吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 2430-2436.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220125
• 农业工程·仿生工程 • 上一篇
基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测
- 1.长春师范大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130032
2.北华大学,吉林省 吉林市 132013
Prediction of soil moisture based on a deep learning model
Qing-tian GENG1( ),Zhi LIU1,Qing-liang LI1(
),Zhi LIU1,Qing-liang LI1( ),Fan-hua YU2,Xiao-ning LI1
),Fan-hua YU2,Xiao-ning LI1
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun Normal University,Changchun 130032,China
2.Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
摘要:
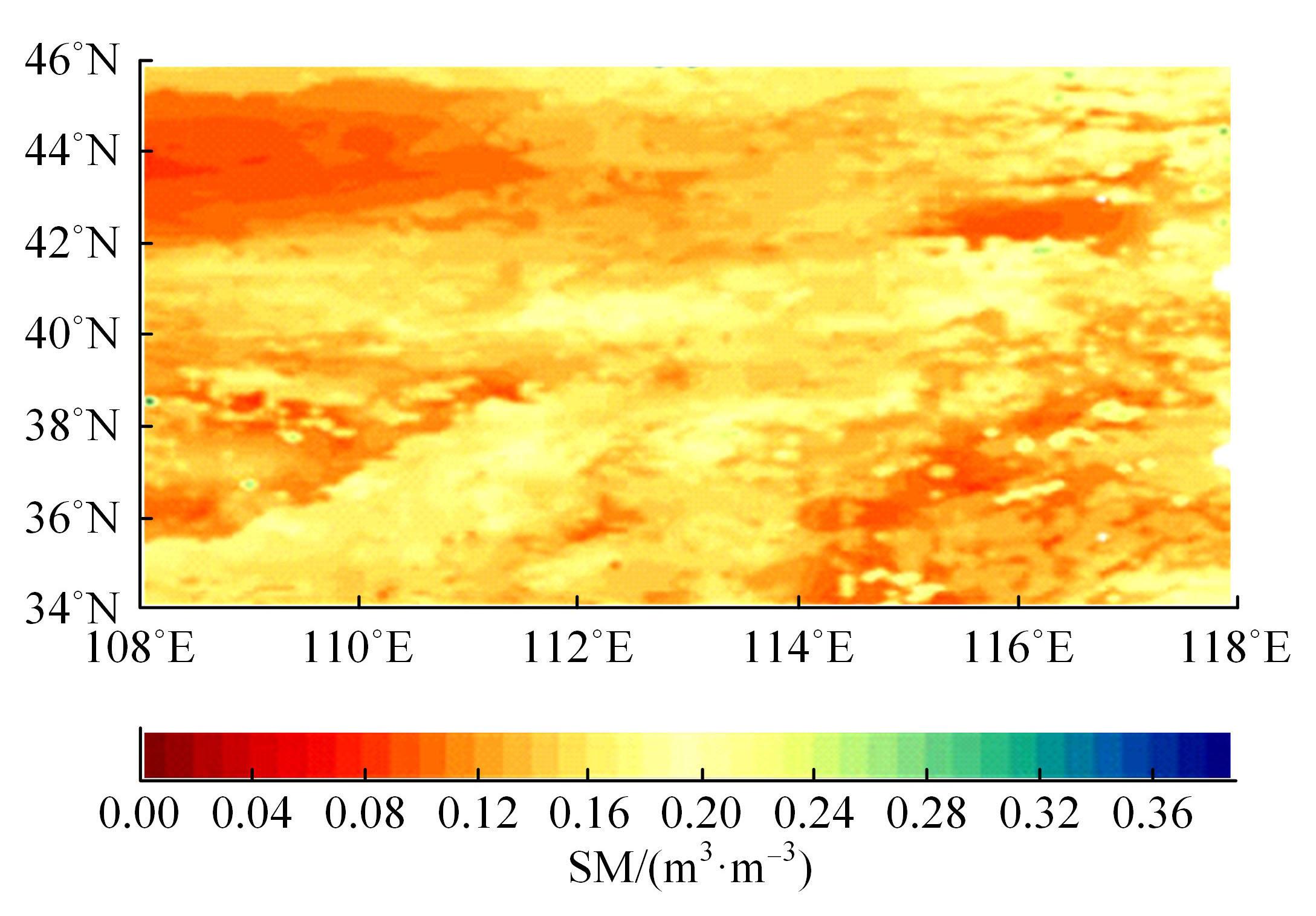
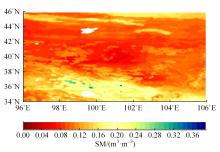
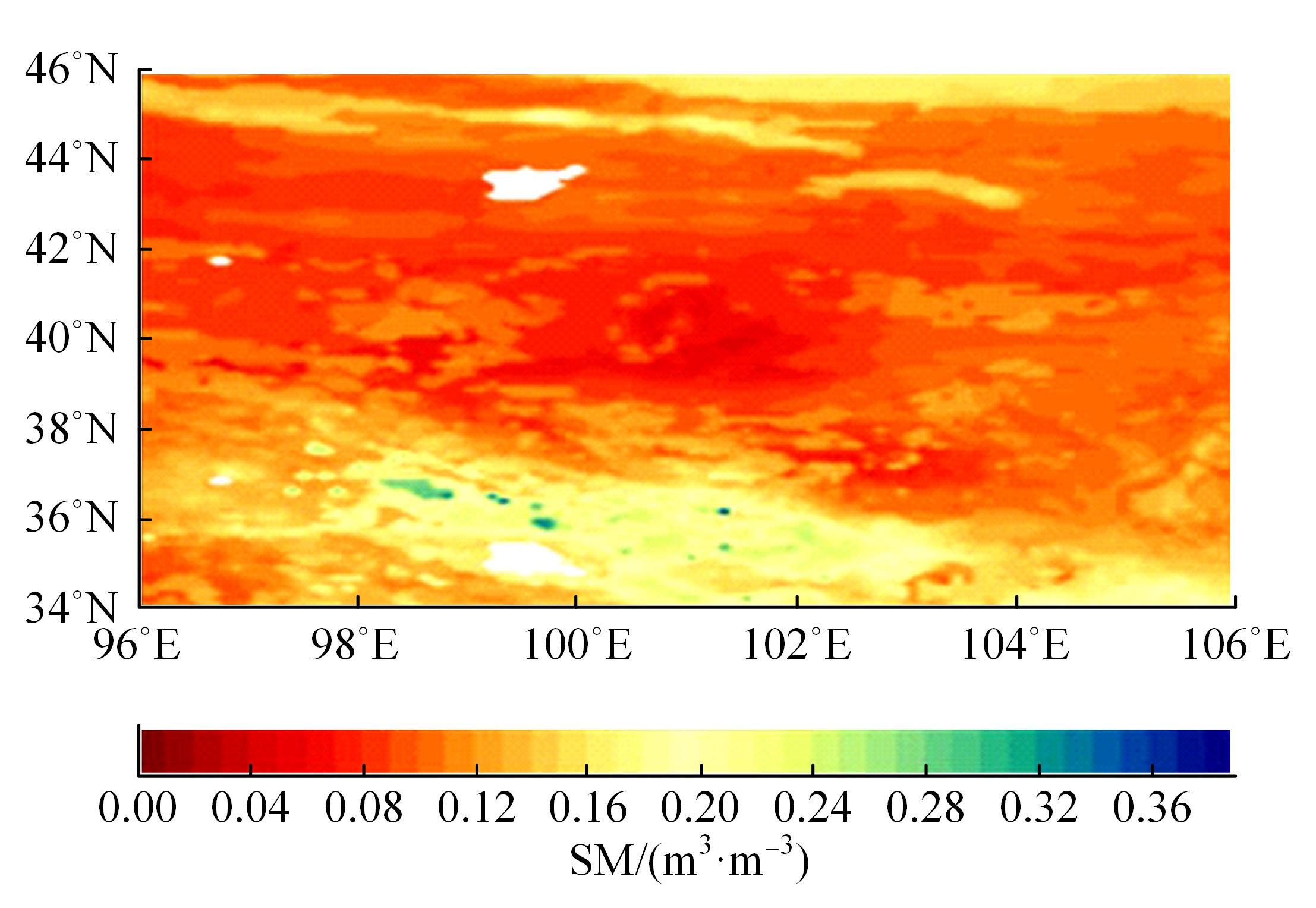
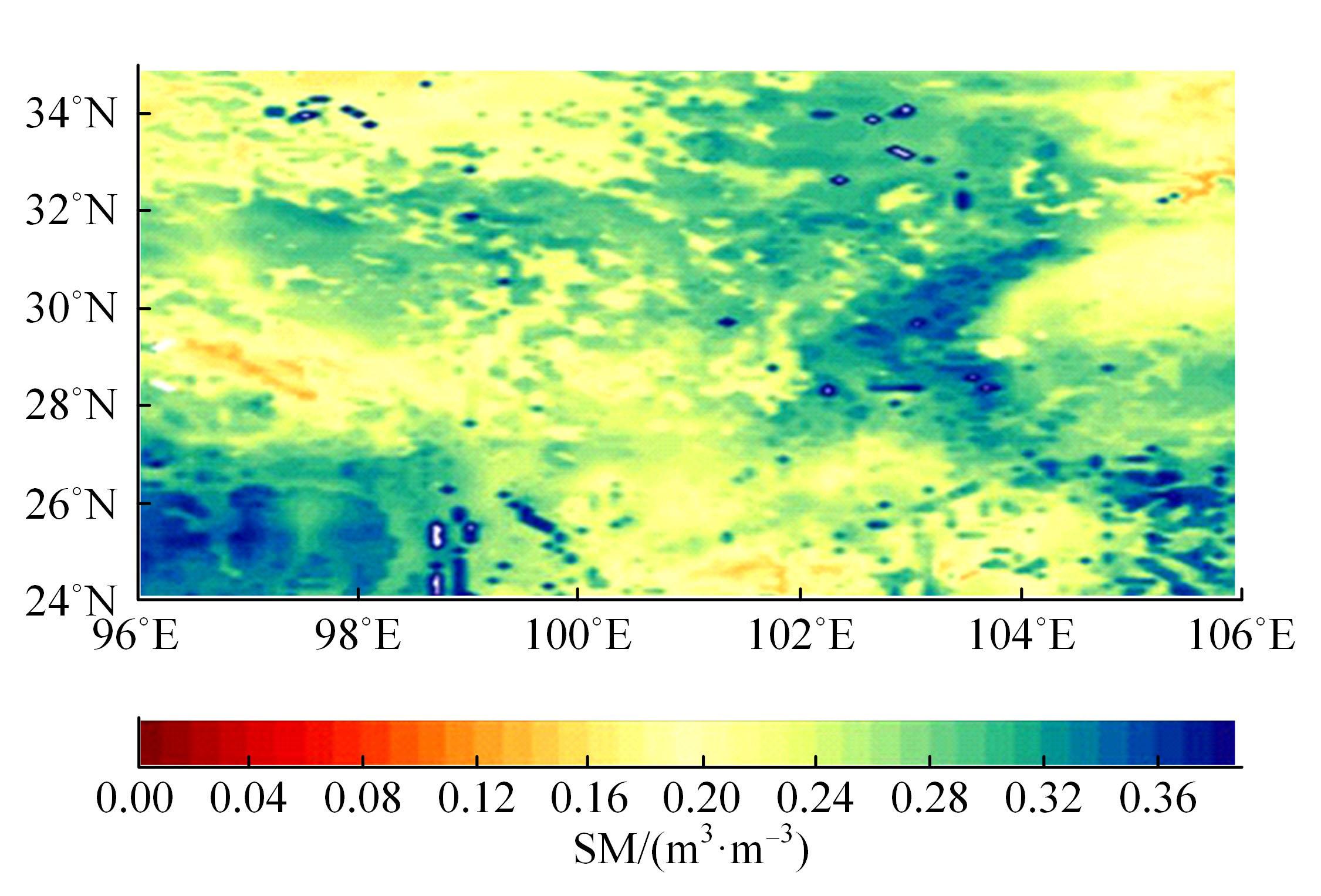
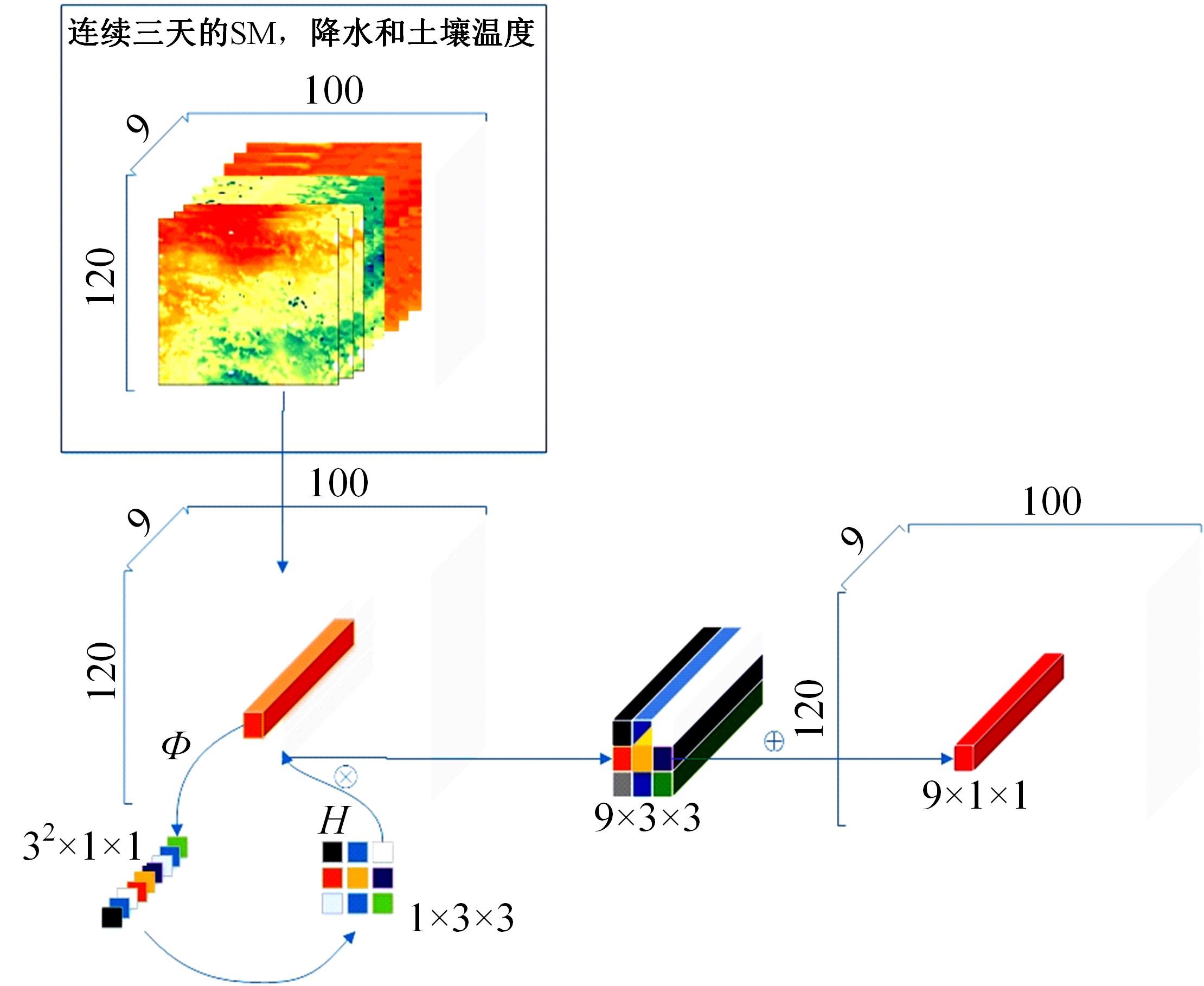
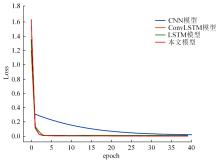
针对传统基于深度学习的水文预测模型在反映土壤水分时空特异性有一定局限性的问题,提出了一种具有channel-agnostic和spatial-specific结构的时空预测深度学习模型。该模型通过spatial-specific性质在不同空间位置自适应分配网络权值提取不同区域土壤湿度的空间特征;通过channel-agnostic性质用一维卷积提取单个grid点通道中土壤湿度和predict的时间特征,准确捕获单点的土壤湿度和其预测因子的变换关系,将lagged和预测因子作为模型输入在单个网格点进行预测。