吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 543-548.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181087
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
考虑空间异质性的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响
- 北京交通大学 综合交通运输大数据应用技术交通运输行业重点实验室,北京 100044
Influence of built environment on commuting mode choice considering spatial heterogeneity
Chao-ying YIN( ),Chun-fu SHAO(
),Chun-fu SHAO( ),Xiao-quan WANG,Zhi-hua XIONG
),Xiao-quan WANG,Zhi-hua XIONG
- Key Laboratory of Transport Industry of Big Data Application Technologies for Comprehensive Transport, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
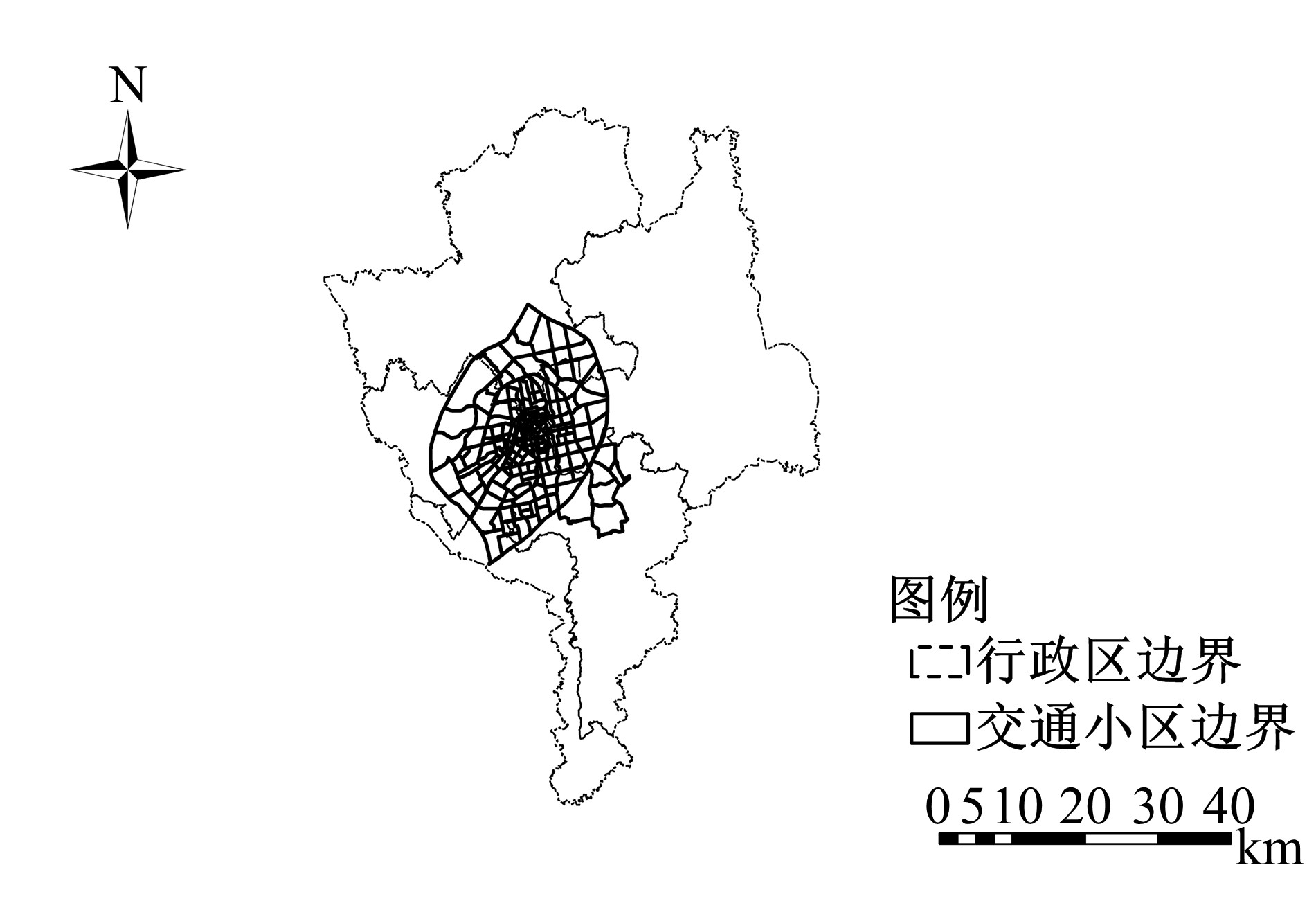
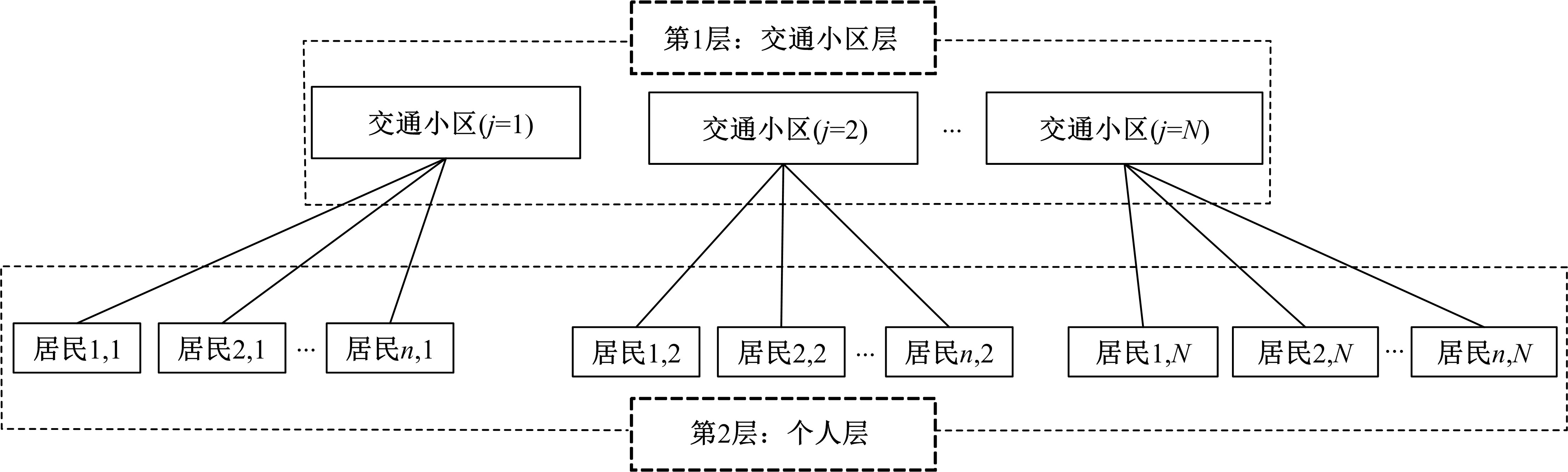
为探讨交通小区层面建成环境各因素对居民通勤方式选择的影响,构建了考虑空间异质性的多层logistic模型,以长春市为例开展了实证研究。模型同时考虑了个体层面和交通小区层面变量对通勤行为的影响,并借助HLM软件标定模型参数。结果表明:居民通勤方式选择的空间异质性是显著存在的;在控制了空间异质性后,个体层面变量中性别、年龄、教育水平、户口类型、家庭收入、家庭小汽车拥有和出行属性中的通勤距离均对居民通勤方式选择有显著影响;交通小区层面中,居住地土地利用混合度越高、公共交通站点及道路交叉口密度越大,居民选择小汽车通勤的可能性越低,而居住在距离城市中心商务区较远的居民更倾向选择小汽车通勤。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | 秦焕美, 高建强, 和士辉, 等. 基于奖罚措施的小汽车通勤者出行行为研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18( 1): 115- 120. |
| Qin Huan-mei, Gao Jian-qiang, He Shi-hui, et al. Car commuters’ travel behavior based on rewarding and punishments strategies[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18( 1): 115- 120. | |
| 2 | Wang X Q, Shao C F, Yin C Y, et al. Application of bayesian multilevel models using small and medium size city in China: the case of Changchun[EB/OL]. ( 2018-02-11).[ 2018-11-20]. . |
| 3 | 尹超英, 邵春福, 王晓全. 考虑停车可用性的建成环境对小汽车通勤出行的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49( 3): 714- 719. |
| Yin Chao⁃ying, Shao Chun⁃fu, Wang Xiao⁃quan. Influence of urban built environment on car commuting considering parking availability[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49( 3): 714- 719. | |
| 4 | 孙斌栋, 但波. 上海城市建成环境对居民通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70( 10): 1664- 1674. |
