久性研究[J]. 公路工程, 2019, 44(1): 171-178. |
| Tian Ying-chun, Han Sen. Study on road performance and durability of RET compounded rubber power modified asphalt and asphalt mixture[J]. Highway Engineering, 2019, 44(1): 171-178. | |
| 16 | Khairuddin F H, Alamawi M Y, Yusoff N I M, et al. Physicochemical and thermal analyses of polyurethane modified bitumen incorporated with cecabase and rediset: optimization using response surface methodology[J]. Fuel, 2019, 254: 115662. |
| 17 | He R, Zheng S, Chen H, et al. Investigation of the physical and rheological properties of trinidad lake asphalt modified bitumen[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 203: 734-739. |
| 18 | He R, Liang Y, Gao L, et al. Preparation and performance assessment of asphalt emulsion modified by the fabricated SBS latex[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020, 2020: 1-11. |
| 19 | Zhang F, Hu C. The research for SBS and SBR compound modified asphalts with polyphosphoric acid and sulfur[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2013, 43: 461-468. |
| 20 | He R, Wu S, Wang X, et al. Temperature sensitivity characteristics of SBS/CRP-modified bitumen after different aging processes[J]. Materials, 2018, 11(11): 11112136. |
| 21 | Fang C, Guo N, You Z, et al. Investigating fatigue life prediction of rubber asphalt mixture based on damage evolution using residual strain analysis approach[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 257: 119476. |
| [1] | 关博文,邸文锦,王发平,吴佳育,张硕文,贾治勋. 干湿循环与交变荷载作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1112-1121. |
| [2] | 杨帆,李琛琛,李盛,刘海伦. 温缩作用下双层连续配筋混凝土路面配筋率设计参数对比分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1122-1132. |
| [3] | 魏海斌,马子鹏,毕海鹏,刘汉涛,韩栓业. 基于力学响应分析方法的导电橡胶复合路面铺装技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 531-537. |
| [4] | 刘状壮,张有为,季鹏宇,Abshir Ismail Yusuf,李林,郝亚真. 电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 523-530. |
| [5] | 郭庆林,刘强,吴春利,李黎丽,李懿明,刘富春. 导电沥青及混合料裂缝局部温度场及愈合效果[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1386-1393. |
| [6] | 时成林,王勇,吴春利,宋文祝. 路堤挡土墙主动土压力计算方法修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1394-1403. |
| [7] | 姚玉权,仰建岗,高杰,宋亮. 基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
| [8] | 夏全平,高江平,罗浩原,张其功,李志杰,杨飞. 用于高模量沥青砼的复合改性硬质沥青低温性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [9] | 叶奋,胡诗园. 考虑旧水泥路面接缝传荷能力的超薄罩面力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2636-2643. |
| [10] | 于晓贺,罗蓉,柳子尧,黄婷婷,束裕. 沥青路面典型裂缝湿度场数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2343-2351. |
| [11] | 杨彦海,崔宏,杨野,张怀志,刘赫. 冻融循环作用对非饱和乳化沥青冷再生混合料性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2352-2359. |
| [12] | 冉武平,陈慧敏,李玲,冯立群. 干湿循环下粗粒土回弹模量演变规律及模型预估和修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2079-2086. |
| [13] | 董伟智,张爽,朱福. 基于可拓层次分析法的沥青混合料路用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2137-2143. |
| [14] | 许哲谱,杨群. 基于实时路况地图的短期养护作业开始时间优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1763-1774. |
| [15] | 文畅平,任睆遐. 基于Lade模型的生物酶改良膨胀土双屈服面本构关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1716-1723. |
|
||