吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 1592-1600.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230145
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于动力特性和改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷深度识别
谭国金1( ),孔庆雯1,何昕1(
),孔庆雯1,何昕1( ),张攀2,杨润超3,朝阳军4,杨忠4
),张攀2,杨润超3,朝阳军4,杨忠4
- 1.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
2.长春市建设工程安全监督站,长春 130012
3.吉林省公路管理局,长春 130021
4.吉林省交通规划设计院,长春 130021
Bridge scour depth identification based on dynamic characteristics and improved particle swarm optimization algorithm
Guo-jin TAN1( ),Qing-wen KONG1,Xin HE1(
),Qing-wen KONG1,Xin HE1( ),Pan ZHANG2,Run-chao YANG3,Yang-jun CHAO4,Zhong YANG4
),Pan ZHANG2,Run-chao YANG3,Yang-jun CHAO4,Zhong YANG4
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Changchun Construction Project Safety Supervision Station,Changchun 130012,China
3.Jilin Provincial Highway Administration,Changchun 130021,China
4.Jilin Traffic Planning and Design Institute,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
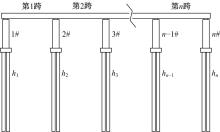
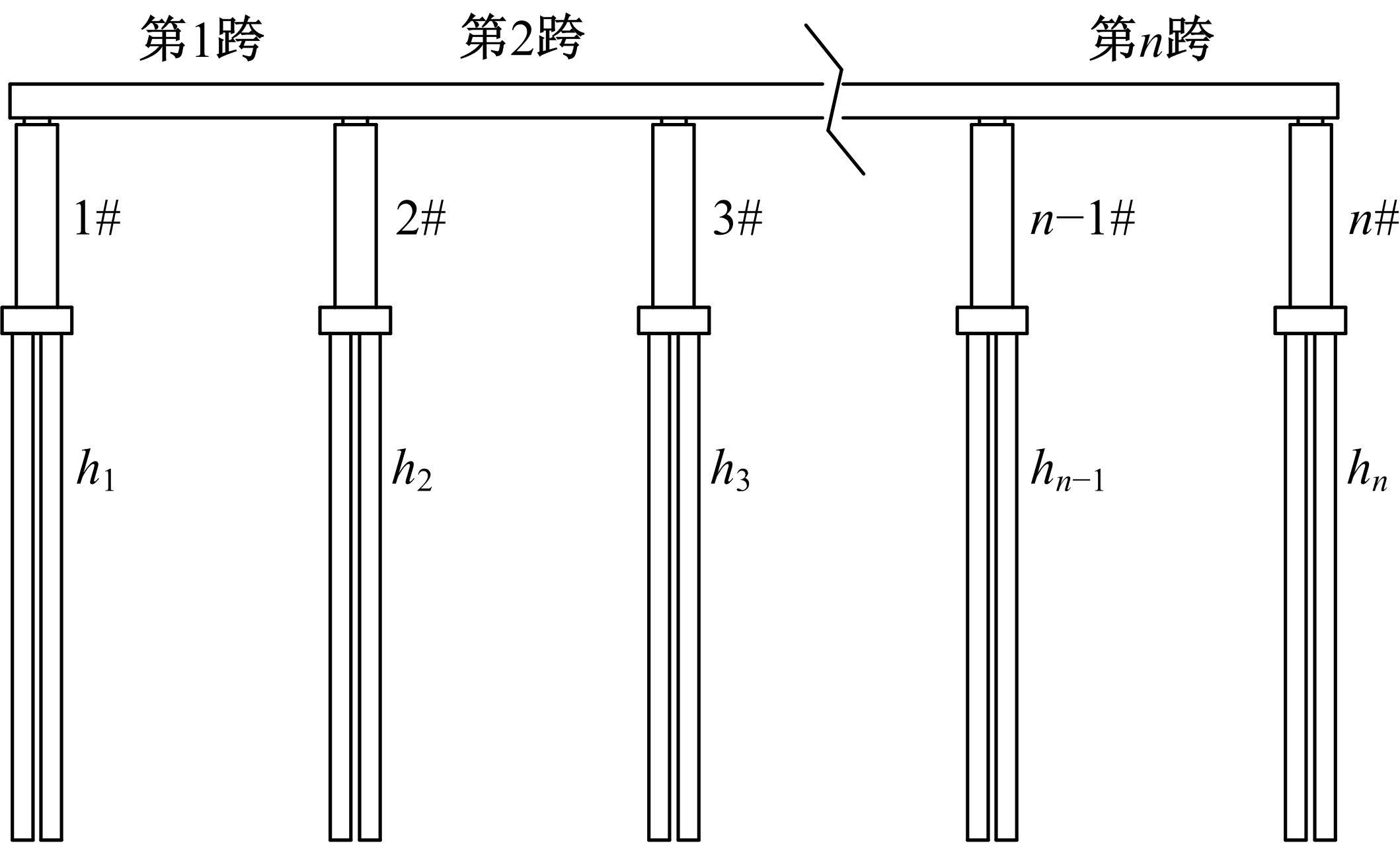
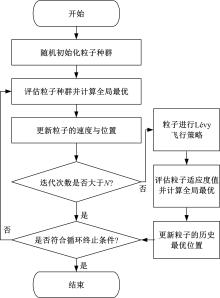
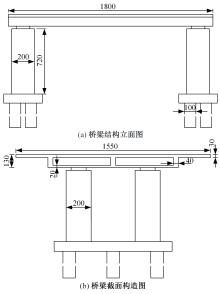
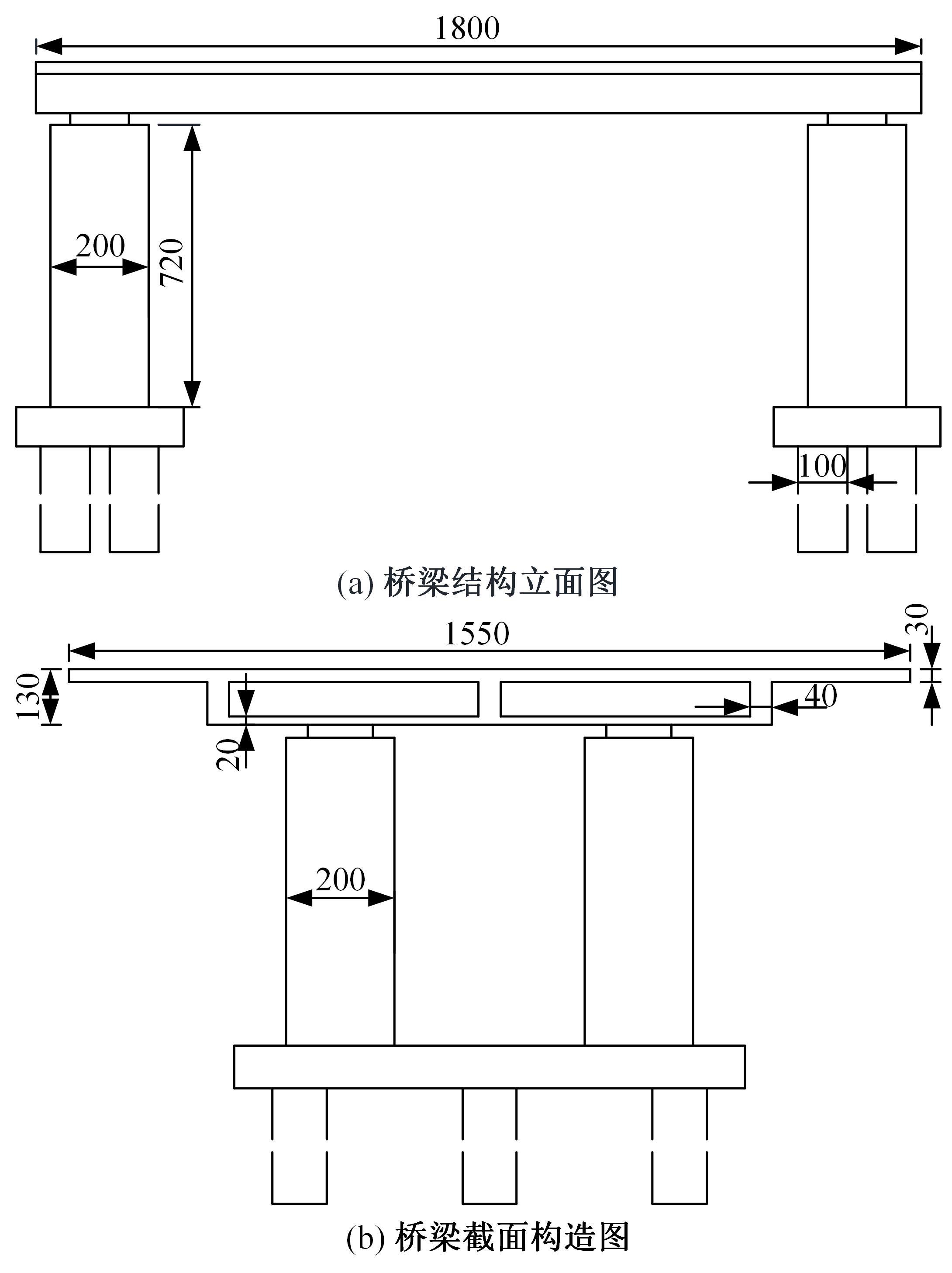
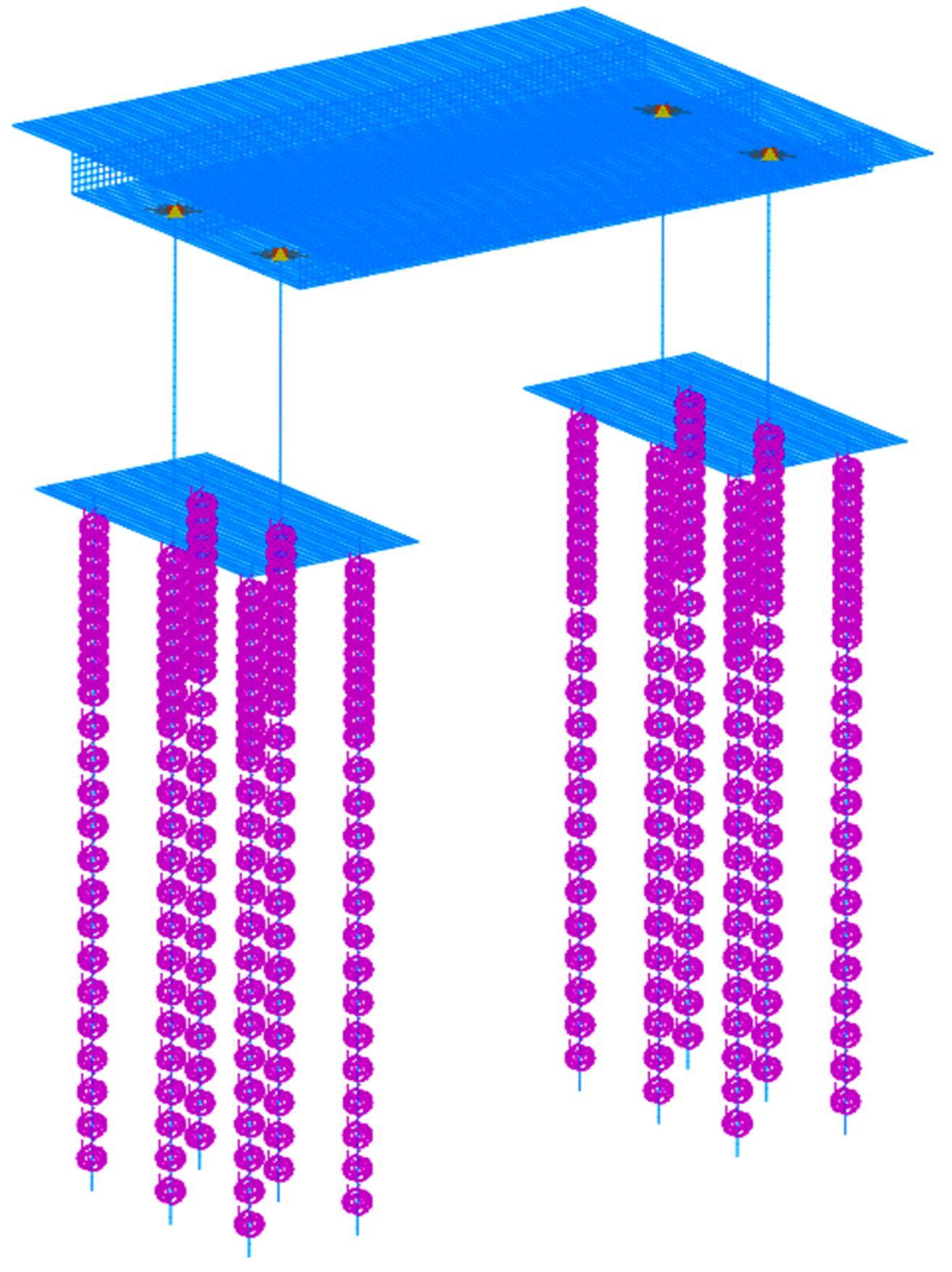
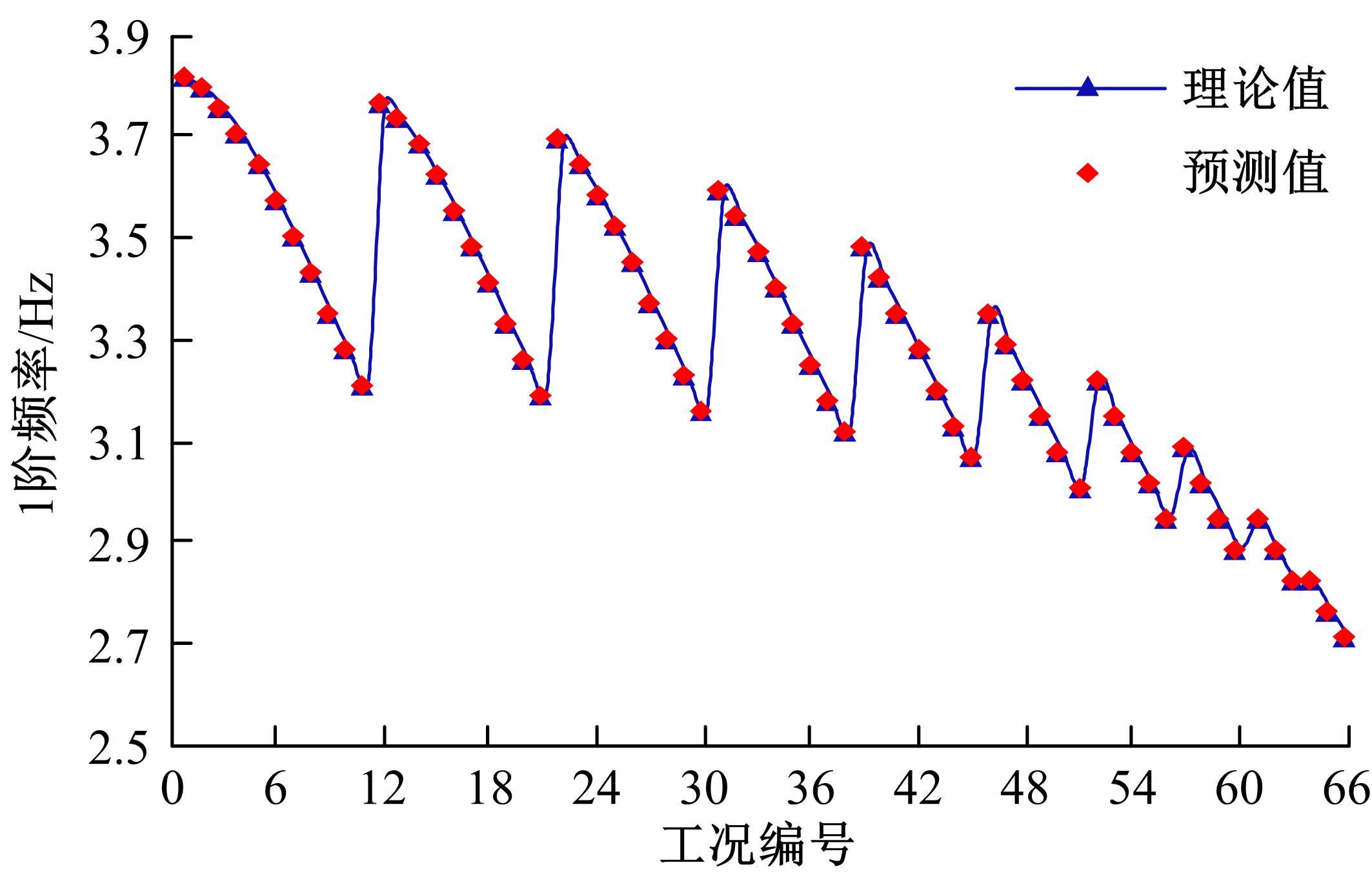
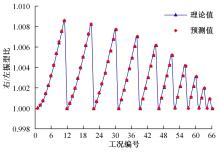
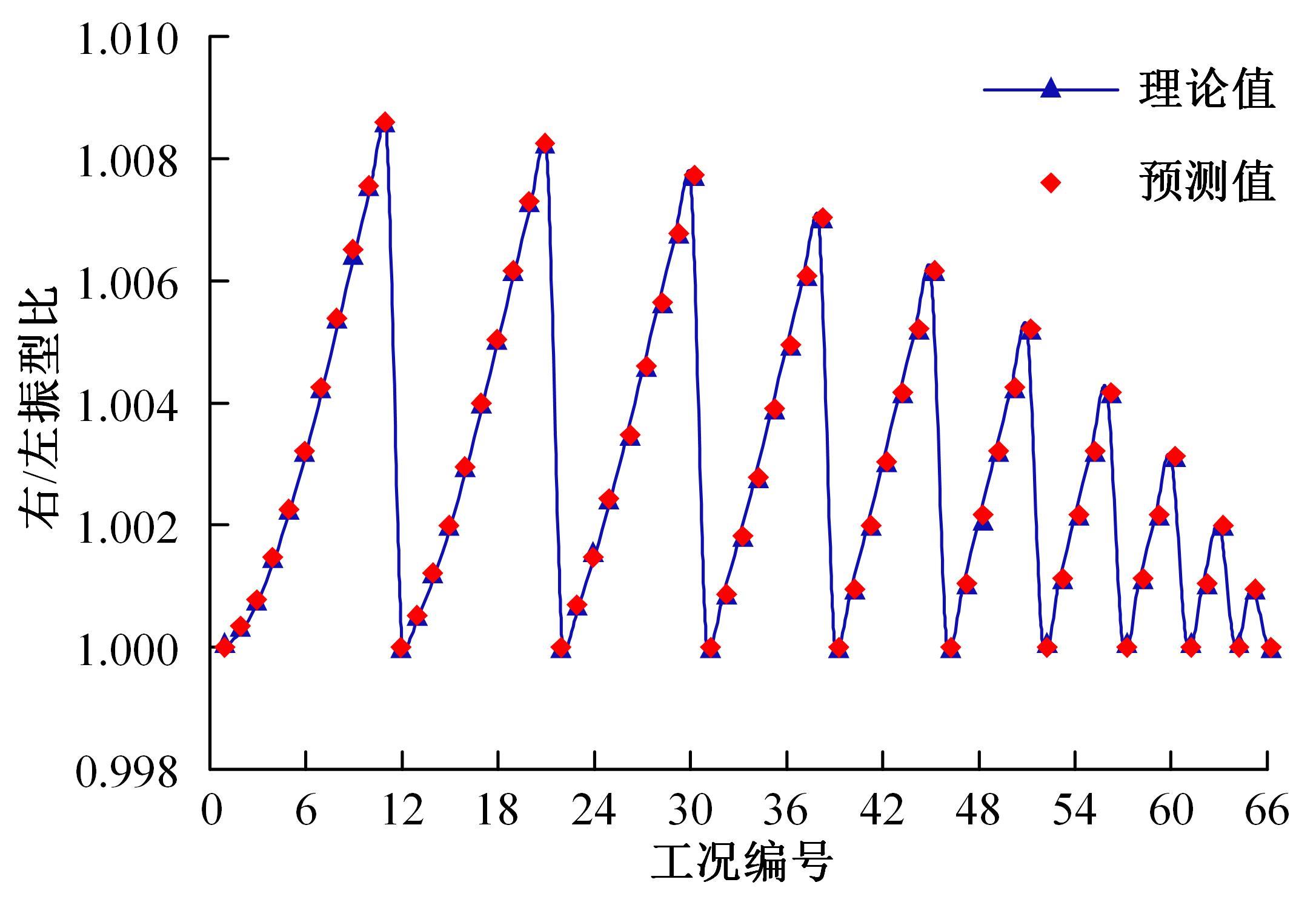
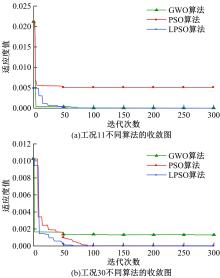
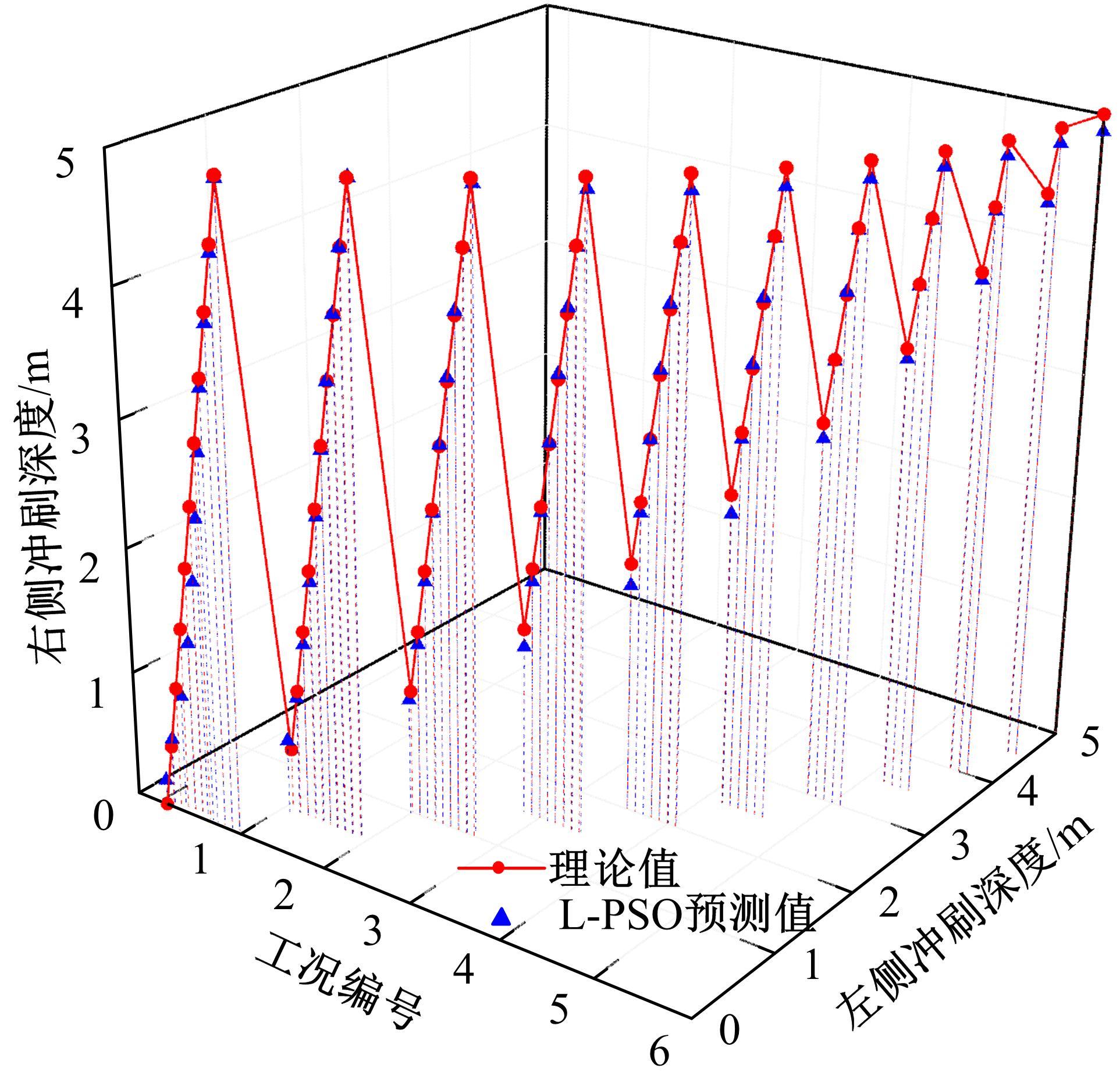
为了快速、准确地识别出桥梁冲刷损伤的位置和程度,提出了一种基于桥梁结构动力特性和改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷识别方法。该方法先将桥梁结构动力特性与单位力作用下墩顶静力位移作为桥梁冲刷识别参数;然后,利用多元非线性回归得到冲刷识别参数与不同桥墩冲刷深度之间的定量关联,根据桥梁实测时获取的动力特性值便可识别出桥墩左、右两侧不均匀冲刷深度;最后,对一座简支梁桥进行数值分析,演示了本文基于改进粒子群优化算法的桥梁冲刷识别方法的具体应用步骤。研究结果表明:本文方法可识别出桥梁冲刷位置和冲刷深度,且识别结果具有一定的准确性。在实际工程中,通过常规桥梁检测即可实现桥梁基础冲刷损伤识别,避免了水下作业带来的操作难题,且可快速对桥梁冲刷状态进行准确评估。
中图分类号:
- U446
| 1 | 熊文, 魏乐永, 张学峰, 等. 大跨度缆索支承桥梁基础冲刷动力识别方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2019, 51(3): 92-98. |
