吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 674-681.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20221434
• 通信与控制工程 • 上一篇
考虑周车信息的自车期望轨迹预测
- 1.吉林大学 通信工程学院,长春 130022
2.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Expected trajectory prediction of vehicle considering surrounding vehicle information
Yan-tao TIAN1( ),Fu-qiang XU1,Kai-ge WANG1,Zi-xu HAO1,2
),Fu-qiang XU1,Kai-ge WANG1,Zi-xu HAO1,2
- 1.College of Communication Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
摘要:
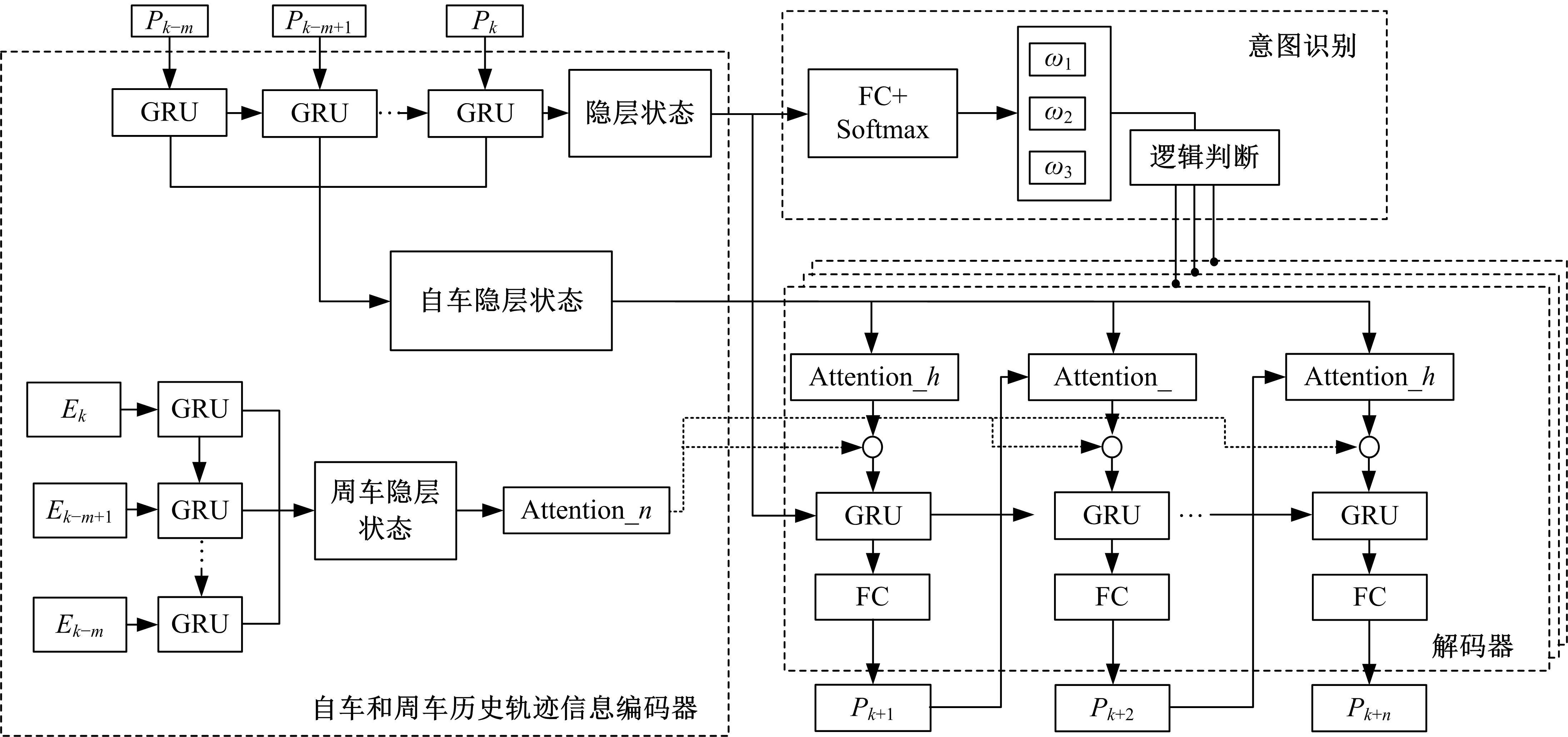
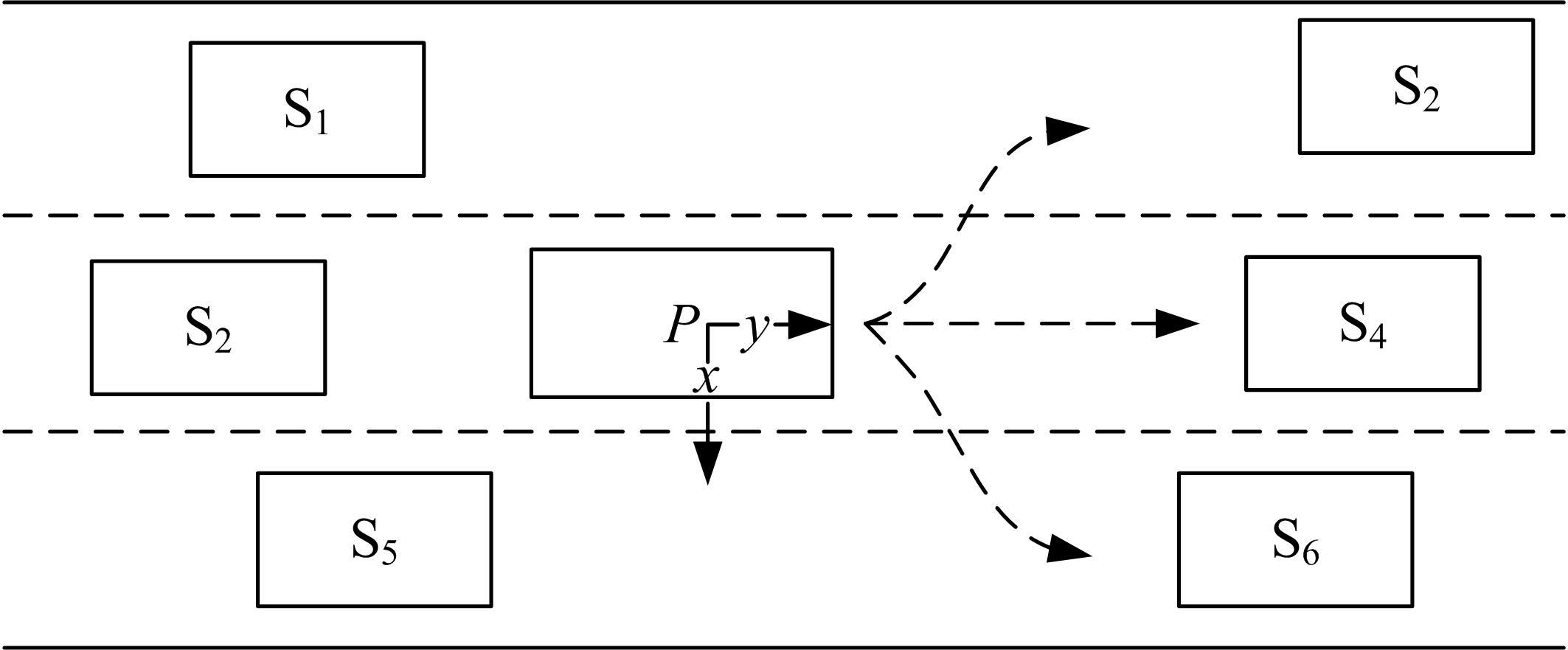
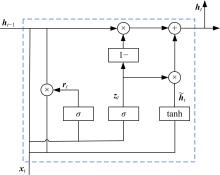
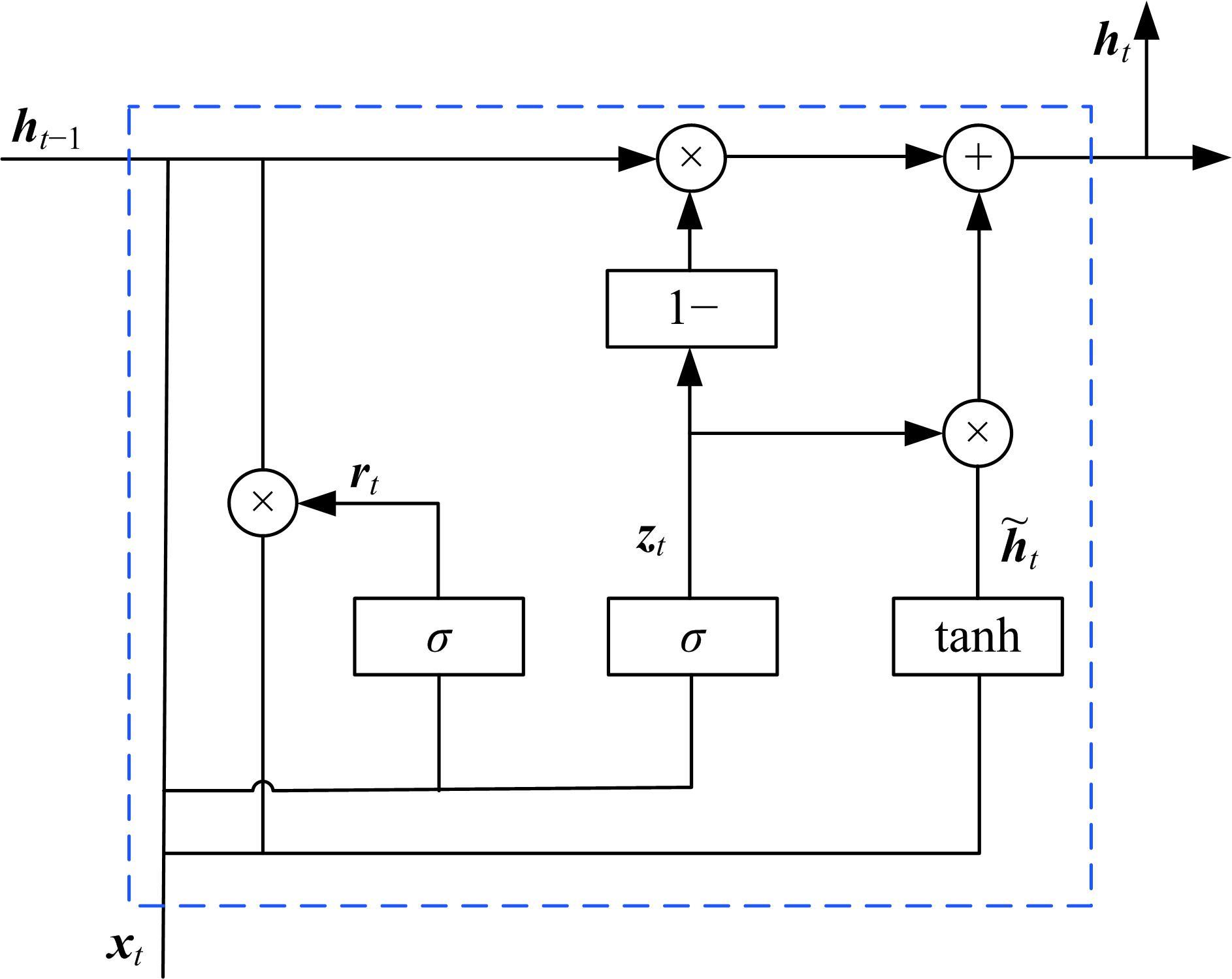
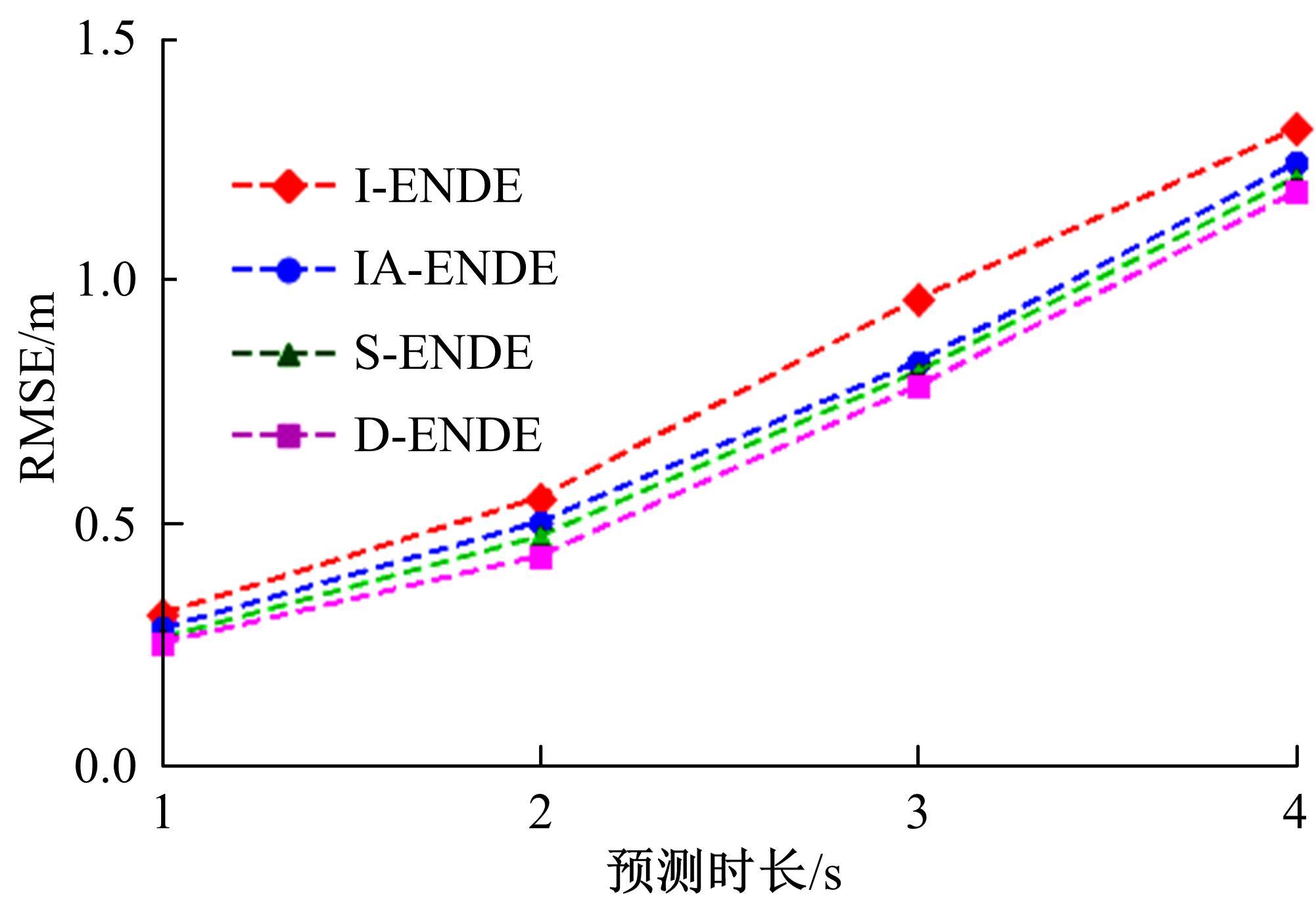
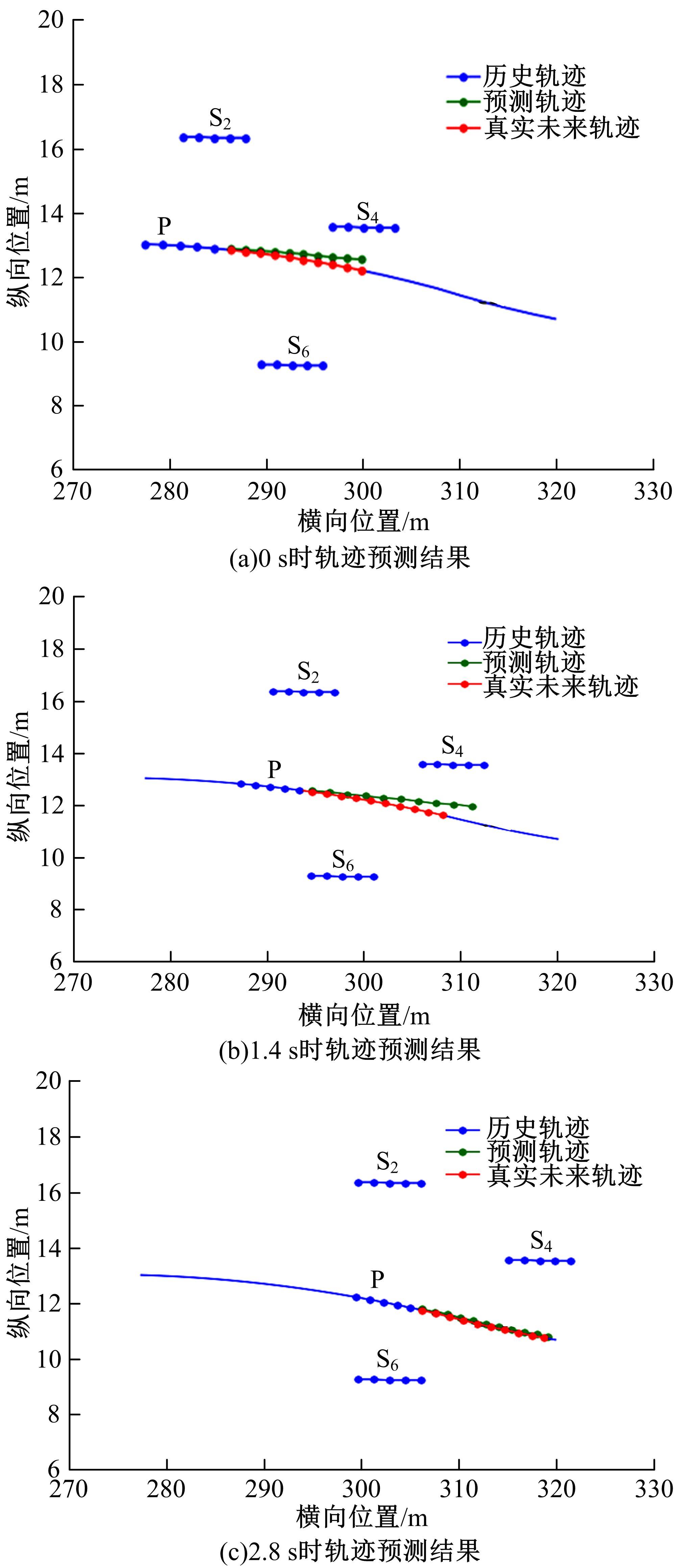
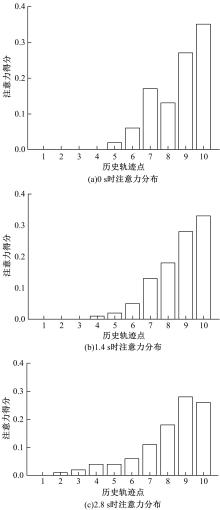
