吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 523-530.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210671
电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性研究
刘状壮1,2( ),张有为1,季鹏宇1,Abshir Ismail Yusuf1,李林1,郝亚真1
),张有为1,季鹏宇1,Abshir Ismail Yusuf1,李林1,郝亚真1
- 1.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710064
2.长安大学 特殊地区公路工程教育部重点实验室,西安 710064
Study on heat transfer characteristics of electric heating snow melting asphalt pavement
Zhuang-zhuang LIU1,2( ),You-wei ZHANG1,Peng-yu JI1,Abshir Ismail Yusuf1,Lin LI1,Ya-zhen HAO1
),You-wei ZHANG1,Peng-yu JI1,Abshir Ismail Yusuf1,Lin LI1,Ya-zhen HAO1
- 1.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.Key Laboratory of Special Area Highway Engineering,Ministry of Education,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
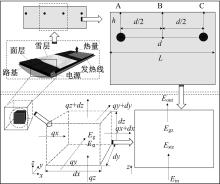
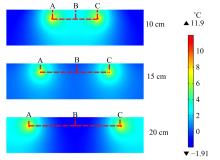
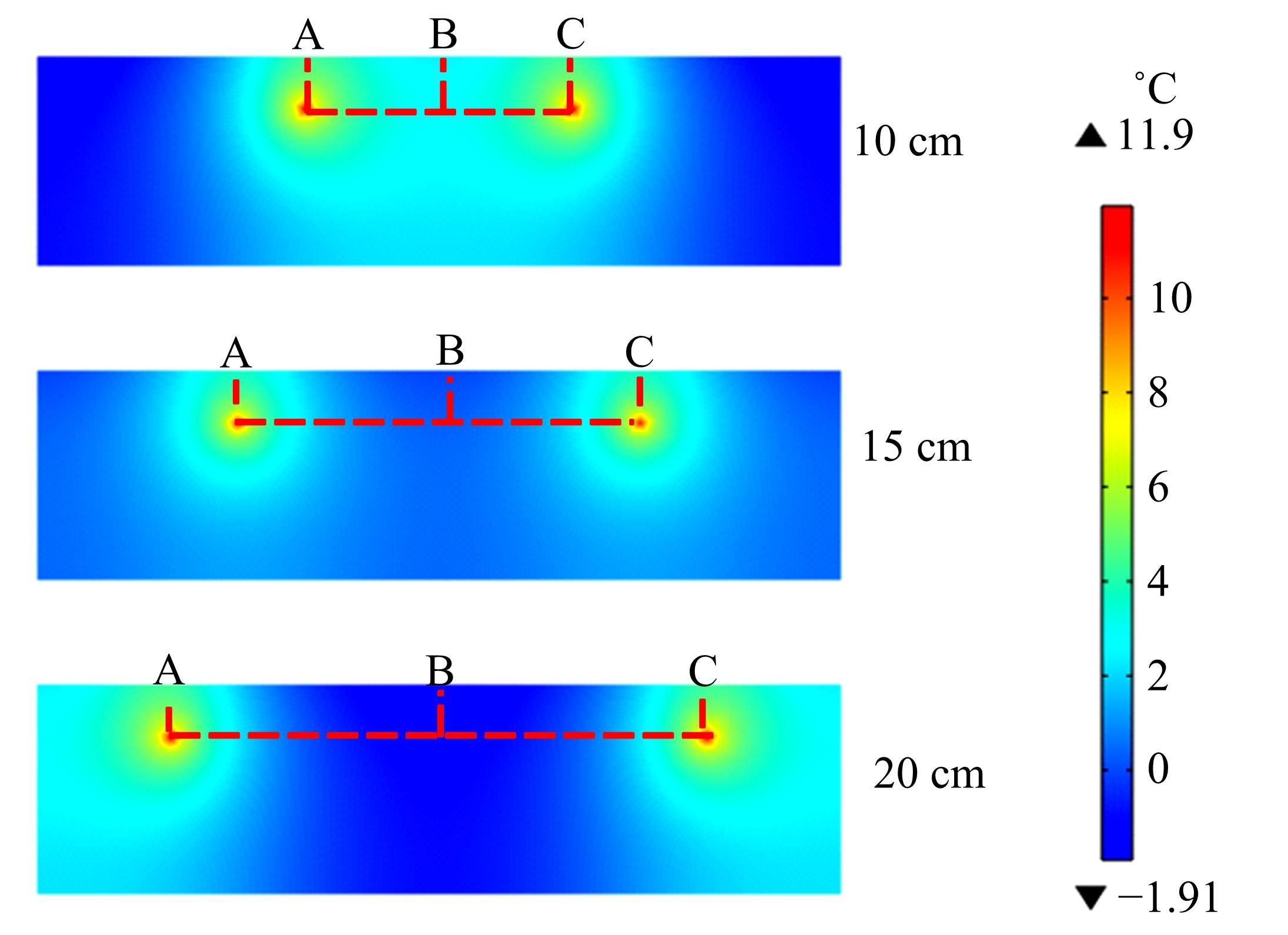
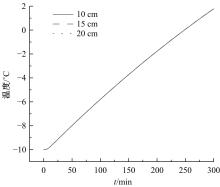
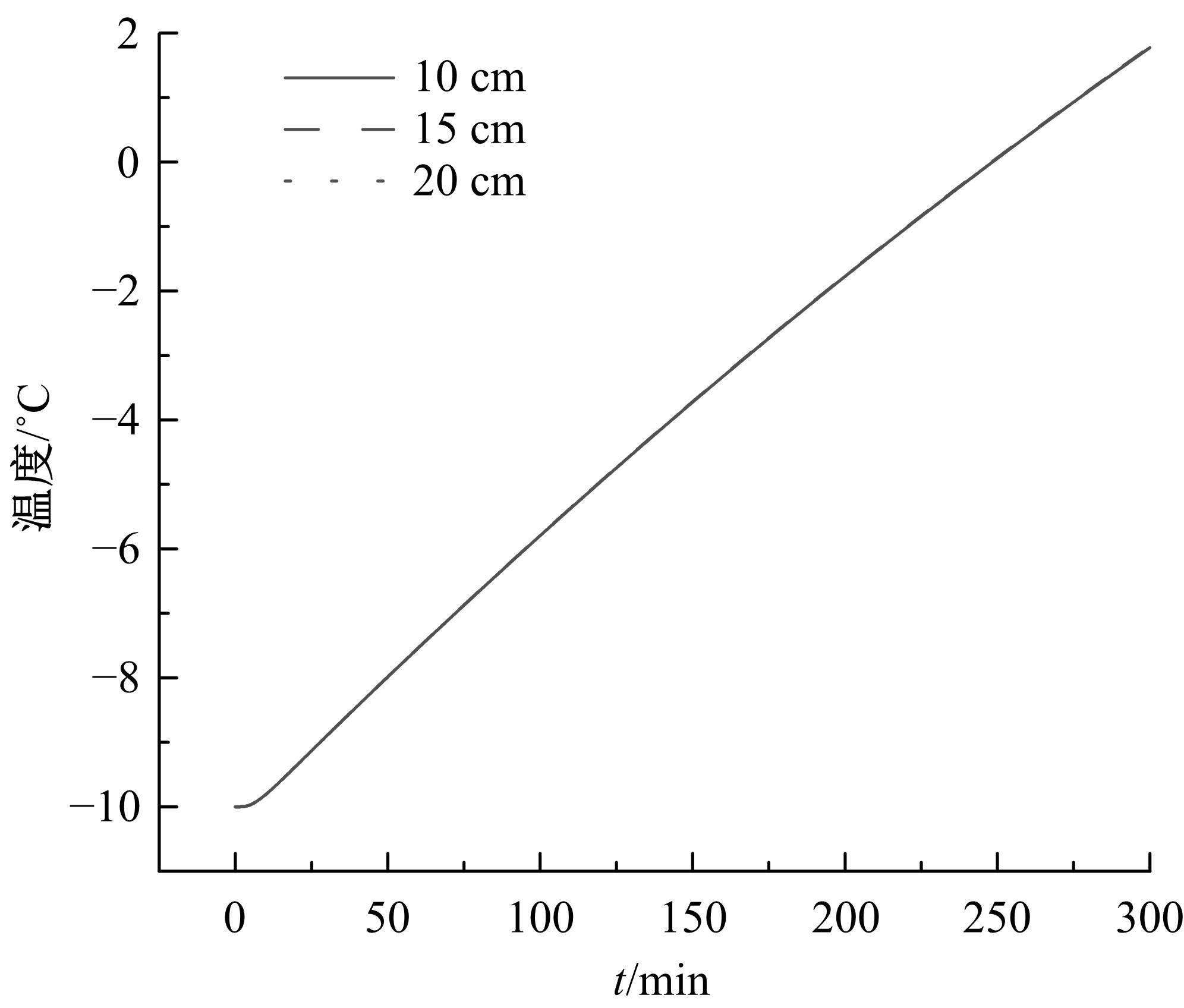
