吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (1): 216-226.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20190013
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于补充改进集合经验模态分析法⁃多尺度排列熵分析桥梁振动信号优化滤波方法
- 1. 吉林大学 建设工程学院,长春 130021
2. 长春市智慧城市科技有限公司,长春 130033
Bridge vibration signal optimization filtering method based on improved CEEMD⁃multi⁃scale permutation entropy analysis
Bo-xin WANG1( ),Hai-tao YANG1,Qing WANG1,Xin GAO1(
),Hai-tao YANG1,Qing WANG1,Xin GAO1( ),Xiao-xu CHEN2
),Xiao-xu CHEN2
- 1. College of Construction Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, China
2. Changchun Smart City Science and Technology Co. Ltd. , Changchun 130033, China
摘要:
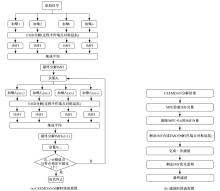
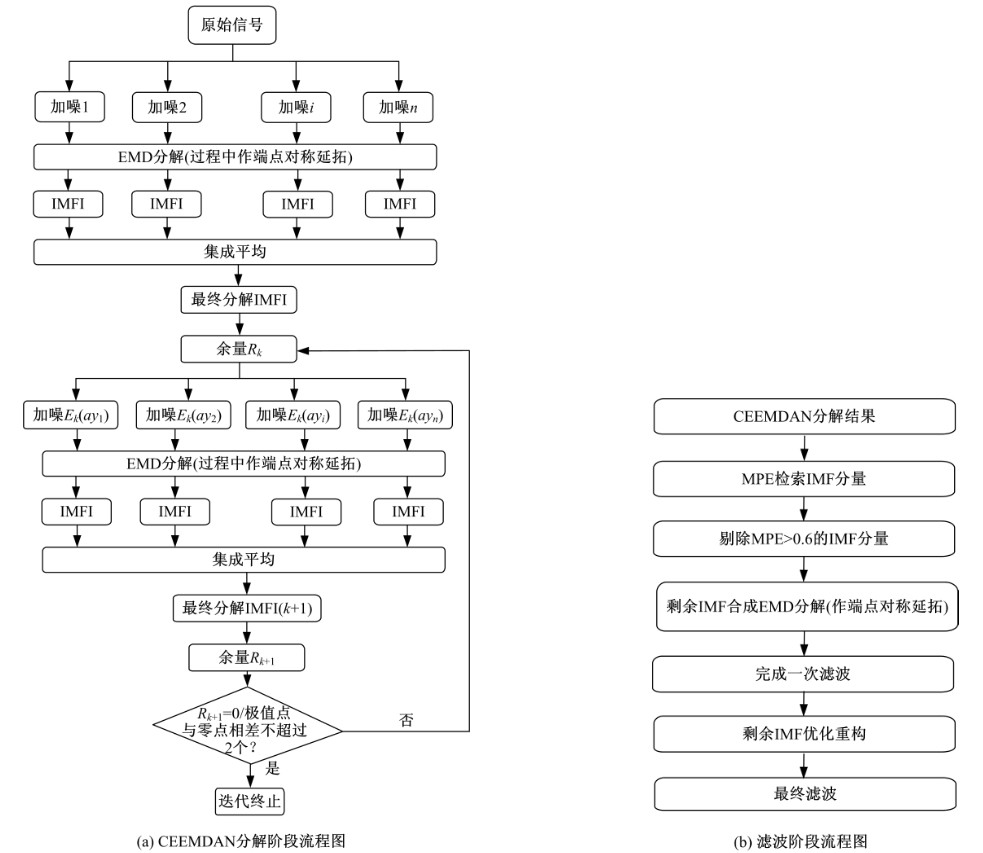
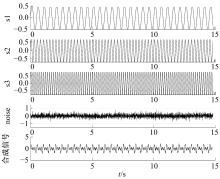
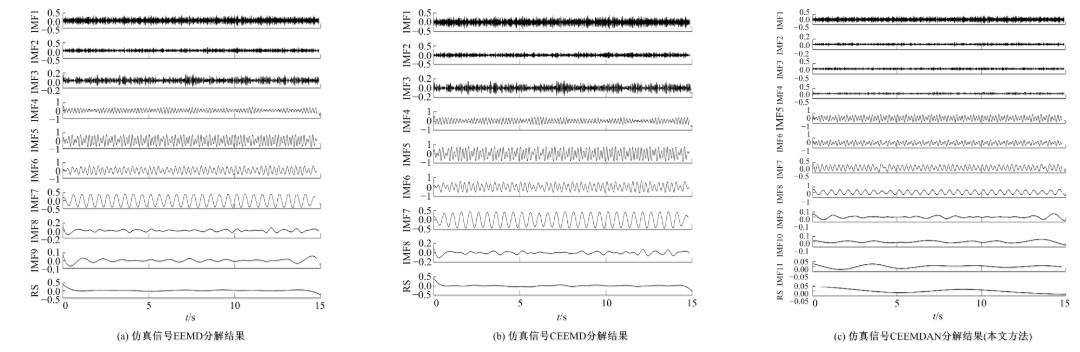
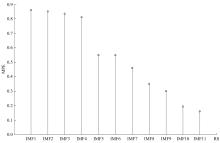
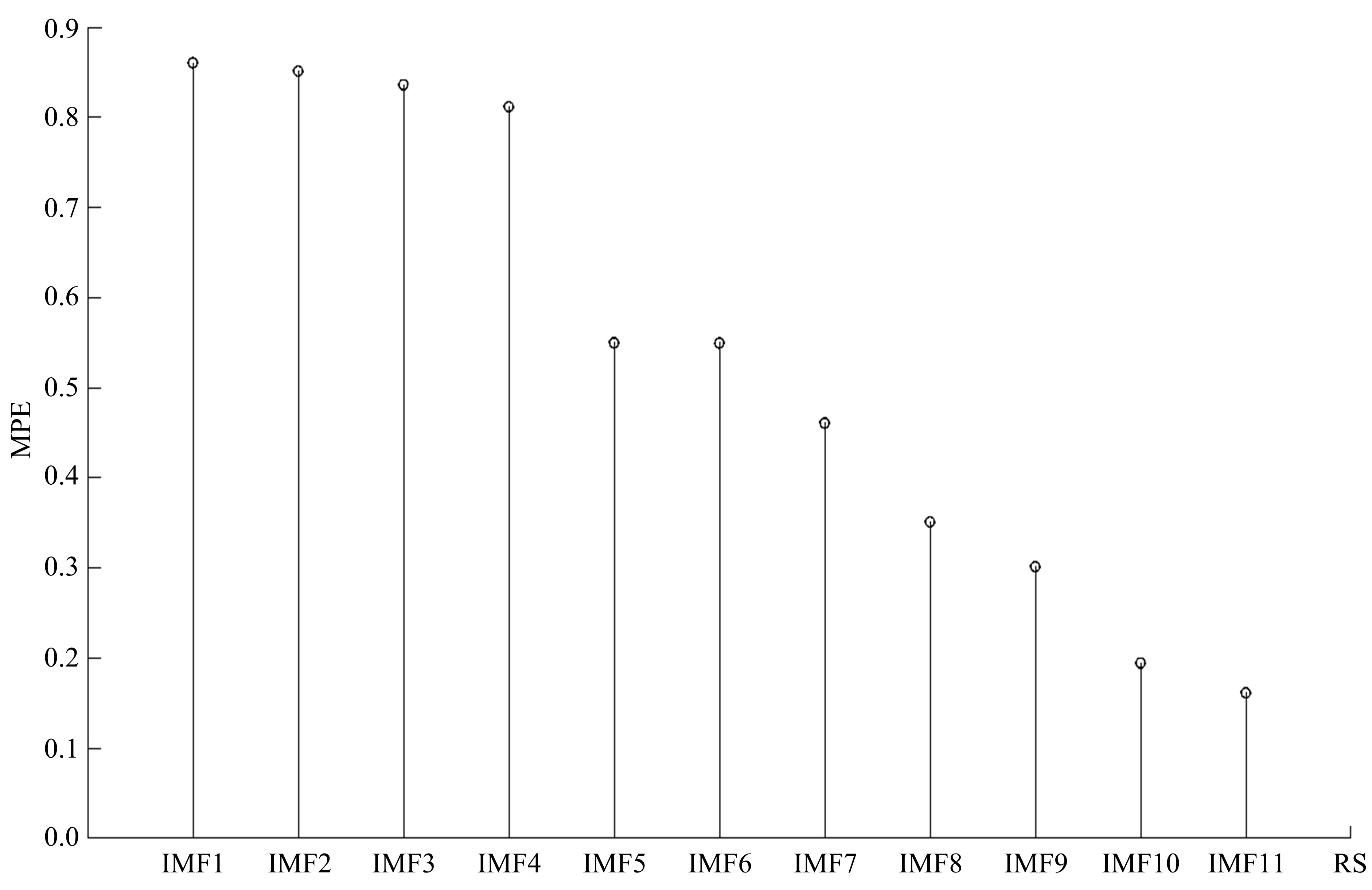
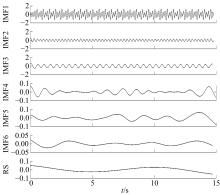
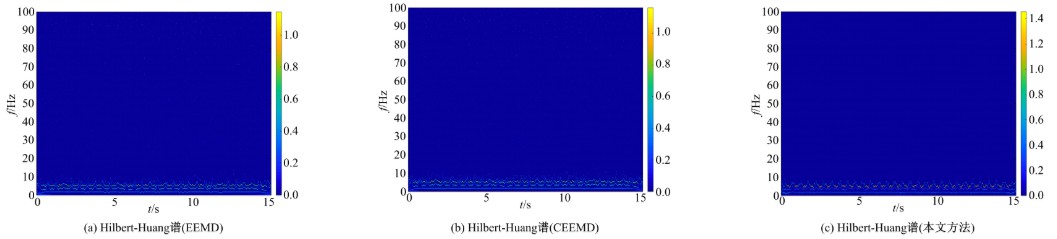
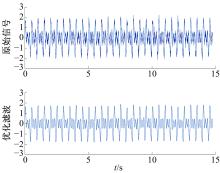
