吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (9): 2591-2600.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220044
基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的轻量级虹膜分割模型
霍光1( ),林大为1,刘元宁2,3(
),林大为1,刘元宁2,3( ),朱晓冬2,3,袁梦2,盖迪4
),朱晓冬2,3,袁梦2,盖迪4
- 1.东北电力大学 计算机学院,吉林省 吉林市 132012
2.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
3.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
4.南昌大学 软件学院,南昌 330047
Lightweight iris segmentation model based on multiscale feature and attention mechanism
Guang HUO1( ),Da-wei LIN1,Yuan-ning LIU2,3(
),Da-wei LIN1,Yuan-ning LIU2,3( ),Xiao-dong ZHU2,3,Meng YUAN2,Di GAI4
),Xiao-dong ZHU2,3,Meng YUAN2,Di GAI4
- 1.College of Computer Science,Northeast Electric Power University,Jilin 132012,China
2.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
4.School of Software,Nanchang University,Nanchang 330047,China
摘要:
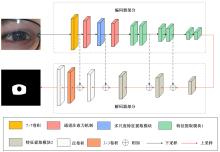
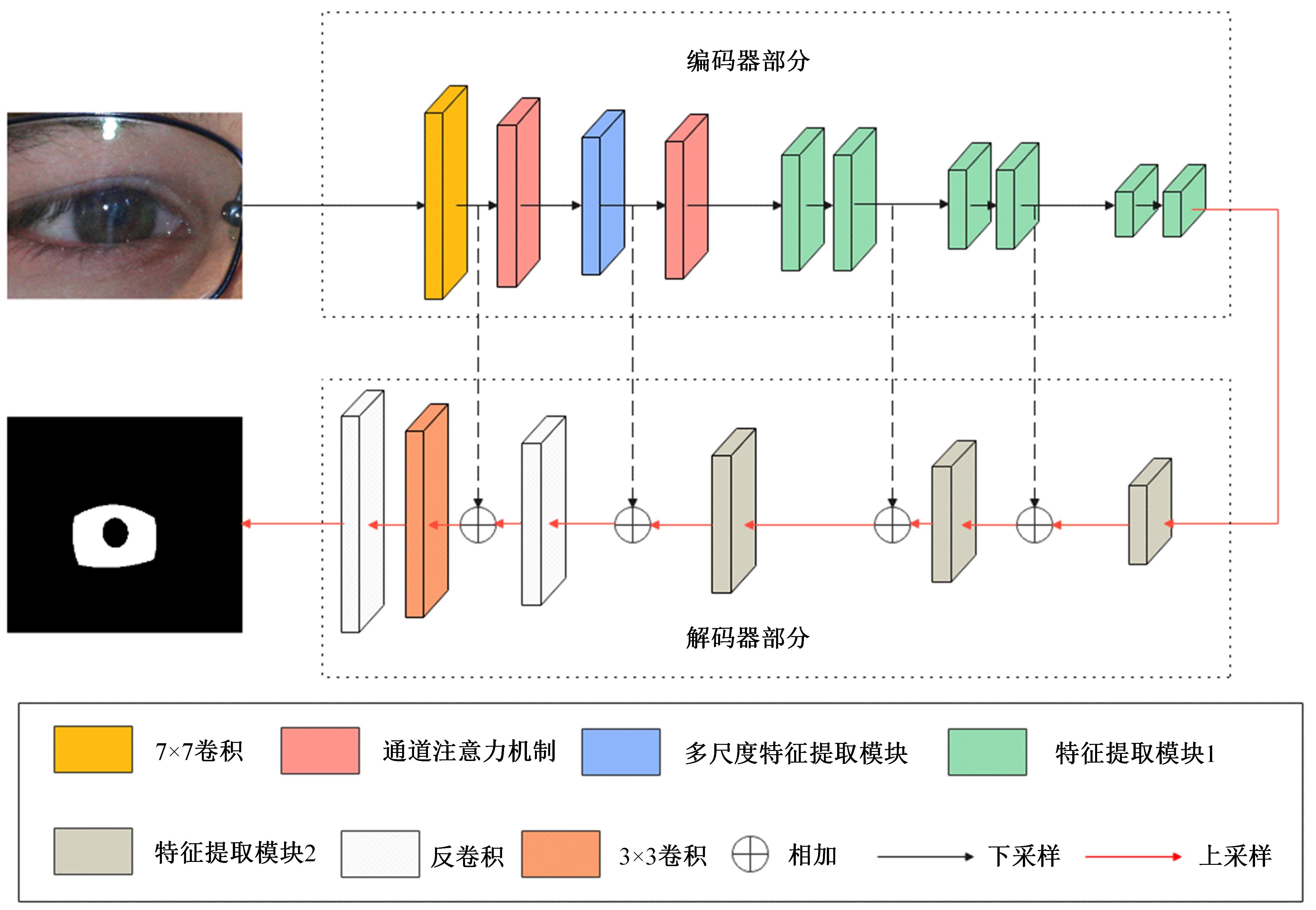
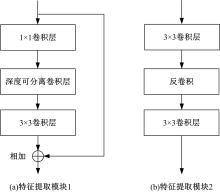
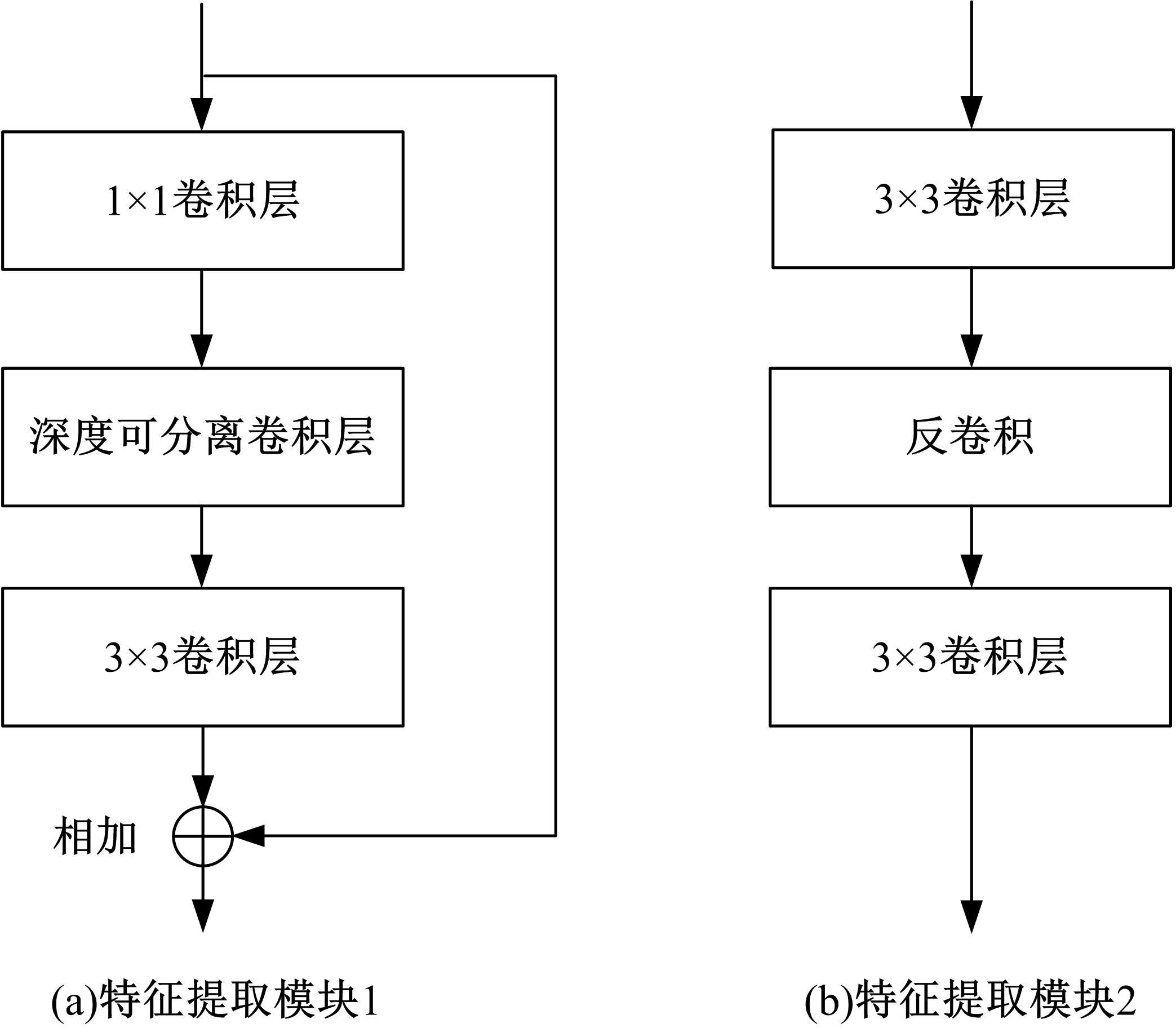
