吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 3050-3057.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221587
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
噪声环境下外骨骼设备语音信号的特征提取
陈文杰1,2( ),苏振兴1,2,孙先涛1,2,刘远远1,胡祥涛1,智亚丽1
),苏振兴1,2,孙先涛1,2,刘远远1,胡祥涛1,智亚丽1
- 1.安徽大学 电气工程与自动化学院,合肥 230601
2.安徽大学 安徽省人机共融系统与智能装备工程实验室,合肥 230601
Feature extraction of speech signals of exoskeleton devices in noise environments
Wen-jie CHEN1,2( ),Zhen-xing SU1,2,Xian-tao SUN1,2,Yuan-yuan LIU1,Xiang-tao HU1,Ya-li ZHI1
),Zhen-xing SU1,2,Xian-tao SUN1,2,Yuan-yuan LIU1,Xiang-tao HU1,Ya-li ZHI1
- 1.School of Electrical Engineering and Automation,Anhui University,Hefei 230601,China
2.Anhui Engineering Laboratory of Human-Robot Collaboration System and Intelligent Equipment,Anhui University,Hefei 230601,China
摘要:
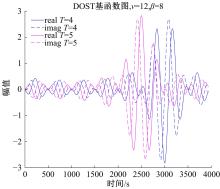
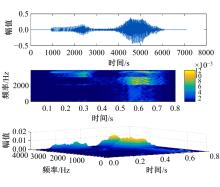
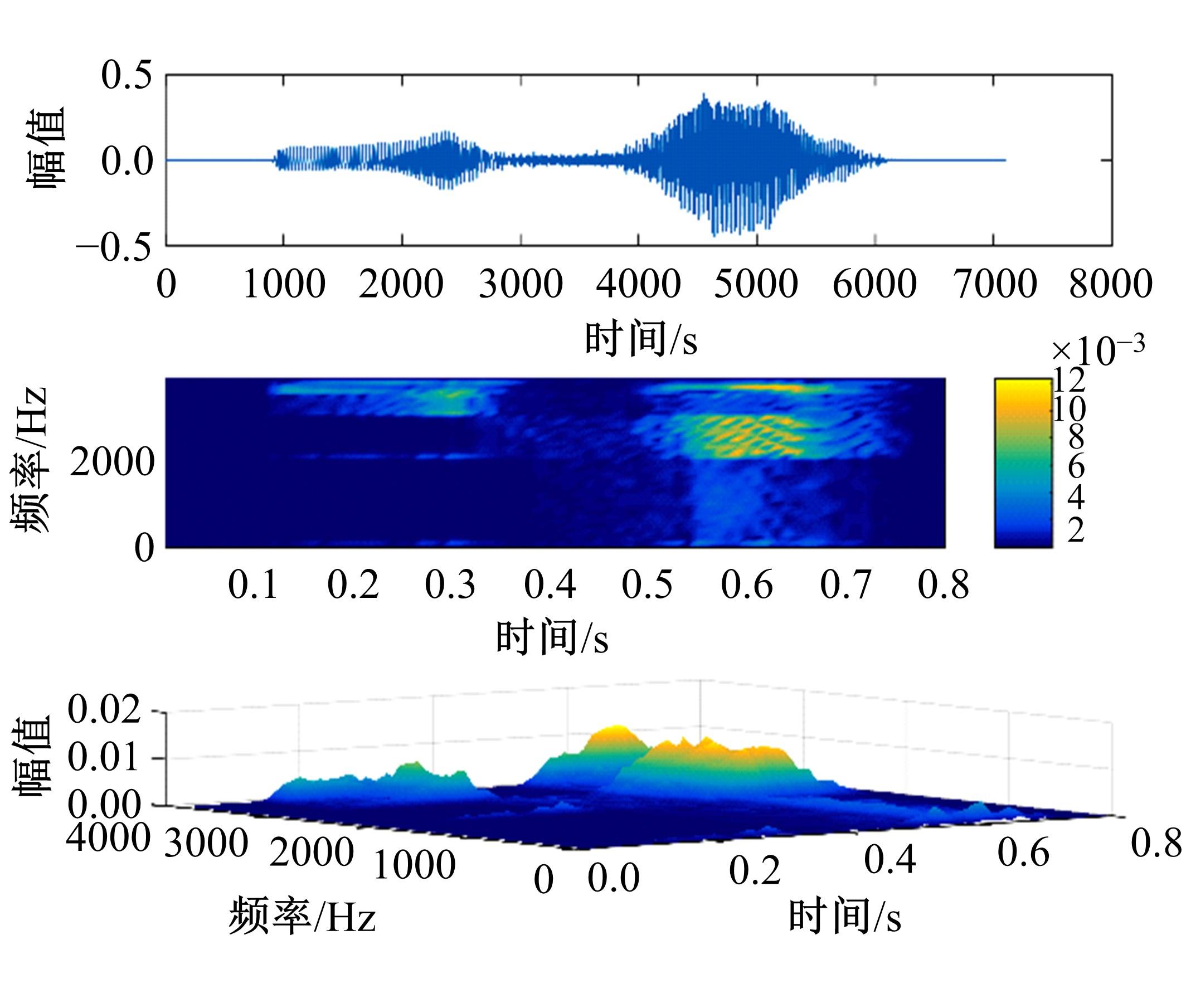
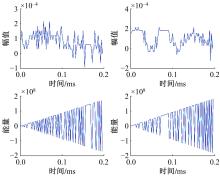
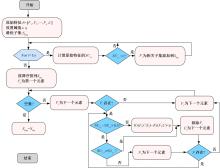
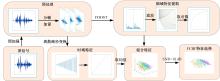
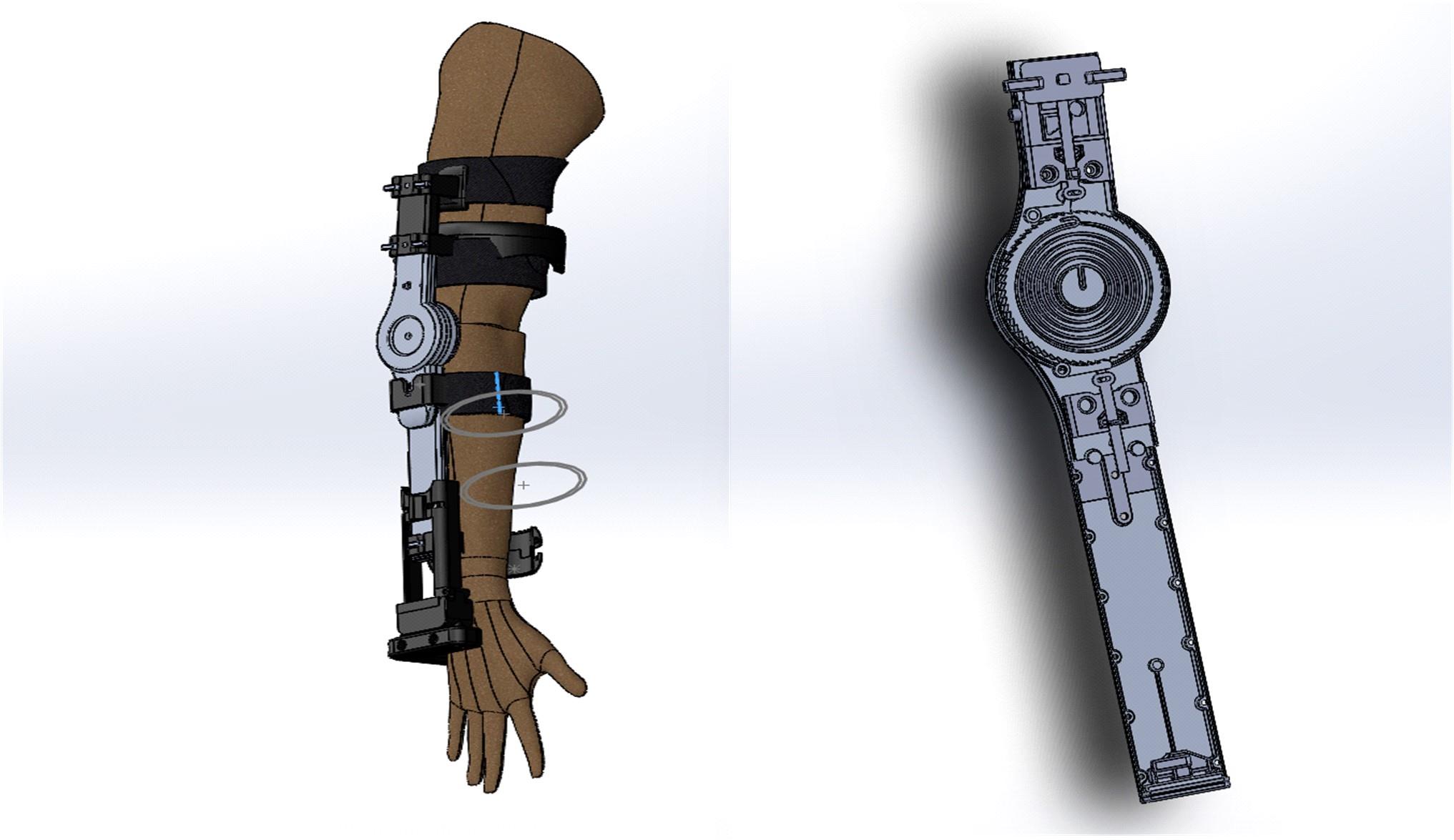
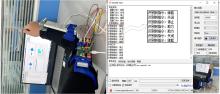
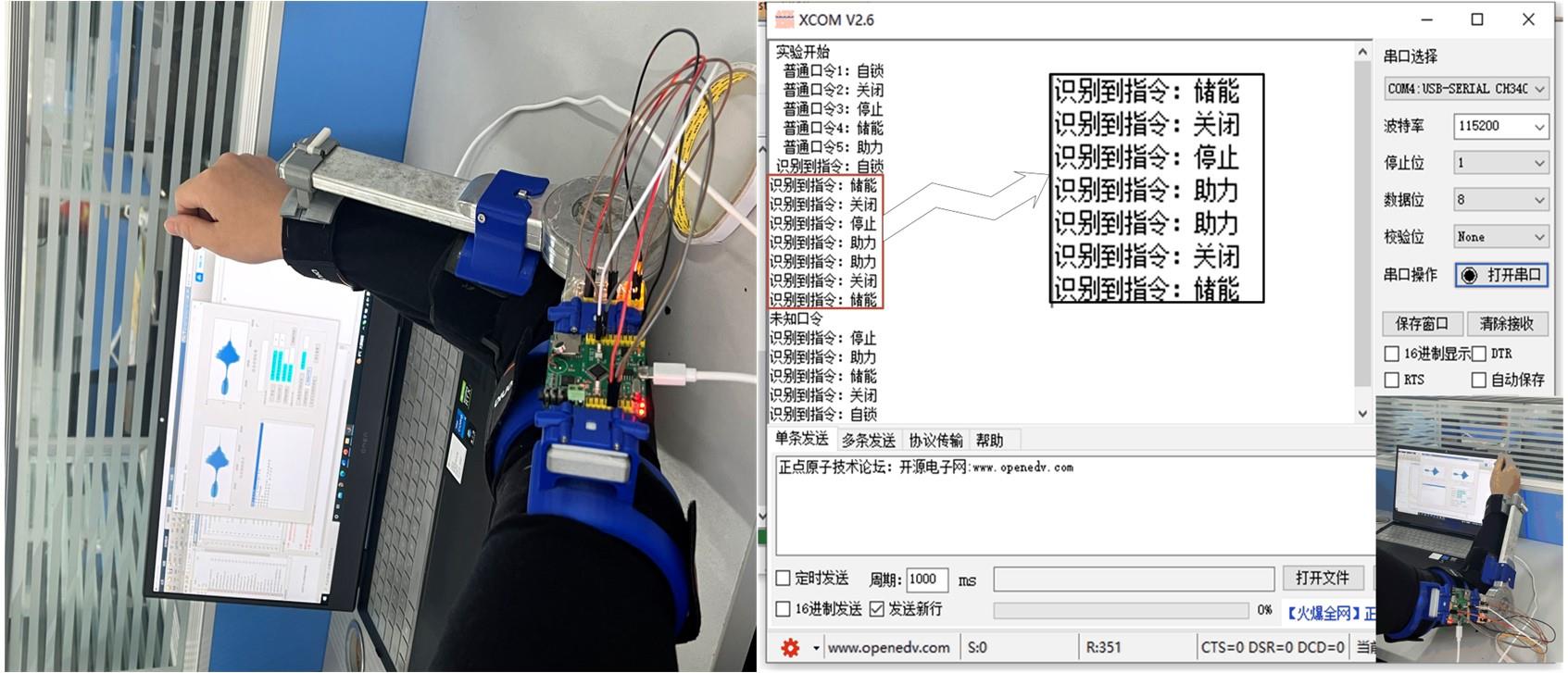