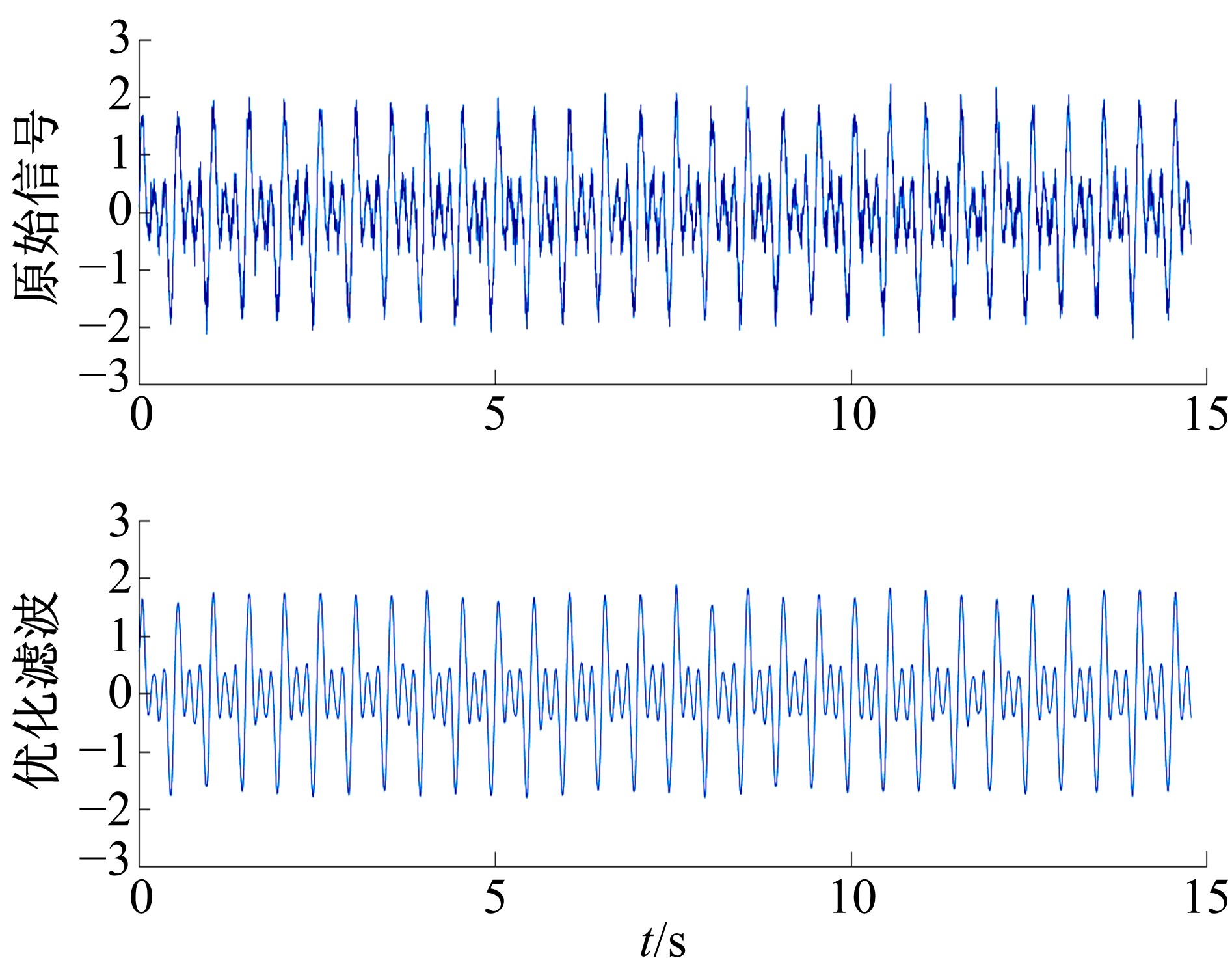
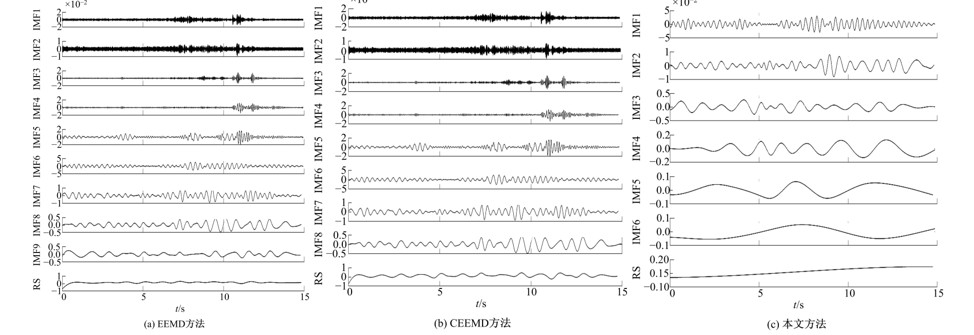
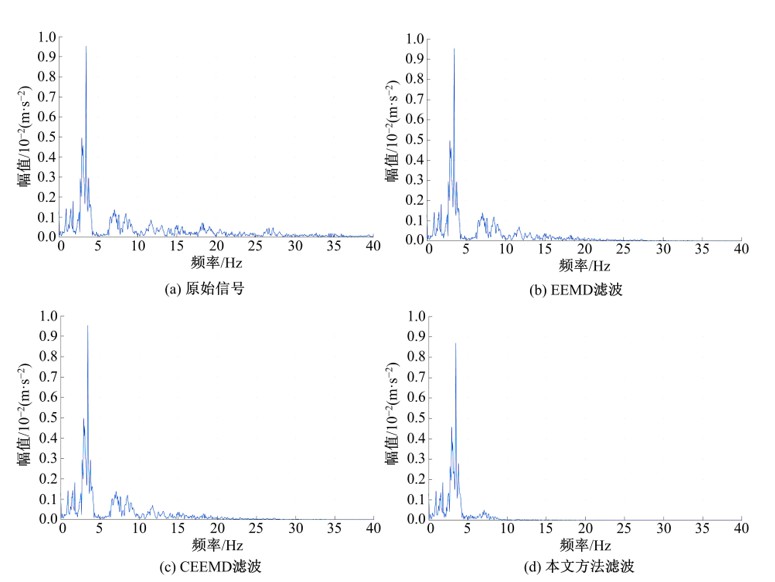
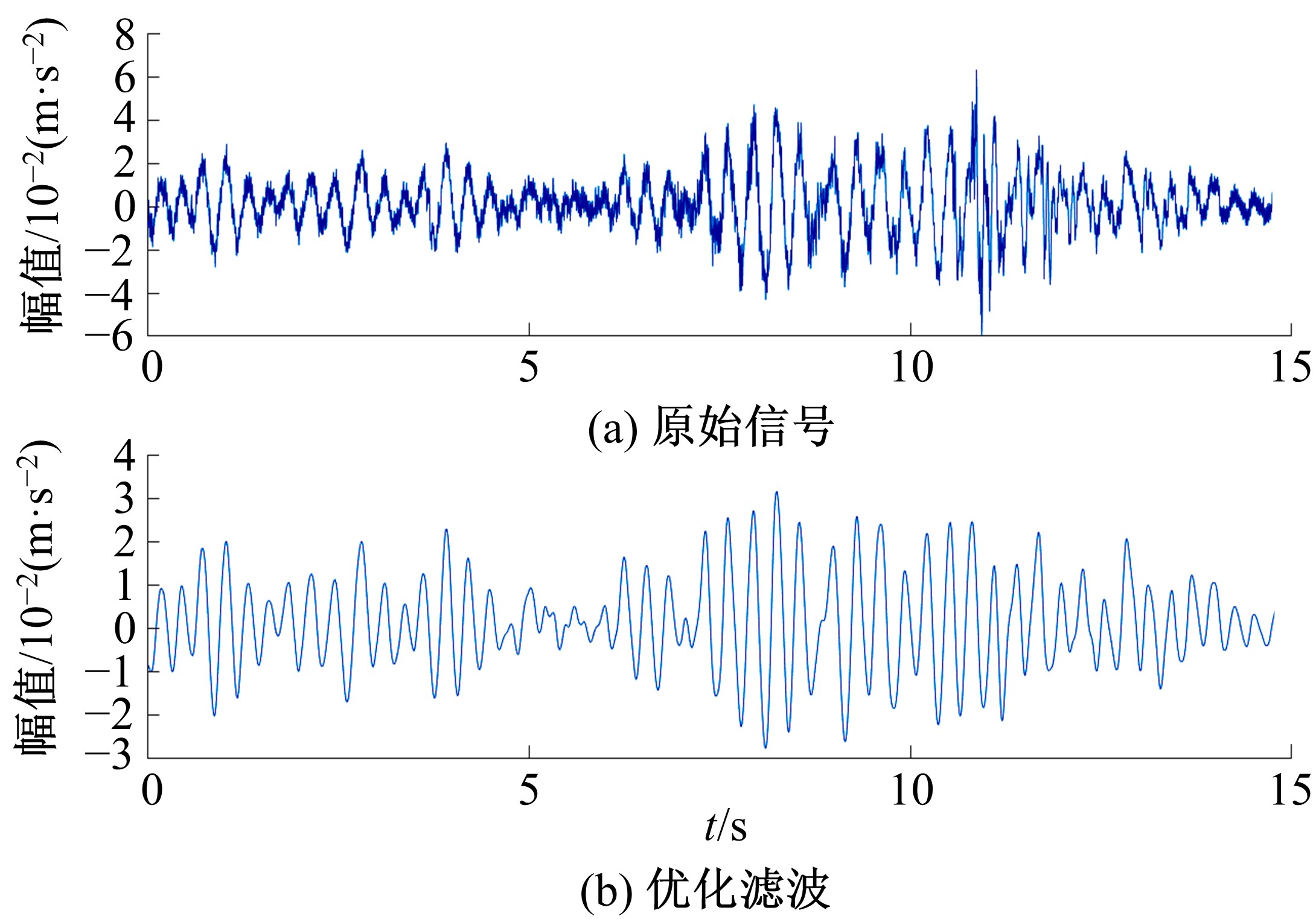
针对桥梁振动信号高度非平稳特征和含噪声成分严重的问题,提出了一种应用于桥梁健康监测领域的信号自适应分解与重构的优化滤波方法。该方法以自适应加噪的完备集合经验模态分解(CEEMDAN)为核心算法,将原始振动信号逐级分解为多个不同特征时间尺度相对平稳的固有模态函数(IMF),采用端点对称延拓法抑制端点效应,引入多尺度排列熵(MPE)分析各IMF在不同尺度上的熵均值,检索随机程度较大的IMF分量,将含噪严重与由于加噪分解产生的伪分量剔除完成一次滤波,为了择优选取剩余IMF进行信号重构保证滤波具有较好的相似度与光滑度,建立了优化重构模型完成两次滤波。研究表明:本文方法在自适应分解阶段较常用的集合经验模态分解(EEMD)、补充集合经验模态分解(CEEMD)方法具有更好的完备性、正交性与计算效率,在一定程度上抑制了模态混叠现象,端点效应问题有所改善,并对IMF进行优化重构,经分析最终的滤波信号具有较高的信噪比,通过对真实桥梁振动信号分析再一次验证了本文方法的优势,该方法的滤波结果可以作为实现桥梁健康监测技术的可靠依据。
中图分类号:
- U448.27
| 1 | Huang N E , Shen Z , Long S R , et al . The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceeding of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995. |
| 2 | Gai G H . The processing of rotor startup signals based on empirical mode decomposition[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2006, 20(1): 222-235. |
| 3 | Huang N E , Shen Z , Long S R . A new view of non-linear water waves: the hilbert spectrum[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1999, 31(1): 417-457. |