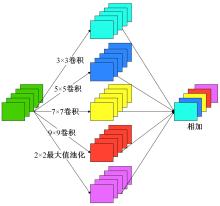
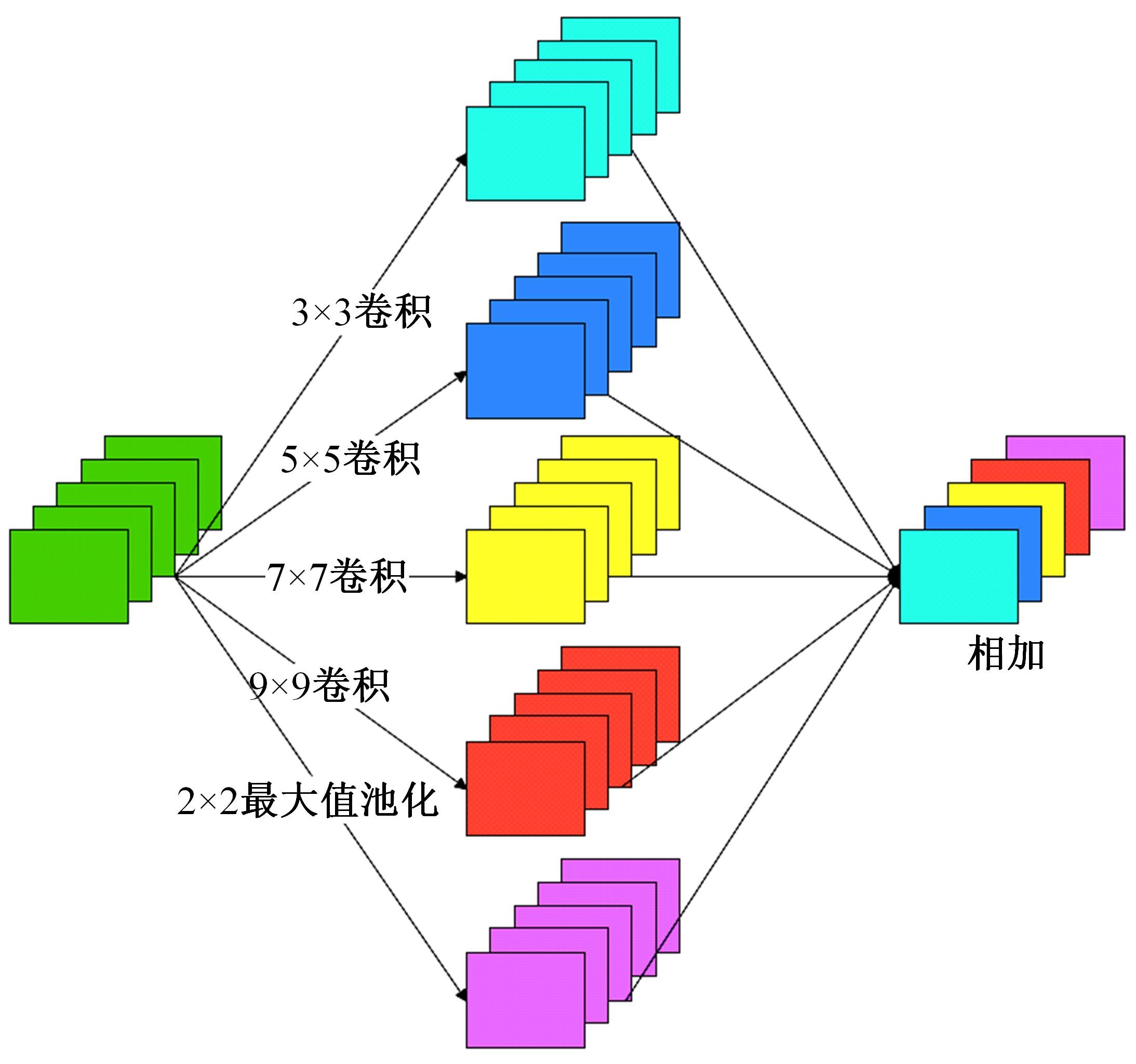
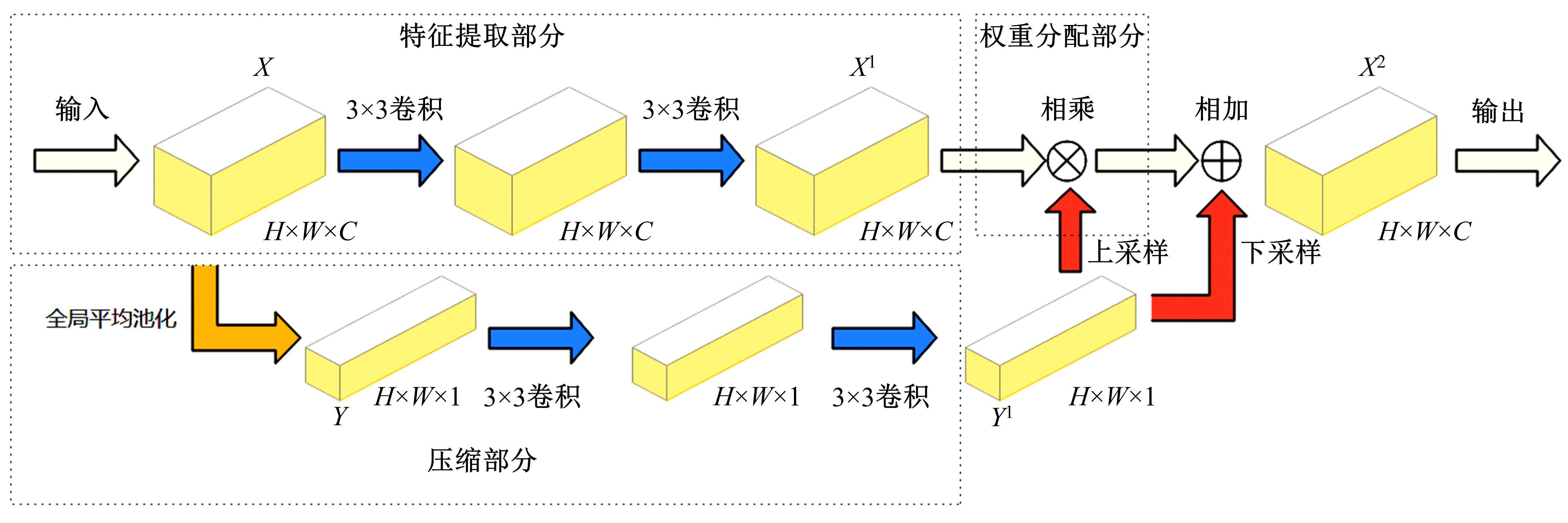
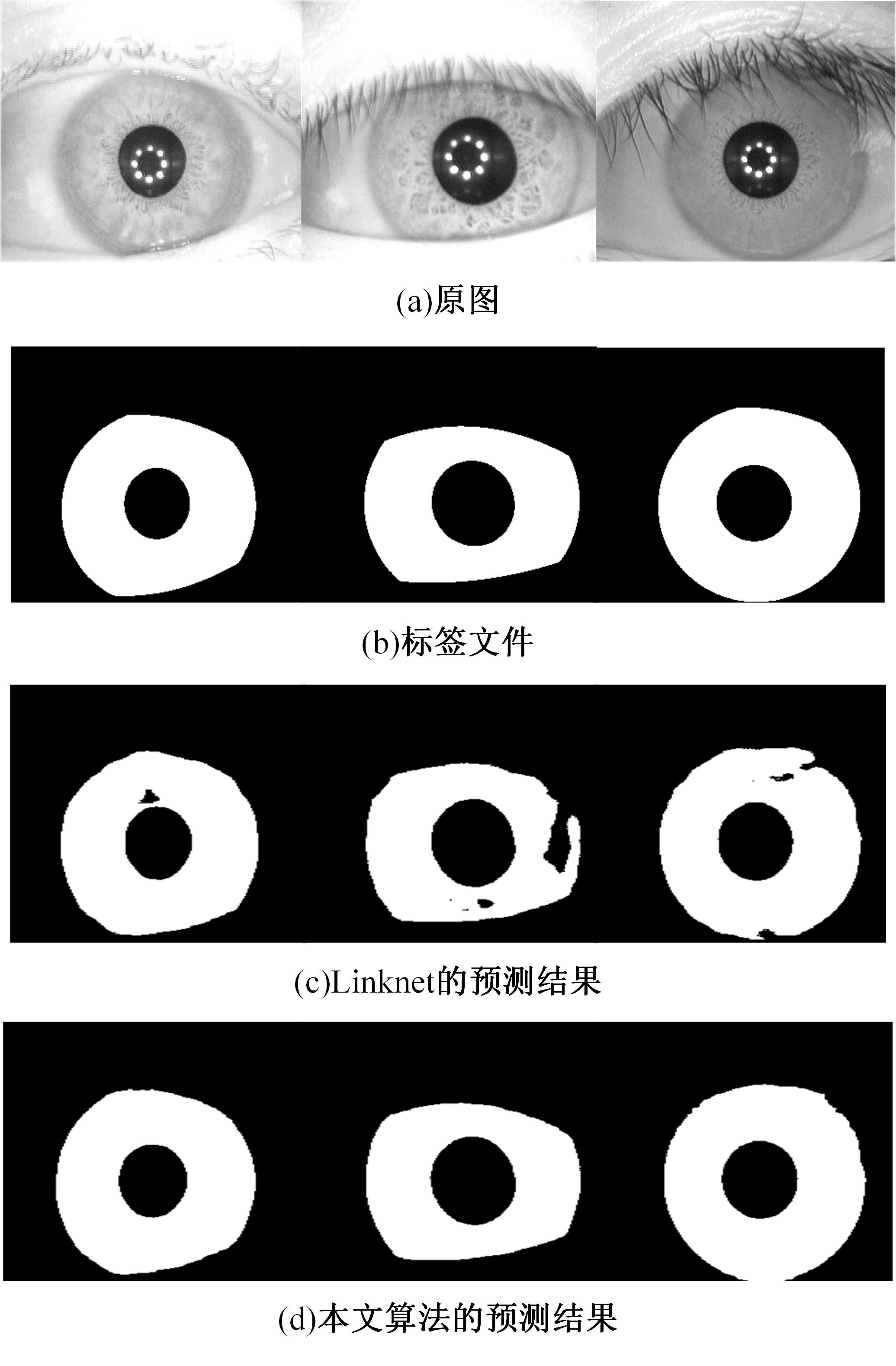
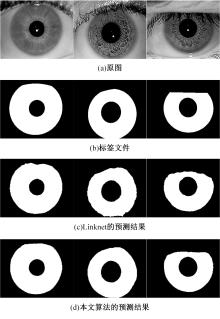
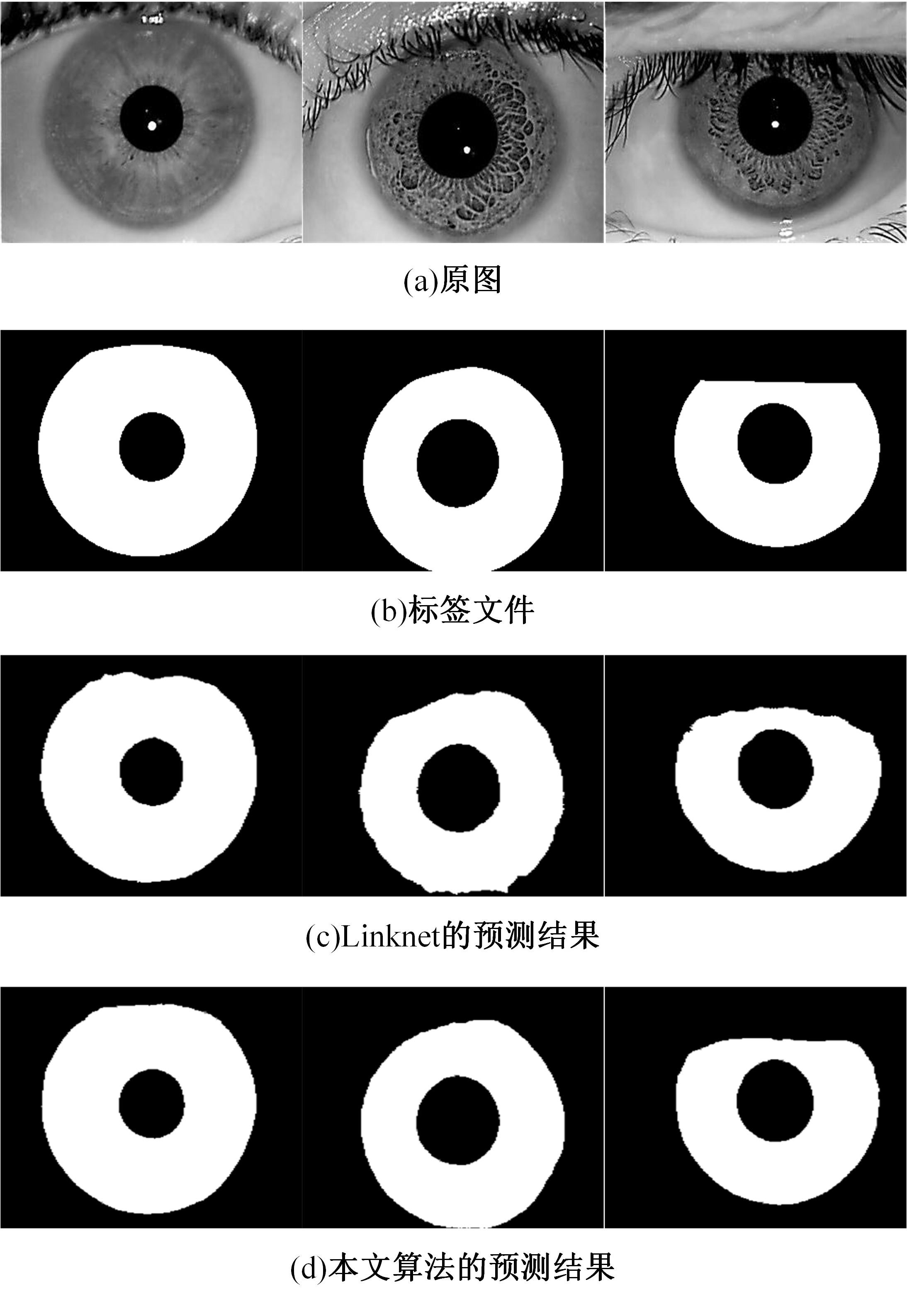
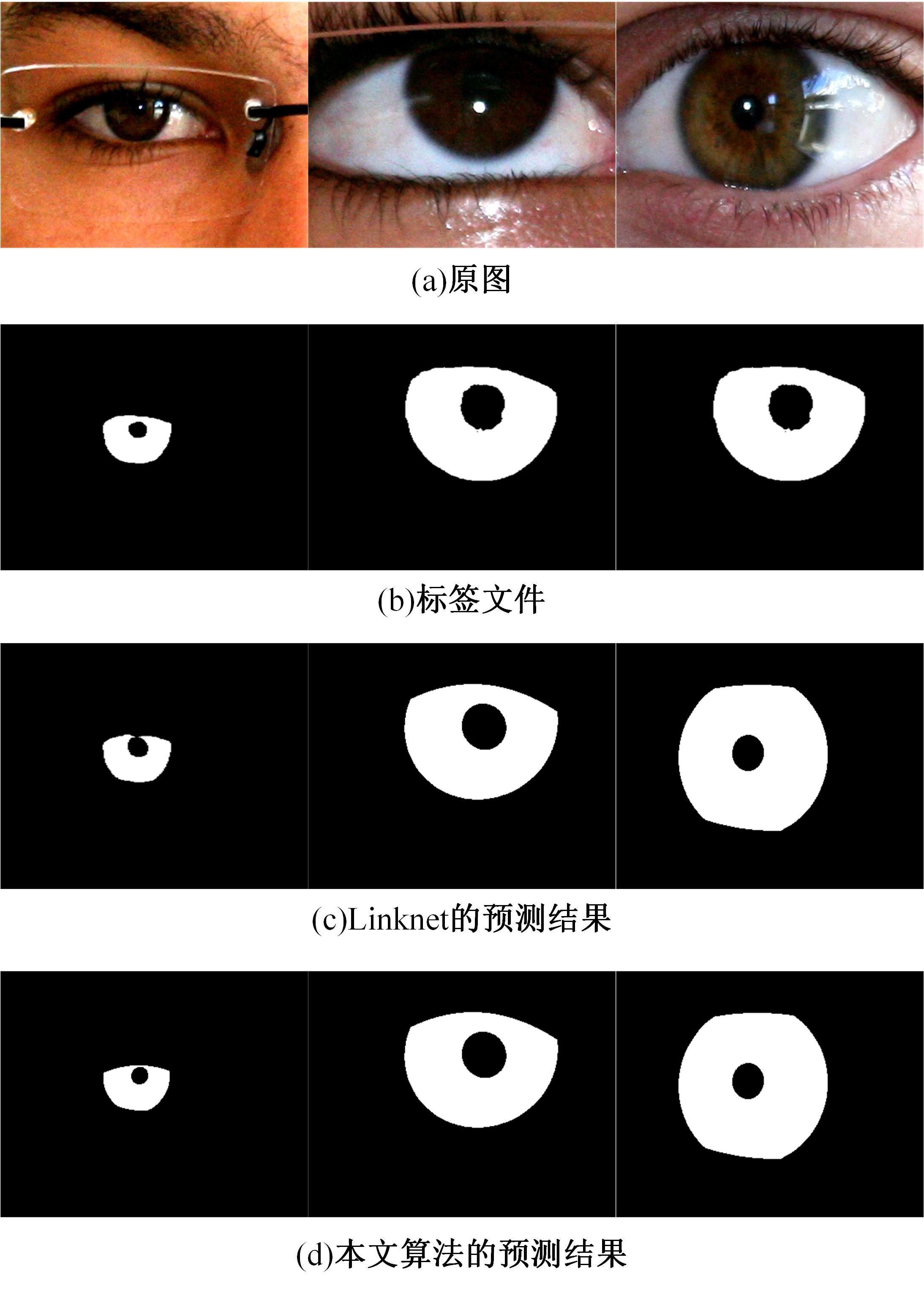
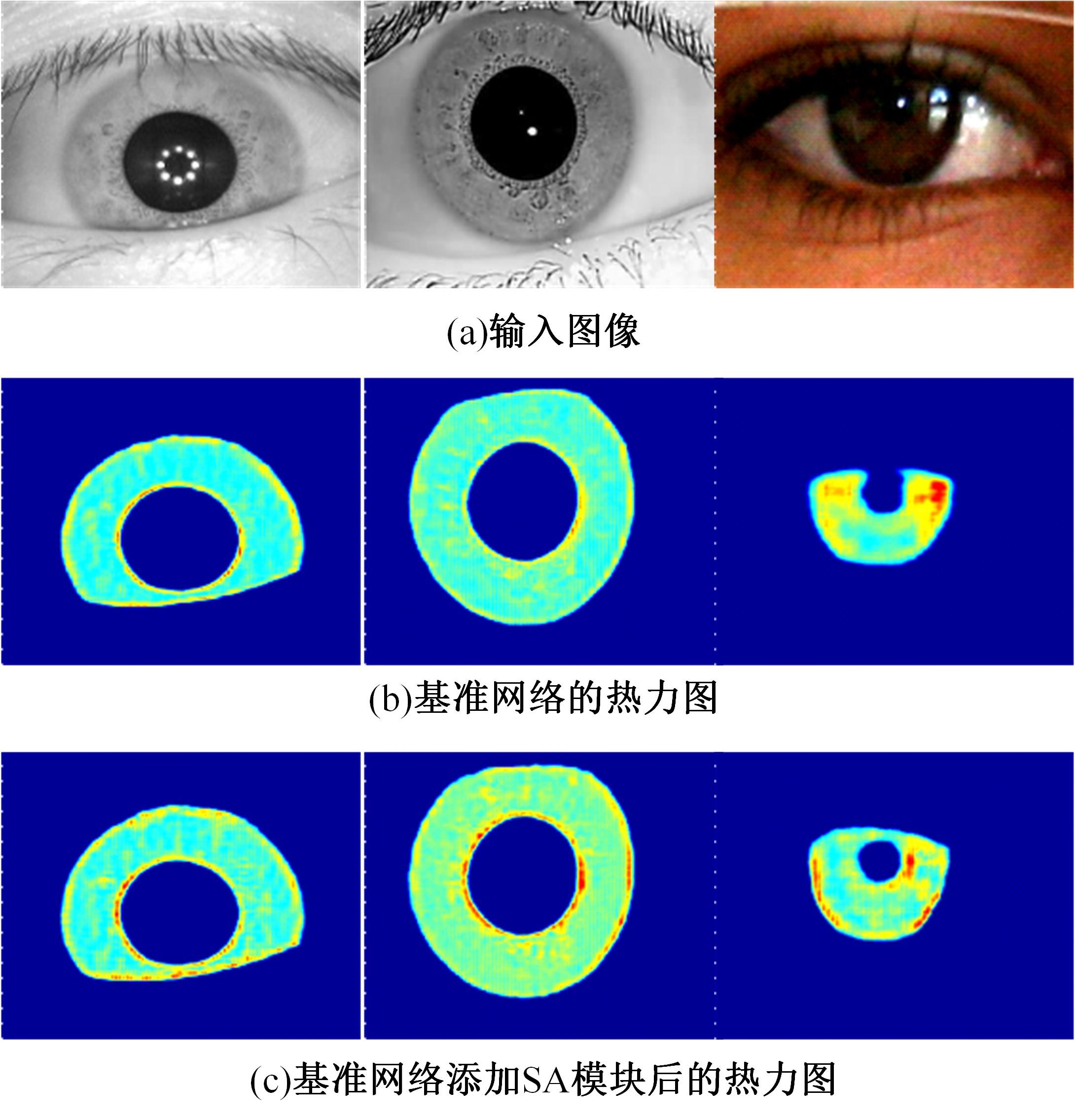
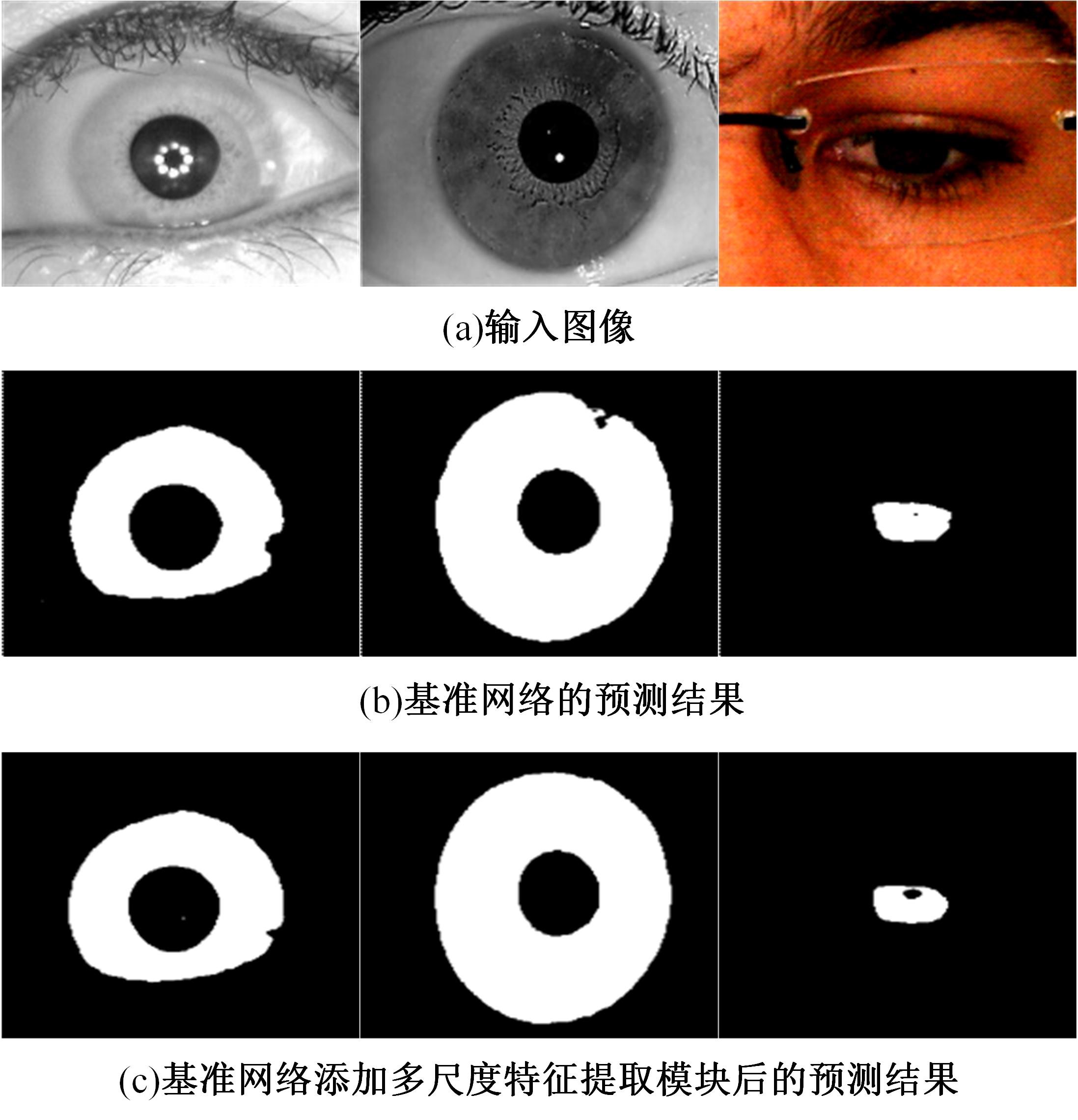
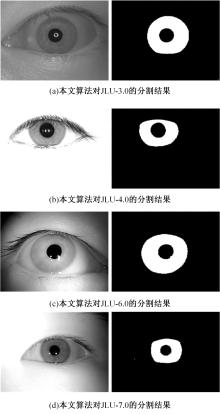
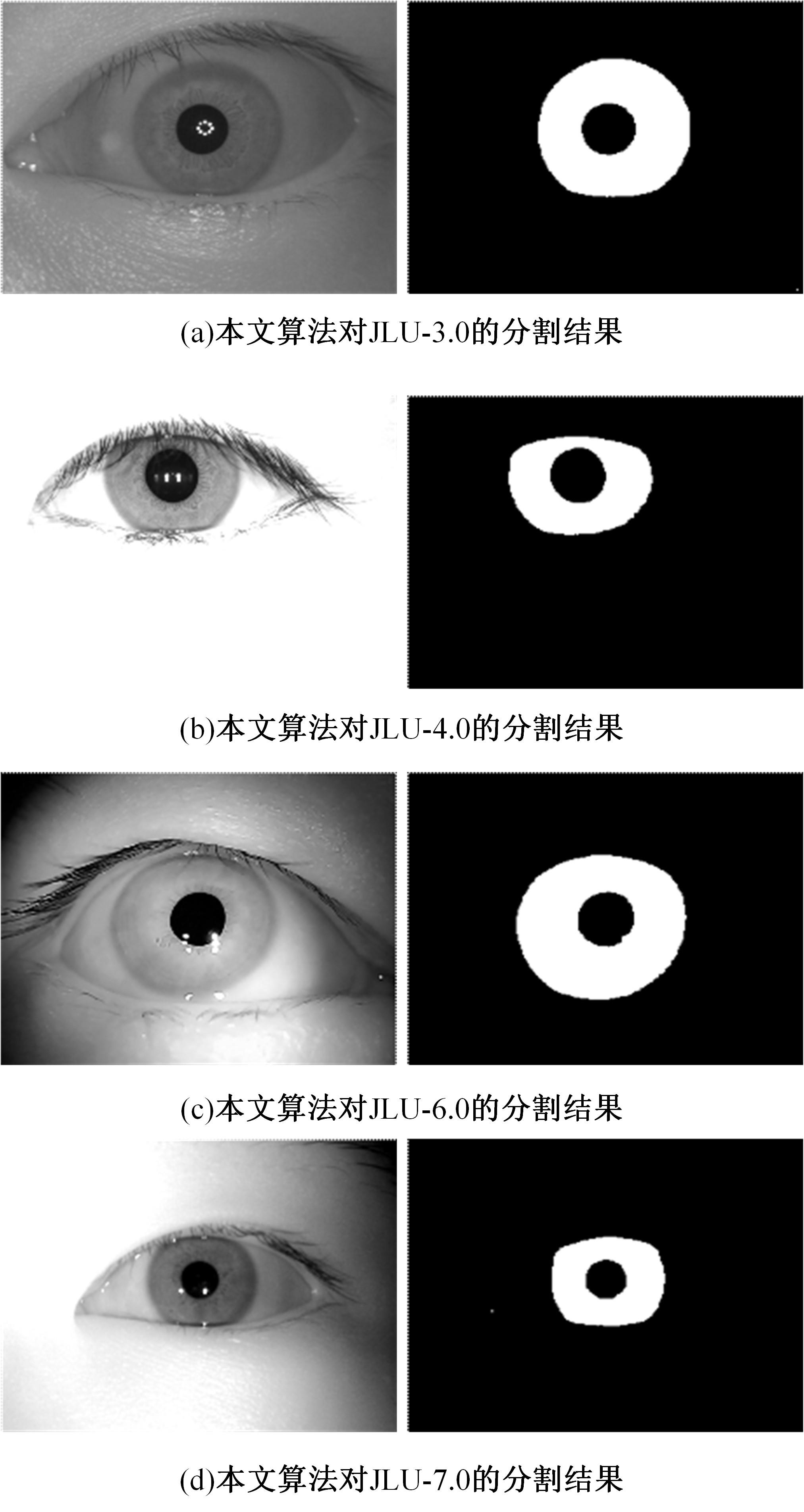
针对基于深度学习的虹膜分割模型存在参数量大、计算量大、占用空间大的问题,提出了一种轻量级的虹膜分割模型。首先,将Linknet中特征提取网络替换为改进的轻量级网络MobileNetv3。这种设计在保持准确性的同时显著地提高了模型效率。其次,为了减少虹膜特征信息丢失,设计了一个多尺度特征提取模块。再次,引入了通道注意力机制,抑制无关噪声,加大虹膜区域的权重。最后,在3个虹膜数据库上将本文模型与其他虹膜分割模型进行比较,结果表明,本文模型在虹膜分割准确率和效率之间取得了更好的平衡。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Arsalan M, Naqvi R A, Kim D S, et al. IrisDenseNet: robust iris segmentation using densely connected fully convolutional networks in the images by visible light and near-infrared light camera sensors[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): No.1501. |
