吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (2): 478-484.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220963
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑交通梗塞的合流区交通状况诊断
- 南京理工大学 自动化学院,南京 210094
Traffic condition diagnosis of confluence areas considering traffic infarction
Xin ZHANG( ),Qi-zhou HU,Jun HE,Xiao-yu WU
),Qi-zhou HU,Jun HE,Xiao-yu WU
- School of Automation,Nanjing University of Science and Technology,Nanjing 210094,China
摘要:
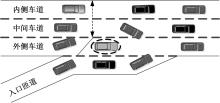
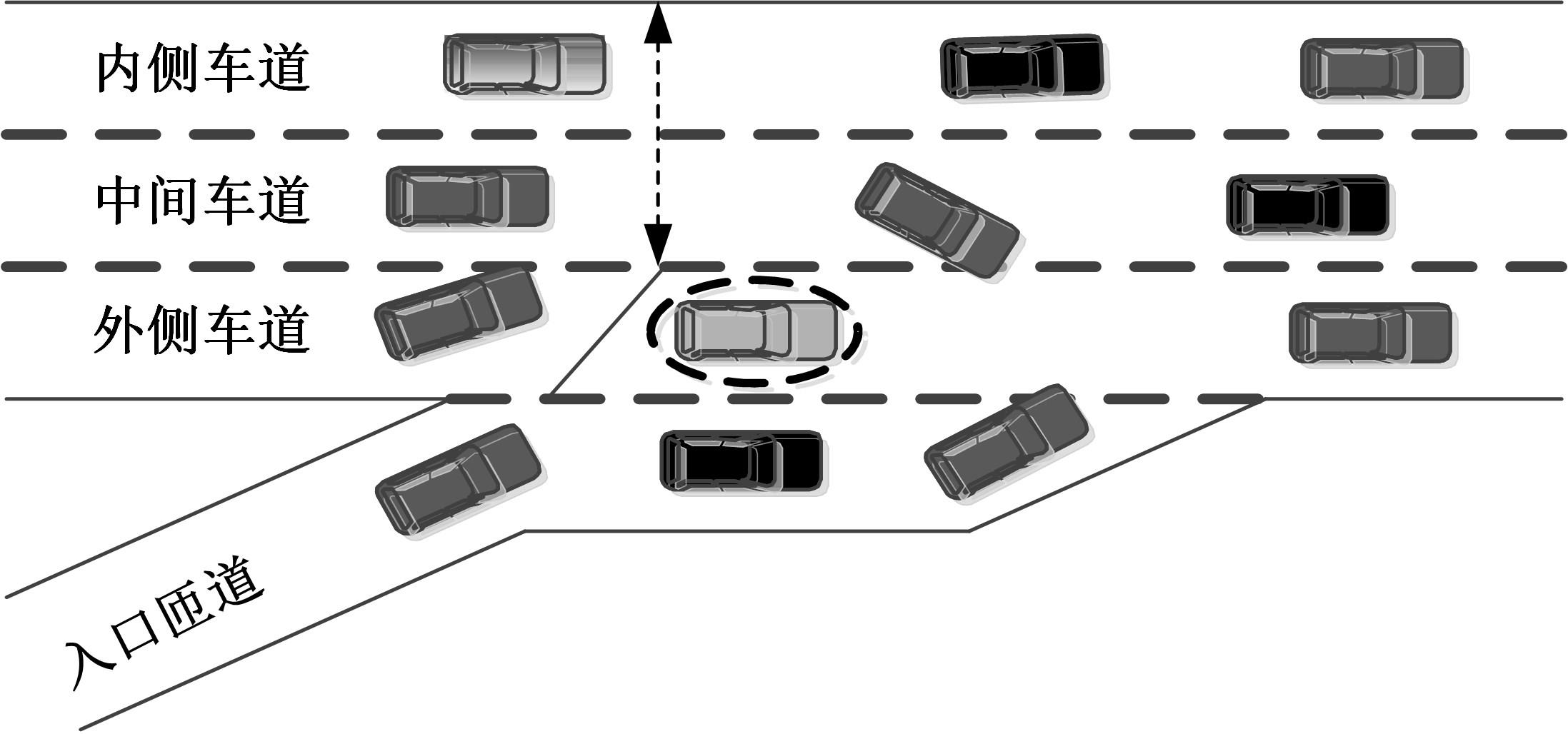
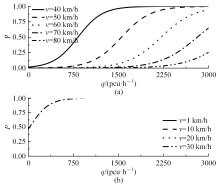
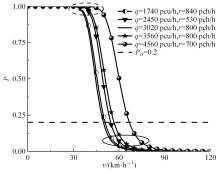
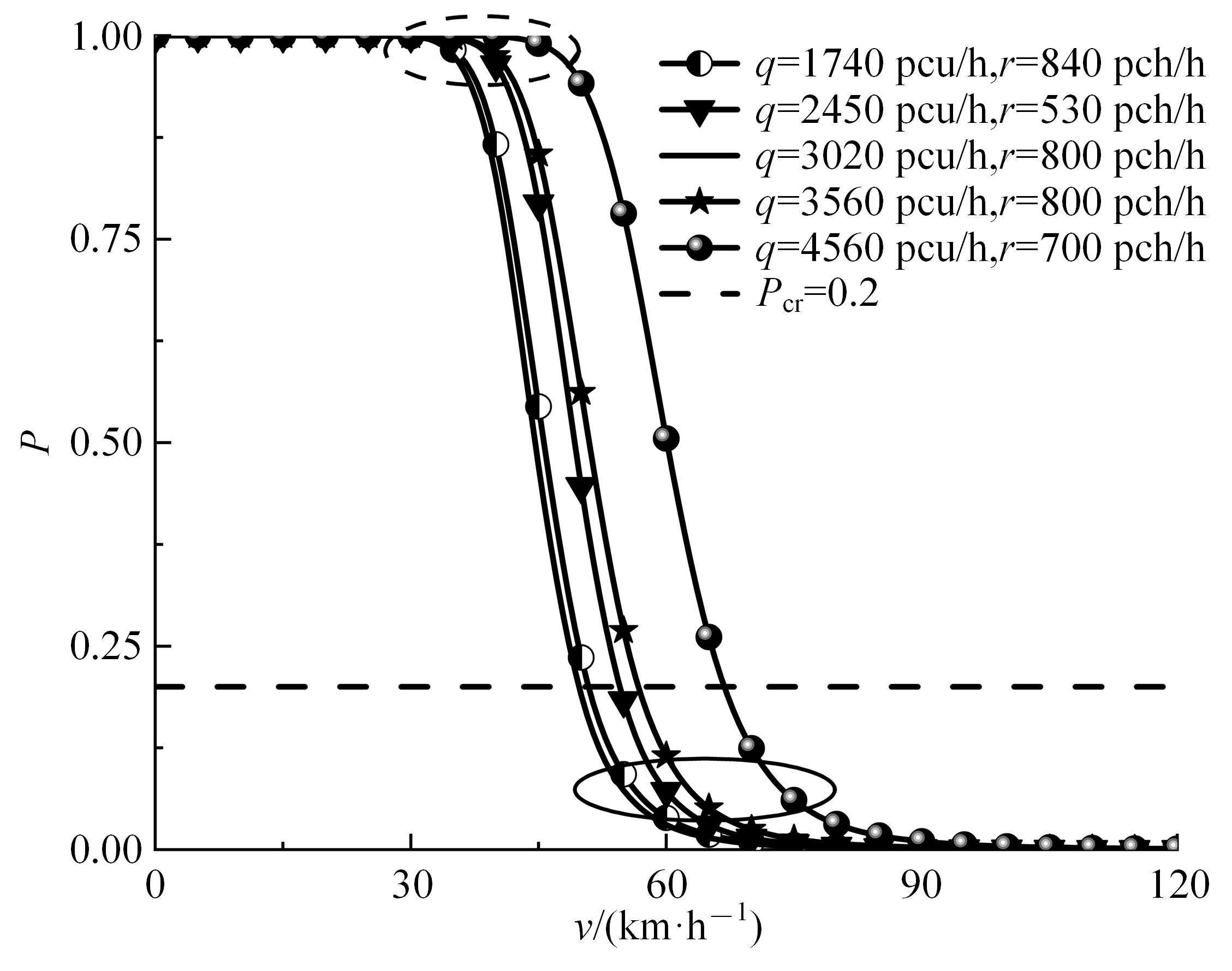
为了从交通梗塞角度诊断合流区交通状况,以交通流breakdown概率为交通梗塞指标并提出了合流区交通状况诊断模型。基于该模型,一方面探究了模型参数的满足条件;另一方面结合控制变量法和标定后的模型探究了交通状况,同时讨论了分析结果并提出了管控策略。结果表明:车流在v较小时难以及时驶离合流区,此时q或r继续增大将增大P;车流在v较大时可及时驶离合流区,P相对较小,但随着q或r继续增大而增大;在已知交通流时,适当调整v可有助于降低P。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 朱洁玉, 马艳丽. 合流区域多车交互风险实时评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(7): 1574-1581. |
| Zhu Jie-yu, Ma Yan-li. Real-time risk assessment method of multi-vehicle interaction at merging area[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(7): 1574-1581. | |
| 2 | 温惠英,吴嘉彬,漆巍巍,等. 高速公路入口匝道合流区的 CP-CS 融合模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 48(2): 50-57. |
| Wen Hui-ying, Wu Jia-bin, Qi Wei-wei, et al. CP-CS fusion model for on-ramp merging area on the Highway[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(2): 50-57. | |
| 3 | 吴文静,战勇斌,杨丽丽,等. 考虑安全间距的合流区可变限速协调控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. |
| Wu Wen-jing, Zhan Yong-bin, Yang Li-li, et al. Coordinated control method of variable speed limit in on⁃ramp area considering safety distance[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1315-1323. | |