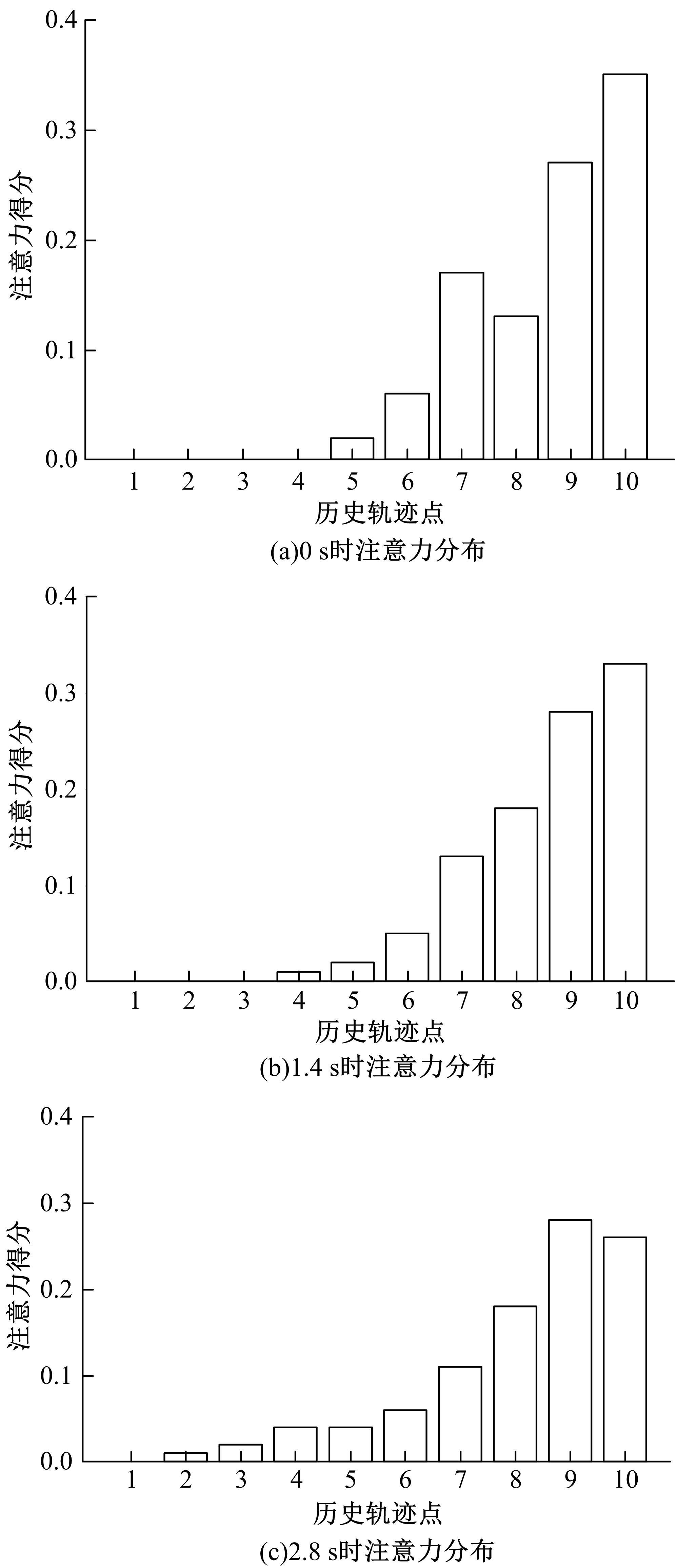
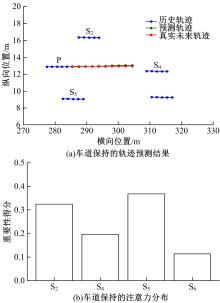
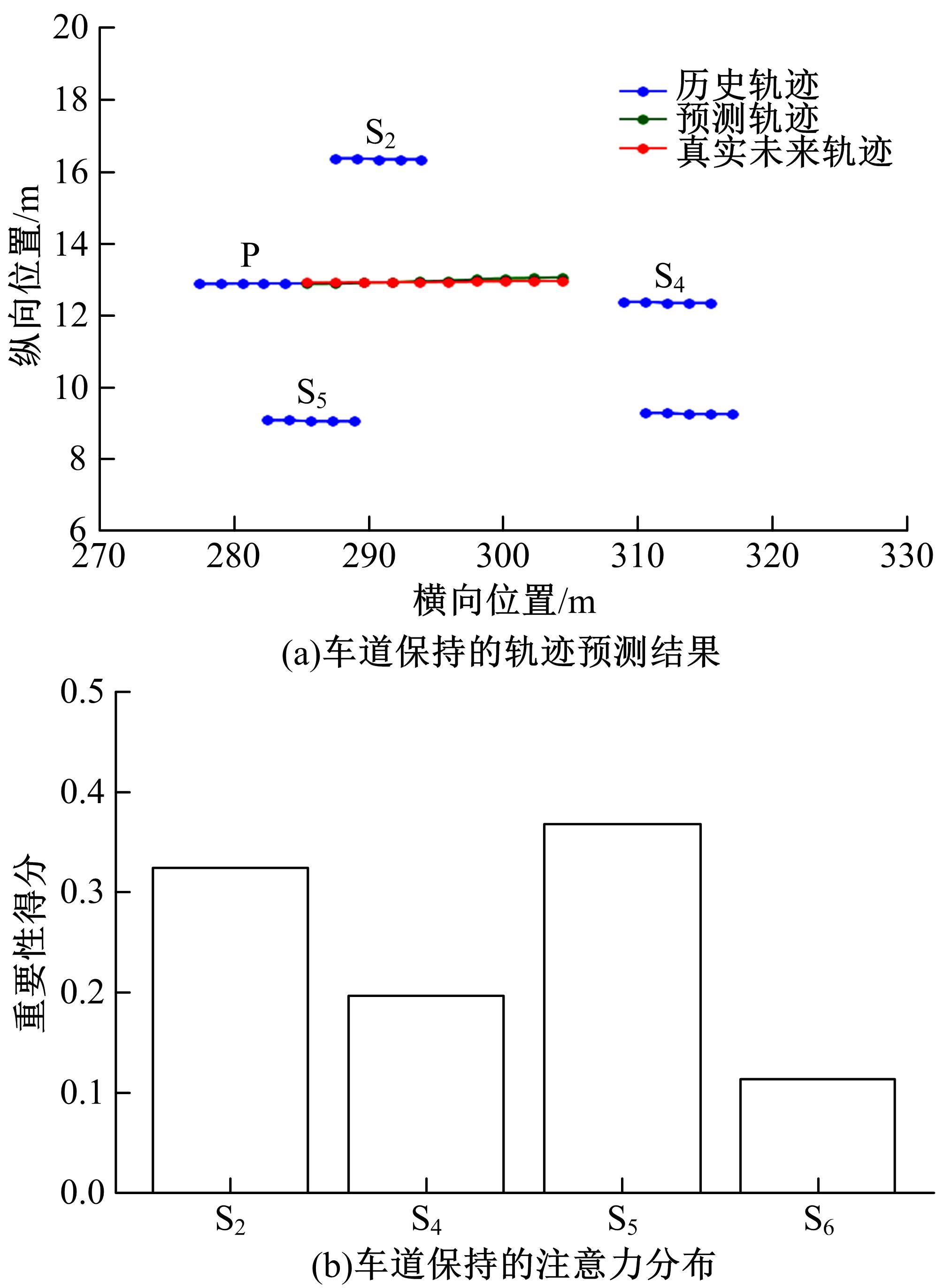
针对驾驶员期望轨迹预测问题,设计了一种考虑周车信息的自车期望轨迹预测模型。建立了单独的自车和周车历史轨迹信息编码器,将编码后的自车历史轨迹信息送往意图识别模块用于识别驾驶员意图;通过注意力机制对自车和周车编码信息进行处理,并与意图识别的结果共同作为解码器模块的输入,最终输出车辆未来位置。最后,采用数据集对模型进行训练,验证了模型的有效性。
中图分类号:
- U495
| 1 | Doshi A, Trivedi M M. On the roles of eye gaze and head dynamics in predicting driver's intent to change lanes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009, 10(3): 453-462. |
| 2 | Ohn-Bar E, Trivedi M M. Looking at humans in the age of self-driving and highly automated vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2016, 1 ( 1 ) : 90-104. |
| 3 | 郭应时, 付锐, 赵凯, 等. 驾驶人换道意图实时识别模型评价及测试 [J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(6): 1836-1844. |
