吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2601-2610.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211169
基于动态图卷积的图像情感分布预测
- 1.天津大学 电气自动化与信息工程学院,天津 300072
2.天津大学 国际工程师学院,天津 300072
Dynamic graph convolutional neural network for image sentiment distribution prediction
Yu-ting SU1,2( ),Ji WANG2,Wei ZHAO1,Pei-guang JING1,2(
),Ji WANG2,Wei ZHAO1,Pei-guang JING1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Electrical and Information Engineering,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
2.Tianjin International Engineering Institute,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
摘要:
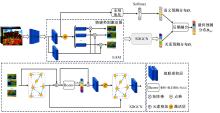
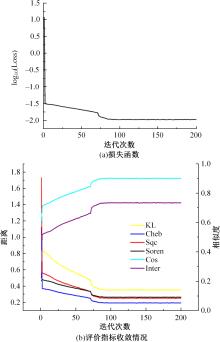
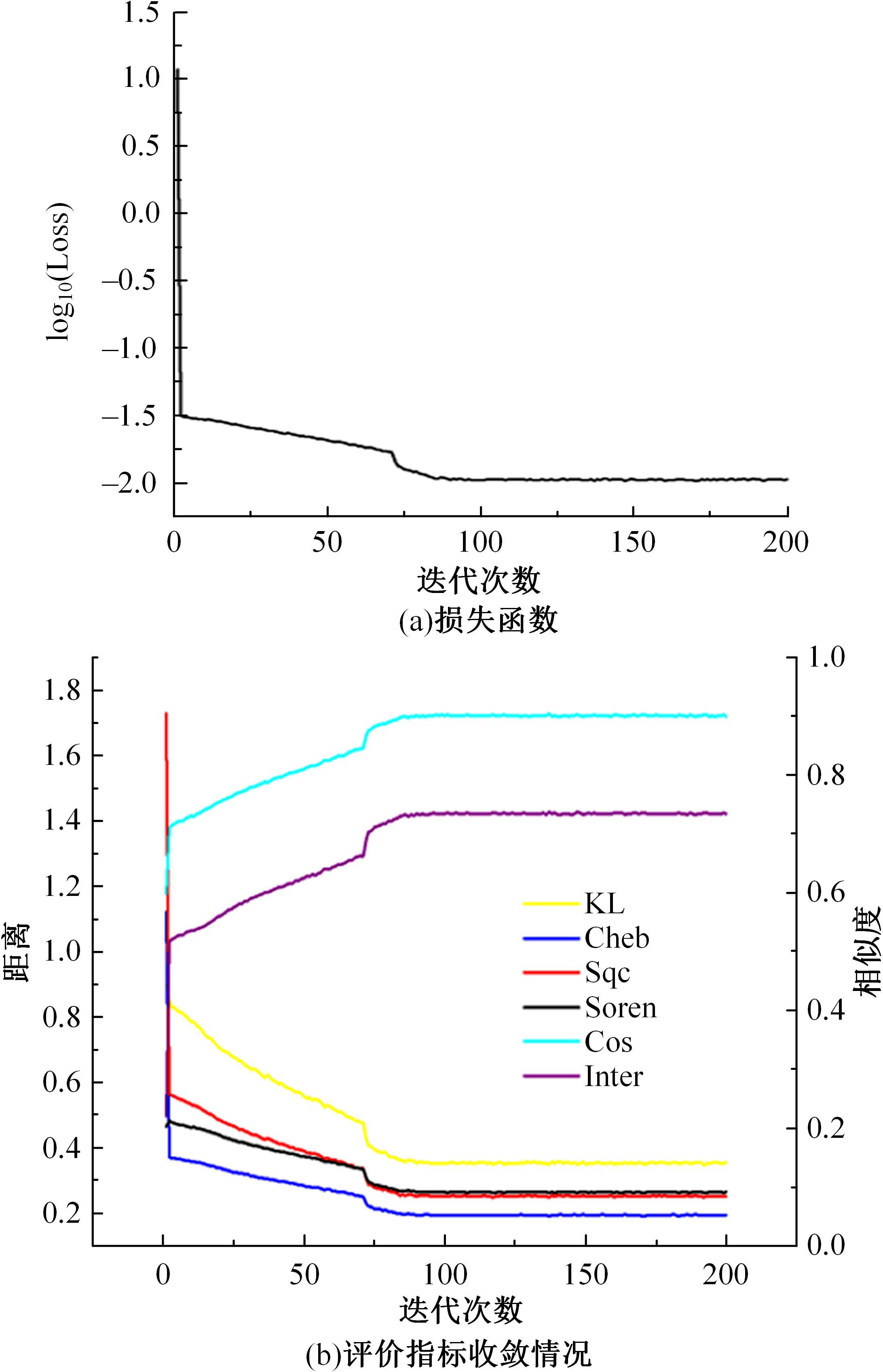
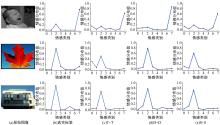
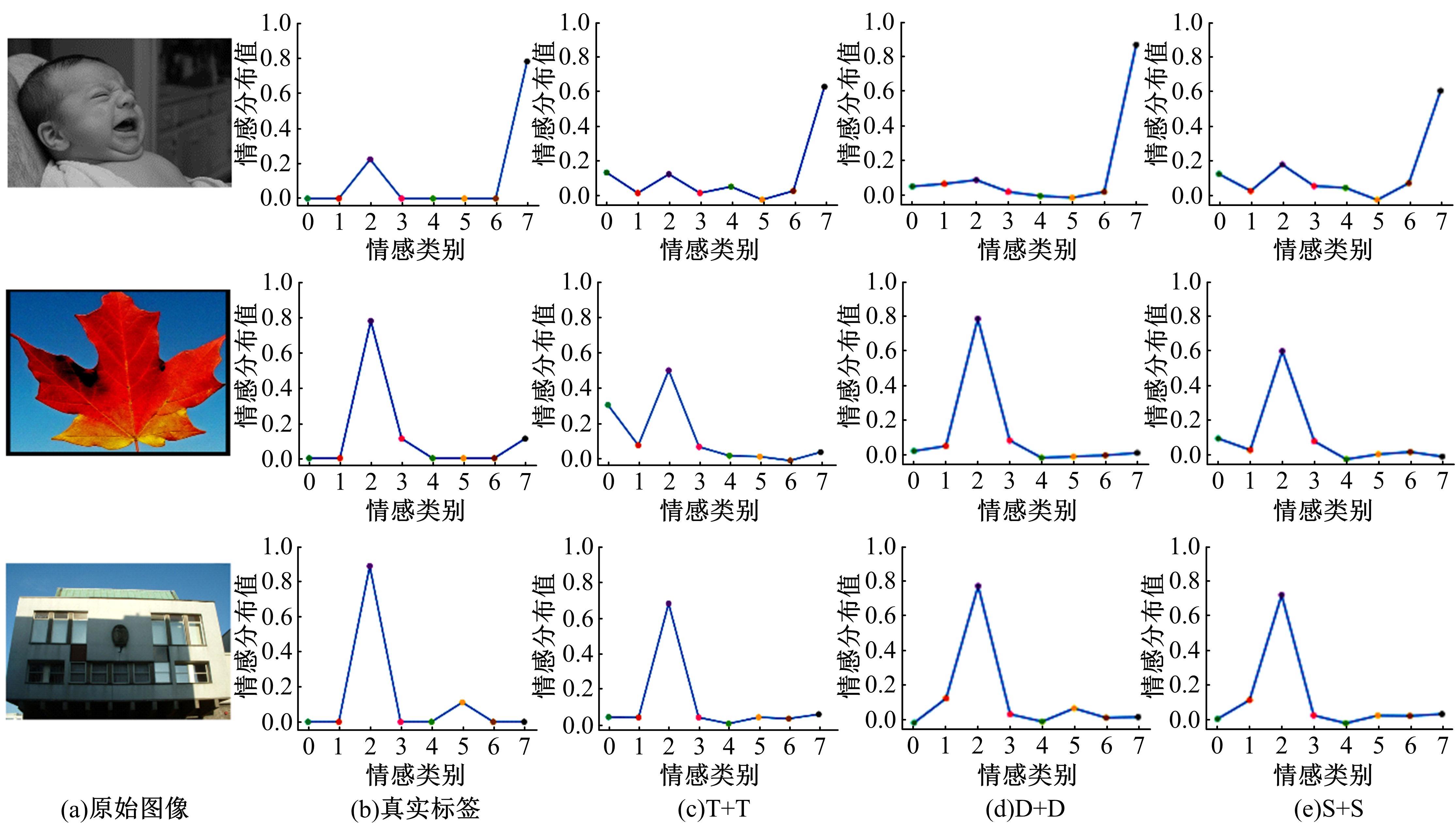
针对图像情感分布学习中,视觉特征与高阶情感语义之间存在语义鸿沟以及情感标签具有主观性和模糊性的问题,提出了一种情感语义动态图卷积网络模型。该模型通过情感激活模块自动定位情感语义区域,从而有效挖掘契合情感语义的内容表征;通过动态图卷积模块自适应地捕获图像情感标签之间的语义关联性;最终构建并行结构输出联合局部语义和标签相关性的情感预测分布。在3个公开情感数据集上的实验结果证明了本文算法在图像情感分布预测任务中的有效性。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Zhou L, Fan X, Ma Y, et al. Uncertainty-aware cross-dataset facial expression recognition via regularized conditional alignment[C]∥Proceedings of ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, USA, 2020: 2964-2972. |
| 2 | Farzaneh A H, Qi X. Discriminant distribution-agnostic loss for facial expression recognition in the wild[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Piscataway, USA, 2020: 406-407. |
| 3 | 卢洋, 王世刚, 赵文婷, 等. 基于离散Shearlet类别可分性测度的人脸表情识别方法[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(5): 1715-1725. |
| Lu Yang, Wang Shi-gang, Zhao Wen-ting, et al. Facial expression recognition based on separability assessment of discrete Shearlet transform[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1715-1725. | |
| 4 | 方明, 陈文强. 结合残差网络及目标掩膜的人脸微表情识别[J].吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(1): 303-313. |
| Fang Ming, Chen Wen-qiang. Face micro-expression recognition based on ResNet with object mask[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(1): 303-313. | |
| 5 | Huang F, Wei K, Weng J, et al. Attention-based modality-gated networks for image-text sentiment analysis[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2020, 16(3): 1-19. |
| 6 | Ji R, Chen F, Cao L, et al. Cross-modality microblog sentiment prediction via bi-layer multimodal hypergraph learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 21(4): 1062-1075. |
| 7 | Jian M, Dong J, Gong M, et al. Learning the traditional art of Chinese calligraphy via three-dimensional reconstruction and assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 22(4): 970-979. |