| Xiong Wen, Wei Le-yong, Zhang Xue-feng, et al. Dynamic-based bridge scour identification of super-span cable-supported bridges[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019, 51(3): 92-98. | |
| 2 | Lu J Y, Shi Z Z, Hong J H, et al. Temporal variation of scour depth at nonuniform cylindrical piers[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2011, 137(1): 45-56. |
| 3 | Bao T, Liu Z, Bird K. Influence of soil characteristics on natural frequency-based bridge scour detection[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2019, 446(1): 195-210. |
| 4 | 张佰战, 李付军. 桥墩局部冲刷计算研究[J]. 中国铁道科学, 2004, 25(2): 48-51. |
| Zhang Bai-zhan, Li Fu-jun. Bridge pier local scour calculation[J]. China Railway Science, 2004, 25(2): 48-51. | |
| 5 | 詹义正, 王军, 谈广鸣, 等. 桥墩局部冲刷的试验研究[J]. 武汉大学学报, 2006, 39(6): 3-4. |
| Zhan Yi-zheng, Wang Jun, Tan Guang-ming, et al. Experimental study on bridge pier local scour[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2006, 39(6): 3-4. | |
| 6 | Hong J H, Guo W D, Chiew Y M, et al. A new practical method to simulate flood-induced bridge pier scour—a case study of mingchu bridge piers on the cho-shui river[J]. Water, 2016, 8(6): 238. |
| 7 | Deng L, Cai C S. Bridge scour: prediction, modeling, monitoring and countermeasures-review[J]. Practice Periodical on Structural Design & Construction, 2010, 15(2): 125-134. |
| 8 | Zounemat-Kermani A, Beheshti A, Ataie-Ashtiani B. Estimation of current-induced scour depth around pile groups using neural network and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2009, 9(2): 746-755. |
| 9 | 熊文, 张愉, 李飞泉, 等. 基于时频分析与神经网络的桥梁冲刷动力评估[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版, 2020, 53(4): 397-404. |
| Xiong Wen, Zhang Yu, Li Fei-quan, et al. Dynamic assessment of bridge scour based on time-frequency analysis and neural network[J]. Journal of Tianjin University(Science and Technology), 2020, 53(4): 397-404. | |
