吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1708-1715.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200535
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于张量分解理论的车道级交通流数据修复算法
- 1.东南大学 交通学院,南京 211189
2.北京交通大学 综合交通运输大数据应用技术行业重点实验室,北京 100044
Data imputation approach for lane⁃scale traffic flow based on tensor decomposition theory
Wen-qi LU1( ),Tian ZHOU2,Yuan-li GU2,Yi-kang RUI1(
),Tian ZHOU2,Yuan-li GU2,Yi-kang RUI1( ),Bin RAN1
),Bin RAN1
- 1.School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 211189,China
2.Key Laboratory of Transport Industry of Big Data Application Technologies for Comprehensive Transport,Ministry of Transport,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
摘要:
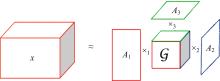
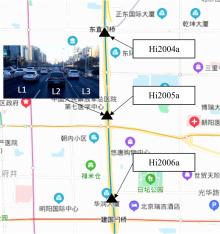
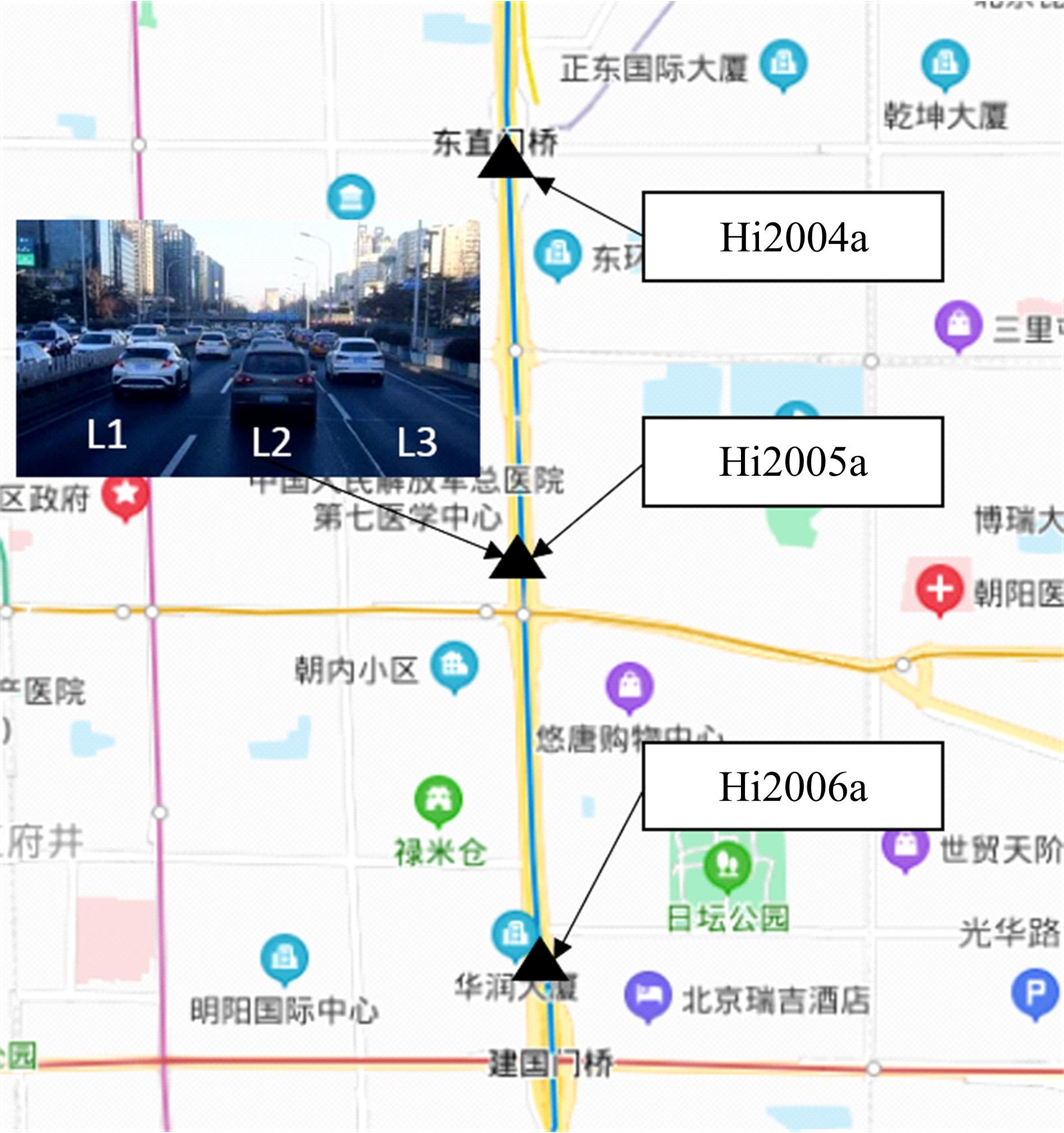
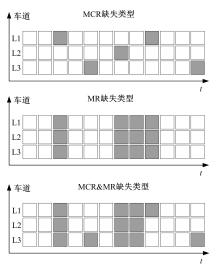
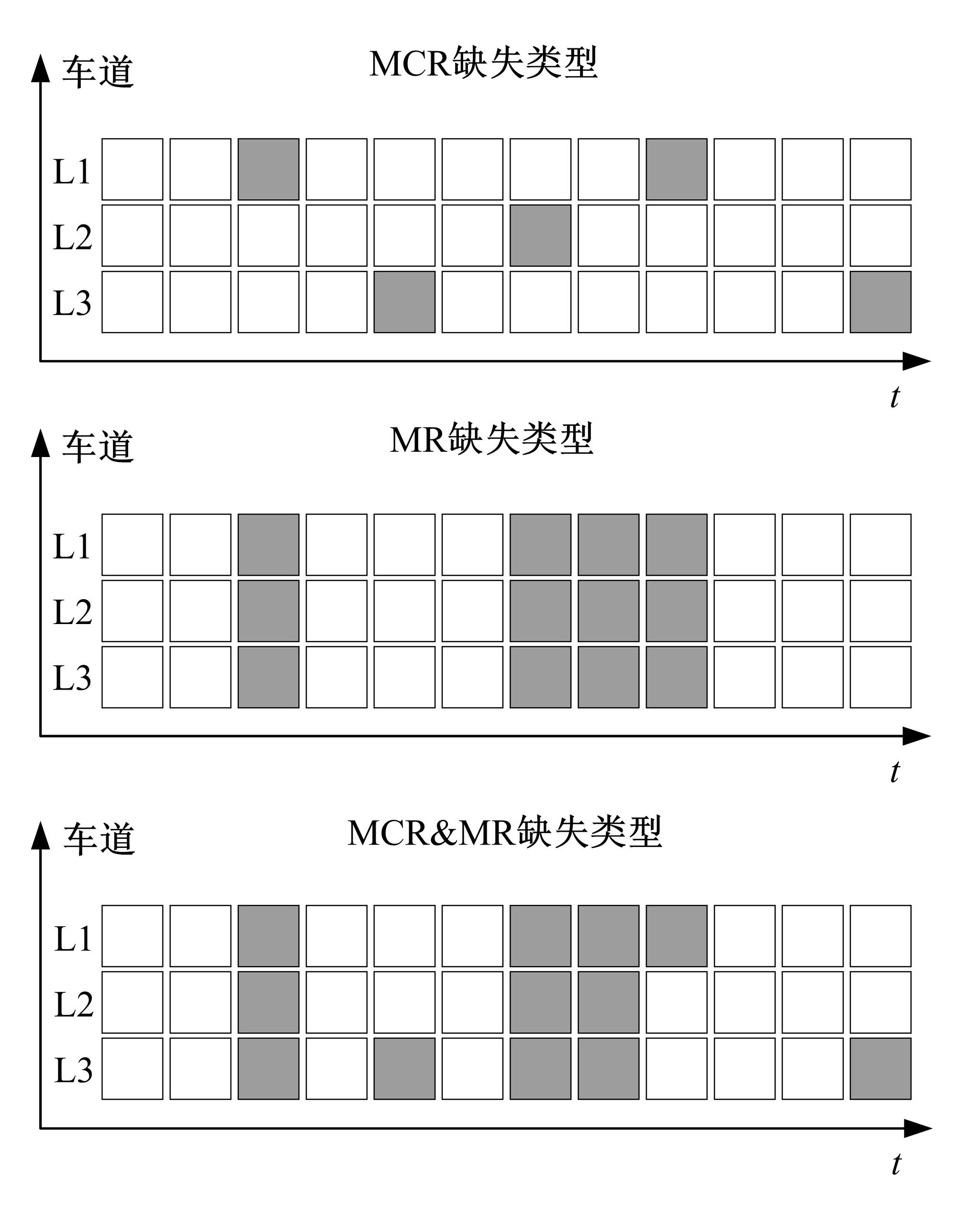
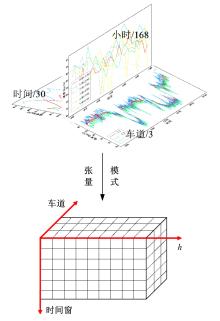
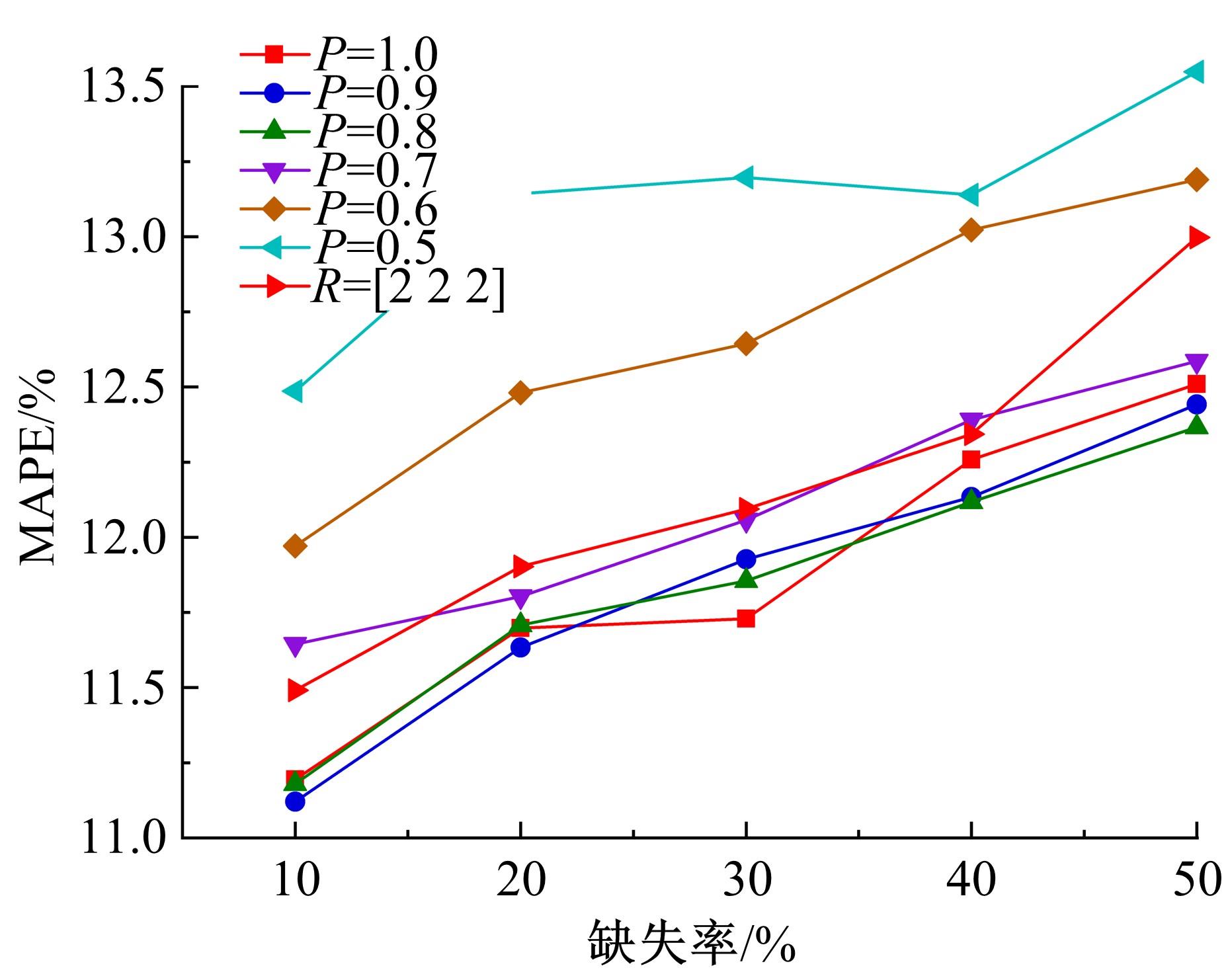
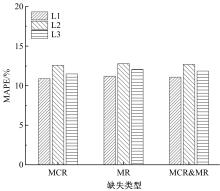
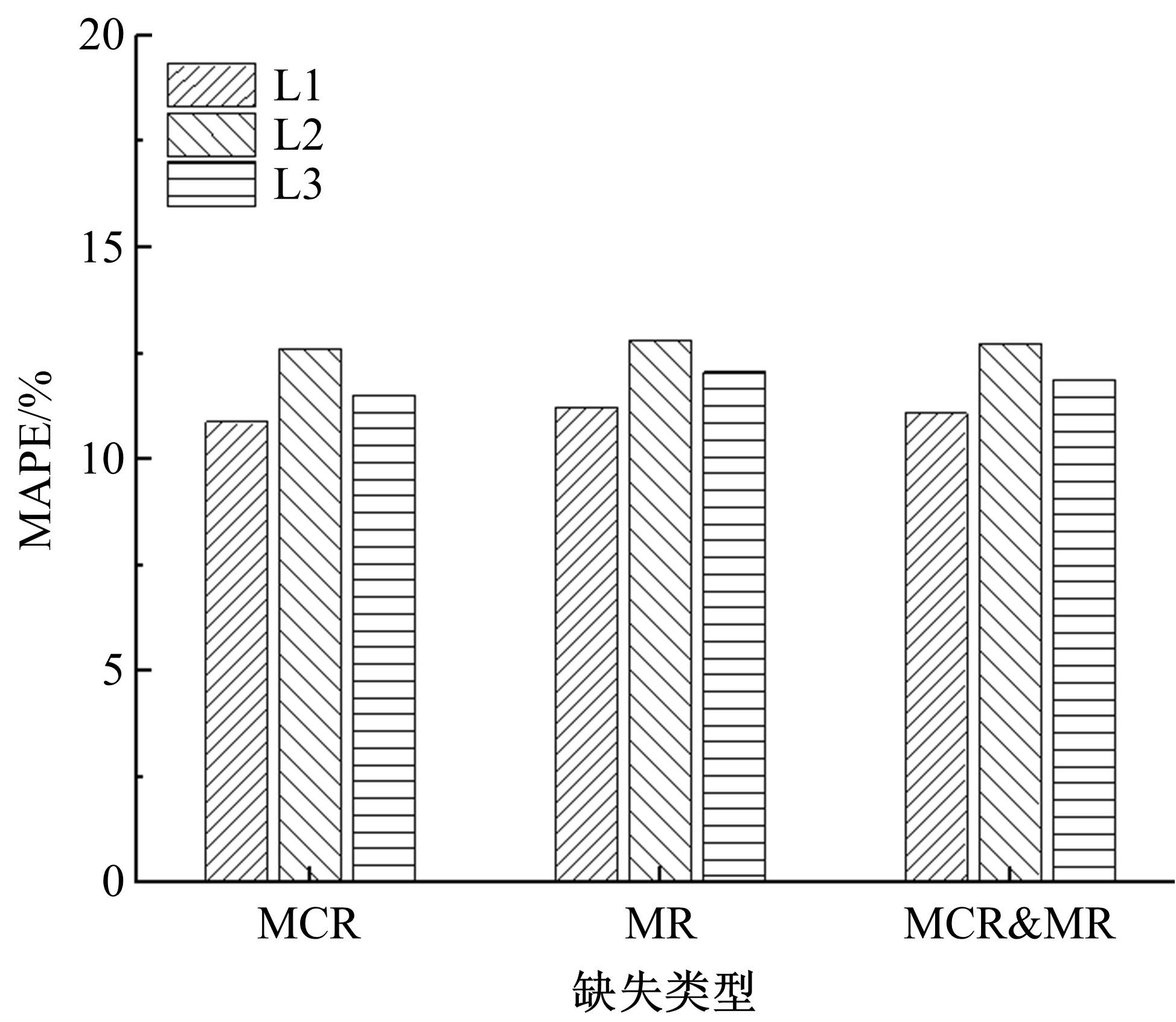
为减少数据缺失对交通流量预测、高级驾驶辅助、交通状态估计等应用的影响,提升交通流数据质量,提出一种基于自适应秩Tucker分解的插补方法(ARTDI)用于多车道交通流数据修复。将多车道交通流数据表征为张量模式,以充分利用交通流时空特性。通过张量Tucker分解构建修复目标函数,并利用动量梯度下降法求解。本文采用北京快速路多断面车道交通流速度数据构建完全随机缺失、随机缺失、混合缺失3种缺失模式进行算法验证,实验结果显示,ARTDI算法在3种缺失类型下对3个断面数据修复的平均绝对百分误差(MAPE)分别为11.67%、12.03%、11.89%。此外,随着数据缺失率的增长,ARTDI模型在不同缺失模式下的修复精度均优于对比模型,并且修复误差无显著增长,体现出ARTDI模型良好的稳定性和适用性。