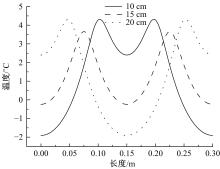
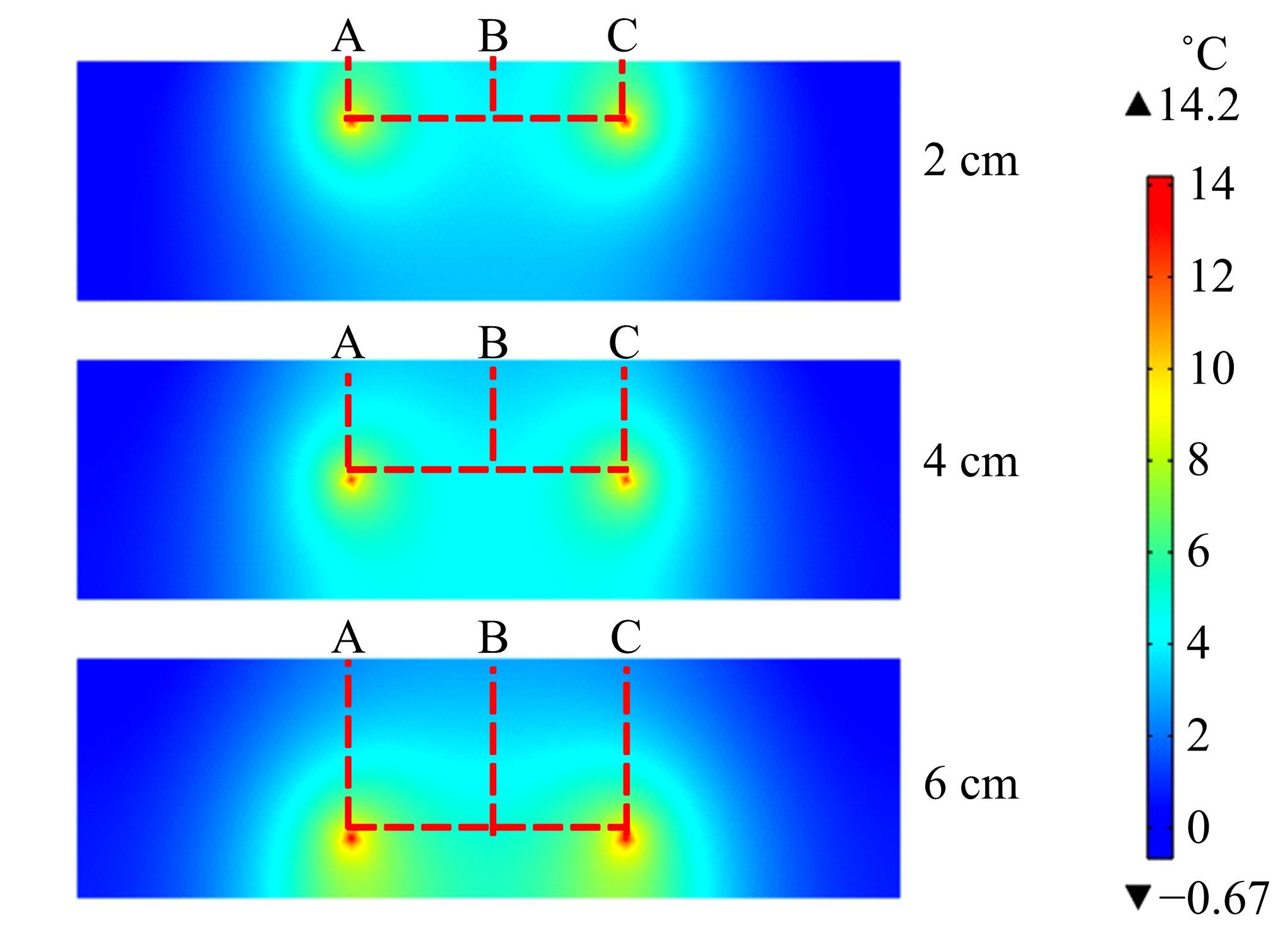
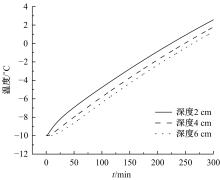
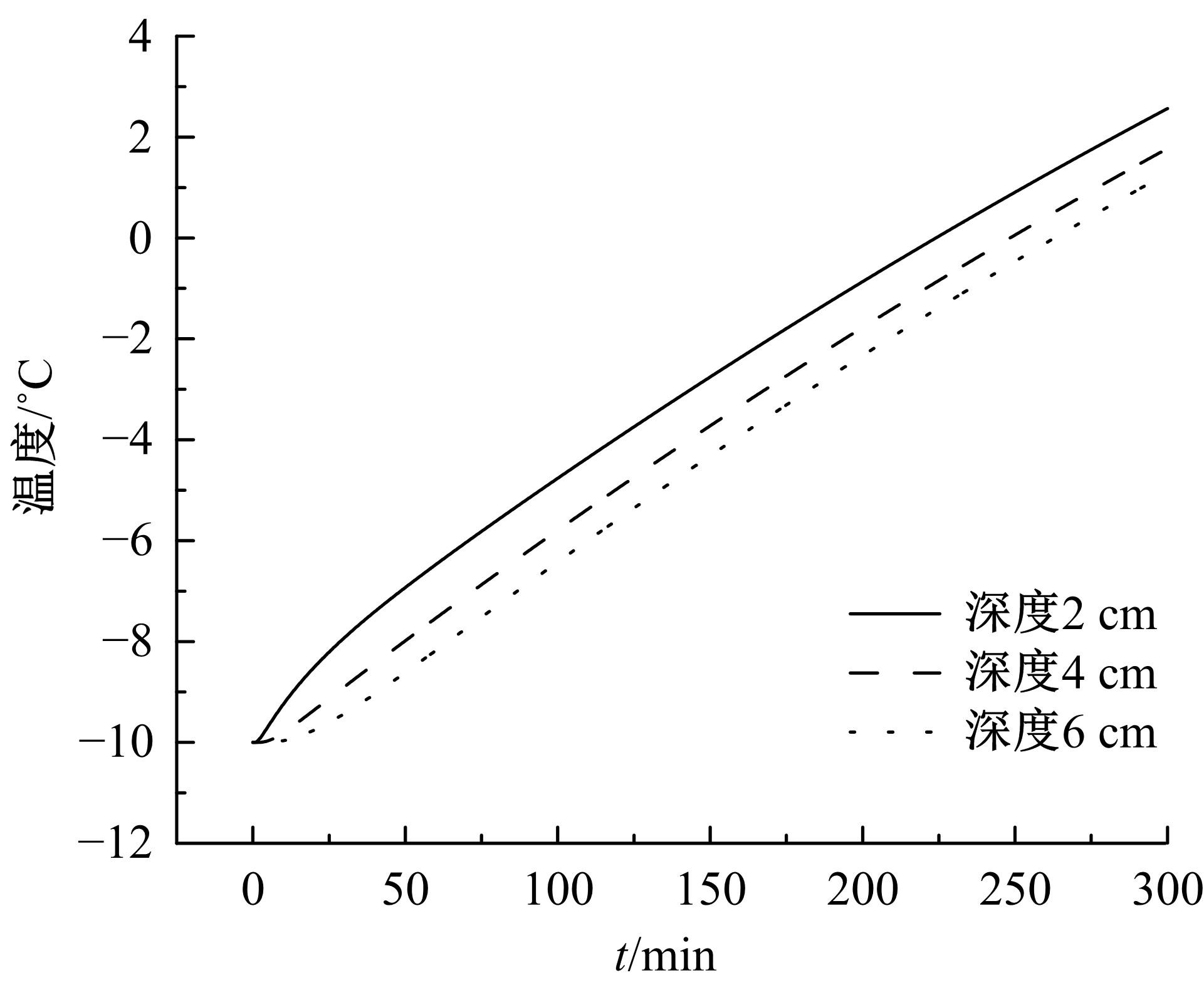
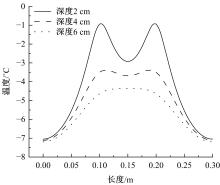
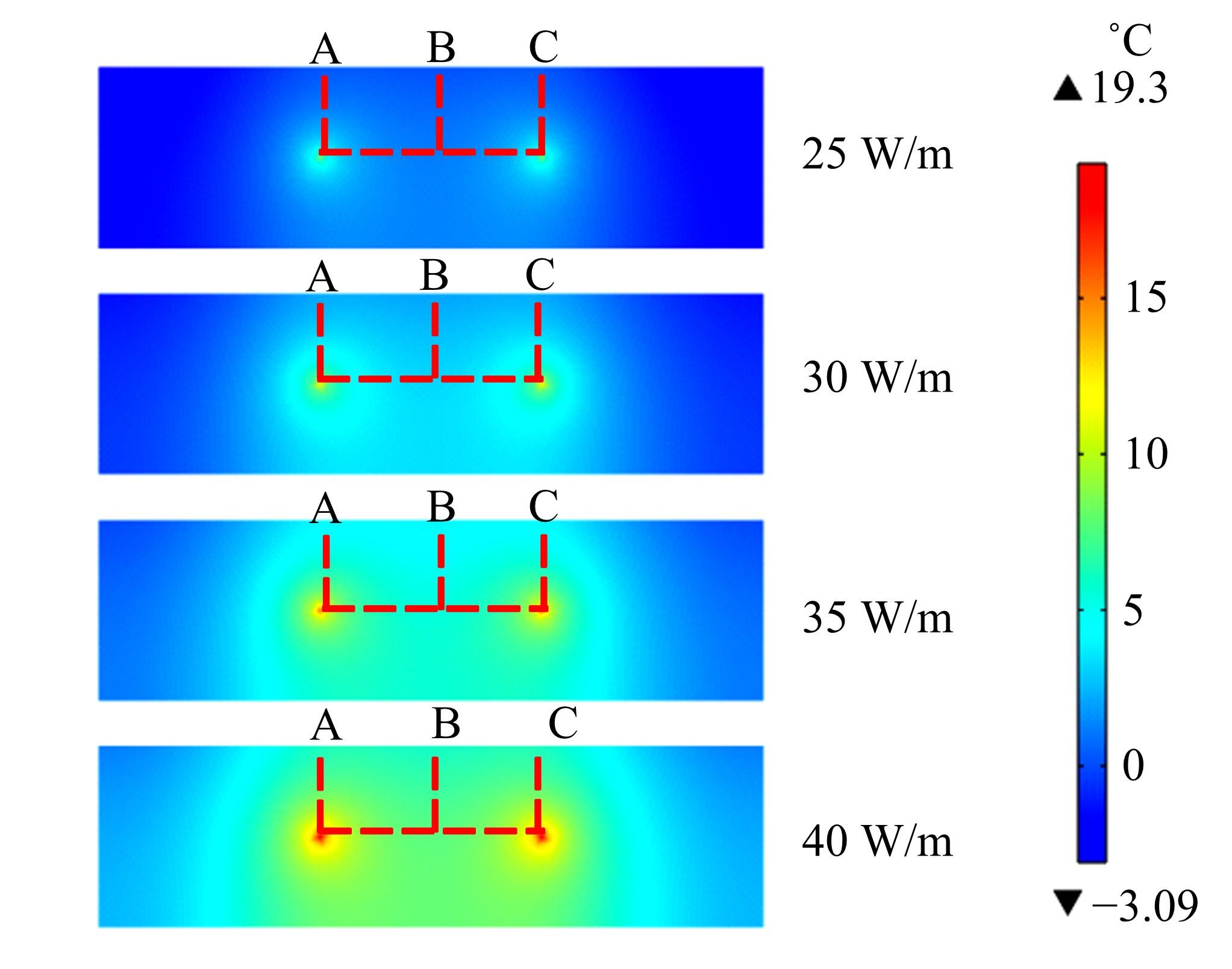
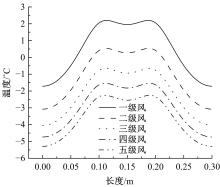
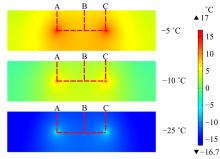
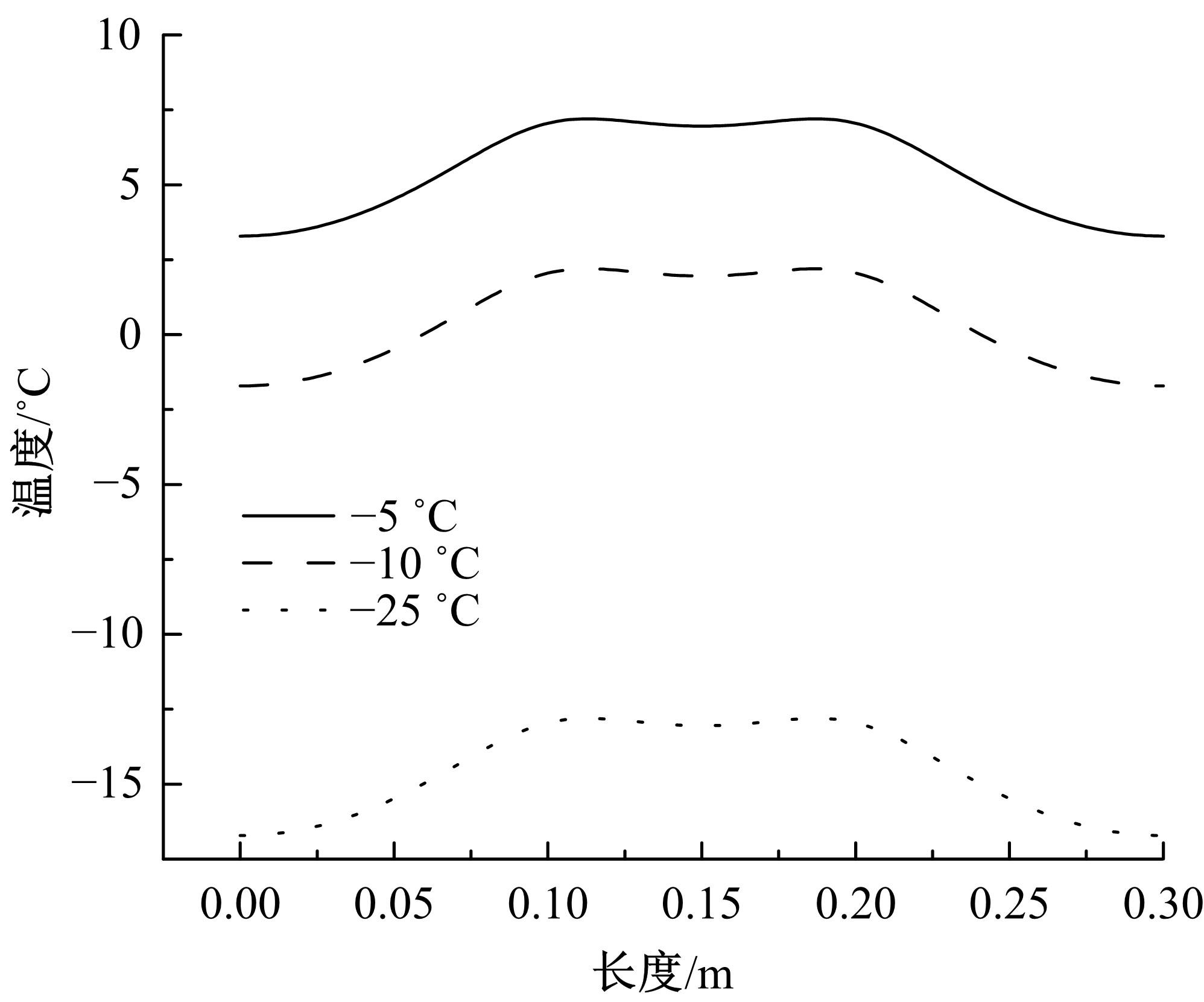
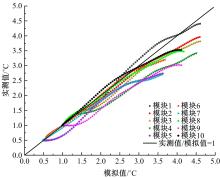
为研究电热型融雪沥青路面传热特性及其影响规律,采用有限元方法建立了二维传热模型,分析了发热系统设计参数(布设间距、埋设深度、输入功率)以及环境因素(风速、环境温度)对路表温度分布和升温速率的影响,并通过试验段实测数据验证模型的准确性和有效性。结果表明:二维传热模型可以很好地预测电热型融雪沥青路面路表温度值,平均最大绝对误差为1.1 ℃,平均精度为88.1%,最大精度为96.6%;在发热系统设计参数及外界环境等影响因素中,布设间距是影响路表温度均匀性的主要因素,其次是埋设深度;输入功率和环境因素主要影响电热型融雪沥青路面温度升温速率和最大温度值。
中图分类号:
- U421.4
| 1 | 张成博.冰雪条件下高速公路交通态势预估及智能管控技术[D]. 长春:吉林大学建设工程学院,2020. |
| Zhang Cheng-bo. Traffic situation and intelligent control technology of expressway under ice and snow pavement conditions[D]. Changchun: College of Construction Engineering, Jilin University, 2020. | |
