吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 996-1010.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200166
基于DNST和卷积稀疏表示的红外与可见光图像融合
- 1.长春理工大学 电子信息工程学院,长春 130022
2.吉林铁道职业技术学院 高铁综合技术学院,吉林省 吉林市 132200
Infrared and visible image fusion based on discrete nonseparable shearlet transform and convolutional sparse representation
Guang-qiu CHEN1( ),Yu-cun CHEN1,Jia-yue LI1,2,Guang-wen LIU1
),Yu-cun CHEN1,Jia-yue LI1,2,Guang-wen LIU1
- 1.School of Electronic and Information Engineering,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.High Speed Railway Comprehensive Technical College,Jilin Railway Technology College,Jilin 132200,China
摘要:
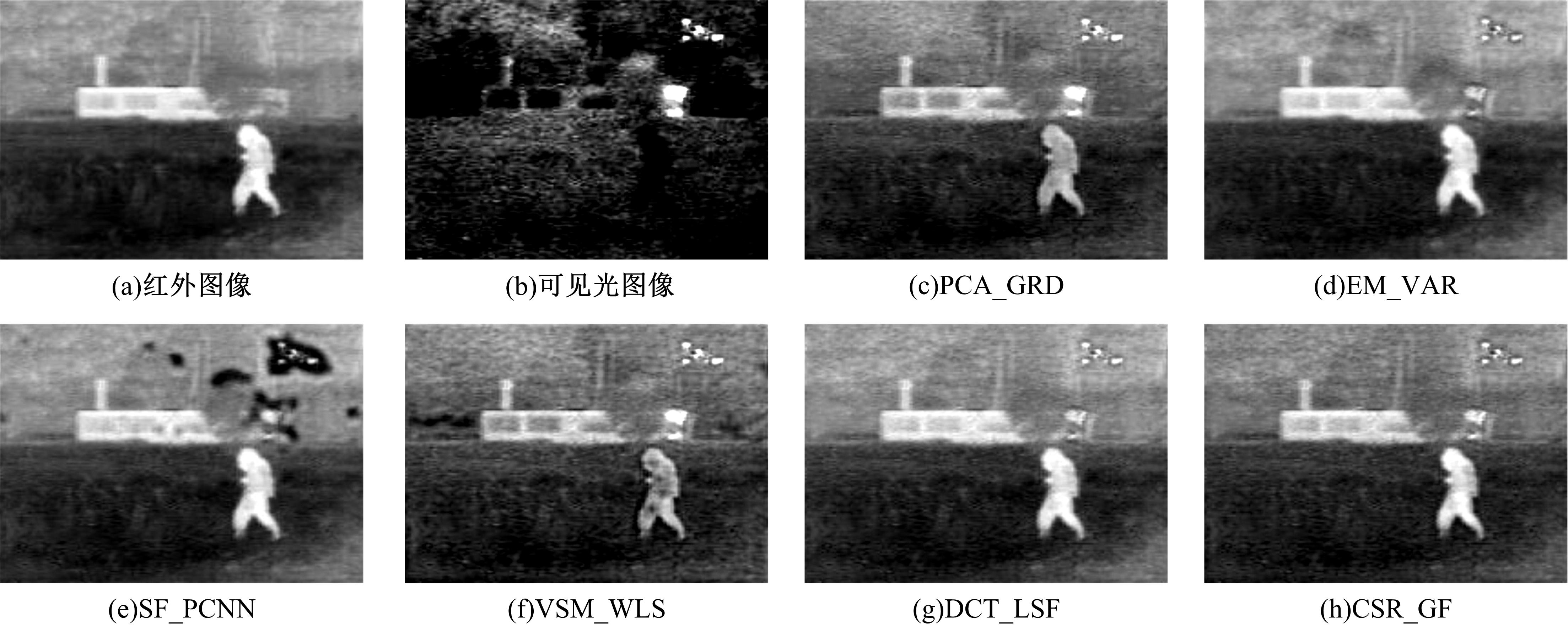
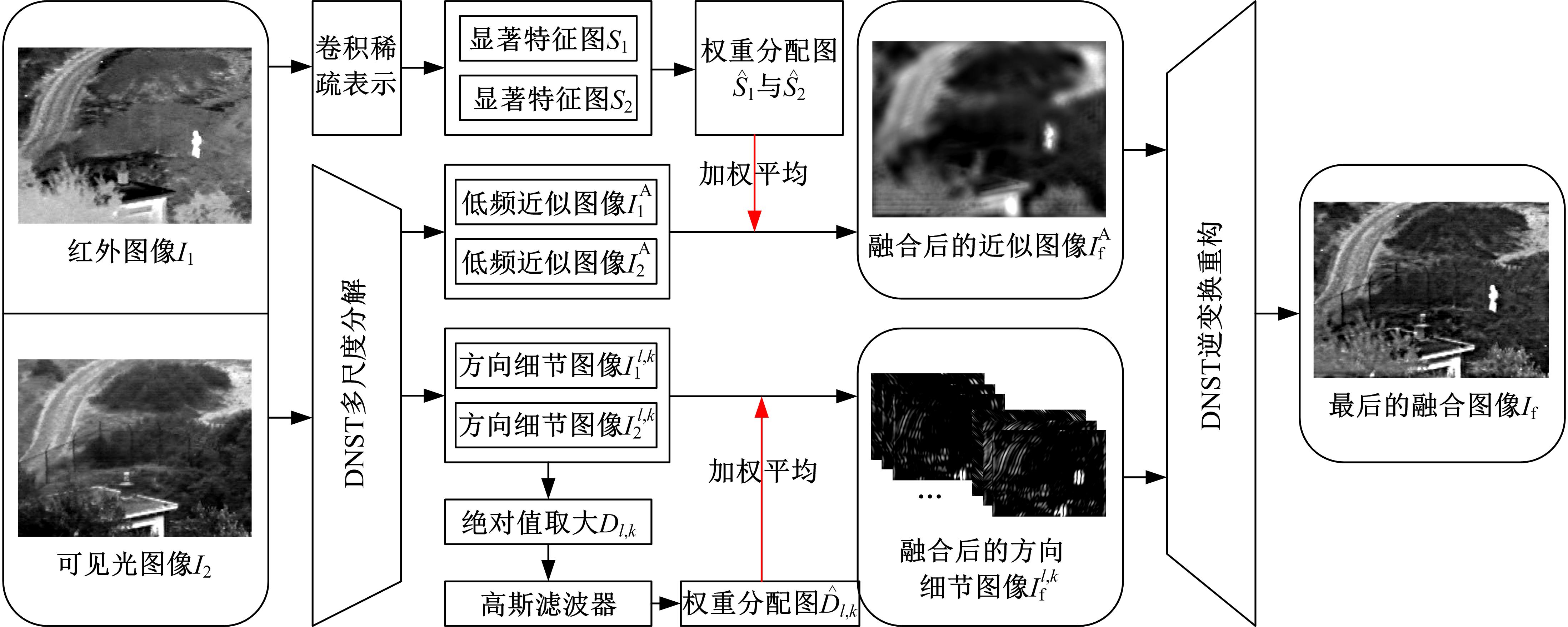
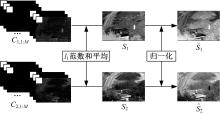
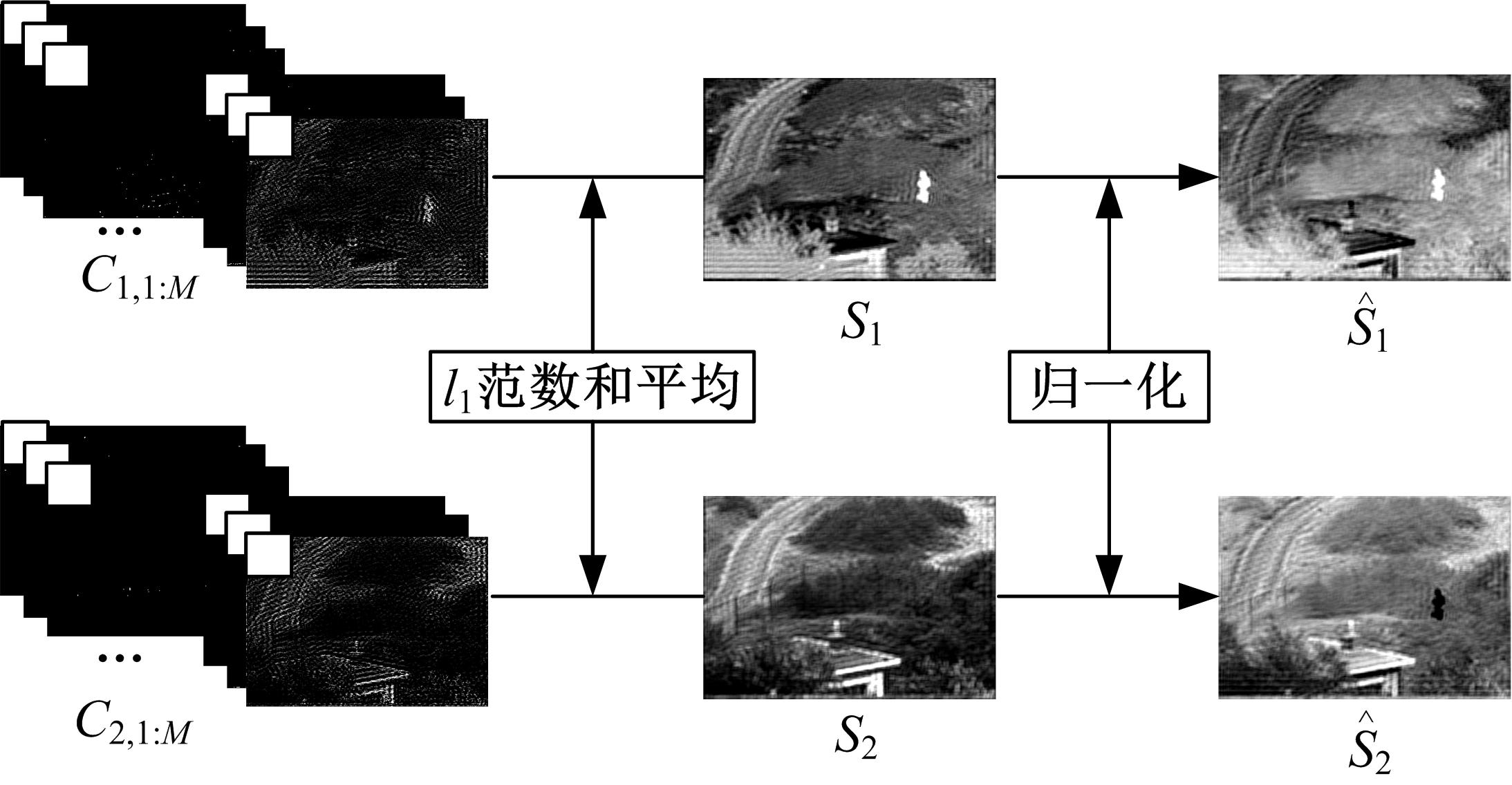
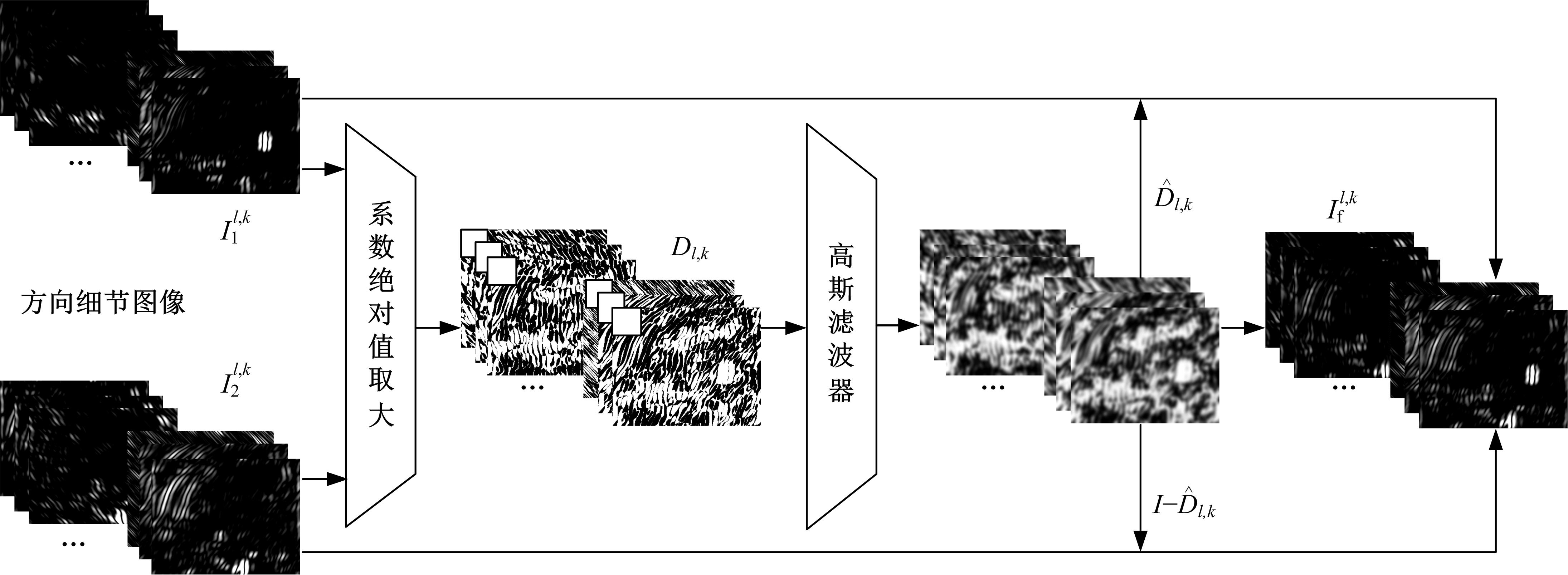
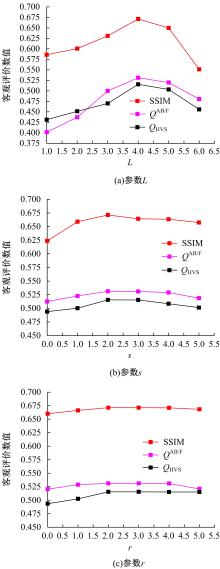
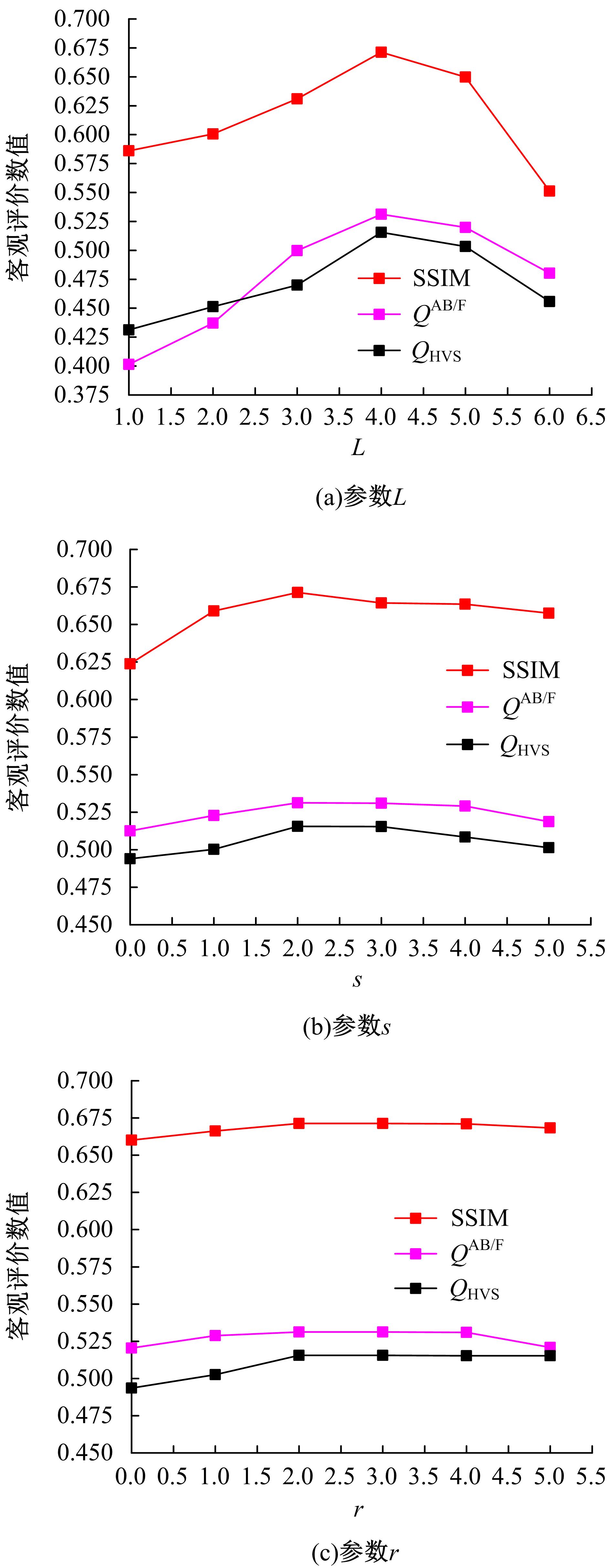
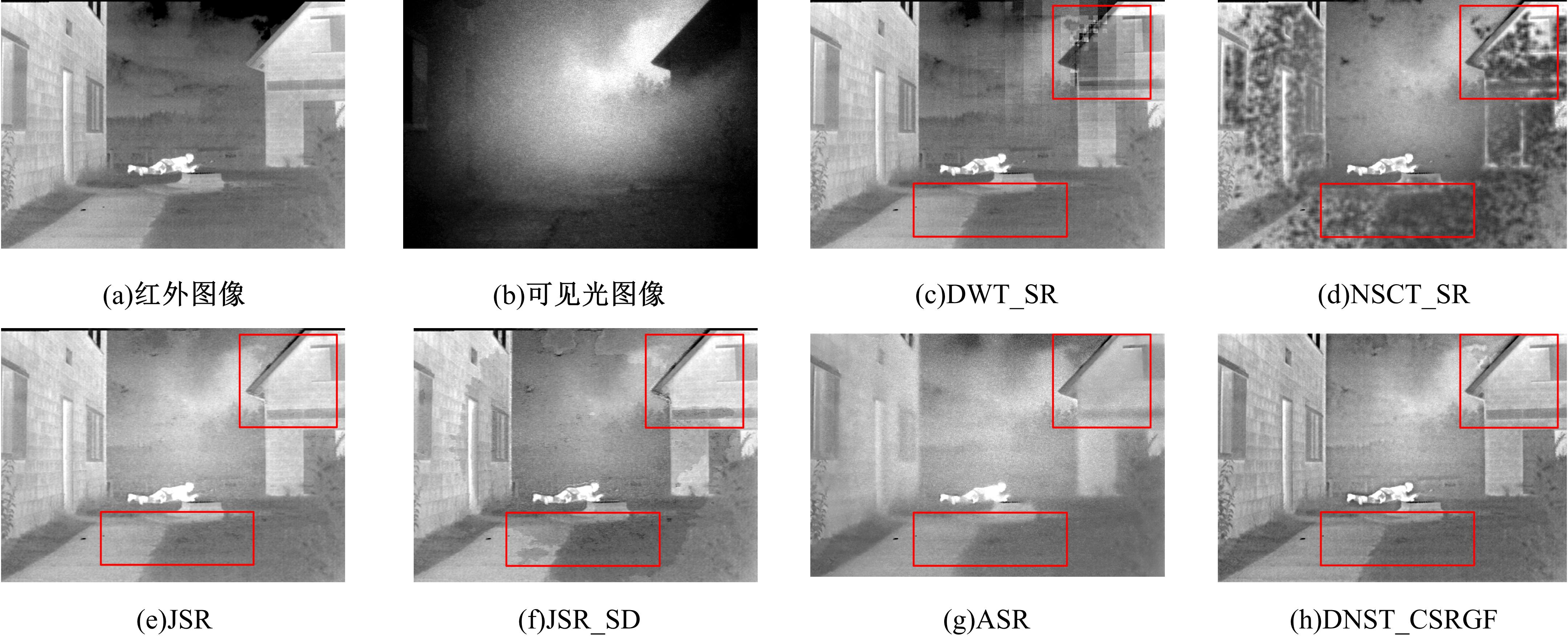
为了克服传统红外与可见光图像融合方法的不足,本文提出了一种基于离散不可分离剪切波与卷积稀疏表示的融合方法。首先,利用离散不可分离剪切波将源图像分解为近似图像和方向细节图像,相比较于其他多尺度分解工具,离散不可分离剪切波能够在不同尺度内更好地分离出图像中重叠的重要特征信息。其次,利用源图像的显著特征图加权平均融合近似图像,保持融合图像的亮度和能量不丢失。卷积稀疏表示能够深度提取图像的显著特征,利用多维系数的l1范数作为活性测度构造显著特征图,生成近似图像的权重分配决策图。方向细节图像的融合规则采用“系数绝对值取大-高斯滤波”规则,通过“系数绝对值取大”规则获得初始权重分配决策图,利用高斯滤波器对决策图进行滤波处理,降低噪声的敏感度,同时增加可见光图像信息比例。最后,通过离散不可分离剪切波逆变换对融合后的系数进行重构,得到最后的融合图像。实验结果表明,相比较于已有文献的其他典型融合方法,本文融合方法在主观视觉和客观评价准则方面都取得了较好的融合性能。