| 4 | Wu Z H , Huang N E , Chen X Y . The multi-dimensional ensemble empirical mode decomposition method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(3): 339-472. |
| 5 | Wu Z H , Huang N E . Ensemble empirical mode decomposition:a noise assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41. |
| 6 | Yeh J R , Shieh J S , Huang N E . Complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition: a novel noise enhanced data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2010, 2(2): 135-156. |
| 7 | Huang N E , Wu M , Long S R , et al . A confidence limit for the empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A, 2003, 459: 2317-2345. |
| 8 | 刘薇娜, 周小龙, 姜振海, 等 . 基于最优特征的改进经验模态分解方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(6): 1957-1963. |
| Liu Wei-na , Zhou Xiao-long , Jiang Zhen-hai , et al . Improved empirical mode decomposition method based on optimal features[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(6): 1957-1963. | |
| 9 | 吴琛, 项洪, 杜喜朋 . 基于数据/极值联合对称延拓的端点效应处理及其应用[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(22): 178-184. |
| Wu Chen , Xiang Hong , Du Xi-peng . A process method for end effects of HHT based on data/extrema symmetrical extension and its application[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(22): 178-184. | |
| 10 | 刘慧婷, 张旻, 程家兴 . 基于多项式拟合算法的EMD端点问题的处理[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2004, 40(16): 84-86, 100. |
| Liu Hui-ting , Zhang Min , Cheng Jia-xing . Dealing with the end issue of EMD based on polynomial fitting algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2004, 40(16): 84-86, 100. | |
| 11 | 徐健, 周志祥, 赵丽娜 . 基于AEEMD和改进DATA-SSI算法桥梁结构模态参数自动化识别[J]. 土木工程学报, 2017, 50(7): 87-98. |
| Xu Jian , Zhou Zhi-xiang , Zhao Li-na . Automatic identification of modal parameter for bridges based on AEEMD and improved DATA-SSI[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2017, 50(7): 87-98. | |
| 12 | 陈永高, 钟振宇 . 基于CEEMD分解和DATA-SSI算法的斜拉桥模态参数识别[J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(8): 166-172, 200. |