| Guo Ying-shi, Fu Rui, Zhao Kai, et al. Evaluation and test of real-time identification models of driver's lane change intention[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(6): 1836-1844. | |
| 4 | Li K, Wang X, Xu Y, et al. Lane changing intention recognition based on speech recognition models[J].Transportation Research Part C-emerging Technologies, 2016, 69: 497-514. |
| 5 | Jain A, Koppula H S, Raghavan B, et al. Car that knows before you do: anticipating maneuvers via learning temporal driving models[C]∥2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 3182-3190. |
| 6 | Driggs-Campbell K, Bajcsy R. Identifying modes of intent from driver behaviors in dynamic environments[C]∥2015 IEEE 18th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Gran Canaria, Spain, 2015: 739-744. |
| 7 | Deo N, Rangesh A, Trivedi M M. How would surround vehicles move? A unified framework for maneuver classification and motion prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2018, 3(2): 129-140. |
| 8 | Bahram M, Hubmann C, Lawitzky A, et al. A combined model and learning-based framework for interaction-aware maneuver prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(6): 1538-1550. |
| 9 | Bahram M, Lawitzky A, Friedrichs J, et al. A game-theoretic approach to replanning-aware interactive scene prediction and planning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(6): 3981-3992. |
| 10 | Shalev-Shwartz S, Ben-Zrihem N, Cohen A, et al. Long-term planning by short-term prediction[J/OL]. [2022-10-15]. |