| 2 | 陈永恒,刘鑫山,熊帅, 等. 冰雪条件下快速路汇流s区可变限速控制[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018, 48(3): 677-687. |
| Chen Yong-heng, Liu Xin-shan, Xiong Shuai, et al. Variable speed limit control under snow and ice conditions for urban expressway in junction bottleneck area[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(3): 677-687. | |
| 3 | 刘状壮,沙爱民,蒋玮. 蓄盐沥青路面研究进展:盐化物材料、混合料及其性能与评价[J].中国公路学报, 2019, 32(4): 18-31, 72. |
| Liu Zhuang-zhuang, Sha Ai-min, Jiang Wei.Advances in asphalt pavements containing salts:additives, mixtures, performances, and evaluation[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(4): 18-31, 72. | |
| 4 | Liu Z Z, Sha A M, He R, et al. Antifreeze asphalt mixtures design and antifreeze performances prediction based on the phase equilibrium of natural solution[J]. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 2016, 129: 104-113. |
| 5 | 邹笛, 赵天宇, 温亚梅, 等. 氯化钠和醋酸钙镁两种融雪剂对土壤中典型重金属结合态的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报:理学版, 2019, 57(2): 445-453. |
| Zou Di, Zhao Tian-yu, Wen Ya-mei, et al.Effects of NaCI and CMA deicing salts on binding states of typical heavy metals in soil[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Science Edition), 2019, 57(2): 445-453. | |
| 6 | 谭忆秋,张驰,徐慧宁,等.主动除冰雪路面融雪化冰特性及路用性能研究综述[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(4): 1-17. |
| Tan Yi-qiu, Zhang Chi, Xu Hui-ning, et al. Snow melting and deicing characteristics and pavement performance of active deicing and snow melting pavement[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(4): 1-17. | |
| 7 | Yang T, Yang Z J, Singla M, et al. Experimental study on carbon fiber tape-based deicing technology[J]. Journal of Cold Regions Engineering, 2012, 26(2): 55-70. |
| 8 | Zhao W K, Li L, Wang W, et al. Thermal performances of porous snow by a hydronic heating system at different weather conditions[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2020, 141(5): 1519-1528. |
| 9 | 黄勇, 高青, 马纯强, 等. 道路融雪化冰过程冰层的热融特性[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2010, 40(2): 391-396. |