中图分类号:
- U491
| 1 | Raza A, Zhong M. Hybrid artificial neural network and locally weighted regression models for lane-based short-term urban traffic flow forecasting[J]. Transportation Planning and Technology, 2018, 41(8): 901-917. |
| 2 | Gu Y L, Lu W Q, Qin L Q, et al. Short-term prediction of lane-level traffic speeds: a fusion deep learning model[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2019, 106: 1-16. |
| 3 | Lu W Q, Rui Y K, Yi Z W, et al. A hybrid model for lane-level traffic flow forecasting based on complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition and extreme gradient boosting[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 42042-42054. |
| 4 | Zhong M, Sharma S, Lingras P. Genetically designed models for accurate imputation of missing traffic counts[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2004(1879): 71-79. |
| 5 | Williams B M, Hoel L A. Modeling and forecasting vehicular traffic flow as a seasonal ARIMA process: Theoretical basis and empirical results[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2003, 129(6): 664-672. |
| 6 | Bermúdez J D, Corberán-Vallet A, Vercher E. Forecasting time series with missing data using Holt's model[J]. Journal of Statistical Planning & Inference, 2009, 139(8): 2791-2799. |
| 7 | 王新颖, 隽志才, 吴庆妍, 等. KNN算法的数据优化策略[J]. 吉林大学学报: 信息科学版, 2010, 28(3): 309-313. |
| Wang Xin-ying, Zhi-cai Juan, Wu Qing-yan, et al. Data optimization strategy of KNN algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Information Science Edition), 2010, 28(3): 309-313. | |
| 8 | 陈亮, 王金泓, 何涛, 等. 基于SVR的区域交通碳排放预测研究[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2018, 18(2): 13-19. |
| Chen Liang, Wang Jing-hong, He Tao, et al. Forecast study of regional transportation carbon emissions based on SVR[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2018, 18(2): 13-19. | |
| 9 | Qu L, Zhang Y, Hu J M, et al. A BPCA based missing value imputing method for traffic flow volume data[J]. IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium, 2008: 985-990. |
| 10 | Qu L, Li L, Zhang Y, et al. PPCA-based missing data imputation for traffic flow volume: a systematical approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2009, 10(3): 512-522. |
| 11 | Acar E, Dunlavy D M, Kolda T G, et al. Scalable tensor factorizations for incomplete data[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2011, 106(1): 41-56. |
