吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1833-1841.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230079
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
融合动静态变量的滑坡多步位移预测方法
- 1.重庆交通大学 智慧城市学院,重庆 402260
2.重庆交通大学 交通土建工程材料国家地方联合工程研究中心,重庆 400074
3.长安大学 公路学院,西安 710054
Multi⁃step prediction method of landslide displacement based on fusion dynamic and static variables
Fei-fei TANG1( ),Hai-lian ZHOU1,Tian-jun TANG1,Hong-zhou ZHU2,Yong WEN3
),Hai-lian ZHOU1,Tian-jun TANG1,Hong-zhou ZHU2,Yong WEN3
- 1.College of Smart City,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 402260,China
2.National & Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Transportation and Civil Engineering Material,Chongqing Jiaotong University,Chongqing 400074,China
3.School of Highway,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710054,China
摘要:
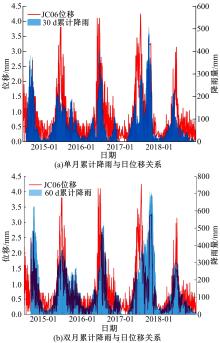
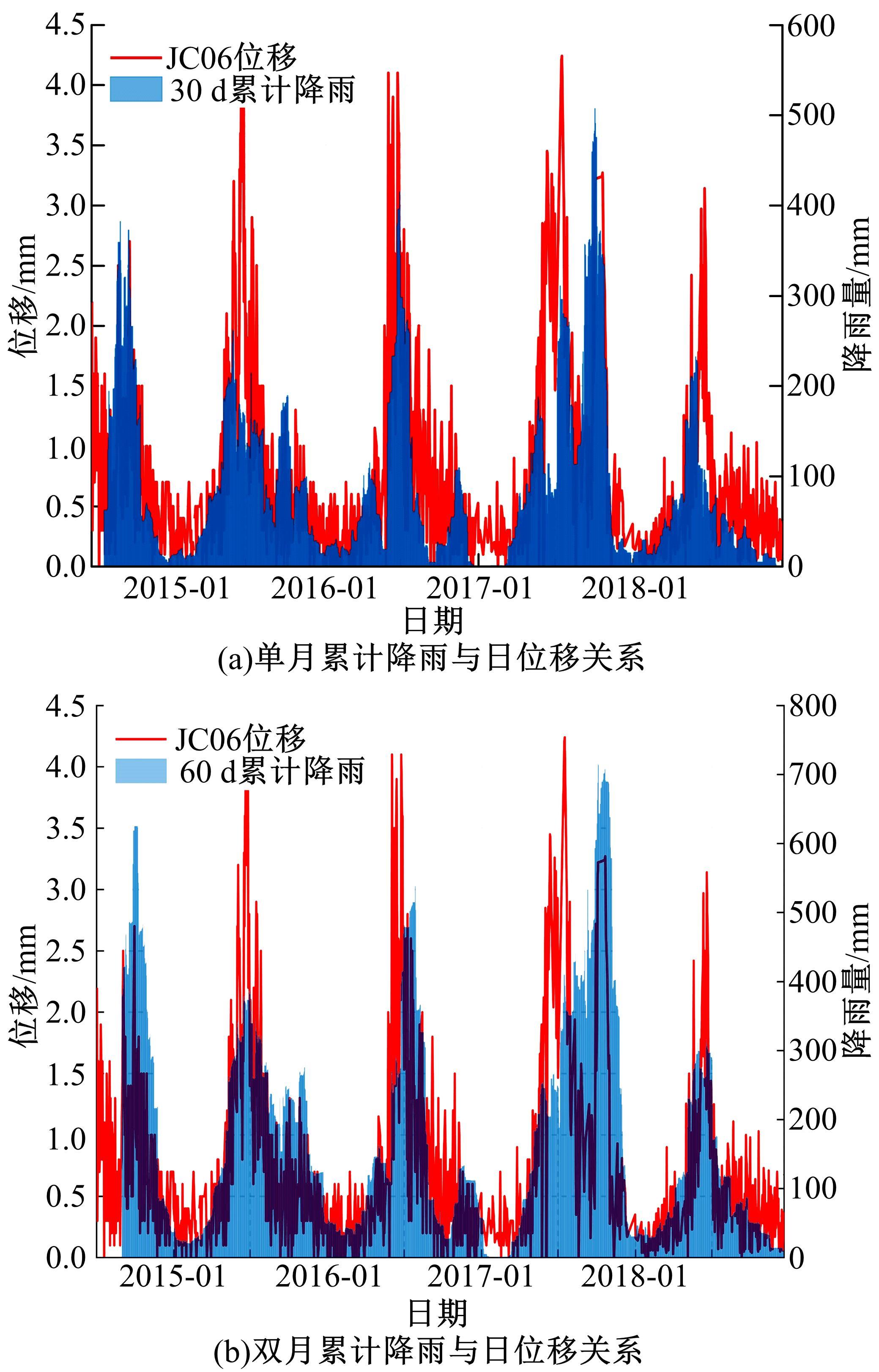
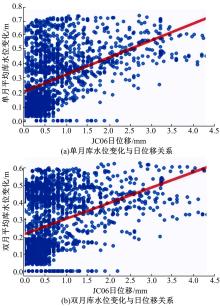
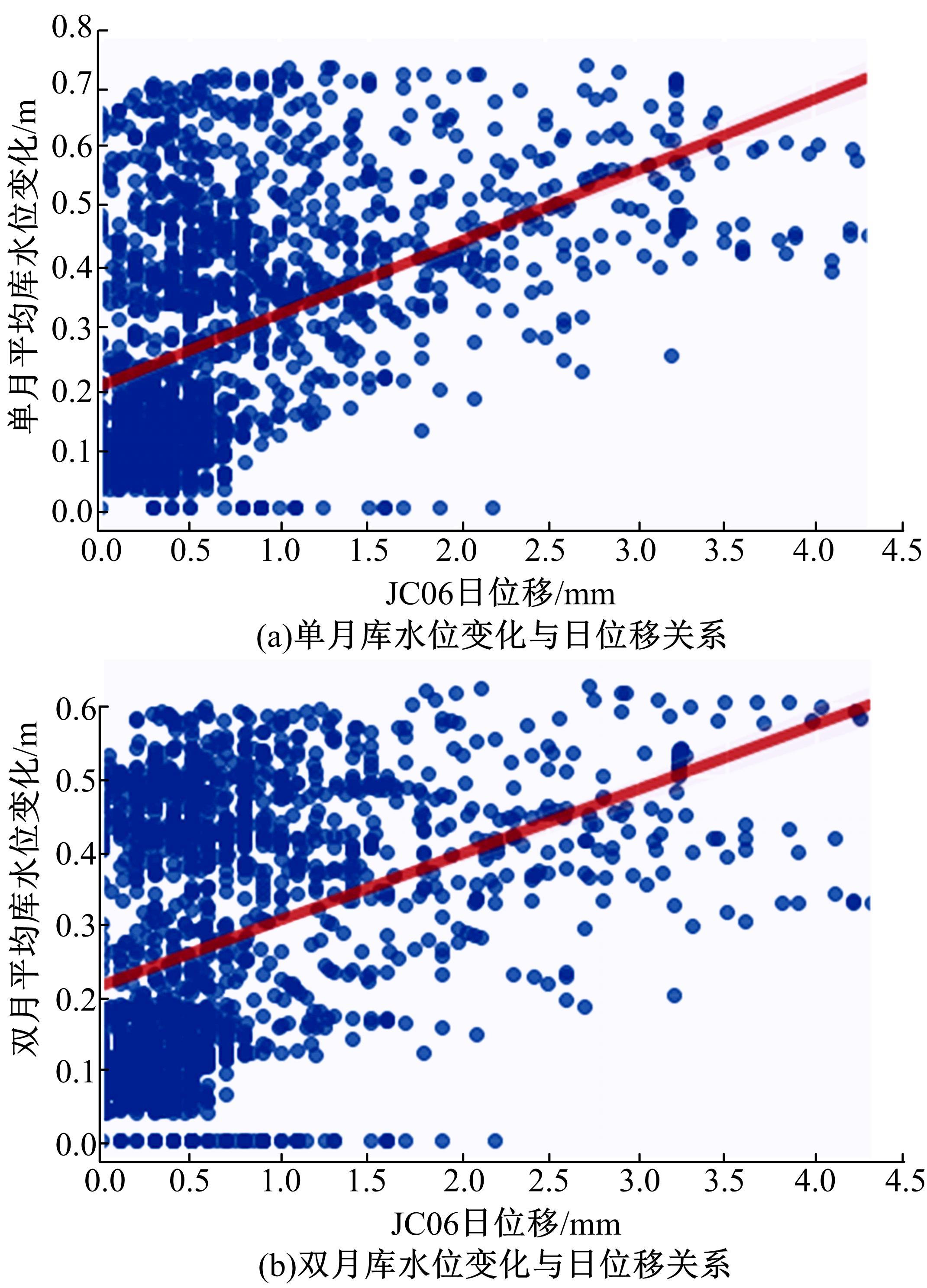
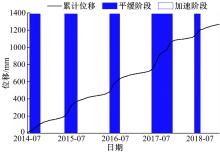
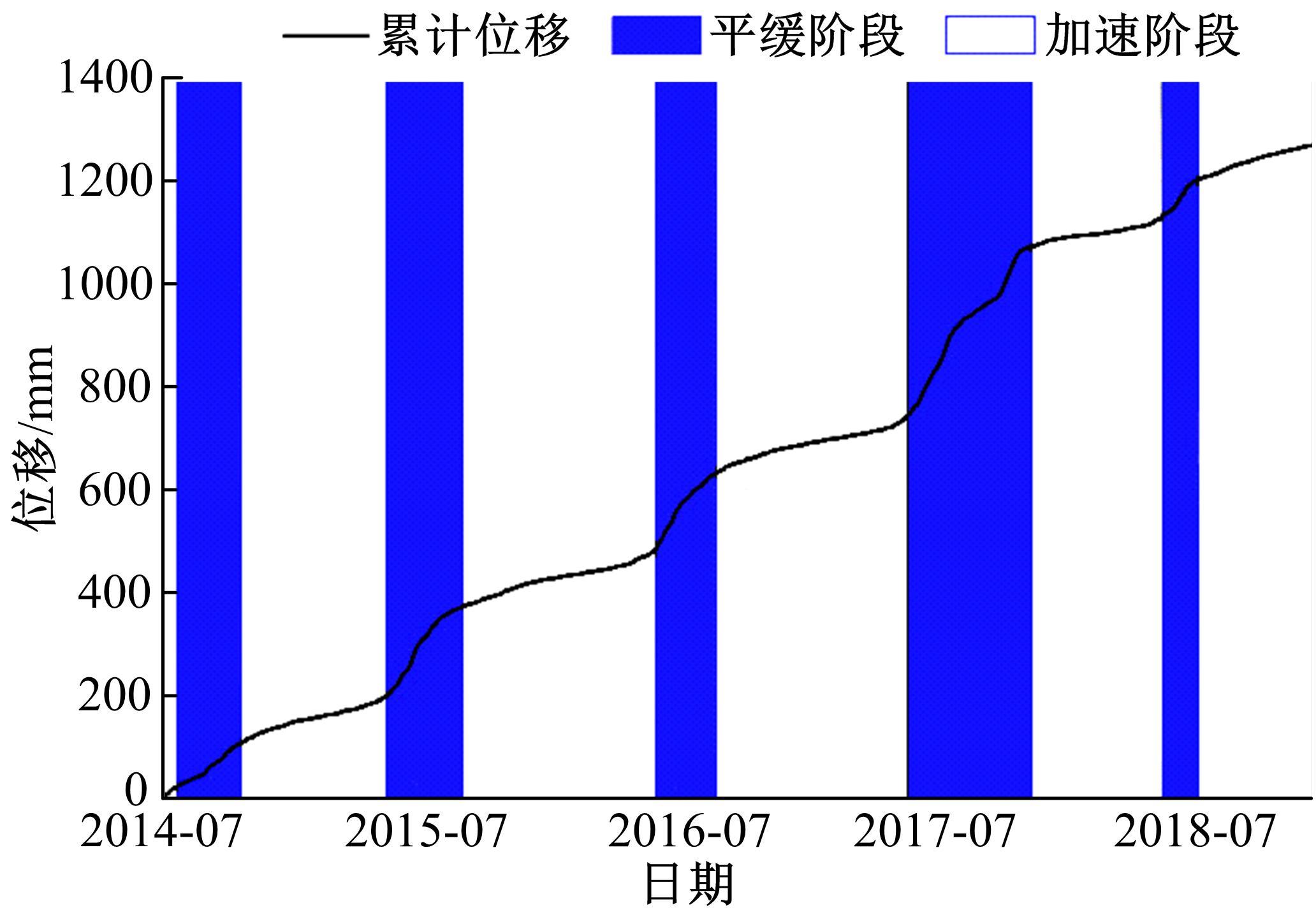
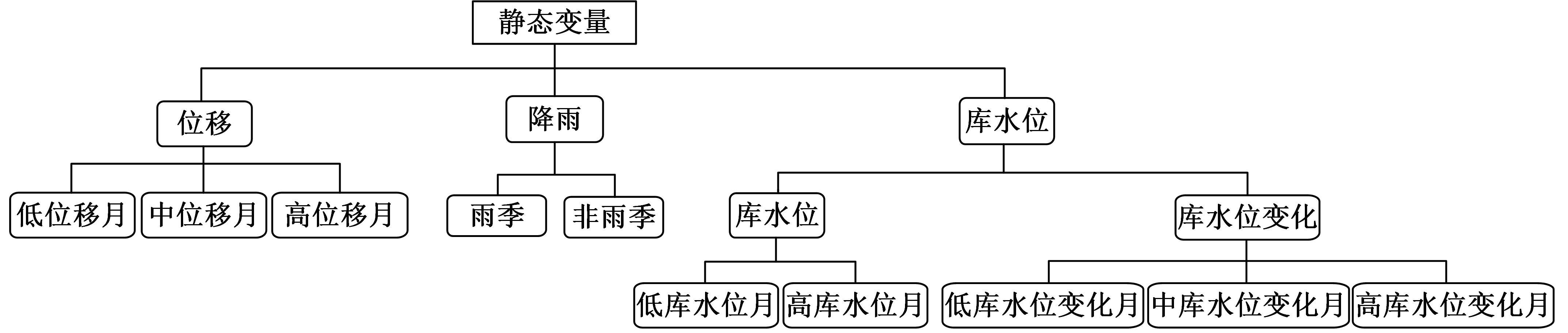
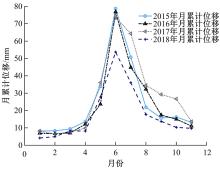
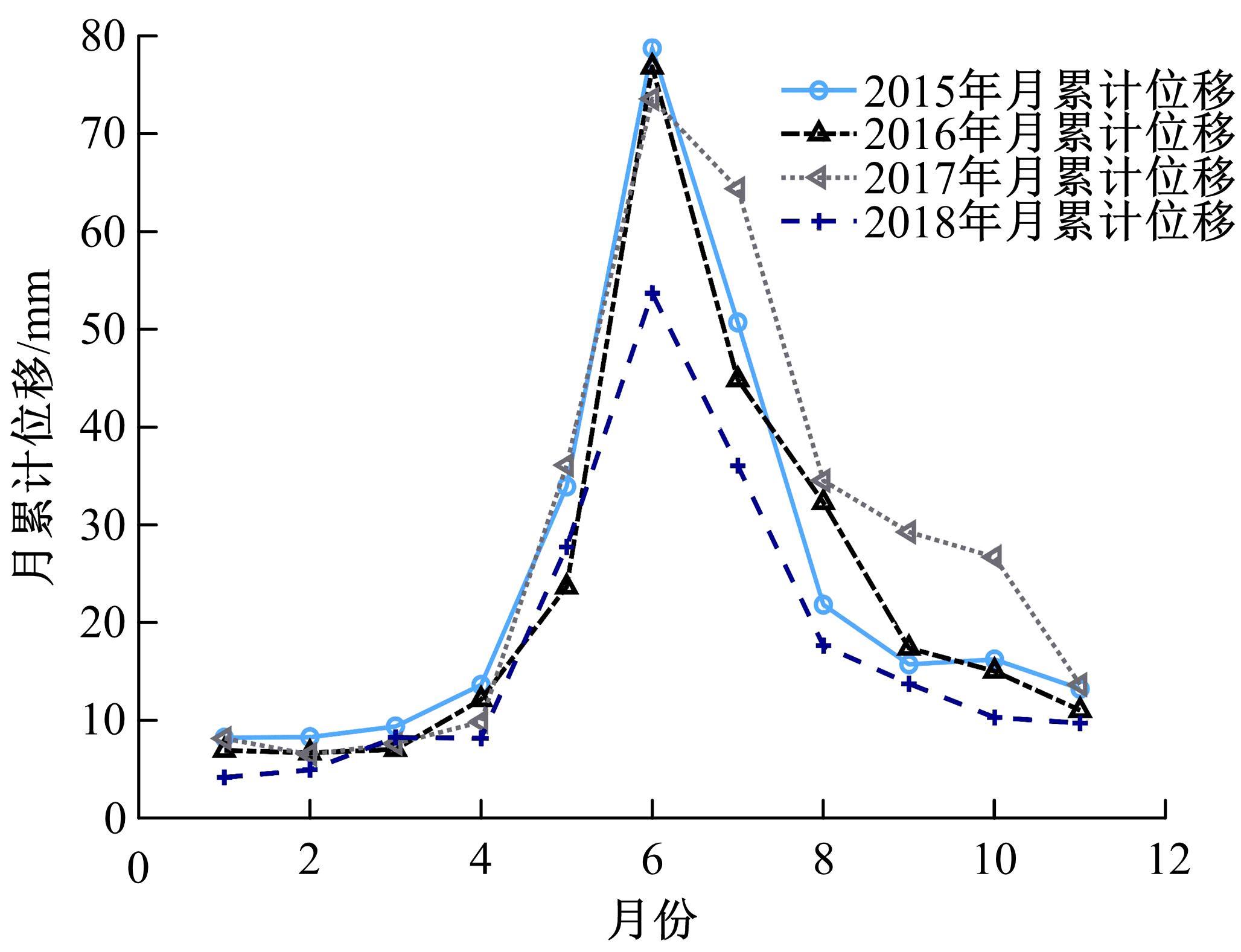
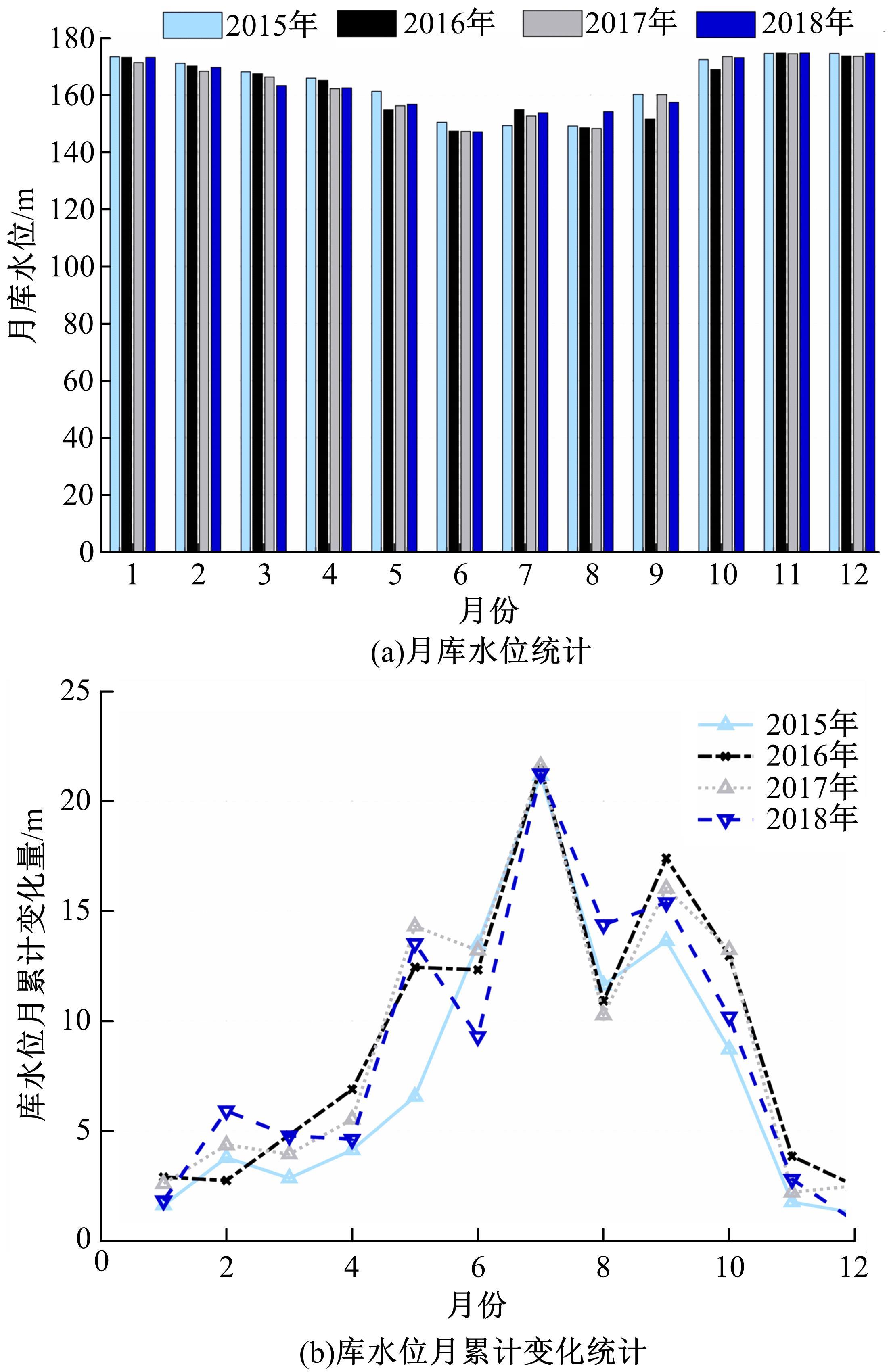
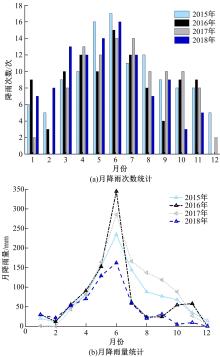
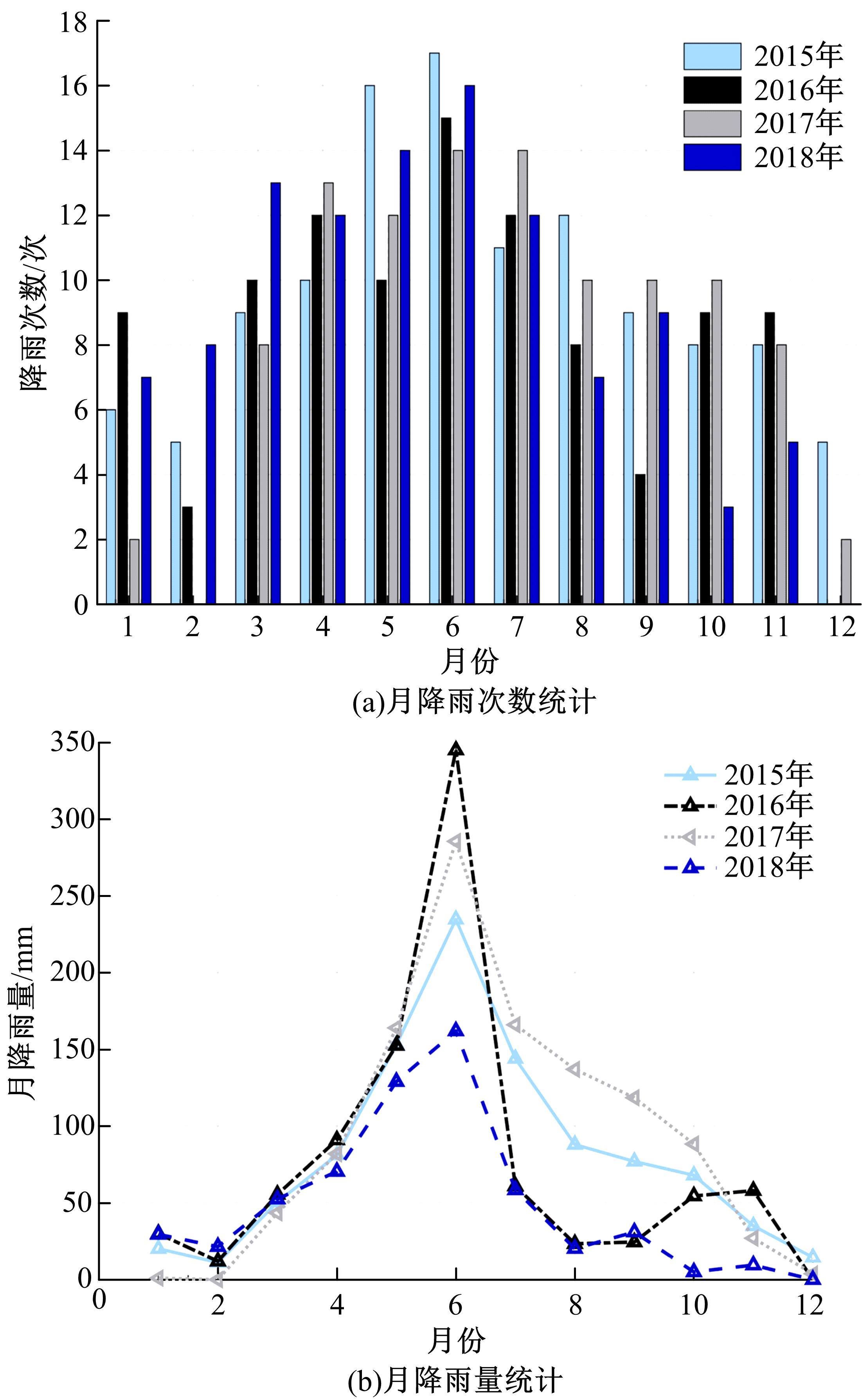
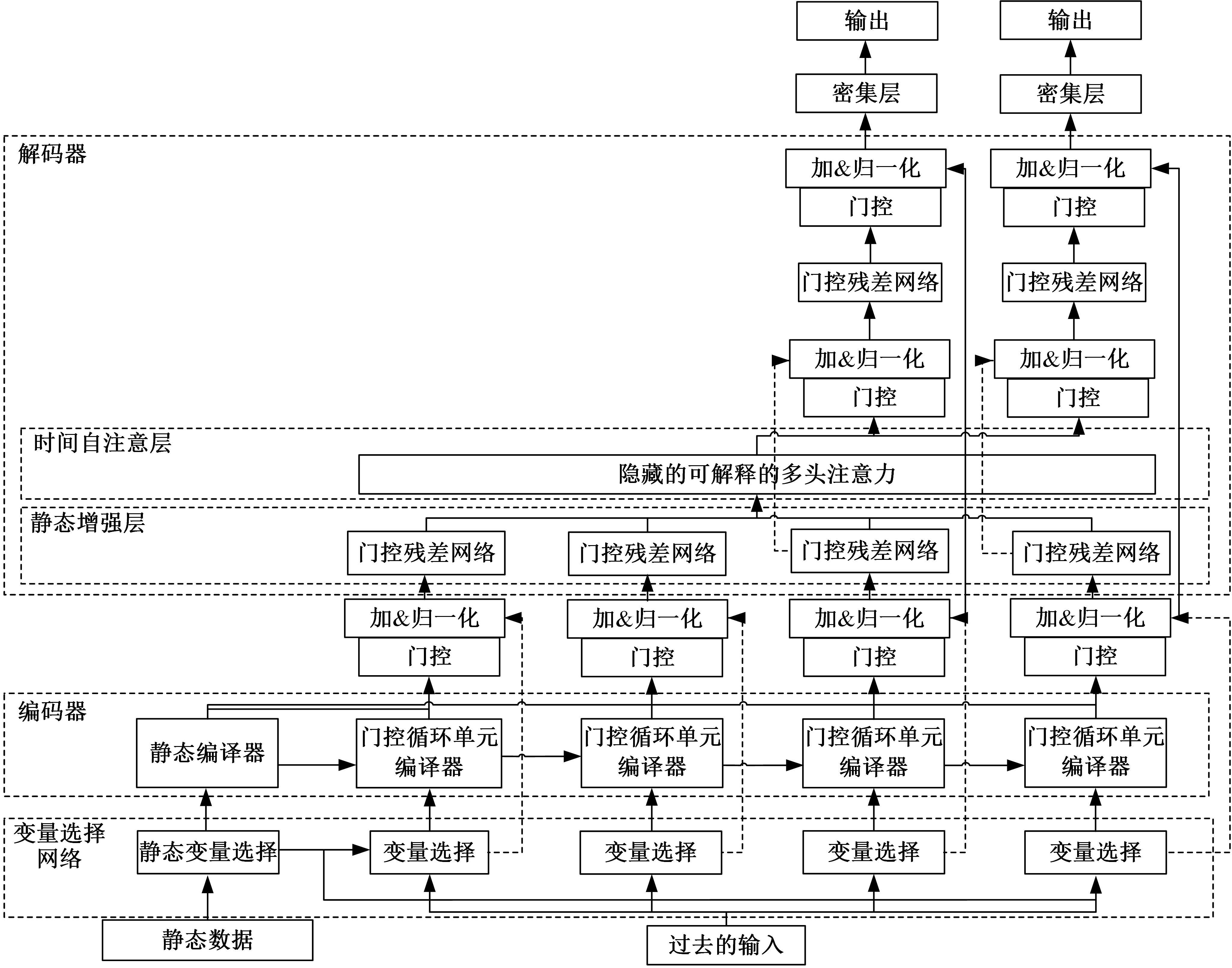
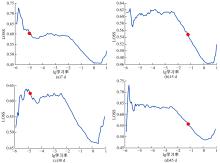
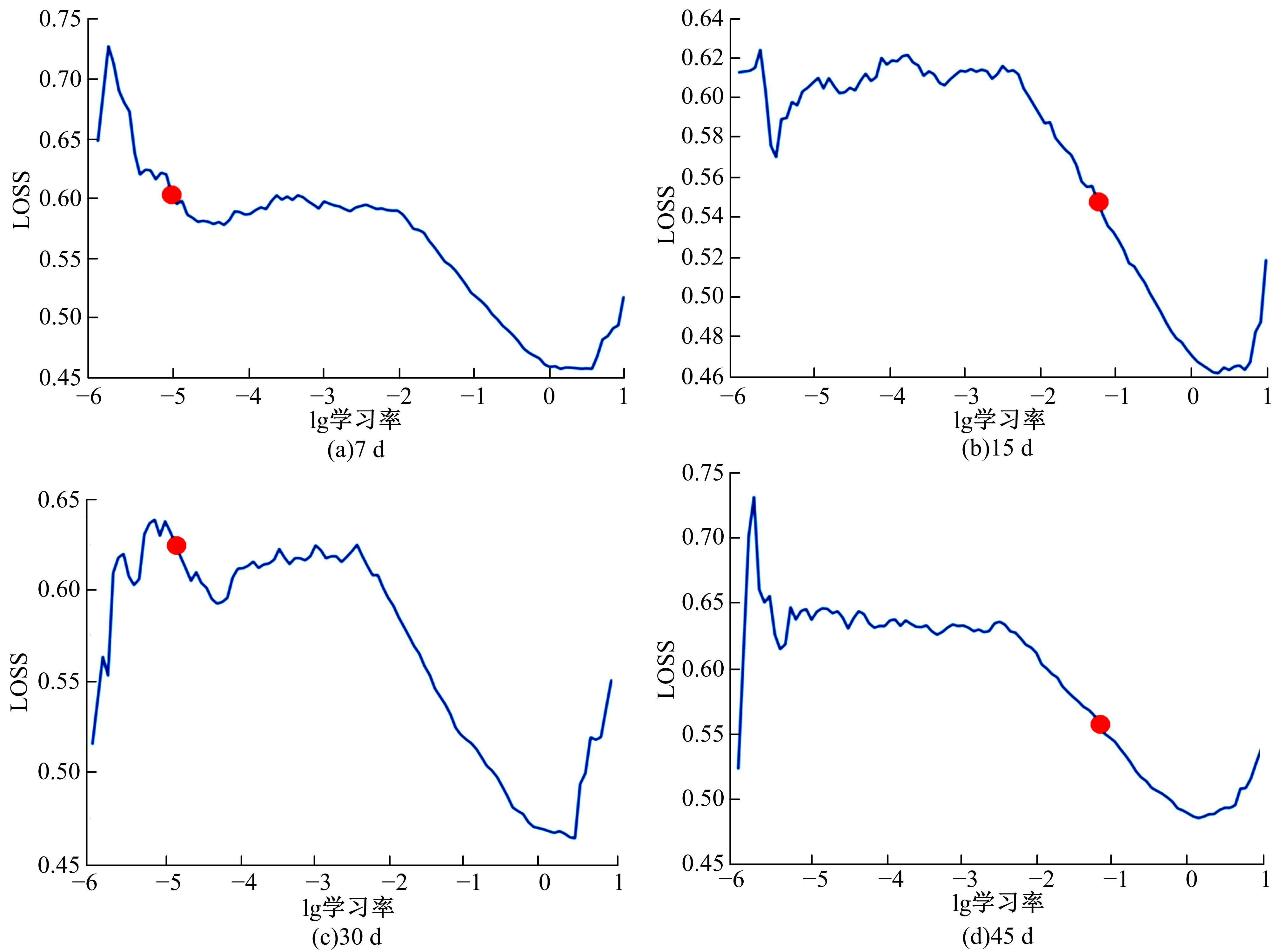
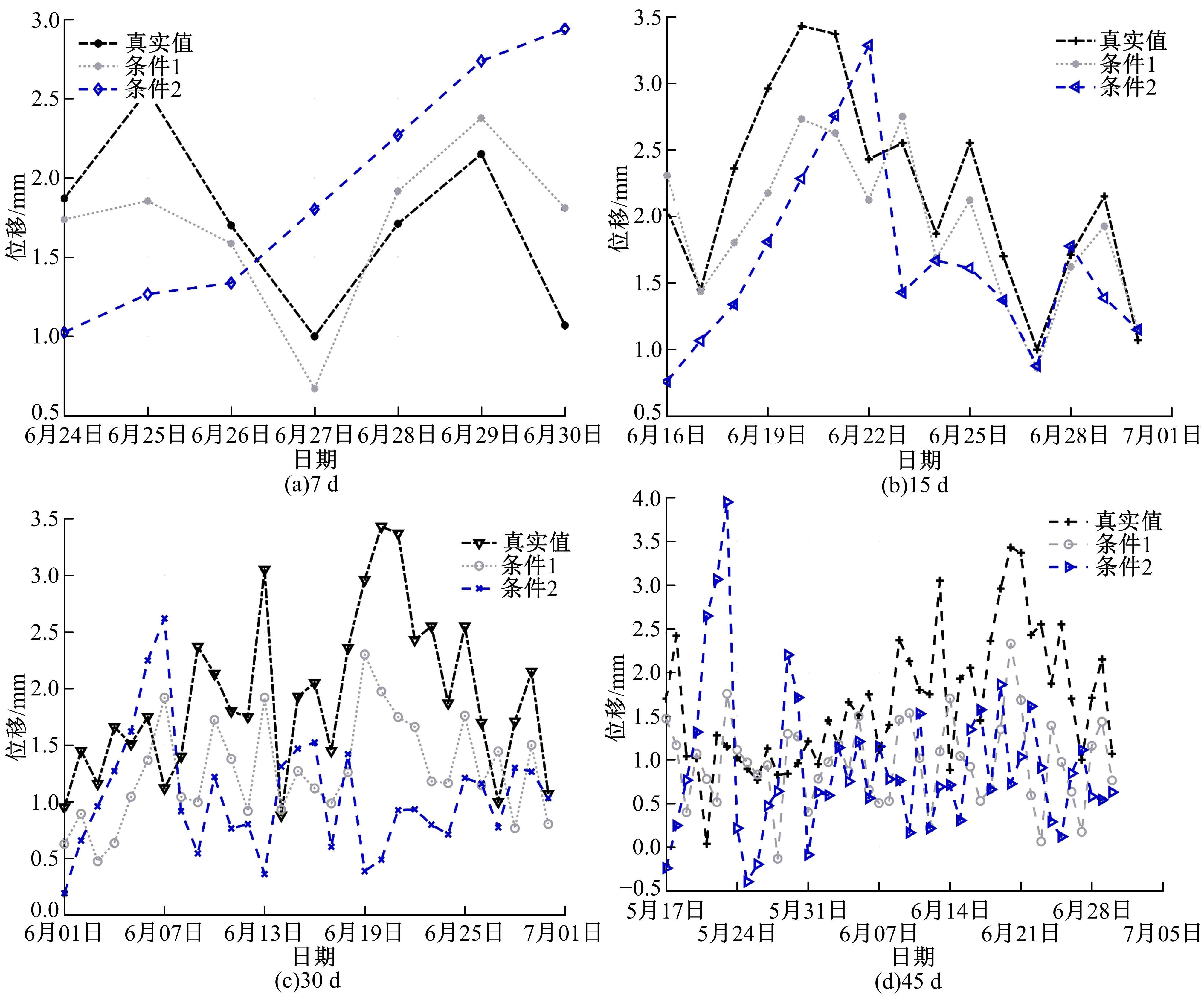
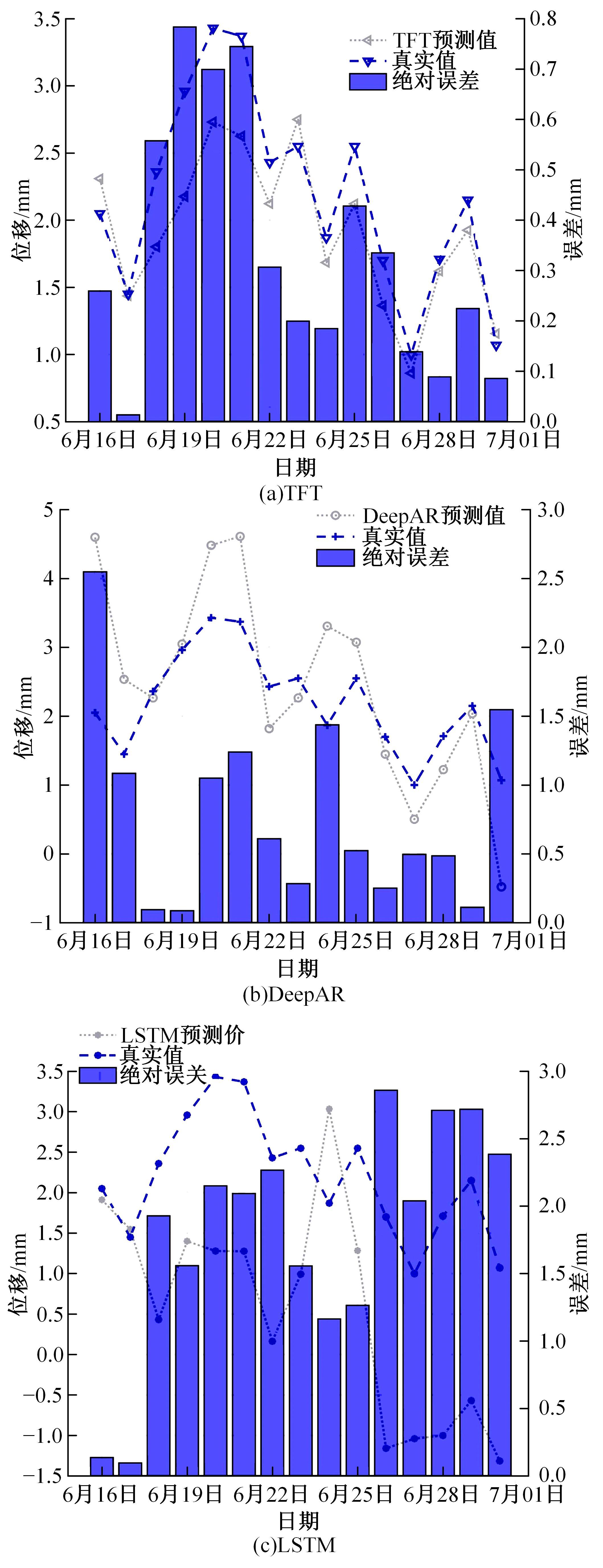
针对目前滑坡位移预测模型多以结合降雨、形变等动态变量的单步预测为主,缺乏对多步位移影响因素相关的时间周期等静态变量考虑的问题,提出了融合动静态变量的滑坡多步位移预测模型。首先,运用变量选择网络对初始输入变量进行选择,挖掘与滑坡日位移相关度高的变量,削弱冗余变量对模型的影响。然后,将静态变量集成于网络中,通过对上下文编码进行时间动态相关性调节。最后,以多头注意力模块捕获时序长期依赖关系,实现滑坡多步位移预测。以重庆市新铺滑坡为例,将本文方法与DeepAR、长短期记忆(LSTM)模型进行实验对比,结果表明,本文方法可实现较为稳健的高精度滑坡多步位移预测。