实验结果表明:本文模型的预测能力相较于传统DL模型有很大提升,在中国北方区域,模型决定系数(R2)相较于卷积神经网络(CNN)提高了80%。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | 刘卉, 汪懋华, 王跃宣, 等. 基于无线传感器网络的农田土壤温湿度监测系统的设计与开发[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2008, 38(3): 604-608. |
| Liu Hui, Wang Mao-hua, Wang Yue-xuan, et al. Development of farmland soil moisture and temperature monitoring system based on wireless sensor network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2008, 38(3): 604-608. | |
| 2 | 王学智, 李清亮, 李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022,52(3): 675-683. |
| Wang Xue-zhi, Li Qing-liang, Li Wen-hui, et al. Spatio-temporal model of soil moisture prediction integrated with transfer learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022,52(3): 675-683. | |
| 3 | Dirmeye P A, Gao X, Zhao M, et al. Multimodel analysis and implications for our perception of the land surface[J]. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 2006, 87: 1381-1397. |
| 4 | Fang K, Shen C, Kifer D, et al. Prolongation of SMAP to spatiotemporally seamless coverage of continental U.S. using a deep learning neural network[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2017, 44(11): 30-39. |
| 5 | Kalakuntla R, Wille T, Provost R L, et al. Analysis of the linearised observation operator in a land surface data assimilation scheme for numerical weather prediction[J]. Toxicology Letters, 2013, 216: 200-205. |
| 6 | Markus R, Gustau CV, Bjorn S, et al. Deep learning and process understanding for data-driven Earth system science[J]. Nature,2019, 566: 195. |
| 7 | LeCun Y, Bengio Y. Convolutional networks for images, speech, and time series[J]. The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks, 1995, 3361: 255-258. |
| 8 | Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J, Long short-term memory [J]. Neural Computation,1997, 9: 1735-1780. |
| 9 | Shi X J, Chen Z R, Wang H, et al. Convolutional LSTM network: a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[J]. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015,28: 802-810. |
| 10 | Sobayo R, Wu H H, Ray R, et al. Improving precipitation estimation using convolutional neural network[J]. Water Resources Research, 2019, 55: 2301-2321. |
| 11 | Zhao Q M, Song Z T, et al. Research on multi-point temperature and humidity prediction method of mushroom room based on CNN-GRU[J]. Transactions of The Chinese Society of Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51: 1000-1298. |