| 2 | Huo Guang, Lin Da-wei, Yuan Meng, et al. Heterogeneous iris segmentation method based on modified U-Net[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2021, 30(6): No.063015. |
| 3 | Umer S, Dhara B C. A fast iris localization using inversion transform and restricted circular hough transform[C]∥Proceedings of the 2015 8th International Conference on Advances in Pattern Recognition, Kolkata, India, 2015: 1-6. |
| 4 | Bendale A, Nigam A, Prakash S, et al. Iris segmentation using improved hough transform[C]∥Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Intelligent Computing, Huangshan, China, 2012: 408-415. |
| 5 | Roy D A, Soni U S. IRIS segmentation using Daughman's method[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Electrical, Electronics, and Optimization Techniques, Chennai, India, 2016: 2668-2676. |
| 6 | 周锐烨, 沈文忠. PI-Unet: 异质虹膜精确分割神经网络模型的研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(15): 223-229. |
| Zhou Rui-ye, Shen Wen-zhong. PI-Unet: research on precise iris segmentation neural network model for heterogeneous iris[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2021, 57(15): 223-229. | |
| 7 | Shelhamer E, Long J, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640-651. |
| 8 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241. |
| 9 | Chaurasia A, Culurciello E. LinkNet: exploiting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing, Petersburg, USA, 2017: 1-4 |
| 10 | Chen Ying, Wang Wen-yuan, Zeng Zhuang, et al. An adaptive CNNs technology for robust iris segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 64517-64532. |
| 11 | Wang Cai-yong, Wang Yun-long, Xu Bo-qiang, et al. A lightweight multi-label segmentation network for mobile iris biometrics[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 1006-1010. |
| 12 | Zhong Z L, Lin Z, Bidart R, et al. Squeeze-and-attention networks for semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 13062-13071. |
| 13 | Biometrics ideal test. CASIA.v4 Database[DB/OL]. [2022-01-06]. |
| 14 | Kumar A, Passi A. Comparison and combination of iris matchers for reliable personal authentication[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(3): 1016-1026. |