中图分类号:
- P694
| 1 | 高彩云. 基于智能算法的滑坡位移预测与危险性评价研究[D]. 北京:中国矿业大学(北京)地球科学与测绘工程学院,2016. |
| Gao Cai-yun. Research on landslide displacement prediction and risk assessment based on intelligent algorithm[D]. Beijing: College of Geoscience and Surveying Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology(Beijing), 2016. | |
| 2 | Wu L Z, Li S H, Huang R Q, et al. A new grey prediction model and its application to predicting landslide displacement[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 95: 106-123. |
| 3 | Huang F, Huang J, Jiang S, et al. Landslide displacement prediction based on multivariate chaotic model and extreme learning machine[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 218: 173-186. |
| 4 | Li S H, Wu L Z, Huang J. A novel mathematical model for predicting landslide displacement[J]. Soft Computing, 2021, 25(3): 2453-2466. |
| 5 | 阚光远, 洪阳, 梁珂. 基于耦合机器学习模型的洪水预报研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2018(10):165-169, 176. |
| Kan Guang-yuan, Hong Yang, Liang Ke. Flood forecasting research based on coupled machine learning model[J]. China Rural Water Resources and Hydropower, 2018(10): 165-169, 176 | |
| 6 | 胡俊涛, 张细香. 基于GA-BP神经网络的滑坡运动距离预测[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2022, 51(8): 22-26, 34. |
| Hu Jun-tao, Zhang Xi-xiang. Prediction of landslide movement distance based on GA-BP neural network[J]. Chemical Minerals and Processing, 2022,51(8): 22-26, 34. | |
| 7 | Zhu X, Xu Q, Tang M, et al. A hybrid machine learning and computing model for forecasting displacement of multifactor-induced landslides[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2018, 30(12): 3825-3835. |