| 12 | Fang K, Shen C,Near-real-time forecast of satellite-based soil moisture using long short-term memory with an adaptive data integration kernel[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2020, 21: 399-413. |
| 13 | Li Q, Zhao Y, Yu F, A novel multichannel long short-term memory method with time series for soil temperature modeling[J]. IEEE Access, 2020(8): 182026-182043. |
| 14 | Mohamed E, Emad H, Ahmed M. A, et al. Assessment of a spatiotemporal deep learning approach for soil moisture prediction and filling the gaps in between soil moisture observations[J]. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 2021(4): 636234. |
| 15 | Kumar S. V, Reichle R. H, Koster R. D,et al. Role of subsurface physics in the assimilation of surface soil moisture observations[J]. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 2009, 10: 1534-1547. |
| [1] | 金小俊,孙艳霞,于佳琳,陈勇. 基于深度学习与图像处理的蔬菜苗期杂草识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2421-2429. |
| [2] | 巫威眺,曾坤,周伟,李鹏,靳文舟. 基于多源数据和响应面优化的公交客流预测深度学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2001-2015. |
| [3] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [4] | 吴飞,农皓业,马晨浩. 基于粒子群优化算法⁃长短时记忆模型的刀具磨损预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 989-997. |
| [5] | 白琳,刘林军,李轩昂,吴沙,刘汝庆. 基于自监督学习的单目图像深度估计算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1139-1145. |
| [6] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [7] | 潘恒彦,张文会,梁婷婷,彭志鹏,高维,王永岗. 基于MIMIC与机器学习的出租车驾驶员交通事故诱因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 457-467. |
| [8] | 高金武,贾志桓,王向阳,邢浩. 基于PSO-LSTM的质子交换膜燃料电池退化趋势预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2192-2202. |
| [9] | 李晓英,杨名,全睿,谭保华. 基于深度学习的不均衡文本分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1889-1895. |
| [10] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [11] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [12] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [13] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [14] | 王学智,李清亮,李文辉. 融合迁移学习的土壤湿度预测时空模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 675-683. |
| [15] | 宋林,王立平,吴军,关立文,刘知贵. 基于信息物理融合和数字孪生的可靠性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 439-449. |
|
||