| 4 | Wei H, Rong D L, Zhang Z L, et al. Stability analysis and speed-coordinated control of mixed traffic flow in expressway merging area[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2022, 148(11): 04022098. |
| 5 | Cho H W, Laval J A. Combined ramp-metering and variable speed limit system for capacity drop control at merge bottlenecks[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2020, 146(6): 04020033. |
| 6 | Jia S, Hui F, Guo J, et al. Study on connected control strategy of urban expressway merging areas[C]∥ 20th COTA International Conference of Transportation, Xi'an, China, 2020: 1962-1973. |
| 7 | 马庆禄, 闫浩, 聂振宇, 等. 匝道合流区智能网联车辆协同控制方法[J/OL]. [2024-01-02]. |
| Ma Qing-lu, Yan Hao, Nie Zhen-yu, et al. Cooperative control method for intelligent networked vehicles in ramp confluence area[J/OL]. [2024-01-02]. | |
| 8 | 薛行健,戈林娟,邓力容,等. 快速路匝道合流区流量, 加速车道长度与通行能力关系[J]. 铁道科学与工程学报, 2020,17(2): 509-515. |
| Xue Xing-jian, Ge Lin-juan, Deng Li-rong, et al. Relationship between acceleration lane length, flow and capacity in the urban expressway ramp merging section[J]. Journal of Railway Science and Engineering, 2020,17(2): 509-515. | |
| 9 | 何烈云,杜心全,王镇波. 基于车流波动理论城市快速路匝道间距比例模型研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(36): 81-85. |
| He Lie-yun, Du Xin-quan, Wang Zhen-bo. The research of urban expressway on-ramp spacing ratio model based on traffic wave theory[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(36): 81-85. | |
| 10 | 吴勇,孙棣华,李蕊,等. 快速路合流区交通事故影响因素研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 2015, 28(9): 98-105. |