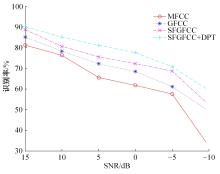
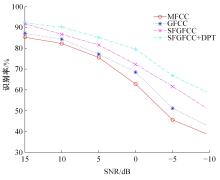
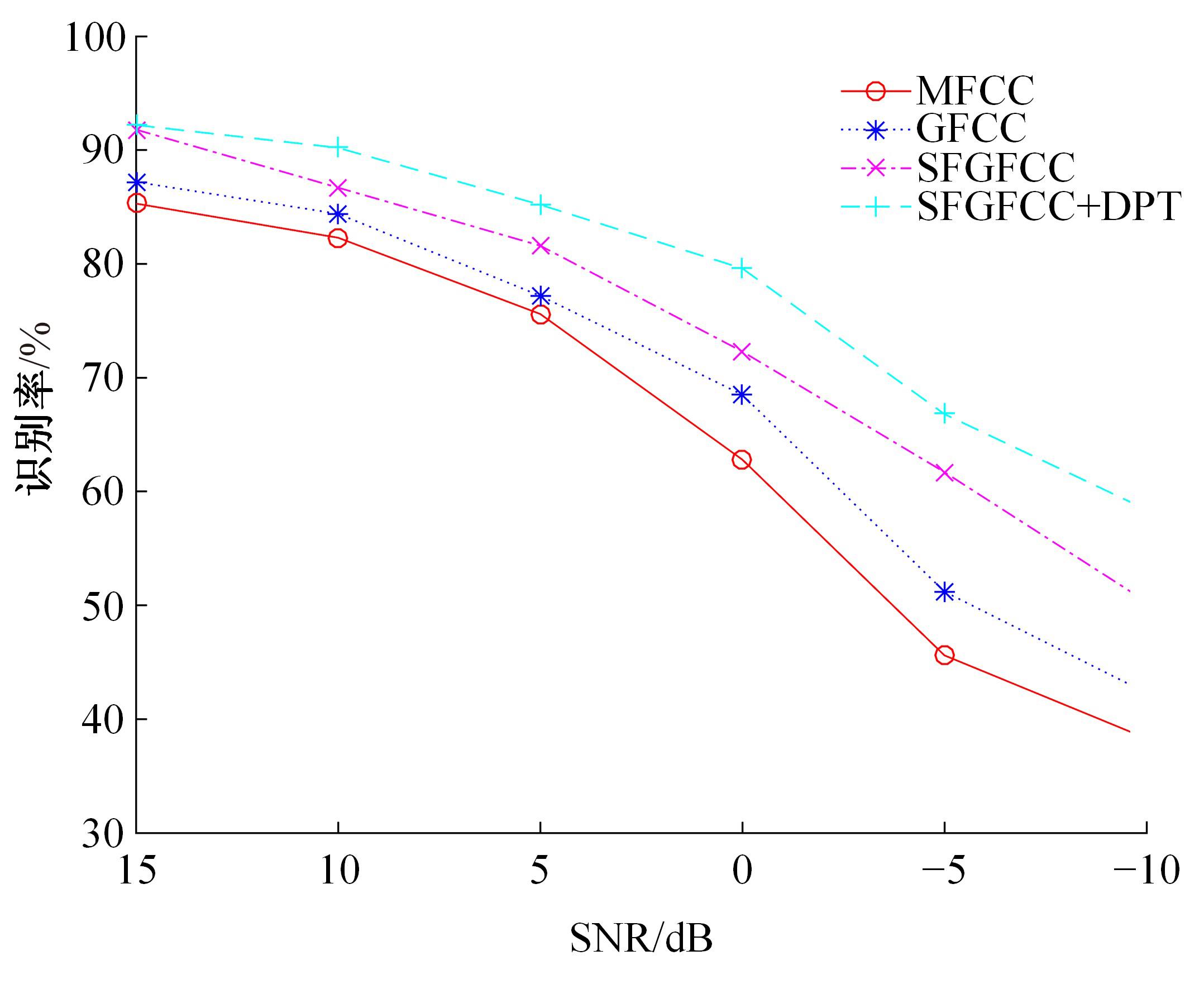
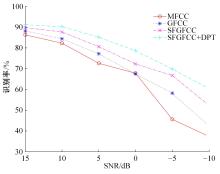
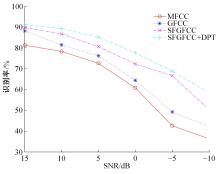
针对外骨骼设备语音系统在实际工作环境中受到环境噪声的影响导致语音指令识别性能差的问题,本文提出基于离散正交斯托克韦尔变换的伽马通滤波器频率倒谱系数的语音特征,结合离散路径变换表征语音信号能量与过零率的时域信息,形成混合特征。在低信噪比情况下,考虑特征之间的冗余性、不相关性和信息互补性,采用改进的相关性快速过滤特征选择算法获取最优特征子集,并将其用于外骨骼设备控制命令的语音系统。实验结果表明:本文方法在低信噪比下更具有鲁棒性和稳健性,在信噪比为零的粉红噪声下,较传统梅尔倒谱系数识别率提高20%左右。
中图分类号:
- TN912.3
| 1 | Shaik R, Venkatramaphanikumar S. Sentiment analysiswith word-based Urdu speech recognition[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2022, 13(5): 2511-2531. |
| 2 | Goyal K, Singh A, Kadyan V. A comparison of laryngeal effect in the dialects of Punjabi language[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2022, 13(5): 2415-2428. |
| 3 | Al-Karawi K A, Mohammed D Y. Improving short utterance speaker verification by combining MFCC and entrocy in noisy conditions[J]. Journal of Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2021, 80(14): 22231-22249. |
| 4 | Kadyan V, Bawa P, Hasija T. In domain training data augmentation on noise robust Punjabi children speech recognition[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2022,13: 2705-2721. |