| 8 | Xu S, Niu R. Displacement prediction of Baijiabao landslide based on empirical mode decomposition and long short-term memory neural network in three gorges area, China[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2018, 111: 87-96. |
| 9 | Zhou C, Yin K, Cao Y, et al. Application of time series analysis and PSO-SVM model in predicting the Bazimen landslide in the three gorges reservoir, China[J]. Engineering geology, 2016, 204: 108-120. |
| 10 | 郭子正, 杨玉飞, 何俊, 等. 考虑注意力机制的新型深度学习模型预测滑坡位移[J/OL]. [2023-01-14]. |
| Guo Zi-zheng, Yang Yu-fei, He Jun, et al. A new deep learning model considering attention mechanism to predict landslide displacement[J/OL]. [2023-01-14]. | |
| 11 | Yang B, Yin K, Lacasse S, et al. Time series analysis and long short-term memory neural network to predict landslide displacement[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(4): 677-694. |
| 12 | 宋宇飞, 曹琰波, 范文, 等. 基于贝叶斯方法的降雨诱发滑坡概率型预警模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(3): 558-574. |
| Song Yu-fei, Cao Yan-bo, Fan Wen, et al. Study on the probability early warning model of rain-induced landslide based on Bayesian method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(3): 558-574. | |
| 13 | 刘勇, 秦志萌, 余宏明, 等. 基于ENN广义预测控制算法的滑坡位移多步预测[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 255-259. |
| Liu Yong, Qin Zhi-meng, Yu Hong-ming, et al. Multi-step prediction of landslide displacement based on ENN generalized predictive control algorithm[J] Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(4): 255-259. | |
| 14 | 许春青. 滑坡预测预报模型比较分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学航天与建筑工程学院, 2011. |
