吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 535-542.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180790
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
城市潮汐车道优化设计的双层规划模型
- 吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
Bi-level programming model for optimization design of tidal lane
Hong-fei JIA( ),Xin-ru DING,Li-li YANG(
),Xin-ru DING,Li-li YANG( )
)
- College of Transportation, Jilin University, Changchun 130022, China
摘要:
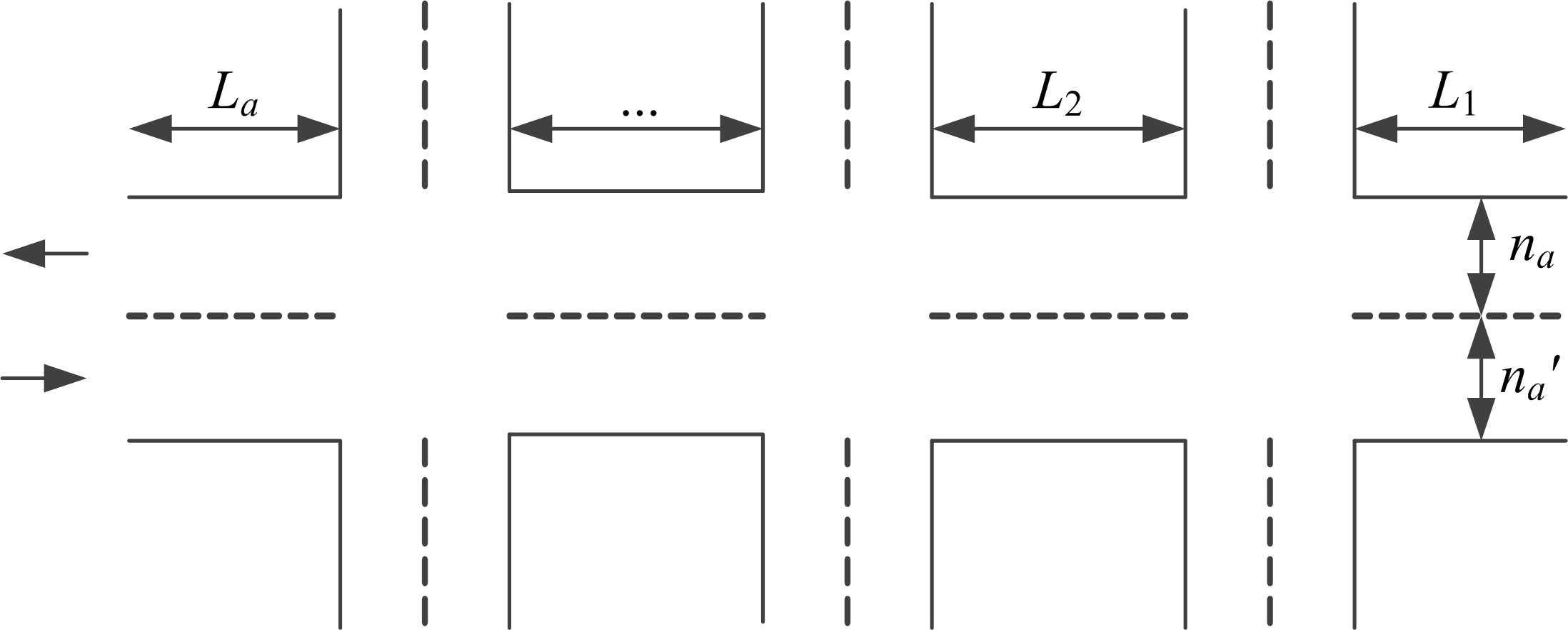
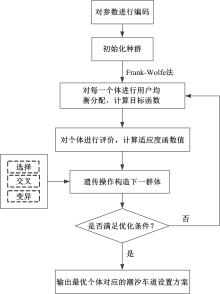
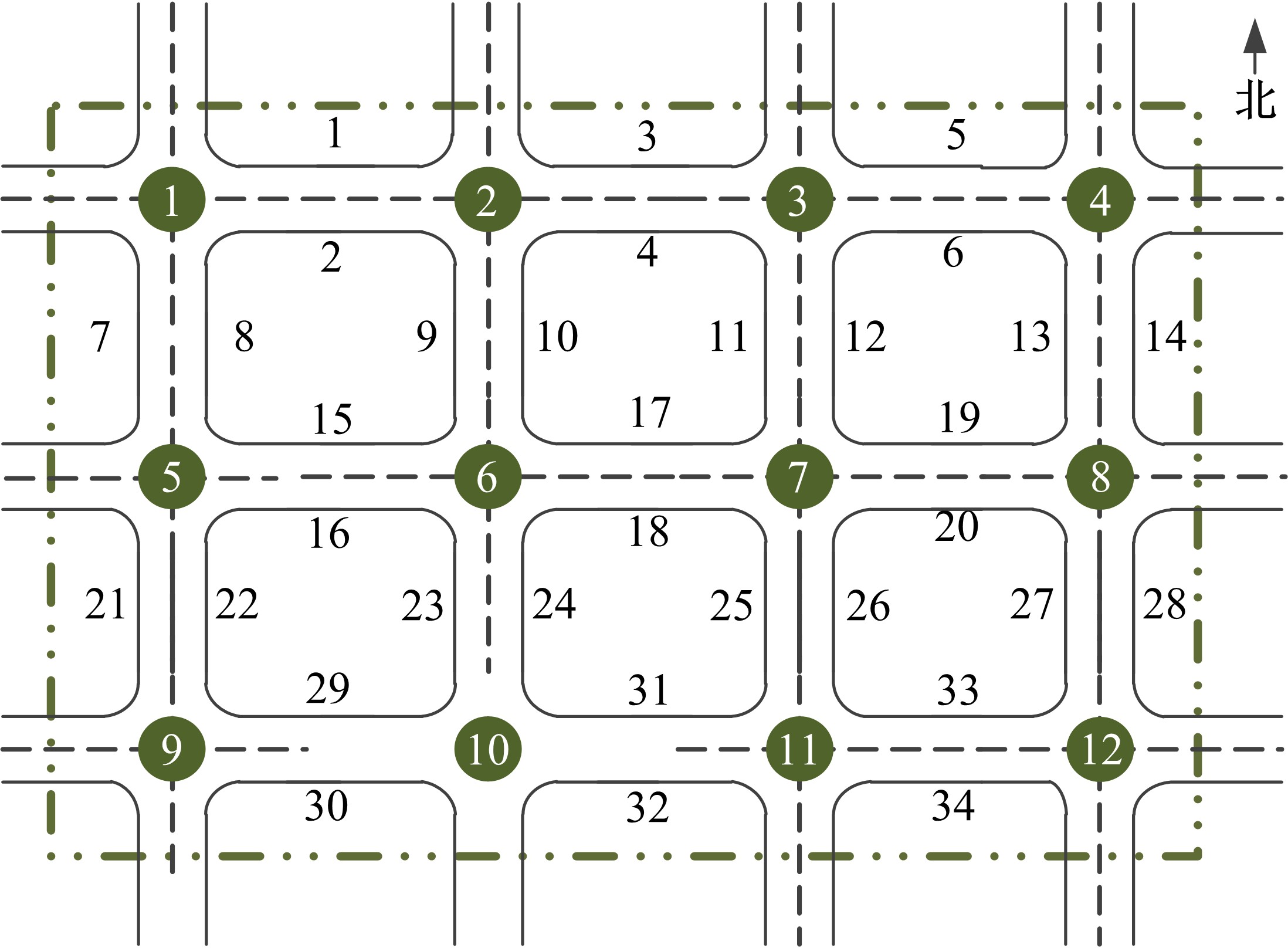
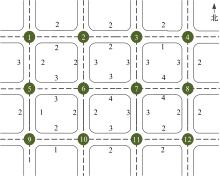
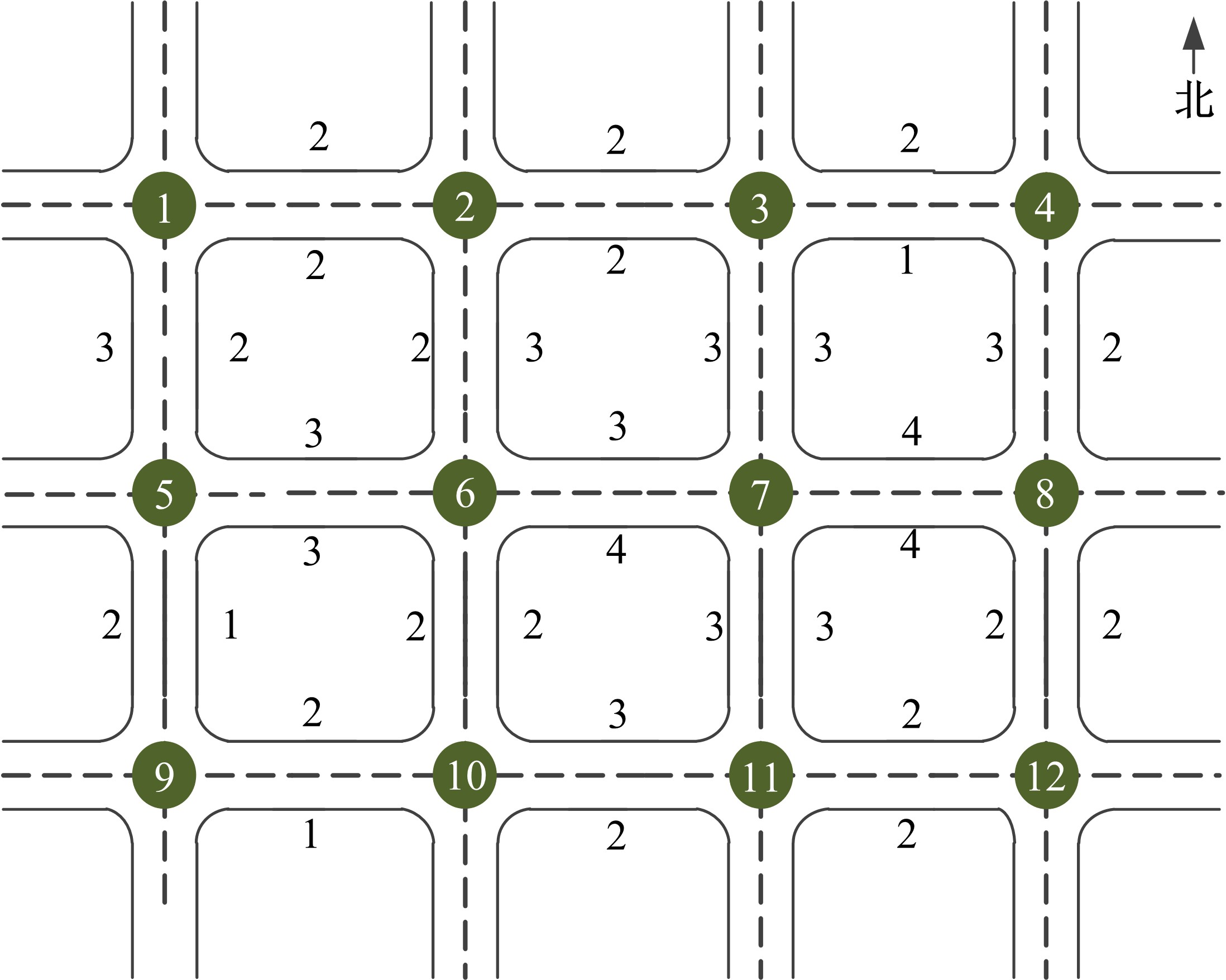
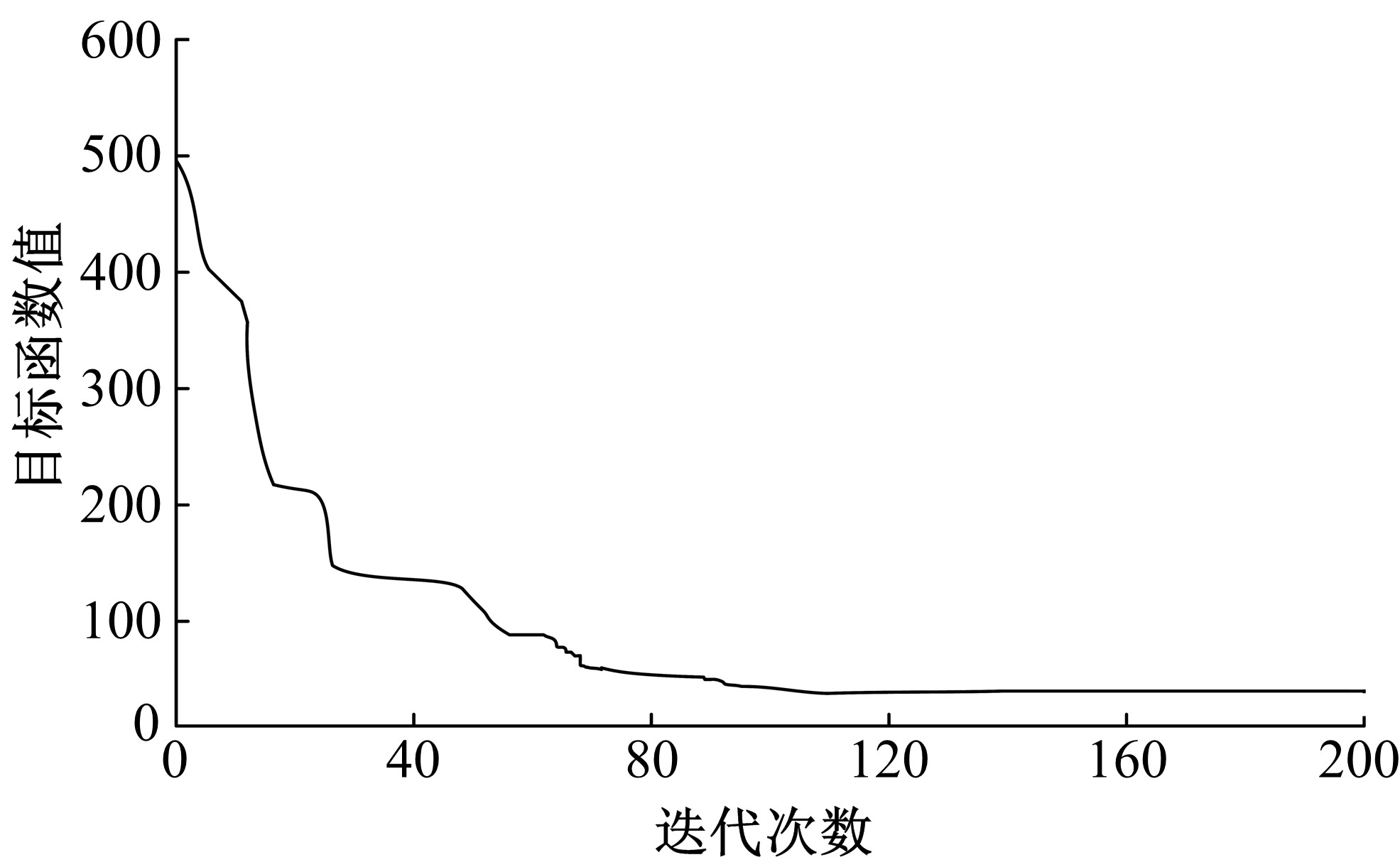
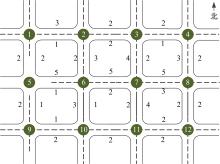
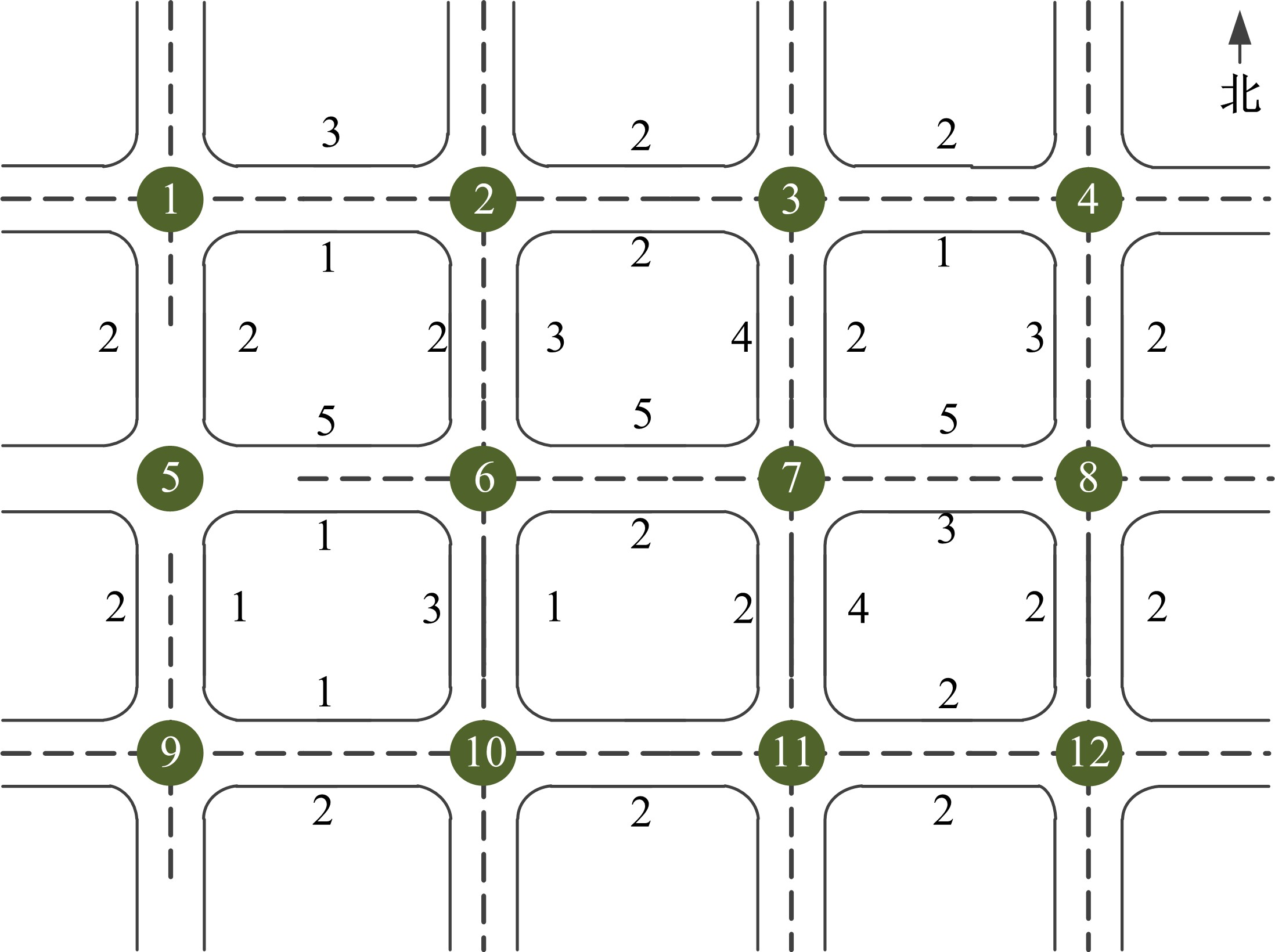
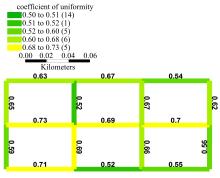
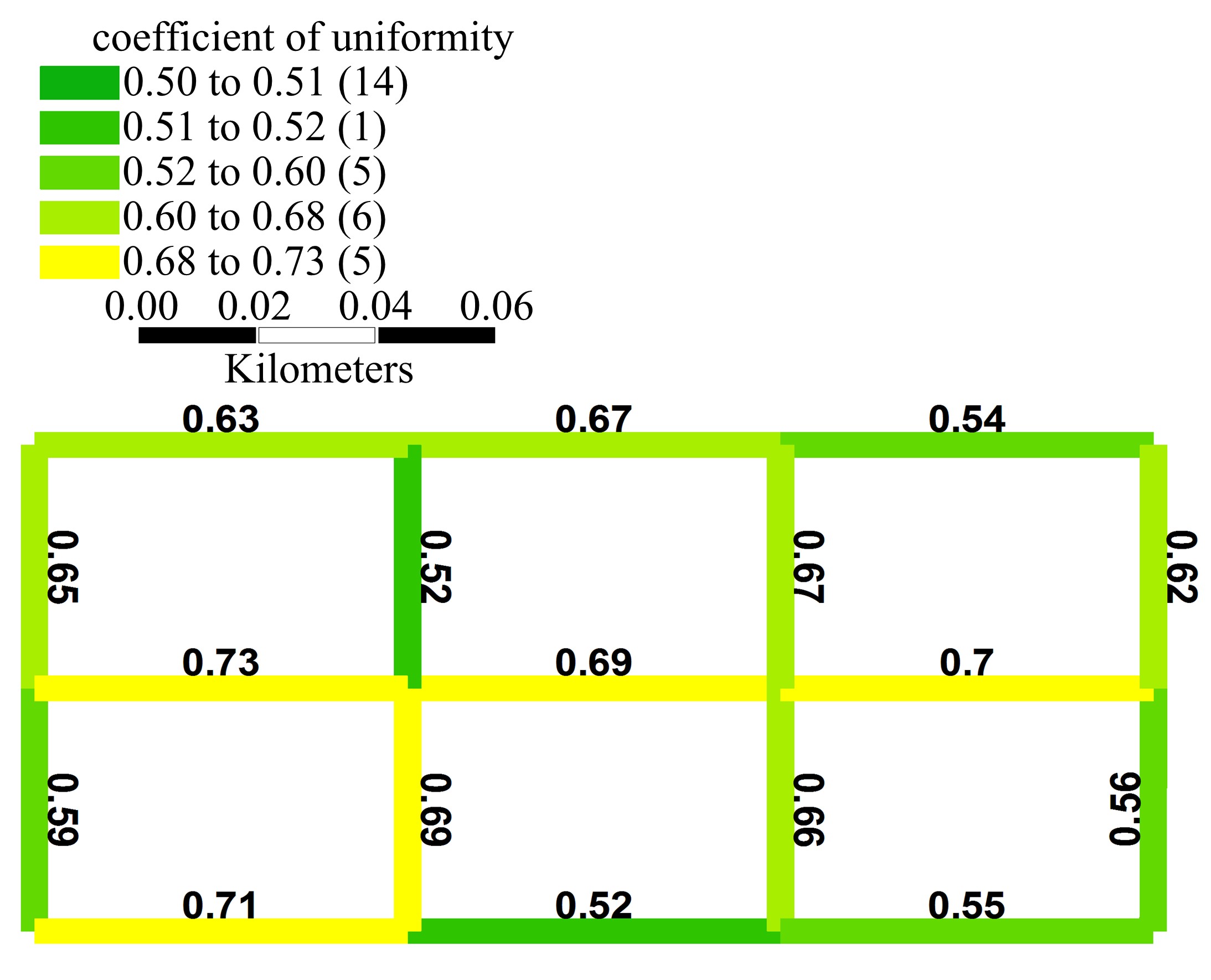
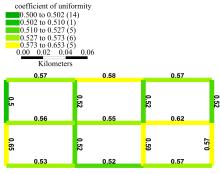
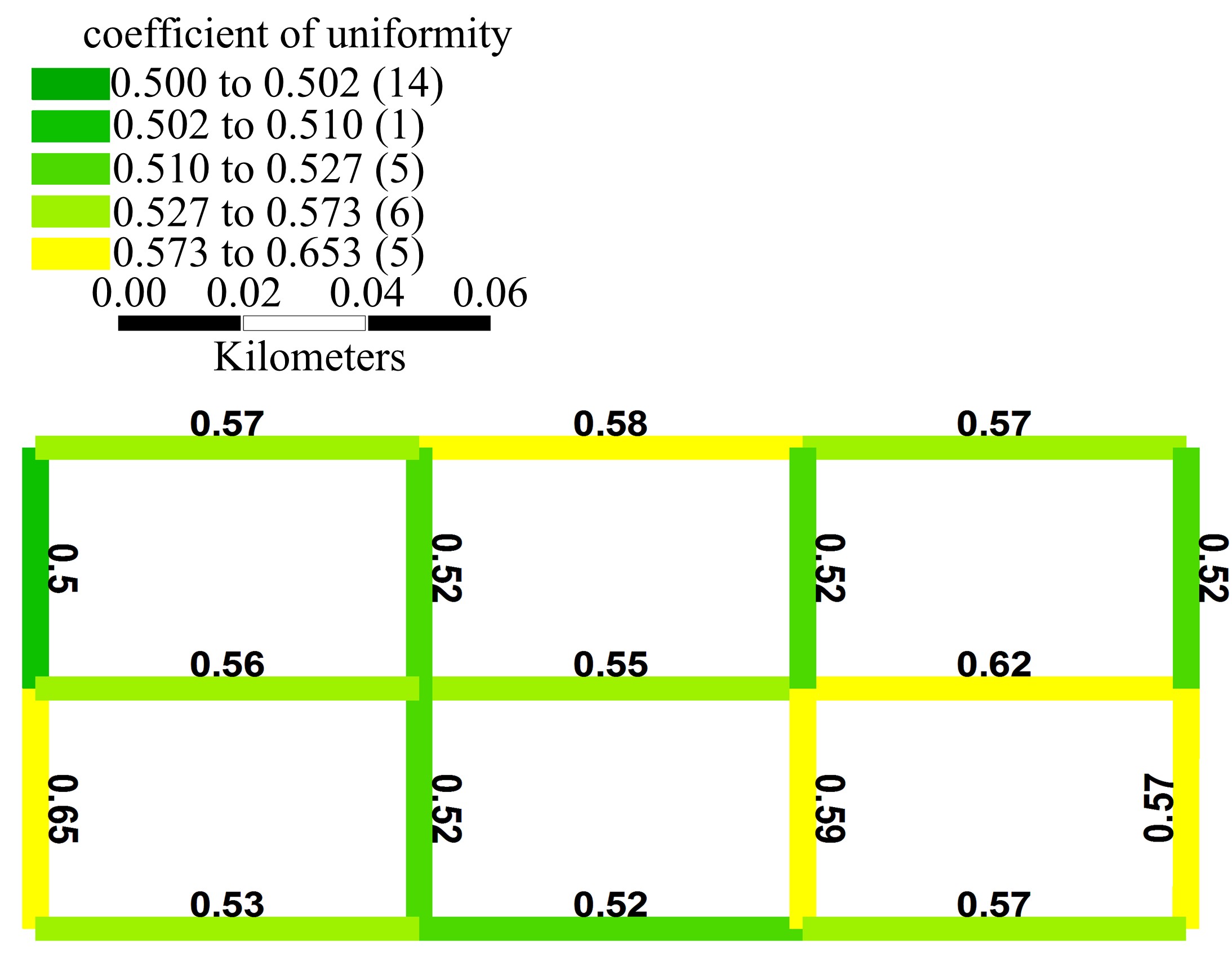
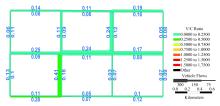
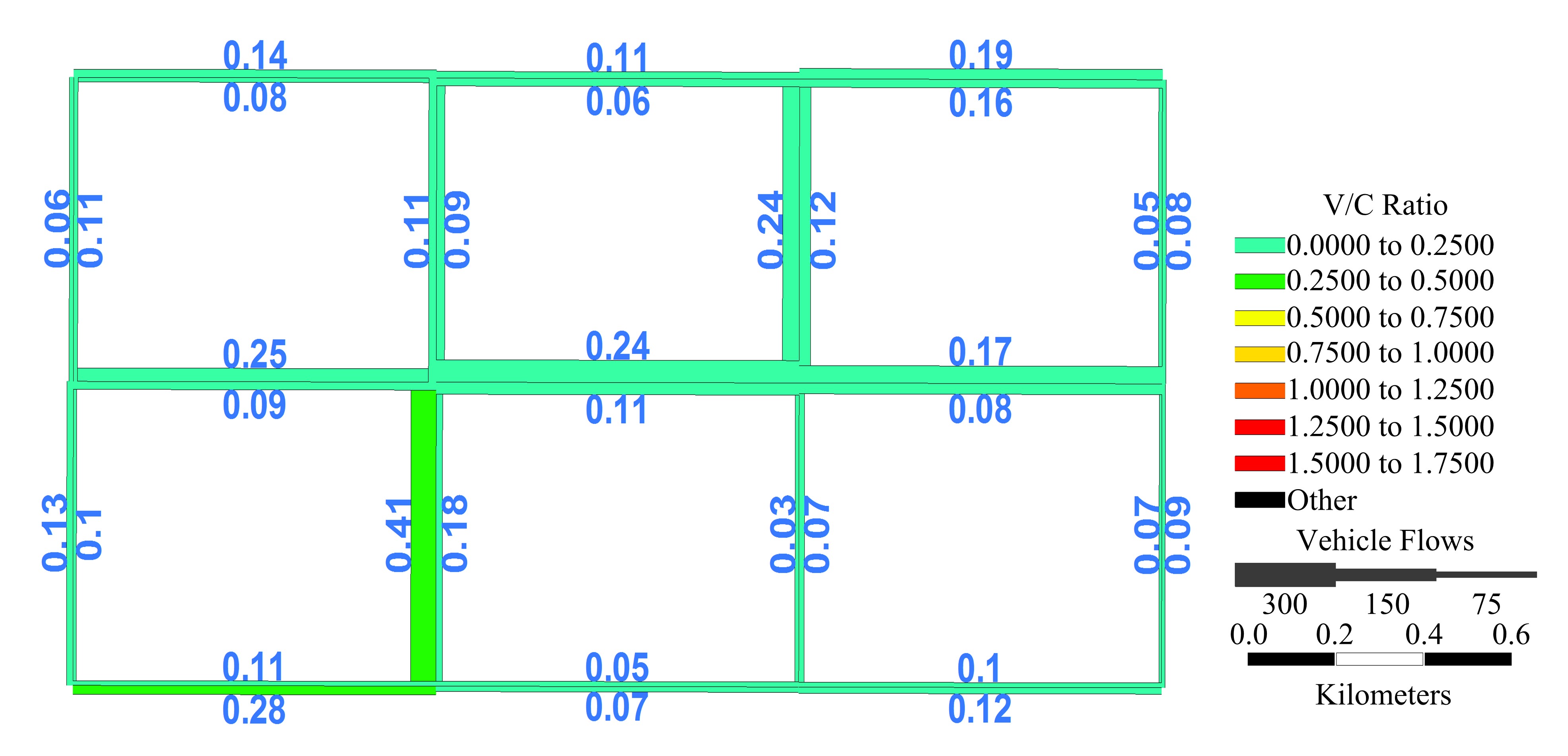