| 5 | 刘国华, 周文斌. 基于卷积神经网络的脉搏波时频域特征混叠分类[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1818-1825. |
| Liu Guo-hua, Zhou Wen-bin. Pulse wave signal classification algorithm based on time frequency domain feature aliasing using convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020,50(5): 1818-1825. | |
| 6 | Wei D, Zhang Y, Li Y M. Linear canonical stockwell transform: theory and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022, 70: 1333-1347. |
| 7 | 李海峰, 房春英, 马琳, 等. 病理语音的S变换特征[J]. 清华大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 56(7): 765-771. |
| Li Hai-feng, Fang Chun-ying, Ma Lin, et al. S-transform feature for pathological speech[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University(Science & Technology), 2016, 56(7): 765-771. | |
| 8 | 袁莉芬, 李松, 尹柏强, 等. 基于自适应快速S变换和 XGBoost的心电信号精确快速分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2023, 45(4): 1464-1474. |
| Yuan Li-fen, Li Song, Yin Bai-qiang, et al. Accurate and fast electrocardiogram classification method based on adaptive fast S-Transform and XGBoost[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information,2023, 45(4): 1464-1474. | |
| 9 | 李峰, 陈皖皖, 杨义. 基于稀疏自适应S变换和深度残差网络的轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2022, 26(8):112-119. |
| Li Feng, Chen Wan-wan, Yang Yi. Research on bearing fault diagnosis based on sparse adaptive S-transform and deep residual network[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2022, 26(8): 112-119. | |
| 10 | Karheily S, Moukadem A, Gourbo J B, et al. sEMG time-frequency features for hand movements classification[J]. Journal of Expert Systems with Applications,2022, 210: No.118282. |
| 11 | Wang Y, Orchard J. Fast discrete orthonormal stockwell transform[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2009, 31(5): 4000-4012. |
| 12 | Guido R C, Pedroso F, Contreras R C, et al. Introducing the discrete path transform(DPT)and its applications in signal analysis, arte factremoval, and spoken word recognition[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 117: No.103158. |
| 13 | Şen B, Peker M. Novel approaches for auto mated epileptic diagnosis using FCBF selection and classifycation algorithms[J]. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, 2013, 21(7): 2092-2109. |
