吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 900-909.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200063
考虑工人负荷的多目标流水车间优化调度
- 1.吉林大学 交通学院,长春 130022
2.一汽-大众汽车有限公司 生产部,长春 130011
Multi⁃objective flow shop optimal scheduling considering worker's load
Bao-feng SUN1( ),Xin-xin REN1,Zai-si ZHENG1,2,Guo-yi Li1
),Xin-xin REN1,Zai-si ZHENG1,2,Guo-yi Li1
- 1.College of Transportation,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.Department of Product,FAW-Volkswagen Auntomobile Co. ,Ltd. ,Changchun 130011,China
摘要:
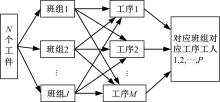
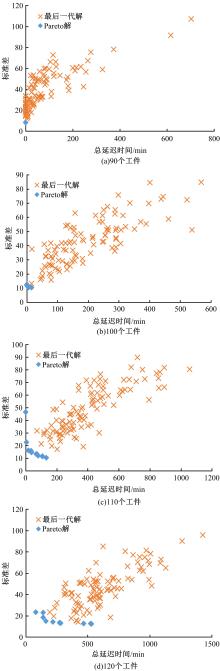
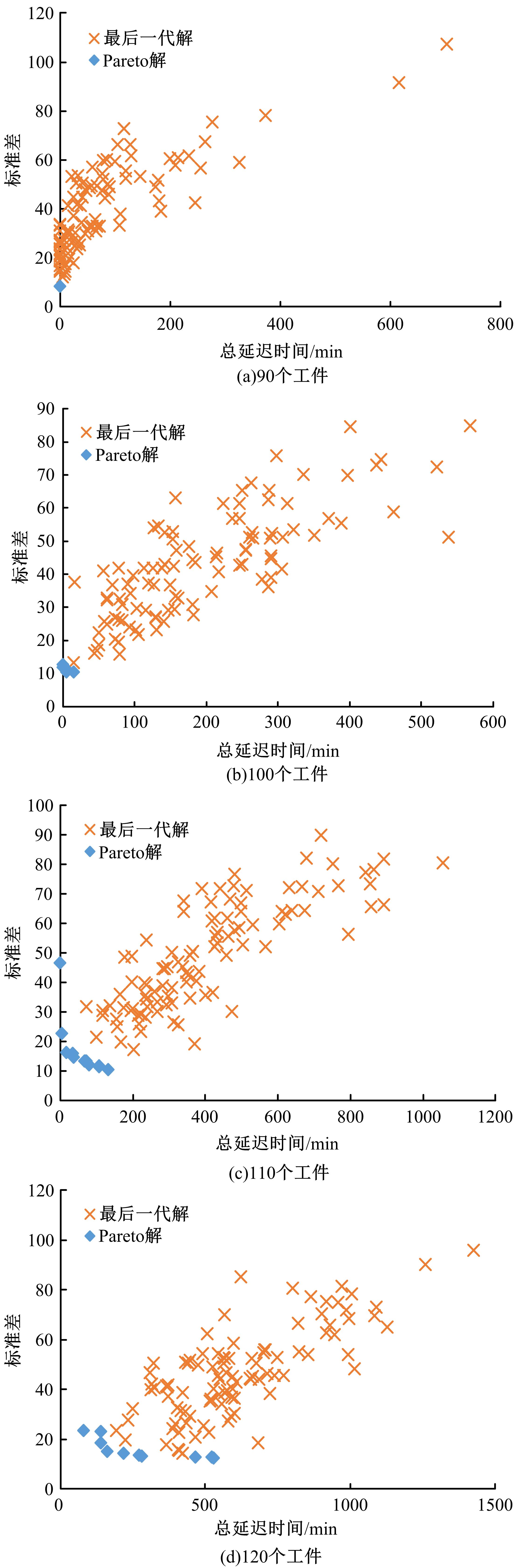
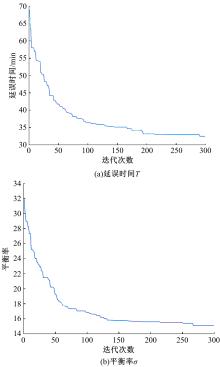
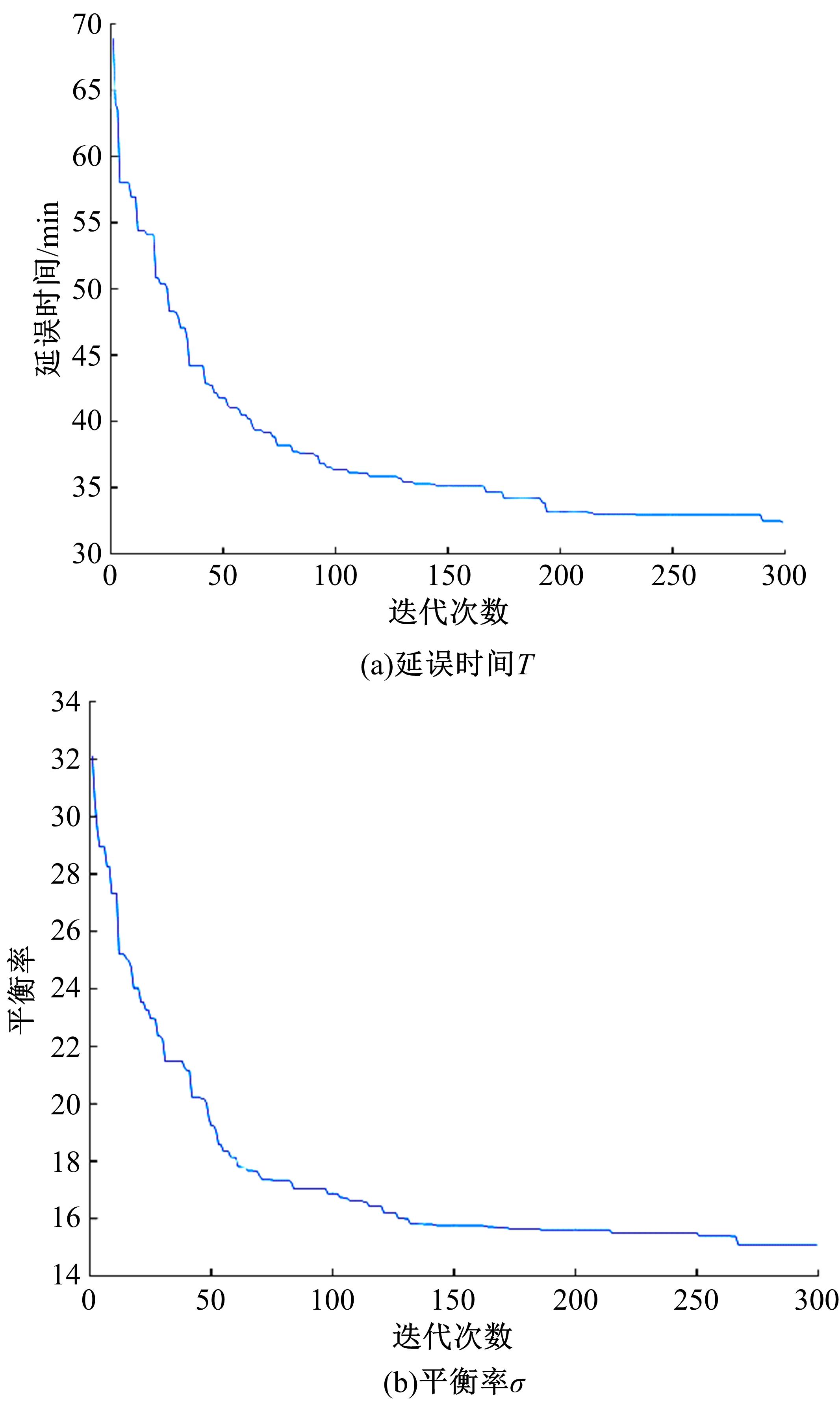
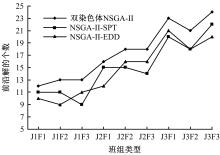
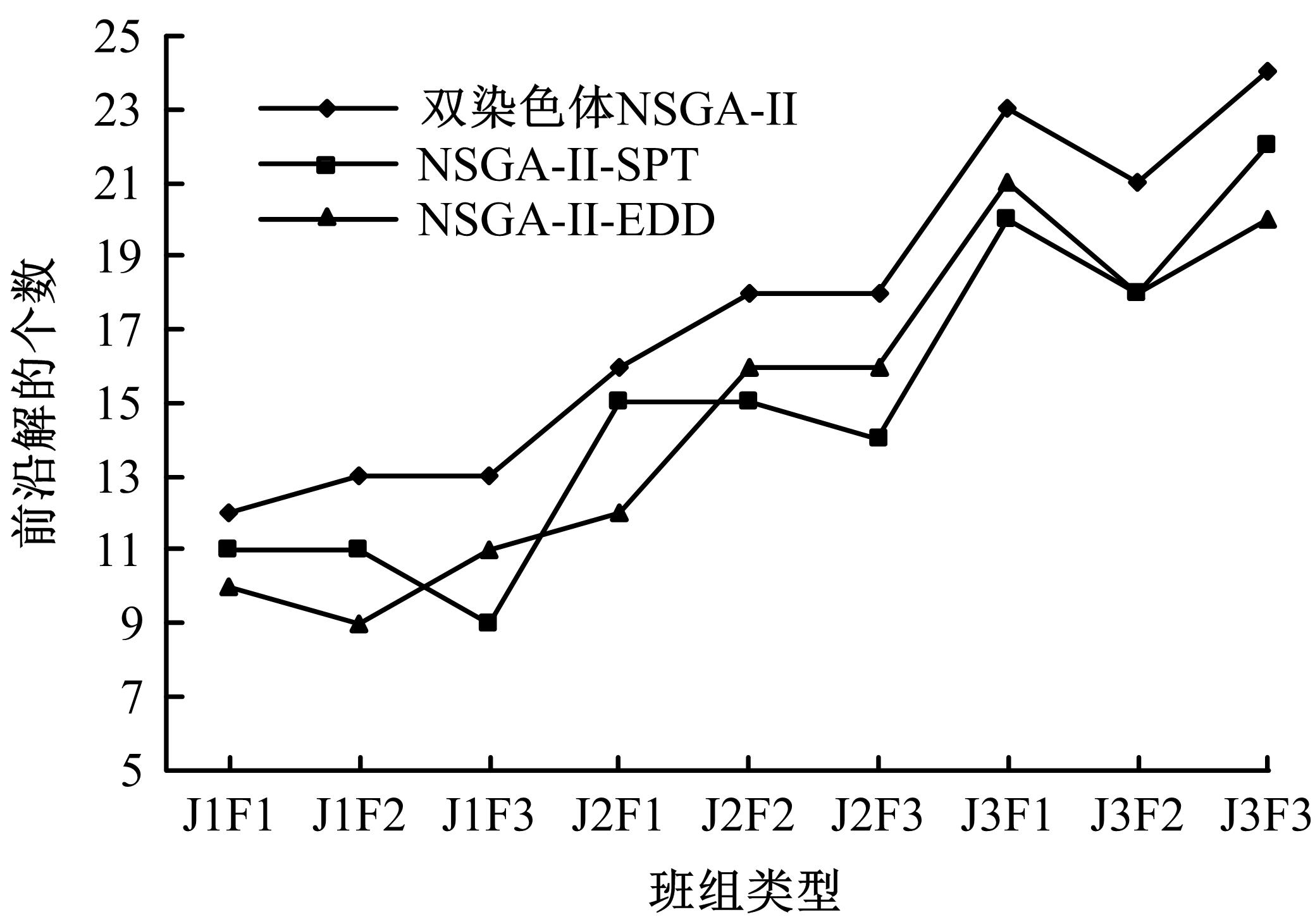
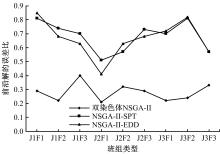
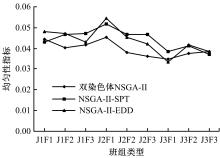
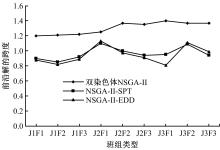
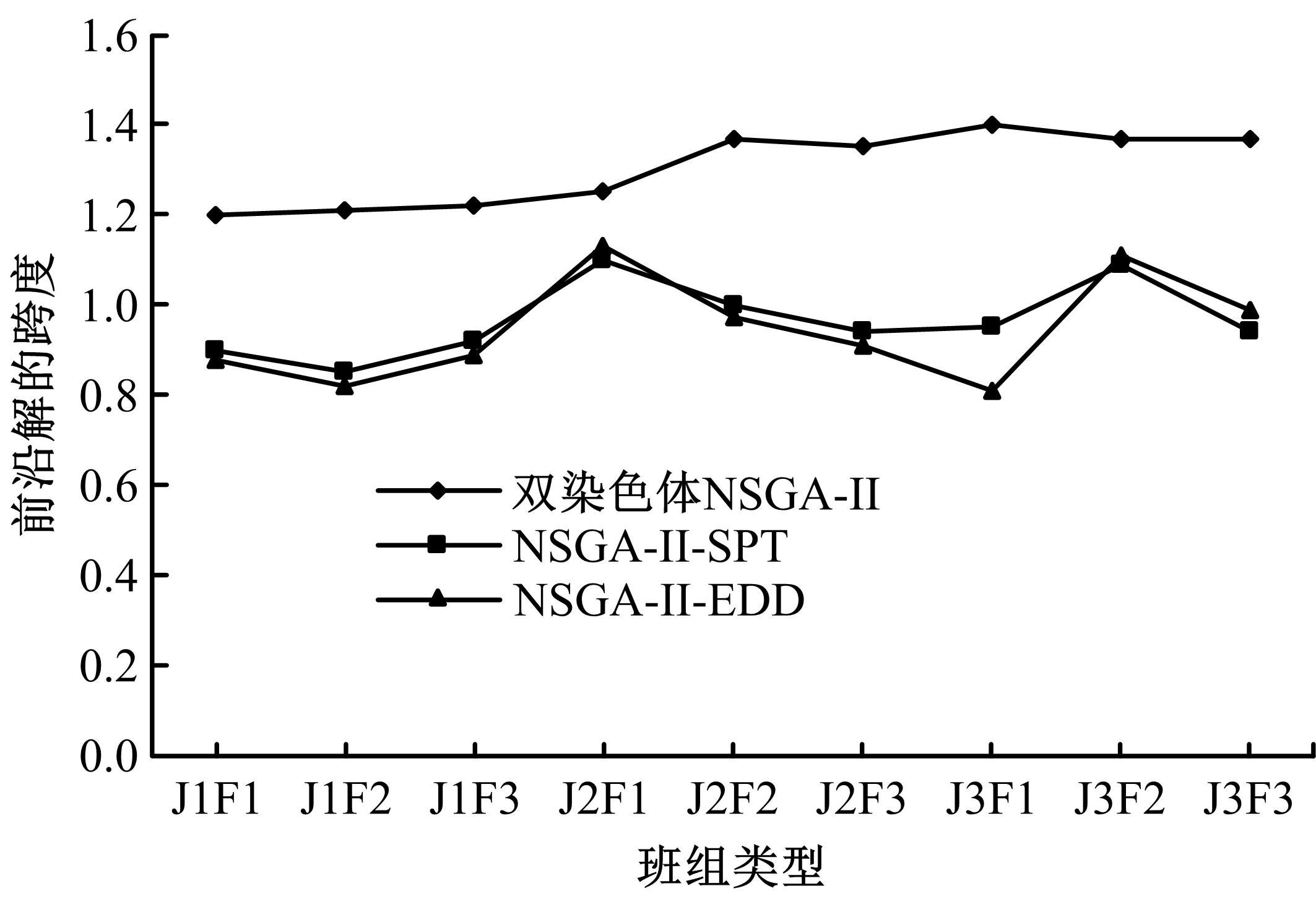
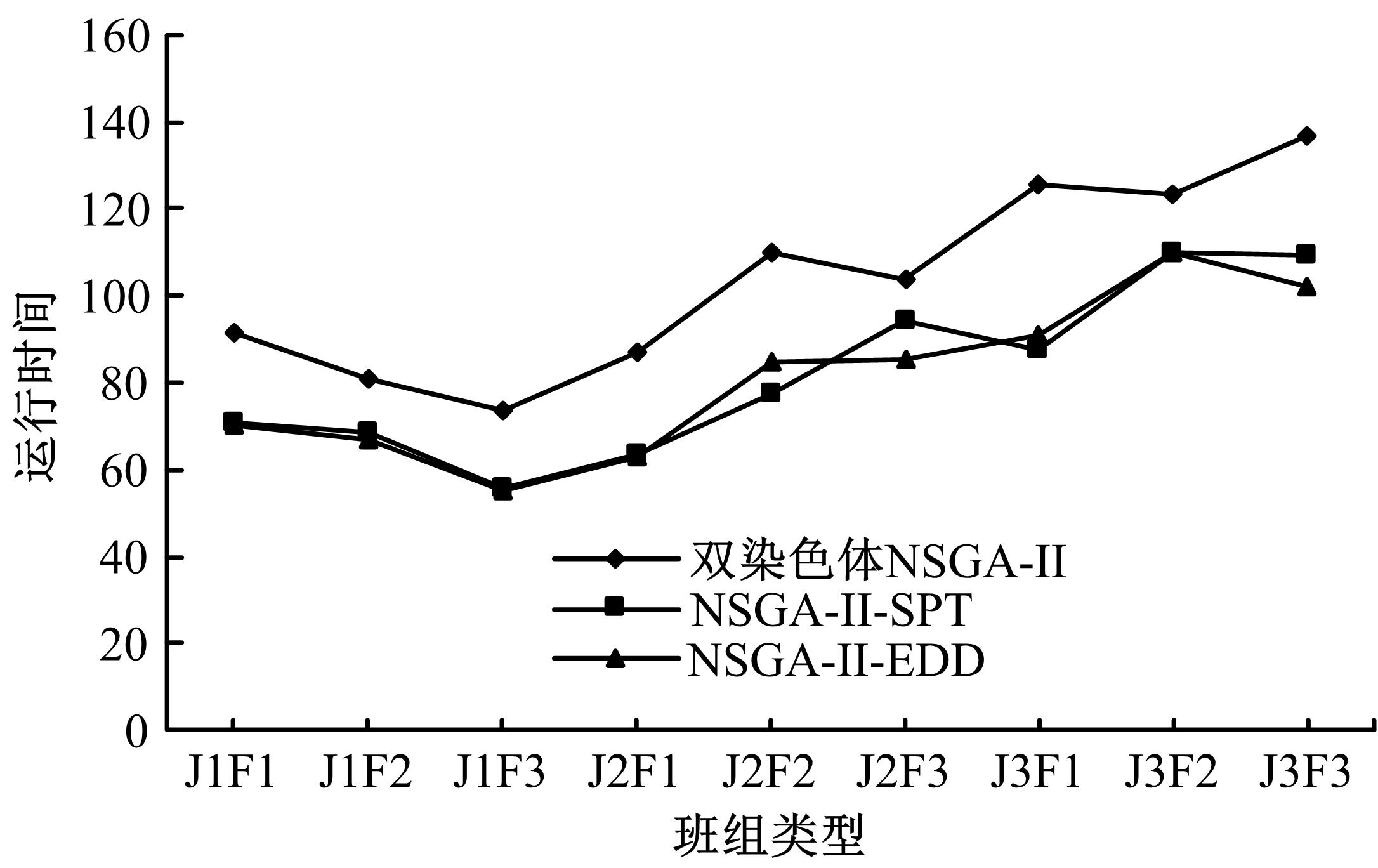