| Wu Yong, Sun Di-hua, Li Rui, et al. Study on crash influencing factors at expressway merge segments[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2015, 28(9): 98-105. | |
| 11 | 李宗平,李林恒. 快速路合流区加速车道长度计算方法[J].东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 46(4): 888-892. |
| Li Zong-ping, Li Lin-heng. Computational method of acceleration lane length in expressway merging area[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 46 (4): 888-892. | |
| 12 | Elefteriadou L, Kondyli A, Brilon W, et al. Enhancing ramp metering algorithms with the use of probability of breakdown models[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2014, 140(4): 634-647. |
| 13 | 郝媛,孙立军,徐天东. 交通流 Breakdown 现象与交通扰动演化模型[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 37(9): 1178-1184. |
| Hao Yuan, Sun Li-jun, Xu Tian-dong. Traffic breakdown phenomenon and evolution Model of traffic perturbation[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2009, 37(9): 1178-1184. | |
| 14 | Banks J H. Two-capacity phenomenon at freeway bottlenecks: a basis for ramp metering?[J]. Transportation Research Record, 1991(1320): 83-90. |
| 15 | Persaud B, Yagar S, Tsui D, et al. Breakdown-related capacity for freeway with ramp metering[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2001,1748(1):110-115. |
| 16 | 王炜,过秀成. 交通工程学[M]. 南京:东南大学出版社, 2000. |
| 17 | 李林恒,李宗平,李远辉. 合流区匝道交通量控制指标计算方法研究[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2015, 13(3): 64-69. |
| Li Lin-heng, Li Zong-ping, Li Yuan-hui. Computational method of control indicators for ramp traffic volume in the merging area[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2015, 13(3): 64-69. | |
| 18 | 丁悦. 基于交通安全的互通立交合流区交通流特性研究[D]. 南京:东南大学交通学院, 2017. |