针对周期性某时段路段通行能力不均衡所导致的单向拥堵问题,分析了潮汐车道的设置条件与方向分布系数。在此基础上,从路网系统的角度出发,建立潮汐车道设置方案的双层规划模型,上层模型用于路网车道分配,以系统总延误及潮汐车道交通流优化比的和最优为目标,下层模型为路径选择行为符合Wardrop用户平衡准则的用户均衡分配模型。基于遗传算法和Frank-Wolfe算法进行算例分析,并将优化前、后的方向分布系数与路段饱和度进行对比,结果表明:该模型可合理缓解潮汐交通现象,降低路网系统总延误。
中图分类号:
- U491.5
| 1 | 刘鹏, 刘英舜. 潮汐式交通特性分析及应对措施研究[J]. 交通科技与经济, 2011, 13(3): 92-94. |
| Liu Peng, Liu Ying-shun. Study on characters of tidal transpotation and relieve meatures[J]. Technology & Economy in Areas of Communications, 2011, 13(3): 92-94. | |
| 2 | Stone P, Fajardo D, Hausknecht M, et al. Dynamic lane reversal in traffic management[J]. International IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 263(4): 1929-1934. |
| 3 | 刘恋. 可变车道优化控制研究[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学交通运输工程学院, 2014. |
| Liu Lian. The reseach on optimal control of variable lane[D]. Dalian: School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Dalian Jiaotong University, 2014. | |