针对流水车间工人负荷不平衡的现象,构建了工件总延误时间和工人作业分配标准差最小化的双目标优化调度模型。设计了基于两段式染色体编码的NSGA-II算法,获得了模型的Pareto最优解集。引入两种嵌入启发式规则:交货期最接近(EDD)规则和加工时间最短(SPT)规则,形成了NSGA-II-EDD和NSGA-II-SPT两种对比情境。算例分析表明:NSGA-II算法的Pareto解的平均个数N、Pareto前沿解误差比ER、Pareto前沿解空间评价指标S、Pareto前沿跨度K比NSGA-II-EDD和NSGA-II-SPT的性能好,在算法运算时间T上性能较差。
中图分类号:
- TP29
| 1 | Pinedo M L. Scheduling: Theory, Algorithm, and Systems[M]. 5th ed. New York: Springer, 2015. |
| 2 | Pan Quan-ke, Wang Ling, Li Jun-qing, et al. A novel discrete artificial bee colony algorithm for the hybrid flowshop scheduling problem with makespan minimization[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2014, 45:42-56. |
| 3 | 周炳海,彭涛. 混流装配线准时化物料配送调度优化[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2017,47(4): 1253-1261. |
| Zhou Bing-hai, Peng Tao. Optimal schedule of just-in-time part distribution for mixed-model assembly lines[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017,47(4): 1253-1261. | |
| 4 | 陈海鹏,邱际伦,邱峰,等. 基于Pi演算的前沿调度算法并行性建模及实现[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版,2019,49(1):242-247. |
| Chen Hai-peng, Qiu Ji-lun, Qiu Feng, et al. Modeling and implementation of frontier scheduling parallelism algorithm based on Pi calculus[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019,49(1):242-247. | |