| 15 | Proena H, Filipe S, Santos R, et al. The UBIRIS.v2: a database of visible wavelength iris images captured on-the-move and at-a-distance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(8): 1529-1535. |
| 16 | Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi S A. V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Conference on 3D Vision, Stanford, USA, 2016: 565-571. |
| 17 | Rathgeb C. Iris Biometrics from Segmentation to Template Security[M]. Iris Biometrics: From Segmentation to Template Security, 2012. |
| 18 | Wild P, Hofbauer H, Ferryman J, et al. Segmentation-level fusion for iris recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group, Darmstadt, Germany, 2015: 1-6. |
| 19 | Uhl A, Wild P. Weighted adaptive hough and ellipsopolar transforms for real-time iris segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2012 5th IAPR International Conference on Biometrics, New Delhi, India, 2012: 283-290. |
| 20 | A biometric reference system for iris, ersion osiris V 4.1[EB/OL]. [2022-01-06]. |
| 21 | Uhl A, Wild P. Multi-stage visible wavelength and near infrared iris segmentation framework[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition, Aveiro, Portugal, 2012: 1-10. |
| 22 | Ahmad S, Fuller B. Unconstrained iris segmentation using convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2018: 450-466. |
| 23 | Alonsofern J O. Iris boundaries segmentation using the generalized structure tensor—a study on the effects of image degradation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2012 5th IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems, Arlington, USA, 2012: 426-431. |
| 24 | Ehsaneddin J, Andreas U. Iris segmentation using fully convolutional encoder-decoder Networks[C]∥Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, USA, 2017: 133-155. |
| 25 | 尤轩昂, 赵鹏, 慕晓冬, 等. 融合注意力机制与密集多尺度特征的异质噪声虹膜分割方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2022, 59(4): 109-120 |
| You Xuan-ang, Zhao Peng, Mu Xiao-dong, et al. Heterogeneous noise iris segmentation based on attention mechanism and dense multi-scale features[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(4): 109-120. | |