| Huang Yong, Gao Qing, Ma Chun-qiang,et al.Heat melting characteristic of ice layer in ice-snow melting process on road pavement[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition),2010,40(2): 391-396. | |
| 10 | Xu H N, Wang D W, Tan Y Q, et al. Investigation of design alternatives for hydronic snow melting pavement systems in China[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 170: 1413-1422. |
| 11 | Liu X B, Rees S J, Spitler J D. Modeling snow melting on heated pavement surfaces. Part I: model development[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2007, 27(5/6): 1115-1124. |
| 12 | 许庚. 基于内置电加热方式的路面表面物理除冰雪技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学交通科学与工程学院, 2013. |
| Xu Geng. Research on ice and snow removing technique on pavement surface through built-in electric heating[D]. Harbin: School of Transportation Science and Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013. | |
| 13 | 罗新欣. 内置碳纤维发热电缆的桥面融冰化雪技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2015. |
| Luo Xin-xin. A study of applied technology in deicing and melting snow on the bridge surface by built-in carbon fiber heating wire[D]. Xi'an: School of Highway, Chang'an University, 2015. | |
| 14 | 徐慧宁, 谭忆秋, Spitler J D. 太阳能-土壤源热能流体加热道路融雪系统融雪模型的建立[J]. 太阳能学报, 2014, 35(5): 802-808. |
| Xu Hui-ning, Tan Yi-qiu, Spitler J D. Study on the heat and mass coupled snow melting model for solar-ground source coupled heated pavement[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2014, 35(5): 802-808. | |
| 15 | Liu K, Huang S L, Xie H Z . et al. Multi-objective optimization of the design and operation for snow-melting pavement with electric heating pipes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 122: 359-367. |
| 16 | Bergman T L, Lavin A S, Incropera F P, et al. Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer, 6th ed[M].Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2006. |
| 17 | 赵宏明. 布置碳纤维发热线的混凝土路面及桥面融雪化冰试验研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学土木工程学院, 2010. |