| 5 | 陆志强,张思源,崔维伟. 集成预防性维护和流水线调度的鲁棒性优化研究[J]. 自动化学报,2015,41(5):906-913. |
| Lu Zhi-qiang, Zhang Si-yuan, Cui Wei-wei. Integrating production scheduling and maintenance policy for robustness in flow shop problems[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015,41(5):906-913. | |
| 6 | Rock H. The three-machine no-wait flow shop is NP-complete[J]. Journal of the Acm, 1984, 31(2): 336-345. |
| 7 | Li P H, Fan Z J, Zhou J. Optimizing and simulating production line balance based on human factors[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2012(214): 495-499. |
| 8 | 吴瑕. 基于人因的混流装配系统复杂性优化研究[D]. 天津:天津大学管理学院,2012. |
| Wu Xia. Optimization of assembly complexity in mixed-model assembly systems based on human factors[D]. Tianjin: School of Management, Tianjin University, 2012. | |
| 9 | Battini D, Delorme X, Dolgui A, et al. Ergonomics in assembly line balancing based on energy expenditure: a multi-objective model[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2015, 54(3):824-845. |
| 10 | Sun X Y, Zhao L, Zhang P F, et al. Enhanced NSGA-II with evolving directions prediction for interval multi-objective optimization[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2019,49:124-133. |