| 8 | Yang J, She D, Lai Y K, et al. Retrieving and classifying affective images via deep metric learning[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2018: 491-498. |
| 9 | Yao X, She D, Zhao S, et al. Attention-aware polarity sensitive embedding for affective image retrieval[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway, USA, 2019: 1140-1150. |
| 10 | Li Z, Liu J, Zhu X, et al. Image annotation using multi-correlation probabilistic matrix factorization[C]∥Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, USA, 2010: 1187-1190. |
| 11 | Li Z, Tang J, He X. Robust structured nonnegative matrix factorization for image representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 29(5): 1947-1960. |
| 12 | Yang X, Song X, Feng F, et al. Attribute-wise explainable fashion compatibility modeling[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2021, 17(1): 1-21. |
| 13 | Yang X, Song X, Han X, et al. Generative attribute manipulation scheme for flexible fashion search[C]∥Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, New York, USA, 2020: 941-950. |
| 14 | Geng X. Label distribution learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2016, 28(7): 1734-1748. |
| 15 | Peng K C, Chen T, Sadovnik A, et al. A mixed bag of emotions: model, predict, and transfer emotion distributions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Piscataway, USA, 2015: 860-868. |
| 16 | Geng X, Yin C, Zhou Z H. Facial age estimation by learning from label distributions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(10): 2401-2412. |
| 17 | Yang J, Sun M, Sun X. Label distribution learning via augmented conditional probability neural network[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2017: 224-230. |
| 18 | Zhou Y, Xue H, Geng X. Emotion distribution recognition from facial expressions[C]∥Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, USA, 2015: 1247-1250. |
| 19 | Ren T, Jia X, Li W, et al. Label distribution learning with label-specific features[C]∥Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Mateo, USA, 2019: 3318-3324. |
| 20 | Zhao S, Yao H, Gao Y, et al. Continuous probability distribution prediction of image emotions via multitask shared sparse regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2016, 19(3): 632-645. |
| 21 | Plutchik R. Emotions: a general psychoevolutionary theory[J]. Approaches to Emotion, 1984(1984): 197-219. |
| 22 | Xu M, Zhou Z H. Incomplete label distribution learning[C]∥Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on artificial intelligence, San Mateo, USA, 2017: 3175-3181. |
| 23 | Jia X, Li Z, Zheng X, et al. Label distribution learning with label correlations on local samples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2019, 33(4): 1619-1631. |