| Zhao Hong-ming. Experimental investigation on concrete pavement and bridge deck deicing with carbon fiber heating wire[D]. Dalian :School of Civil Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2010. | |
| 18 | 鲍梦捷. 内置碳纤维融冰路面设计方法[D]. 西安: 长安大学公路学院, 2017. |
| Bao Meng-jie. Study on deicing pavement of built-in carbon fiber heating wire[D]. Xi'an: School of Highway, Chang'an University, 2017. |
| [1] | 魏海斌,马子鹏,毕海鹏,刘汉涛,韩栓业. 基于力学响应分析方法的导电橡胶复合路面铺装技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 531-537. |
| [2] | 郑植,耿波,王福敏,董俊宏,魏思斯. 既有低等级混凝土护栏防护能力提升[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1362-1374. |
| [3] | 时成林,王勇,吴春利,宋文祝. 路堤挡土墙主动土压力计算方法修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1394-1403. |
| [4] | 郭庆林,刘强,吴春利,李黎丽,李懿明,刘富春. 导电沥青及混合料裂缝局部温度场及愈合效果[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1386-1393. |
| [5] | 华琛,牛润新,余彪. 地面车辆机动性评估方法与应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1229-1244. |
| [6] | 夏全平,高江平,罗浩原,张其功,李志杰,杨飞. 用于高模量沥青砼的复合改性硬质沥青低温性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 541-549. |