中图分类号:
- TP391.41
| 1 | Lee M W, Kwak K C. Performance comparison of infrared and visible image fusion approaches[C]∥International Conference on Control, Artificial Intelligence, Robotics & Optimization (ICCAIRO), Prague, Czech Republic,2017:274-277. |
| 2 | Ma J, Ma Y, Li C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: a survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2019,45:153-178. |
| 3 | 刘斌,辛迦楠, 谌文江,等. 不可分拉普拉斯金字塔构造及其在多光谱图像融合中的应用[J]. 计算机应用, 2019,39(2):564-570. |
| Liu Bin, Xin Jia-nan, Chen Wen-jiang, et al. Construction of non-separable Laplacian pyramid and its application in multi-spectral image fusion[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(2):564-570. | |
| 4 | 李雄飞,宋璐,张小利. 基于协同经验小波变换的遥感图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2019,49(4):1307-1319. |
| Li Xiong-fei, Song Lu, Zhang Xiao-li. Remote sensing image fusion based on cooperative empirical wavelet transform [J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition),2019,49(4):1307-1319. | |
| 5 | 郭全民,王言,李翰山. 改进IHS-Curvelet变换融合可见光与红外图像抗晕光方法[J]. 红外与激光工程,2018,47(11):1126002. |
| Guo Quan-min, Wang Yan, Li Han-shan. Anti-halation method of visible and infrared image fusion based on Improved IHS-Curvelet transform[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018,47(11):1126002. | |
| 6 | 刘哲,徐涛,宋余庆,等. 基于NSCT变换和相似信息鲁棒主成分分析模型的图像融合技术[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018,48(5):1614-1620. |
| Liu Zhe, Xu Tao, Song Yu-qing, et al. Image fusion technology based on NSCT and robust principal component analysis model with similar information[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018,48(5):1614-1620. | |
| 7 | Sun Z, Hu H. Off-line fusion of intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography images[J]. Journal of Medical Imaging and Health Informatics,2017,7(7):1531-1538. |
| 8 | Li S, Kang X, Fang L, et al. Pixel-level image fusion: a survey of the state of the art[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 33:100-112. |
| 9 | Kutyniok G, Lim W Q, Reisenhofer R. ShearLab 3D: faithful digital shearlet transforms based on compactly supported shearlets[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2016,42(1):No.5. |
| 10 | 邱泽敏. 结合区域与边缘特征的红外与可见光图像融合算法[J]. 红外技术, 2018,40(5):53-58. |
| Qiu Ze-min. Infrared and visible image fusion algorithm combined with regional characteristics and edge characteristics[J]. Infrared Technology, 2018, 40(5):53-58. | |