| Sun Bin-dong, Dan Bo. Impact of urban built environment on residential choice of commuting mode in Shanghai[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70( 10): 1664- 1674. | |
| 5 | 塔娜, 柴彦威, 关美宝. 建成环境对北京市郊区居民工作日汽车出行的影响[J]. 地理学报, 2015, 70( 10): 1675- 1685. |
| Ta Na, Chai Yan-wei, Guan Mei-bao. The relationship between the built environment and car travel distance on weekdays in Beijing[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70( 10): 1675- 1685. | |
| 6 | Li S X, Zhao P J. Exploring car ownership and car use in neighborhoods near metro stations in Beijing: Does the neighborhood built environment matter?[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2017, 56: 1- 17. |
| 7 | Shen Q, Chen P, Pan H X. Factors affecting car ownership and mode choice in rail transit-supported suburbs of a large Chinese city[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2016, 94: 31- 44. |
| 8 | Xiao Z P, Liu Q, Wang J. How do the effects of local built environment on household vehicle kilometers traveled vary across urban structural zones?[J]. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 2018, 12( 9): 637- 647. |
| 9 | Reid E, Robert C. Travel and the built environment[J]. Journal of the American Planning Association, 2010, 76( 3): 265- 294. |
| 10 | Cao X S, Yang W Y. Examining the effects of the built environment and residential self-selection on commuting trips and the related CO 2 emissions: an empirical study in Guangzhou, China [J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2017, 52: 480- 494. |
| 11 | 尹超英, 邵春福, 王聘玺, 等. 基于多层模型的城市建成环境对通勤行为的影响[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18( 2): 122- 127. |
| Yin Chao-ying, Shao Chun-fu, Wang Pin-xi, et al. Impacts of built environment on commuting behavior based on a multilevel modeling approach[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18( 2): 122- 127. | |
| 12 | Zhao P J. The Impact of the built environment on individual workers’ commuting behavior in Beijing[J]. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 2013, 7( 5): 389- 415. |