| 14 | 周镇镇. 离散余弦S变换及其在医学图像降噪中的应用研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学信息科学与工程学院, 2016. |
| Zhou Zhen-zhen. Discrete cosine S transform and its application in medical image denoising[D]. Jinan: School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong University, 2016. | |
| 15 | 刘振宇. 基于语音的抑郁识别方法及关键技术研究[D].兰州: 兰州大学信息科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Liu Zhen-yu. Research on method and key technology for depression recognition based on speech[D]. Lanzhou: School of Information Science & Engineering, Lanzhou University, 2017. | |
| 16 | Kranthi Kumar L, Alphonse P J A. COVID-19 disease diagnosis with light-weight CNN using modified MFCC and enhanced GFCC from human respiratory sounds[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2022, 231(18): 3329-3346. |
| [1] | 赖丹晖,罗伟峰,袁旭东,邱子良. 复杂环境下多模态手势关键点特征提取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2288-2294. |
| [2] | 张云佐,郑宇鑫,武存宇,张天. 基于双特征提取网络的复杂环境车道线精准检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1894-1902. |
| [3] | 王长建,刘久明,张锦洲,李斌. 基于高速摄影技术的行星减速箱故障激光序列脉冲诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1869-1875. |
| [4] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [5] | 杨志飞,张佳,李泽阳. 基于增量式学习的复杂网络节点攻击检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2963-2968. |
| [6] | 周丰丰,于涛,范雨思. 基于质谱数据的生成对抗自编码器整合投票算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2969-2977. |
| [7] | 宋世军,樊敏. 基于随机森林算法的大数据异常检测模型设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2659-2665. |
| [8] | 龙恩深,班光泽. 基于小波包信包提取的空调制冷压缩机怠速噪声诊断算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1929-1934. |
| [9] | 白琳,刘林军,李轩昂,吴沙,刘汝庆. 基于自监督学习的单目图像深度估计算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1139-1145. |
| [10] | 周丰丰,颜振炜. 基于混合特征的特征选择神经肽预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3238-3245. |
| [11] | 吕晓琪,李浩,谷宇. 基于深度学习算法的人脸图像活体特征变换尺度提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3201-3206. |
| [12] | 郭辉,付接递,李振东,严岩,李虓. 基于改进鲸鱼算法优化SVM参数和特征选择[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2952-2963. |
| [13] | 李佩泽,赵世舜,翁小辉,蒋鑫妹,崔洪博,乔建磊,常志勇. 基于多传感器优化的农药残留快速检测新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1951-1956. |
| [14] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [15] | 王斌,何丙辉,林娜,王伟,李天阳. 基于随机森林特征选择的茶园遥感提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1719-1732. |
|
||