| 4 | 崔凯. 左转逆向可变车道的优化设计与控制策略[D]. 山东: 山东大学控制科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Cui Kai. Optimal design and control strategy of left-turn reverse variable lane[D]. Shandong: Department of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University, 2017. | |
| 5 | Habibollah N, Ali E, Hamed A. Estimation of the logit model for the online contra flow problem[J]. Transport, 2010, 25(4): 433-441. |
| 6 | Matthew H, Au T C, Stone P. Dynamic lane teversal in yraffic management[J]. IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2011, 16(7): 1929-1934. |
| 7 | 高瑞, 龙建成. 基于可变车道优化的交通网络设计问题[J]. 合肥工业大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 38(11): 1446-1450. |
| Gao Rui, Long Jian-cheng. A Transportation network design problem with optimization of variable lanes[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science), 2015, 38(11): 1446-1450. | |
| 8 | 曲大义, 曹俊业, 王进展, 等. 潮汐车道与变向车道协同优化的绿波控制方法[J]. 济南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 31(3): 208-214. |
| Qu Da-yi, Cao Jun-ye, Wang Jin-zhan, et al. Green wave control method of collaborative optimization of tidal lane and variable lane[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2017, 31(3): 208-214. | |
| 9 | Wang J W, Wang H F, Zhang W J, et al. Evacuation planning based on the contra flow technique with consideration of evacuation priorities and traffic setup time[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligeng Transportation Systems, 2013, 14(1): 480-485. |
| 10 | Konstantinos A, Henrique S F, Rodrigo C C. Motorway tidal flow lane control[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(9): 279-284. |
| 11 | 张鹏, 李文权, 常玉林. 可变车道的城市路网备用容量模型[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2010, 45(2): 255-260. |
| Zhang Peng, Li Wen-quan, Chang Yu-lin. Reserve capacity model for urban road network with variable lanes[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2010, 45(2): 255-260. | |
| 12 | Gao Z Y, Song Y F. A reserve capacity model of optimal signal control with user equilibrium route choice[J]. Transportation Research Part B, 2002, 36(4): 313-323. |