| 11 | Jin X, Jiang Q, Yao S, et al. A survey of infrared and visual image fusion methods[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 85:478-501. |
| 12 | Liu Y, Chen X, Wang Z, et al. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 42:158-173. |
| 13 | Zhang Qiang,Liu Yi, Blum R S, et al. Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: a review[J]. Information Fusion,2018,40:50-75. |
| 14 | Liu Y, Chen X, Ward R, et al. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12):1882-1886. |
| 15 | Wohlberg B. Efficient algorithms for convolutional sparse representations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(1):301-315. |
| 16 | Xydeas C, Petrovic V. Objective image fusion performance measure[J]. Electronics Letters, 2000,36(4):308-309. |
| 17 | Ma K, Zeng K, Wang Z. Perceptual quality assessment for multi-exposure image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11):3345-3356. |
| 18 | Aslantas V, Bendes E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: The sum of the correlations of differences[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2015, 69(12):1890-1896. |
| 19 | Chen Y, Blum R S. A new automated quality assessment algorithm for image fusion[J]. Image and Vision Computing,2009,27(10):1421-1432. |
| 20 | Haghighat M, Razian M A. Fast-FMI: non-reference image fusion metric[C]∥2014 IEEE 8th International Conference on Application of Information and Communication Technologies (AICT), Astana, Kazakhstan,2014:1-3. |
| 21 | Zhao W, Lu H. Medical image fusion and denoising with alternating sequential filter and adaptive fractional order total variation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(9):2283-2294. |
| 22 | Zhao J, Feng H, Xu Z, et al. Detail enhanced multi-source fusion using visual weight map extraction based on multi scale edge preserving decomposition[J]. Optics Communications, 2013, 287:45-52. |
| 23 | Zhu Jin, Jin Wei-qi, Li Li, et al. Fusion of the low-light-level visible and infrared images for night-vision context enhancement[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(1):013501. |
| 24 | Du J, Li W, Xiao B. Anatomical-functional image fusion by information of interest in local laplacian filtering domain[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(12):5855-5866. |
| 25 | Hu J, Li S. The multiscale directional bilateral filter and its application to multisensor image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2012,13(3):196-206. |
| 26 | da Cunha A L, Zhou J, Do M N. The nonsubsampled contourlet transform: theory, design, and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(10):3089-3101. |