| 24 | Jia X, Zheng X, Li W, et al. Facial emotion distribution learning by exploiting low-rank label correlations locally[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Piscataway, USA, 2019: 9841-9850. |
| 25 | Chen T, Yu F X, Chen J, et al. Object-based visual sentiment concept analysis and application[C]∥Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, USA, 2014: 367-376. |
| 26 | Su Y T, Zhao W, Jing P G, et al. Exploiting low-rank latent gaussian graphical model estimation for visual sentiment distribution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2022,25: 1243-1255. |
| 27 | 缪裕青, 雷庆庆, 张万桢, 等. 多视觉目标融合的图像情感分析研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(4): 1250-1255. |
| Miao Yu-qing, Lei Qing-qing, Zhang Wan-zhen, et al. Research on image sentiment analysis based on multi-visual object fusion[J] Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(4): 1250-1255. | |
| 28 | 盛家川, 陈雅琦, 王君, 等. 深度学习结构优化的图像情感分类[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(11): 264-273. |
| Sheng Jia-chuan, Chen Ya-qi, Wang Jun, et al. Image sentiment classification via deep learning structure optimization[J] Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2020, 49(11): 264-273. | |
| 29 | Chen T, Borth D, Darrell T, et al. Deepsentibank: visual sentiment concept classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J/OL]. [2021-10-25]. |
| 30 | Zhu X, Li L, Zhang W, et al. Dependency exploitation: a unified CNN-RNN approach for visual emotion recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Mateo, USA, 2017: 3595-3601. |
| 31 | Campos V, Salvador A, Giró-i-Nieto X, et al. Diving deep into sentiment: understanding fine-tuned CNNs for visual sentiment prediction[C]∥Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Affect & Sentiment in Multimedia, New York, USA, 2015: 57-62. |
| 32 | Campos V, Jou B, Giro-i-Nieto X. From pixels to sentiment: fine-tuning CNNs for visual sentiment prediction[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2017, 65(1): 15-22. |
| 33 | You Q, Luo J, Jin H, et al. Robust image sentiment analysis using progressively trained and domain transferred deep networks[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2015: 381-388. |
| 34 | Yang J, She D, Sun M. Joint image emotion classification and distribution learning via deep convolutional neural network[C]∥Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Mateo, USA, 2017: 3266-3272. |
| 35 | 徐冰冰, 岑科廷, 黄俊杰, 等. 图卷积神经网络综述[J].计算机学报, 2020, 43(5): 755-780. |
| Xu Bing-bing, Cen Ke-yan, Huang Jun-jie, et al. A survey on graph convolutional neural network[J] Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(5): 755-780. | |