| 13 | NCHRP. Convertle Roadways and Lanes[R]. Washington DC: Transportation Research Board of the National Academies, 2004. |
| 14 | 王勇. 城市交通网络可变车道设置方案研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2014. |
| Wang Yong. Research for reversible lane plan in urban traffic network[D]. Chengdu: School of Transportation and Logistics, Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014. | |
| 15 | 曹俊业. 基于潮汐流特性的变向车道协同优化控制方法[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学机械与汽车工程学院, 2016. |
| Cao Jun-ye. Control method of variable lane cooperation based on the characteristics of tidal flow[D]. Qingdao: School of Mechanical and Aotomotive Engineering, Qingdao University of Technology, 2016. | |
| 16 | 王雄. 城市道路可变车道设置的一主二从双层规划模型与算法[D]. 长沙: 中南大学交通运输工程学院, 2013. |
| Wang Xiong. Bi-level programming model and algorithm of urban roads convertible lanes[D]. Changsha: School of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, Central South University, 2013. | |
| 17 | 代磊磊, 顾金刚, 俞春俊, 等. 潮汐车道交通流特性与设置方案仿真研究[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2012, 30(1): 15-19. |
| Dai Lei-lei, Gu Jin-gang, Yu Chun-jun, et al. Traffic flow characteristics on reversible lane and its operational plan based on simulation[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2012, 30(1): 15-19. | |
| 18 | 陈雪珍. 基于双层规划的城市轨道交通接驳公交线路研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学交通运输与物流学院, 2016. |
| Chen Xue-zhen. Research of urban rail transit feeder bus routes based on bi-level programming[D]. Nanchang: School of Transportation and Logistics, East China Jiaotong University, 2016. | |
| 19 | 李和成, 王宇平. 求解混合整数双层规划问题的遗传算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(3): 781-786. |
| Li He-cheng, Wang Yu-ping. Genetic algorithms for solving mixed-integer bilevel programming problems[D]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(3): 781-786. | |
| 20 | 董海隆. 大型市政工程施工期间交通微循环改善研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州交通大学交通运输学院, 2013. |