| Ding Yue. Study on traffic flow characteristics of interchange merging-areas basing on traffic safety[D]. Nanjing: School of Transportation, Southeast University, 2017. |
| [1] | 张卫华,刘嘉茗,解立鹏,丁恒. 网联混合环境快速路交织区自动驾驶车辆换道模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 469-477. |
| [2] | 岳昊,张琦悦,杨子玉,任孟杰,张旭. 拥堵空间排队的静态交通流分配迭代加权算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 136-145. |
| [3] | 杜筱婧,姚荣涵. 智能网联公交车出站强制换道的演化博弈机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 124-135. |
| [4] | 李义,吕晨阳,梁继才,梁策. 不规则Y形铝型材多点拉弯成形截面变形分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(1): 105-113. |
| [5] | 马壮林,崔姗姗,胡大伟,王晋. 限行政策下传统小汽车出行者出行方式选择[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1981-1993. |
| [6] | 张雅丽,付锐,袁伟,郭应时. 考虑能耗的进出站驾驶风格分类及识别模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2029-2042. |
| [7] | 尹超英,陆颖,邵春福,马健霄,许得杰. 考虑空间自相关的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1994-2000. |
| [8] | 潘恒彦,王永岗,李德林,陈俊先,宋杰,杨钰泉. 基于交通冲突的长纵坡路段追尾风险评估及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1355-1363. |
| [9] | 宋灿灿,荆迪菲,谢俊峰,康可心. 设置广告牌的高速公路平曲线路段驾驶行为分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1345-1354. |
| [10] | 卢凯,徐广辉,叶志宏,林永杰. 考虑清空时间的双向队首绿波协调控制数解算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 421-429. |
| [11] | 曹倩,李志慧,陶鹏飞,马永建,杨晨曦. 考虑风险异质特性的路网交通事故风险评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2817-2825. |
| [12] | 朱洁玉,马艳丽. 合流区域多车交互风险实时评估方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1574-1581. |
| [13] | 张鑫,张卫华. 快速路合流区主线不同交通状态下的安全性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1308-1314. |
| [14] | 曲大义,赵梓旭,贾彦峰,王韬,刘琼辉. 基于Lennard-Jones势的车辆跟驰动力学特性及模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2549-2557. |
| [15] | 董春娇,董黛悦,诸葛承祥,甄理. 电动自行车出行特性及骑行决策行为建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2618-2625. |
|
||