| Xu Chun-qing. Comparative analysis of landslide prediction models[D]. Harbin: College of Aerospace and Civil Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, 2011. | |
| 15 | Lim B, Ark S, Loeff N, et al. Temporal fusion transformers for interpretable multi-horizon time series forecasting[J]. International Journal of Forecasting, 2021(1): 15-35. |
| [1] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [2] | 吕卫,韩镓泽,褚晶辉,井佩光. 基于多模态自注意力网络的视频记忆度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1211-1219. |
| [3] | 田彦涛,许富强,王凯歌,郝子绪. 考虑周车信息的自车期望轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
| [4] | 吴剑,许斌. 基于CEEMDAN理论的堆积层滑坡位移区间预测模型及仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 562-568. |
| [5] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [6] | 李先通,全威,王华,孙鹏程,安鹏进,满永兴. 基于时空特征深度学习模型的路径行程时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 557-563. |
| [7] | 陈晓雷,孙永峰,李策,林冬梅. 基于卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆的稳定抗噪声滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [8] | 周大可,张超,杨欣. 基于多尺度特征融合及双重注意力机制的自监督三维人脸重建[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2428-2437. |
| [9] | 王德兴,吴若有,袁红春,宫鹏,王越. 基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [10] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [11] | 刘元宁,吴迪,朱晓冬,张齐贤,李双双,郭书君,王超. 基于YOLOv3改进的用户界面组件检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1026-1033. |
| [12] | 赵海英,周伟,侯小刚,张小利. 基于多任务学习的传统服饰图像双层标注[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 293-302. |
| [13] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [14] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [15] | 欧阳丹彤,肖君,叶育鑫. 基于实体对弱约束的远监督关系抽取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 912-919. |
|
||