| 10 | 张效忠, 孙延华, 孙国民. 基于支持向量机的桥梁冲刷深度识别方法研究[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报, 2016, 14(3): 206-210. |
| Zhang Xiao-zhong, Sun Yan-hua, Sun Guo-min. Identification method of scour depth for bridge based on ERA and SVM[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2016, 14(3): 206-210. | |
| 11 | Ju S H. Determination of scoured bridge natural frequencies with soil-structure interaction[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2013, 55: 247-254. |
| 12 | Kong X, Cai C S. Scour effect on bridge and vehicle responses under bridge-vehicle-wave interaction[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21(4): No.04015083. |
| 13 | 熊文, 邹晨, 叶见曙. 基于动力特性识别的桥墩冲刷状态分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(5): 89-96. |
| Xiong Wen, Zou Chen, Ye Jian-shu. Condition assessment of bridge scour by tracing dynamic performances of bridges[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(5): 89-96. | |
| 14 | 于繁华, 刘寒冰. 基于支持向量机和粒子群算法的结构损伤识别[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2008, 38(2): 434-439. |
| Yu Fan-hua, Liu Han-bing. Structural damage identification by support vector machine and particle swarm algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2008, 38(2): 434-439. | |
| 15 | 王学武, 严益鑫, 丁冬雁, 等. 基于Lévy-PSO算法的焊接机器人避障路径规划[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2016, 50(10): 1517-1520. |
| Wang Xue-wu, Yan Yi-xin, Ding Dong-yan, et al. Collision free path planning for welding robot based on Lévy-PSO[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2016, 50(10): 1517-1520. | |
| 16 | 孟宪猛, 蔡翠翠. 基于精英反向学习和Lévy飞行的鲸鱼优化算法[J]. 电子测量技术, 2021, 44(20): 82-87. |
| Meng Xian-meng, Cai Cui-cui. Whale optimization algorithm based on elite reverse learning and Lévy flight[J]. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2021, 44(20): 82-87. | |