| 11 | Sundararghavan P S, Kunnathur A S, Viswanathan I. Minimizing makespan in parallel flowshops[J]. Journal of the Operational Research Society, 1997, 48(8): 834-842. |
| 12 | Marichelvam M K, Prabaharan T. Performance evaluation of an improved hybrid genetic scatter search (IHGSS) algorithm for multistage hybrid flow shop scheduling problems with missing operations[J]. International Journal of Industrial and Systems Engineering, 2014,16(1):120-141. |
| 13 | Rosenberg R S. Stimulation of genetic populations with biochemical properties: I. The model[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 1970,7(3/4):223-257. |
| 14 | Zhou B H, Liu W L. Energy-efficient multi-objective scheduling algorithm for hybrid flow shop with fuzzy processing time[J]. Journal of Systems and Control Engineering, 2019, 233(10):1282-1297. |
| 15 | Azadeh A, Shoja B M, Ghanei S, et al. A multi-objective optimization problem for multi-state series-parallel systems: a two-stage flow-shop manufacturing system[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2015, 136:62-74. |
| 16 | Zelazny D, Pempera J. Solving multi-objective permutation flowshop scheduling problem using CUDA[C]∥2015 20th International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR), Miedzyzdroje, Poland,2015:347-352. |
| 17 | Srinivas N, Deb K. Multi-objetive function optimization using non-dominated sorting genetic algorithms[J]. Evolutionary Computation, 1995,2:221-248. |
| 18 | Wang H F, Fu Y P, Huang M, et al. A NSGA-II based memetic algorithm for multiobjective parallel flowshop scheduling problem[J]. Computer & Industrial Engineering,2017,113:185-194. |
| 19 | Deb K, Amrit P, Sameer A, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation,2002,6(2): 182-197. |
| 20 | 石英,王秀红,祁丽霞,等. 人因工程学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社,2011:103-104. |
| [1] | 王淑敏,陈伟. 基于连续密度隐马尔可夫模型的矿下异常行为识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1067-1072. |
| [2] | 刘元宁,吴迪,朱晓冬,张齐贤,李双双,郭书君,王超. 基于YOLOv3改进的用户界面组件检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1026-1033. |
| [3] | 朱小龙,谢忠. 基于机器学习的地理空间数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1011-1016. |
