吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 2973-2981.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211386
基于注意力机制的LSTM和ARIMA集成方法在土壤温度中应用
- 1.长春师范大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130032
2.北华大学 计算机科学与技术学院,吉林省 吉林市 132013
Integrated LSTM and ARIMA method based on attention model for soil temperature
Qing-tian GENG1( ),Yang ZHAO1,Qing-liang LI1(
),Yang ZHAO1,Qing-liang LI1( ),Fan-hua YU2,Xiao-ning LI1
),Fan-hua YU2,Xiao-ning LI1
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Changchun Normal University,Changchun 130032,China
2.College of Computer Science and Technology,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
摘要:
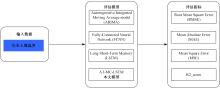
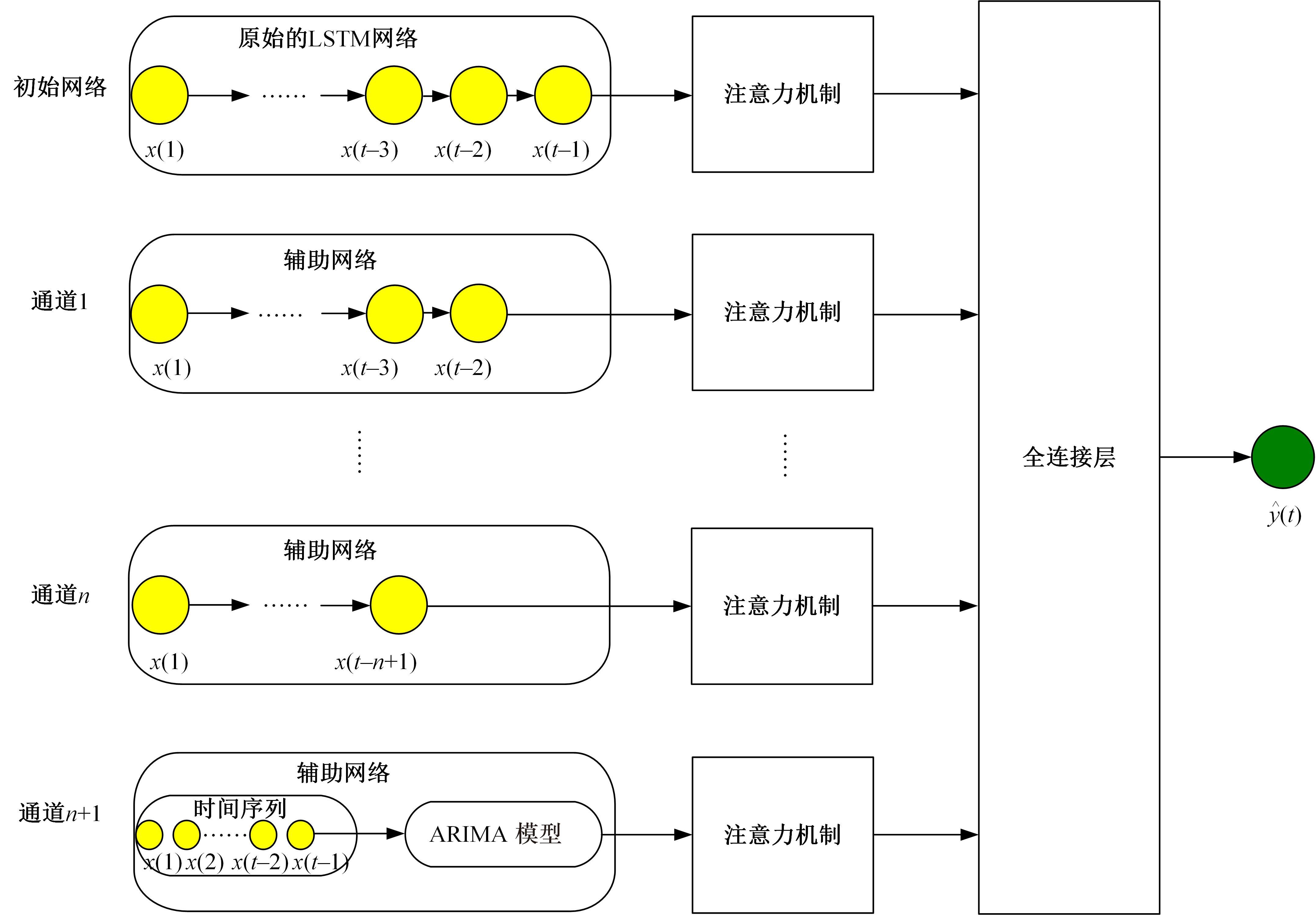
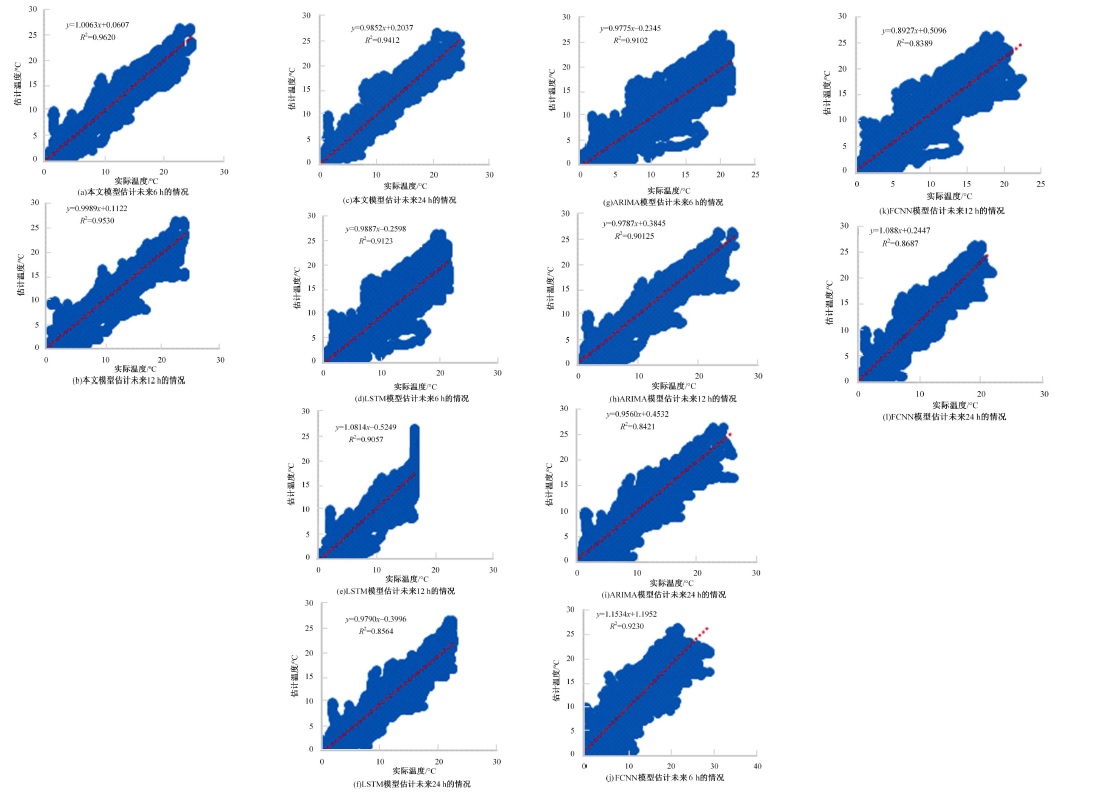
为准确分析土壤温度特性问题,提出了基于注意力机制的多通道长短期记忆网络(LSTM)融合ARIMA算法的预测模型。通过提取长短期不同时刻重要时间特征,并利用ARIMA时间序列模型提取线性特征优势更准确预测土壤温度。为验证该模型,本文在瑞士两个气象站(Laegern和Fluehli气象站)测试了未来6、12和24 h内,同时间土壤深度5、10和15 cm下土壤温度的均方根误差、平均绝对误差、均方误差和决定系数,并以4个评价指标进行验证。与自回归综合移动平均模型、LSTM和全连接网络相比,本文模型具有最优性能,尤其在未来6 h内对Fluehli站(10 cm土壤深度)土壤温度模型中改善最为显著;取得了最高的相对决定系数值0.9965,最低的均方根误差为0.3414,平均绝对误差为0.2310,均方误差为0.1165。因此,本文模型可以作为备选土壤温度估计的替代方法。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Lai L M, Zhao X C, Jiang L H, et al., Soil respiration in different agricultural and natural ecosystems in an arid region[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(10): 1-9. |
| 2 | Kisi O, Sanikhani H. Modelling long-term monthly temperatures by several data-driven methods using geographical inputs[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 2015, 35(13): 3834-3846. |