| Chen Yong-gao , Zhong Zhen-yu . Modal parameter identification of a cable-stayed bridge based on CEEMD and DATA-SSI algorithm[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(8): 166-172, 200. | |
| 13 | 单德山, 李乔, 黄珍 . 桥梁动力测试信号的自适应分解与重构[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(3): 1-6, 13. |
| Shan De-shan , Li Qiao , Huang Zhen . Adaptive decomposition and reconstruction for bridge dynamic testing signals[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(3): 1-6, 13. | |
| 14 | 郑近德, 程军圣, 杨宇 . 改进的EEMD算法及其应用研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(21): 21-26, 46. |
| Zheng Jin-de , Cheng Jun-sheng , Yang Yu . Modified EEMD algorithm and its applications[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(21): 21-26, 46. | |
| 15 | 胡显能, 蔡改贫, 罗小燕, 等 . 基于CEEMDAN和多尺度排列熵的球磨机负荷识别方法[J]. 噪声与振动控制, 2018, 38(3): 146-151. |
| Hu Xian-neng , Cai Gai-pin , Luo Xiao-yan , et al . Load identification method for ball mills based on CEEMDAN and multi-scale permutation entropy[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2018, 38(3): 146-151. | |
| 16 | Bandt C , Pompe B . Permutation entropy: a natural complexity measure for time series[J]. Physical Review Letters, The American Physiological Society, 2002, 88(17): 174102. |
| 17 | 姚文坡, 刘铁兵, 戴加飞, 等 . 脑电信号的多尺度排列熵分析[J]. 物理学报, 2014, 63(7): 078704. |
| Yao Wen-po , Liu Tie-bing , Dai Jia-fei , et al . Multiscale permutation entropy analysis of electro encephalogram[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(7): 078704. |
| [1] | 张淼,钱永久,张方,朱守芹. 基于增大截面法的混凝土加固石拱桥空间受力性能试验分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 210-215. |
| [2] | 贾毅,赵人达,王永宝,李福海. 多跨长联连续梁桥粘滞阻尼器参数敏感性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1871-1883. |
| [3] | 钟春玲,梁东,张云龙,王静. 体外预应力加固简支梁自振频率计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1884-1890. |
| [4] | 刘恩泽,吴文福. 基于综合指标品质评价算法的单色水果生长状态检测互联网架构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 2019-2026. |
| [5] | 白伦华,沈锐利,张兴标,王路. 自锚式悬索桥的面内稳定性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1500-1508. |