| 11 | 季学武, 费聪, 何祥坤, 等. 基于LSTM网络的驾驶意图识别及车辆轨迹预测[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(6): 34-42. |
| Ji Xue-wu, Fei Cong, He Xiang-kun, et al. Intention recognition and trajectory prediction for vehicles using LSTM network[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(6): 34-42. | |
| 12 | Deo N, Trivedi M M. Convolutional social pooling for vehicle trajectory prediction[C]∥2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA,2018:1549-1557. |
| 13 | Park S H, Kim B, Kang C M, et al. Sequence-to-sequence prediction of vehicle trajectory via LSTM encoder-decoder architecture[C]∥2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, Changshu, China, 2018:1672-1678. |
| 14 | 柴进. 基于聚类和LSTM算法的车辆轨迹预测模型研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学电子信息工程学院, 2020. |
| Chai Jin. On vehicle trajectory prediction model based on combined clustering and LSTM algorithm [D]. Beijing:School of Electronic and Information Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2020. | |
| 15 | Graves A, Jaitly N. Towards end-to-end speech recognition with recurrent neural networks[C]∥International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 2014: 1764-1772. |
| 16 | Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks[C]∥International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 3104-3112. |
| 17 | Cho K, van Merriënboer B, Gulcehre C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[J/OL]. [2022-10-18]. |
| [1] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [2] | 何科,丁海涛,许男,郭孔辉. 基于摄像头和车道线的增强定位系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 663-673. |