| [7] | 姚玉权,仰建岗,高杰,宋亮. 基于性能-费用模型的厂拌再生沥青混合料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 585-595. |
| [8] | 孙健,彭斌,朱兵国. 新型无油涡旋压缩机内部热力学特性和性能测试[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2778-2787. |
| [9] | 叶奋,胡诗园. 考虑旧水泥路面接缝传荷能力的超薄罩面力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2636-2643. |
| [10] | 于晓贺,罗蓉,柳子尧,黄婷婷,束裕. 沥青路面典型裂缝湿度场数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2343-2351. |
| [11] | 杨彦海,崔宏,杨野,张怀志,刘赫. 冻融循环作用对非饱和乳化沥青冷再生混合料性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2352-2359. |
| [12] | 冉武平,陈慧敏,李玲,冯立群. 干湿循环下粗粒土回弹模量演变规律及模型预估和修正[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2079-2086. |
| [13] | 董伟智,张爽,朱福. 基于可拓层次分析法的沥青混合料路用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2137-2143. |
| [14] | 商拥辉,徐林荣,刘维正,蔡雨. 重载铁路改良土和A组填料过渡段的动力特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2128-2136. |
| [15] | 文畅平,任睆遐. 基于Lade模型的生物酶改良膨胀土双屈服面本构关系[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1716-1723. |
|