| 36 | Chen T, Xu M, Hui X, et al. Learning semantic-specific graph representation for multi-label image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Piscataway, USA, 2019: 522-531. |
| 37 | He T, Jin X. Image emotion distribution learning with graph convolutional networks[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, New York, USA, 2019: 382-390. |
| 38 | Zhou B, Khosla A, Lapedriza A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Alamitos, USA, 2016: 2921-2929. |
| 39 | Yang J, Sun M, Sun X. Label distribution learning via augmented conditional probability neural network[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2017: 224-230. |
| 40 | Peng K C, Chen T, Sadovnik A, et al. A mixed bag of emotions: model, predict, and transfer emotion distributions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Piscataway, USA, 2015: 860-868. |
| 41 | Jia X, Li W, Liu J, et al. Label distribution learning by exploiting label correlations[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2018: 3310-3317. |
| 42 | Xiong H, Liu H, Zhong B, et al. Structured and sparse annotations for image emotion distribution learning[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2019: 363-370. |
| [1] | 陈绵书,于录录,李晓妮,郑宏宇. 基于均匀ORB特征的回环检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2666-2675. |
| [2] | 国强,朱国会,李万臣. 基于混沌麻雀搜索算法的TDOA/FDOA定位[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 593-600. |
| [3] | 李厚杰,王法胜,贺建军,周瑜,李威,窦宇轩. 基于伪样本正则化Faster R⁃CNN的交通标志检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1251-1260. |
| [4] | 蒋华伟,杨震,张鑫,董前林. 图像去雾算法研究进展[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1169-1181. |
| [5] | 王德兴,吴若有,袁红春,宫鹏,王越. 基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [6] | 金静,党建武,王阳萍,申东. 融合模糊统计纹理特征的多线索粒子滤波跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1111-1120. |
| [7] | 郭继昌,乔珊珊. 基于深度图的水下图像复原[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 677-684. |
| [8] | 刘国华,周文斌. 基于卷积神经网络的脉搏波时频域特征混叠分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1818-1825. |
| [9] | 王柯俨,王迪,赵熹,陈静怡,李云松. 基于卷积神经网络的联合估计图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1771-1777. |
| [10] | 史再峰,李金卓,曹清洁,李慧龙,胡起星. 基于生成对抗网络的低剂量能谱层析成像去噪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1755-1764. |
| [11] | 谌华,郭伟,闫敬文,卓文浩,吴良斌. 基于深度学习的SAR图像道路识别新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1778-1787. |
| [12] | 张薇,韩勇,金铭,乔晓林. 基于托普利兹矩阵集重构的相干信源波达方向估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 703-710. |
| [13] | 程艳芬,姚丽娟,袁巧,陈先桥. 水下视频图像清晰化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 668-677. |
| [14] | 于晓辉,张志成,李新波,孙晓东. 基于状态空间模型的指数衰减正弦信号参数估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2083-2088. |
| [15] | 刘富, 权美静, 王柯, 刘云, 康冰, 韩志武, 侯涛. 仿蝎子振源定位机理的位置指纹室内定位方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2076-2082. |
|