| [3] | 刘近贞,高国辉,熊慧. 用于脑组织分割的多尺度注意网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 576-583. |
| [4] | 张惠臻,高正凯,李建强,王晨曦,潘玉彪,王成,王靖. 基于循环神经网络的城市轨道交通短时客流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 430-438. |
| [5] | 王登峰,陈宏利,那景新,陈鑫. 单双搭接接头经高温老化后的失效对比[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 346-354. |
| [6] | 张佩,王志伟,杜常清,颜伏伍,卢炽华. 车用质子交换膜燃料电池空气系统过氧比控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1996-2003. |
| [7] | 王克勇,鲍大同,周苏. 基于数据驱动的车用燃料电池故障在线自适应诊断算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2107-2118. |
| [8] | 曹起铭,闵海涛,孙维毅,于远彬,蒋俊宇. 质子交换膜燃料电池低温启动水热平衡特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2139-2146. |
| [9] | 隗海林,王泽钊,张家祯,刘洋. 基于Avl-Cruise的燃料电池汽车传动比及能量管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2119-2129. |
| [10] | 刘岩,丁天威,王宇鹏,都京,赵洪辉. 基于自适应控制的燃料电池发动机热管理策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2168-2174. |
| [11] | 李丞,景浩,胡广地,刘晓东,冯彪. 适用于质子交换膜燃料电池系统的高阶滑模观测器[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2203-2212. |
| [12] | 池训逞,侯中军,魏伟,夏增刚,庄琳琳,郭荣. 基于模型的质子交换膜燃料电池系统阳极气体浓度估计技术综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 1957-1970. |
| [13] | 裴尧旺,陈凤祥,胡哲,翟双,裴冯来,张卫东,焦杰然. 基于自适应LQR控制的质子交换膜燃料电池热管理系统温度控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2014-2024. |
| [14] | 李永明,裴小轩,伊曙东. 混合动力汽车动力电池自适应神经网络优化控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2063-2068. |
| [15] | 胡广地,景浩,李丞,冯彪,刘晓东. 基于高阶燃料电池模型的多目标滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2182-2191. |
|
||