| Dong Hai-long. The research of transportation microcirculation improvement during the large-scale municipal construction[D]. Lanzhou: School of Traffic and Transportation, Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2013. | |
| 21 | 祁宏生, 王殿海, 宋现敏. 路网交通状态平衡控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2012, 42(5): 1185-1190. |
| Qi Hong-sheng, Wang Dian-hai, Song Xian-min. Balanced control method for road network traffic state[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2012, 42(5): 1185-1190. |
| [1] | 常玉林,袁才鸿,孙超,张鹏. 基于改进元胞传输模型的城市路网实际阻抗计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 132-139. |
| [2] | 宗长富,文龙,何磊. 基于欧几里得聚类算法的三维激光雷达障碍物检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
| [3] | 隋振,姜源. 基于MIMO类脑情感学习回路的横-纵向综合控制驾驶员模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 140-146. |
| [4] | 别一鸣,姜凯,汤茹茹,王琳虹,熊昕宇. 考虑方案过渡影响的单点交通控制时段划分方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1844-1851. |
| [5] | 贾富淳,孟宪皆,雷雨龙. 基于多目标遗传算法的二自由度动力吸振器优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1969-1976. |
| [6] | 谷远利, 张源, 芮小平, 陆文琦, 李萌, 王硕. 基于免疫算法优化LSSVM的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [7] | 程国柱, 冯思鹤, 冯天军. 占用车行道的路内停车泊位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1858-1864. |
| [8] | 马芳武,韩露,周阳,王世英,蒲永锋. 采用聚乳酸复合材料的汽车零件多材料优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1385-1391. |
| [9] | 龙海波,杨家其,赵学彧. 基于转运延误风险的多方式协同货运载运工具配置优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1492-1499. |
| [10] | 别一鸣,汤茹茹,王运豪,文斌,冯天军,王琳虹. 信号交叉口进口车道饱和流率估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1459-1464. |
| [11] | 梁泉,翁剑成,周伟,荣建. 基于关联规则的公共交通通勤稳定性人群辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1484-1491. |
| [12] | 王宏志,姜方达,周明月. 基于遗传粒子群优化算法的认知无线电系统功率分配[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1363-1368. |
| [13] | 吴文静,陈润超,贾洪飞,罗清玉,孙迪. 车路协同环境下路段掉头区域车辆协同控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1100-1106. |
| [14] | 江亮,贺宜. 电动两轮车风险驾驶行为及事故影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. |
| [15] | 曲昭伟,潘昭天,陈永恒,陶鹏飞,孙迪. 基于最优速度模型的改进安全距离跟驰模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1092-1099. |
|
||