| 3 | Bonakdari H, Moeeni H, Ebtehaj I, et al. New insights into soil temperature time series modeling: linear or nonlinear?[J]. Theoretical & Applied Climatology, 2019, 135(3/4): 1157-1177. |
| 4 | Zhang J, Yan Z, Zhang X, et al. Developing a long short-term memory (LSTM) based model for predicting water table depth in agricultural areas[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 561: 918-929. |
| 5 | Guo J, Xie Z, Qin Y, et al. Short-term abnormal passenger flow prediction based on the fusion of SVR and LSTM[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 42946-42955. |
| 6 | Xiang-yun Qing, Niu Y. Hourly day-ahead solar irradiance prediction using weather forecasts by LSTM[J]. Energy, 2018,148: 461-468. |
| 7 | Cheng J, Dong L, Lapata M. Long short-term memory-networks for machine reading[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, USA,2016. |
| 8 | Li Q, Hao H, Zhao Y, et al. GANs-LSTM model for soil temperature estimation from meteorological: a new approach[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 59427-59443. |
| 9 | Mehdizadeh S, Behmanesh J, Khalili K. Evaluating the performance of artificial intelligence methods for estimation of monthly mean soil temperature without using meteorological data[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2017, 76(8): 325. |
| 10 | Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, et al. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 1929-1958. |
| 11 | Kingma D P, Ba J L. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[C]//The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1-15. |