| [4] | 欧阳丹彤,刘扬,刘杰. 故障响应指导下基于测试集的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1017-1025. |
| [5] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [6] | 沈淑涛,尼玛扎西. 基于区块链技术的双混沌可识篡改图像加密方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1055-1059. |
| [7] | 顾天奇,胡晨捷,涂毅,林述温. 基于移动最小二乘法的稳健重构方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 685-691. |
| [8] | 许骞艺,秦贵和,孙铭会,孟诚训. 基于改进的ResNeSt驾驶员头部状态分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 704-711. |
| [9] | 魏晓辉,周长宝,沈笑先,刘圆圆,童群超. 机器学习加速CALYPSO结构预测的可行性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 667-676. |
| [10] | 黄继承,沈成,纪爱敏,李显旺,张彬,田昆鹏,刘浩鲁. 工业大麻收割机切割⁃输送关键部件作业参数优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 772-780. |
| [11] | 周炳海,吴琼. 基于多目标的机器人装配线平衡算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [12] | 方明,陈文强. 结合残差网络及目标掩膜的人脸微表情识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 303-313. |
| [13] | 宋元,周丹媛,石文昌. 增强OpenStack Swift云存储系统安全功能的方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 314-322. |
| [14] | 王小玉,胡鑫豪,韩昌林. 基于生成对抗网络的人脸铅笔画算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 285-292. |
| [15] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
|
||