| 13 | Hedeker D. A mixed-effects multinomial logistic regression model[J]. Statistics in Medicine, 2003, 22( 9): 1433- 1446. |
| 14 | Ding C, Wang Y P, Tang T Q, et al. Joint analysis of the spatial impacts of built environment on car ownership and travel mode choice[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2016, 60: 28- 40. |
| [1] | 贾洪飞,丁心茹,杨丽丽. 城市潮汐车道优化设计的双层规划模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 535-542. |
| [2] | 宗长富,文龙,何磊. 基于欧几里得聚类算法的三维激光雷达障碍物检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
| [3] | 隋振,姜源. 基于MIMO类脑情感学习回路的横-纵向综合控制驾驶员模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 140-146. |
| [4] | 常玉林,袁才鸿,孙超,张鹏. 基于改进元胞传输模型的城市路网实际阻抗计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 132-139. |
| [5] | 谷远利, 张源, 芮小平, 陆文琦, 李萌, 王硕. 基于免疫算法优化LSSVM的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [6] | 别一鸣,姜凯,汤茹茹,王琳虹,熊昕宇. 考虑方案过渡影响的单点交通控制时段划分方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1844-1851. |
| [7] | 程国柱, 冯思鹤, 冯天军. 占用车行道的路内停车泊位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1858-1864. |
| [8] | 梁泉,翁剑成,周伟,荣建. 基于关联规则的公共交通通勤稳定性人群辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1484-1491. |
| [9] | 龙海波,杨家其,赵学彧. 基于转运延误风险的多方式协同货运载运工具配置优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1492-1499. |
| [10] | 别一鸣,汤茹茹,王运豪,文斌,冯天军,王琳虹. 信号交叉口进口车道饱和流率估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1459-1464. |
| [11] | 吴文静,陈润超,贾洪飞,罗清玉,孙迪. 车路协同环境下路段掉头区域车辆协同控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1100-1106. |
| [12] | 江亮,贺宜. 电动两轮车风险驾驶行为及事故影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. |
| [13] | 曲昭伟,潘昭天,陈永恒,陶鹏飞,孙迪. 基于最优速度模型的改进安全距离跟驰模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1092-1099. |
| [14] | 陈磊,王江锋,谷远利,闫学东. 基于思维进化优化的多源交通数据融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
| [15] | 凃强,程琳,林芬,孙超. 考虑出行者风险态度的最优路径搜索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 720-726. |
|
||