| 12 | Tan H C, Feng G D, Feng J S, et al. A tensor-based method for missing traffic data completion[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2013, 28: 15-27. |
| 13 | Kolda T G, Bader B W. Tensor decompositions and applications[J]. SIAM review, 2009, 51(3): 455-500. |
| 14 | de Lathauwer L, de Moor B, Vandewalle J. A Multilinear singular value decomposition[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 2000, 21(4):1253-1278. |
| 15 | Chen X Y, He Z C, Wang J W. Spatial-temporal traffic speed patterns discovery and incomplete data recovery via SVD-combined tensor decomposition[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 86: 59-77. |
| 16 | Polyak B T. Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iteration methods[J]. USSR Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics, 1964, 4(5): 1-17. |
| 17 | Li L C, Du B W, Wang Y G, et al. Estimation of missing values in heterogeneous traffic data: application of multimodal deep learning model[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 194: 105592. |
| 18 | Chen X Y, He Z C, Sun L J. A bayesian tensor decomposition approach for spatiotemporal traffic data imputation[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 98: 73-84. |
| 19 | 谷远利, 张源, 芮小平, 等. 基于免疫算法优化LSSVM的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| Gu Yuan-li, Zhang Yuan, Rui Xiao-ping, et al. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on LSSVM optimized by immune algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. | |
| 20 | 杨飞, 方滨兴, 王春露, 等. 基于小波和回声状态网络的交通流多步预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2013, 43(3): 646-653. |
| Yang Fei, Fang Bin-xing, Wang Chun-lu, et al. Multi-step traffic flow prediction model based on wavelet and echo state network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2013, 43(3): 646-653. | |
| 21 | 龚勃文, 林赐云, 李静, 等. 基于核自组织映射-前馈神经网络的交通流短时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2011, 41(4): 938-943. |
| Gong Bo-wen, Lin Xi-yun, Li Jing, et al. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on KSOM BP neural network[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2011, 41(4): 938-943. |
| [1] | 卢凯,吴蔚,林观荣,田鑫,徐建闽. 基于KNN回归的客运枢纽聚集人数组合预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1241-1250. |
| [2] | 彭博,张媛媛,王玉婷,唐聚,谢济铭. 基于自动编码机-分类器的视频交通状态自动识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 886-892. |
| [3] | 张健,吴坤润,杨敏,冉斌. 智能网联环境下交叉口双环自适应控制模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 541-548. |