| 27 | Li S, Yang B, Hu J. Performance comparison of different multi-resolution transforms for image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2011, 12(2):74-84. |
| 28 | Li H, Liu L, Huang W, et al. An improved fusion algorithm for infrared and visible images based on multi-scale transform[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016,74:28-37. |
| 29 | 杨风暴, 赵艳霞, 吉琳娜,等. 基于局部能量匹配的红外偏振图像融合[J]. 红外技术, 2016(4):319-324. |
| Yang Feng-bao, Zhao Yan-xia, Ji Lin-na, et al. An infrared polarization image fusion method based on local energy matching[J]. Infrared Technology, 2016(4): 319-324. | |
| 30 | Qu Xiao-bo, Yan Jing-wen, Xiao Hong-zhi,et al. Image fusion algorithm based on spatial frequency-motivated pulse coupled neural networks in nonsubsampled contourlet transform domain[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2008, 34(12):1508-1514. |
| 31 | Ma J, Zhou Z, Wang B, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 82:8-17. |
| 32 | Jin Xin, Jiang Qian, Yao Shao-wen, et al. Infrared and visual image fusion method based on discrete cosine transform and local spatial frequency in discrete stationary wavelet transform domain[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2018,88:1-12. |
| 33 | Liu Y, Liu S, Wang Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation [J]. Information Fusion, 2015, 24:147-164. |