| 26 | Lozej J, Meden B, Struc V, et al. End-to-end iris segmentation using U-Net[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Work Conference on Bioinspired Intelligence,San Carlos, Costa Rica, 2018: 1-6. |
| 27 | Zhang Wei, Lu Xiao-qi, Gu Yu, et al. A robust iris segmentation scheme based on improved U-Net[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 85082-85089. |
| 28 | Wang Qi, Meng Xiang-yue, Sun Ting, et al. A light iris segmentation network[J]. The Visual Computer, 2021, 38: 2591-2601. |
| 29 | He Kai-ming, Zhang Xiang-yu, Ren Shao-qiang, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770-778. |
| [1] | 何颖,王卓然,周旭,刘衍珩. 融合社交地理信息加权矩阵分解的兴趣点推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2632-2639. |
| [2] | 张云佐,董旭,蔡昭权. 拟合下肢几何特征的多视角步态周期检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2611-2619. |
| [3] | 肖明尧,李雄飞,朱芮. 基于NSST域像素相关分析的医学图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2640-2648. |
| [4] | 赵亚慧,李飞雨,崔荣一,金国哲,张振国,李德,金小峰. 基于跨语言预训练模型的朝汉翻译质量评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2371-2379. |
| [5] | 郭晓新,李佳慧,张宝亮. 基于高分辨率网络的视杯和视盘的联合分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2350-2357. |
| [6] | 金小俊,孙艳霞,于佳琳,陈勇. 基于深度学习与图像处理的蔬菜苗期杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2421-2429. |
| [7] | 车翔玖,徐欢,潘明阳,刘全乐. 生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [8] | 耿庆田,刘植,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [9] | 王连明,吴鑫. 基于姿态估计的物体3D运动参数测量方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2099-2108. |
| [10] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [11] | 唐菲菲,周海莲,唐天俊,朱洪洲,温永. 融合动静态变量的滑坡多步位移预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1833-1841. |
| [12] | 刘培勇,董洁,谢罗峰,朱杨洋,殷国富. 基于多支路卷积神经网络的磁瓦表面缺陷检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1449-1457. |
| [13] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [14] | 张则强,梁巍,谢梦柯,郑红斌. 混流双边拆卸线平衡问题的精英差分进化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1297-1304. |
| [15] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
|