| 17 | API. Recommended Practice for Planning, Designing and Constructing Fixed Offshore Platforms-Working Stress Design[M]. 20th ed. Washington DC: API, 2000. |
| 18 | Meidani K, Mirjalili S, Barati F A, et al. Grey Wolf Optimizer[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2014, 69: 46-61. |
| [1] | 江辉,李新,白晓宇. 桥梁抗震结构体系发展述评:从延性到韧性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1550-1565. |
| [2] | 张玥,刘传森,宋飞. 桥台背墙对连续梁桥地震易损性的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1372-1380. |
| [3] | 兰树伟,周东华,陈旭,莫南明. 双柱式高墩桥梁整体稳定性的实用算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1105-1111. |
| [4] | 孙琪凯,张楠,刘潇,周子骥. 基于Timoshenko梁理论的钢-混组合梁动力折减系数[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 488-495. |
| [5] | 叶华文,段智超,刘吉林,周渝,韩冰. 正交异性钢⁃混组合桥面的轮载扩散效应[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1808-1816. |
| [6] | 王立峰,肖子旺,于赛赛. 基于Bayesian网络的多塔斜拉桥挂篮系统风险分析的新方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 865-873. |
| [7] | 张彦玲,王灿,张旭,王昂洋,李运生. 不同吊杆形式悬索桥人致振动分析及舒适度评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2644-2652. |
| [8] | 商拥辉,徐林荣,刘维正,蔡雨. 重载铁路改良土和A组填料过渡段的动力特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2128-2136. |
| [9] | 钟昌均,王忠彬,柳晨阳. 悬索桥主索鞍承载力影响因素及结构优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2068-2078. |
| [10] | 陈巍,万田保,王忠彬,厉萱,沈锐利. 悬索桥主缆除湿的内部送气管道设计与性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1749-1755. |
| [11] | 郭殊伦,钟铁毅,闫志刚. 大跨度斜拉桥拉索的抖振响应计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1756-1762. |
| [12] | 高凯,刘纲. 全局临界强度分枝-约界法的有效强度改进[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 597-603. |
| [13] | 宫亚峰,宋加祥,谭国金,毕海鹏,刘洋,单承新. 多车桥梁动态称重算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 583-596. |
| [14] | 孔庆雯,谭国金,王龙林,王勇,魏志刚,刘寒冰. 基于有限元方法的裂缝箱梁桥自振特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 225-232. |
| [15] | 陈华,陈耀嘉,谢斌,王鹏凯,邓朗妮. CFRP筋粘结式锚固体系界面失效演化机制及粘结强度计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1698-1708. |
|
||