| 34 | Liu C H, Qi Y, Ding W R. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on saliency detection in sparse domain[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017,83:94-102. |
| 35 | Liu Y, Wang Z. Simultaneous image fusion and denoising with adaptive sparse representation[J]. IET Image Processing, 2015, 9(5):347-357. |
| 36 | Zhan Kun, Xie Yuan-ge, Wang Hai-bo, et al. Fast filtering image fusion[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2017,26(6):063004. |
| 37 | Li Wen, Xie Yuan-ge Y.. Zhou Hao-le,et al. Structure-aware image fusion[J]. Optik, 2018, 172:1-11. |
| 38 | Ma J, Chen C, Li C, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 31:100-109. |
| 39 | Zhou Z, Wang B, Li S, et al. Perceptual fusion of infrared and visible images through a hybrid multi-scale decomposition with Gaussian and bilateral filters[J]. Information Fusion, 2016,30:15-26. |
| 40 | Li H, Wu X J, Durrani T S. Infrared and visible image fusion with ResNet and zero-phase component analysis[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2019,102:103039. |
| [1] | 王淑敏,陈伟. 基于连续密度隐马尔可夫模型的矿下异常行为识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1067-1072. |
| [2] | 刘元宁,吴迪,朱晓冬,张齐贤,李双双,郭书君,王超. 基于YOLOv3改进的用户界面组件检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1026-1033. |