| [1] | 霍光,林大为,刘元宁,朱晓冬,袁梦,盖迪. 基于多尺度特征和注意力机制的轻量级虹膜分割模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2591-2600. |
| [2] | 郭晓新,李佳慧,张宝亮. 基于高分辨率网络的视杯和视盘的联合分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2350-2357. |
| [3] | 李爽,林子瑞,叶松,刘旭,赵吉松. 运载火箭推力下降时入轨能力评估与轨迹重构方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2245-2253. |
| [4] | 车翔玖,徐欢,潘明阳,刘全乐. 生物医学命名实体识别的两阶段学习算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2380-2387. |
| [5] | 耿庆田,刘植,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [6] | 刘鹏举. 基于深度神经网络的物联网安全态势自动辨识算法设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 2121-2126. |
| [7] | 吕锋,李念,冯壮壮,张杨航. 面向用户的个性化产品服务系统协同过滤推介方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(7): 1935-1942. |
| [8] | 唐菲菲,周海莲,唐天俊,朱洪洲,温永. 融合动静态变量的滑坡多步位移预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1833-1841. |
| [9] | 刘培勇,董洁,谢罗峰,朱杨洋,殷国富. 基于多支路卷积神经网络的磁瓦表面缺陷检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1449-1457. |
| [10] | 张振海,季坤,党建武. 基于桥梁裂缝识别模型的桥梁裂缝病害识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1418-1426. |
| [11] | 田彦涛,黄兴,卢辉遒,王凯歌,许富强. 基于注意力与深度交互的周车多模态行为轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1474-1480. |
| [12] | 冀汶莉,田忠,柴敬,张丁丁,王斌. 多属性融合分布式光纤导水裂隙带高度预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1200-1210. |
| [13] | 吕卫,韩镓泽,褚晶辉,井佩光. 基于多模态自注意力网络的视频记忆度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(4): 1211-1219. |
| [14] | 姚荣涵,徐文韬,郭伟伟. 基于因子长短期记忆的驾驶人接管行为及意图识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 758-771. |
| [15] | 田彦涛,许富强,王凯歌,郝子绪. 考虑周车信息的自车期望轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 674-681. |
|
||