| [4] | 王殿海,沈辛夷,罗小芹,金盛. 车均延误最小情况下的相位差优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 511-523. |
| [5] | 宋现敏,张明业,李振建,王鑫,张亚南. 动态公交专用道的设置及其仿真分析评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1677-1686. |
| [6] | 贾洪飞,丁心茹,杨丽丽. 城市潮汐车道优化设计的双层规划模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 535-542. |
| [7] | 尹超英,邵春福,王晓全,熊志华. 考虑空间异质性的建成环境对通勤方式选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 543-548. |
| [8] | 张大伟,祝海涛. 考虑行人差异性的人群疏散最优决策理论模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 549-556. |
| [9] | 常玉林,袁才鸿,孙超,张鹏. 基于改进元胞传输模型的城市路网实际阻抗计算方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 132-139. |
| [10] | 宗长富,文龙,何磊. 基于欧几里得聚类算法的三维激光雷达障碍物检测技术[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 107-113. |
| [11] | 隋振,姜源. 基于MIMO类脑情感学习回路的横-纵向综合控制驾驶员模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 140-146. |
| [12] | 别一鸣,姜凯,汤茹茹,王琳虹,熊昕宇. 考虑方案过渡影响的单点交通控制时段划分方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1844-1851. |
| [13] | 谷远利, 张源, 芮小平, 陆文琦, 李萌, 王硕. 基于免疫算法优化LSSVM的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857. |
| [14] | 程国柱, 冯思鹤, 冯天军. 占用车行道的路内停车泊位设置条件[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1858-1864. |
| [15] | 龙海波,杨家其,赵学彧. 基于转运延误风险的多方式协同货运载运工具配置优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1492-1499. |
|
||