| [3] | 朱小龙,谢忠. 基于机器学习的地理空间数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1011-1016. |
| [4] | 孙宝凤,任欣欣,郑再思,李国一. 考虑工人负荷的多目标流水车间优化调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 900-909. |
| [5] | 欧阳丹彤,刘扬,刘杰. 故障响应指导下基于测试集的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1017-1025. |
| [6] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [7] | 沈淑涛,尼玛扎西. 基于区块链技术的双混沌可识篡改图像加密方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1055-1059. |
| [8] | 周炳海,何朝旭. 基于静态半成套策略的多目标准时化物料配送调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 910-916. |
| [9] | 顾天奇,胡晨捷,涂毅,林述温. 基于移动最小二乘法的稳健重构方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 685-691. |
| [10] | 许骞艺,秦贵和,孙铭会,孟诚训. 基于改进的ResNeSt驾驶员头部状态分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 704-711. |
| [11] | 魏晓辉,周长宝,沈笑先,刘圆圆,童群超. 机器学习加速CALYPSO结构预测的可行性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 667-676. |
| [12] | 周炳海,吴琼. 基于多目标的机器人装配线平衡算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [13] | 方明,陈文强. 结合残差网络及目标掩膜的人脸微表情识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 303-313. |
| [14] | 宋元,周丹媛,石文昌. 增强OpenStack Swift云存储系统安全功能的方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 314-322. |
| [15] | 王小玉,胡鑫豪,韩昌林. 基于生成对抗网络的人脸铅笔画算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 285-292. |
|
||