| [6] | 王德军,吕志超,王启明,张建瑞,丁建楠. 基于EKF及调制傅式级数的缸压辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1174-1185. |
| [7] | 万世成,黄侨,关健,郭赵元. 预应力碳纤维板加固钢⁃混凝土组合连续梁负弯矩区试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1114-1123. |
| [8] | 赵金钢,张明,占玉林,谢明志. 基于塑性应变能密度的钢筋混凝土墩柱损伤准则[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1124-1133. |
| [9] | 李静,石求军,刘鹏,户亚威. 基于纵向车速估算的商用车ABS神经网络滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1017-1025. |
| [10] | 李万恒,申林,王少鹏,赵尚传. 基于多阶段分区域动力测试的桥梁结构损伤评估[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 773-780. |
| [11] | 托乎提努尔,张海龙,王杰,王娜,冶鑫晨,王万琼. 基于图形处理器的高速中值滤波算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 979-985. |
| [12] | 李志慧,钟涛,赵永华,胡永利,李海涛,赵景伟. 面向车辆自主驾驶的行人跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 680-687. |
| [13] | 郭立民,陈鑫,陈涛. 基于AlexNet模型的雷达信号调制类型识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 1000-1008. |
| [14] | 李居朋,张祖成,李墨羽,缪德芳. 基于Kalman滤波的电容屏触控轨迹平滑算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1910-1916. |
| [15] | 惠迎新,毛明杰,刘海峰,张尚荣. 跨断层桥梁结构地震响应影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1725-1734. |
|
||