吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1565-1574.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20200603
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于模型群预测法对汽油机稳态原排的预测
陈涛1( ),秦静1,2(
),秦静1,2( ),赵华1,苏庆鹏1,3,吕永3,钟凯1,王膺博1,裴毅强1
),赵华1,苏庆鹏1,3,吕永3,钟凯1,王膺博1,裴毅强1
- 1.天津大学 内燃机燃烧学国家重点实验室,天津 300072
2.天津大学 内燃机研究所,天津 300072
3.广州汽车集团股份有限公司汽车工程研究院,广州 511434
Prediction of gasoline engine steady state exhaust based on model group prediction method
Tao CHEN1( ),Jing QIN1,2(
),Jing QIN1,2( ),Hua ZHAO1,Qing-peng SU1,3,Yong LYU3,Kai ZHONG1,Ying-bo WANG1,Yi-qiang PEI1
),Hua ZHAO1,Qing-peng SU1,3,Yong LYU3,Kai ZHONG1,Ying-bo WANG1,Yi-qiang PEI1
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Engines,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
2.Internal Combustion Engine Research Institute,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300072,China
3.GAC Automotive Research & Development Center,Guangzhou 511434,China
摘要:
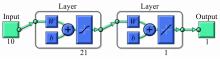
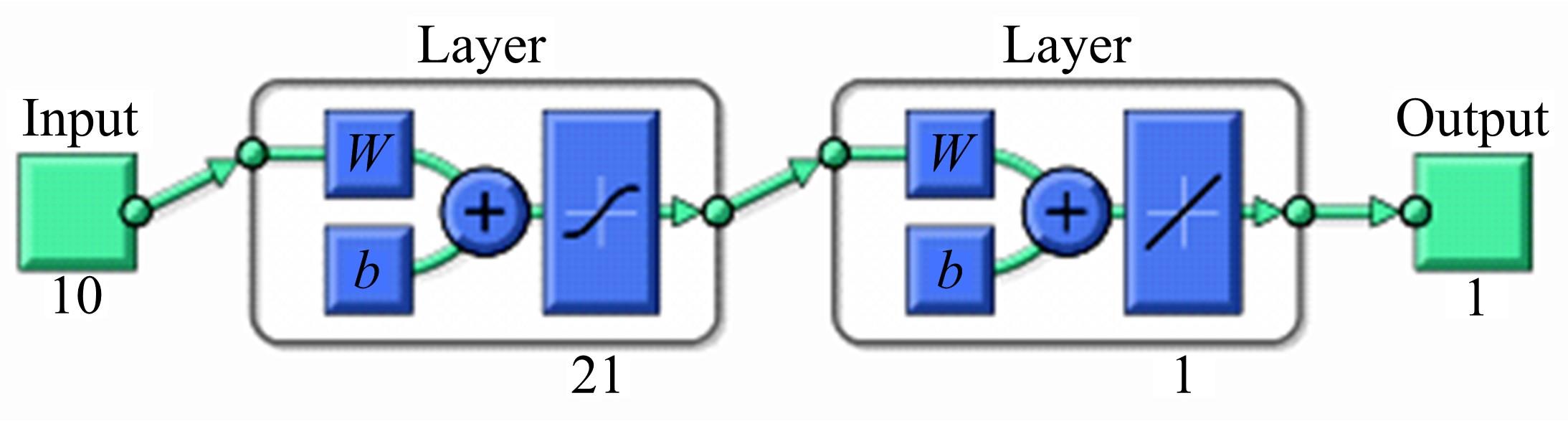
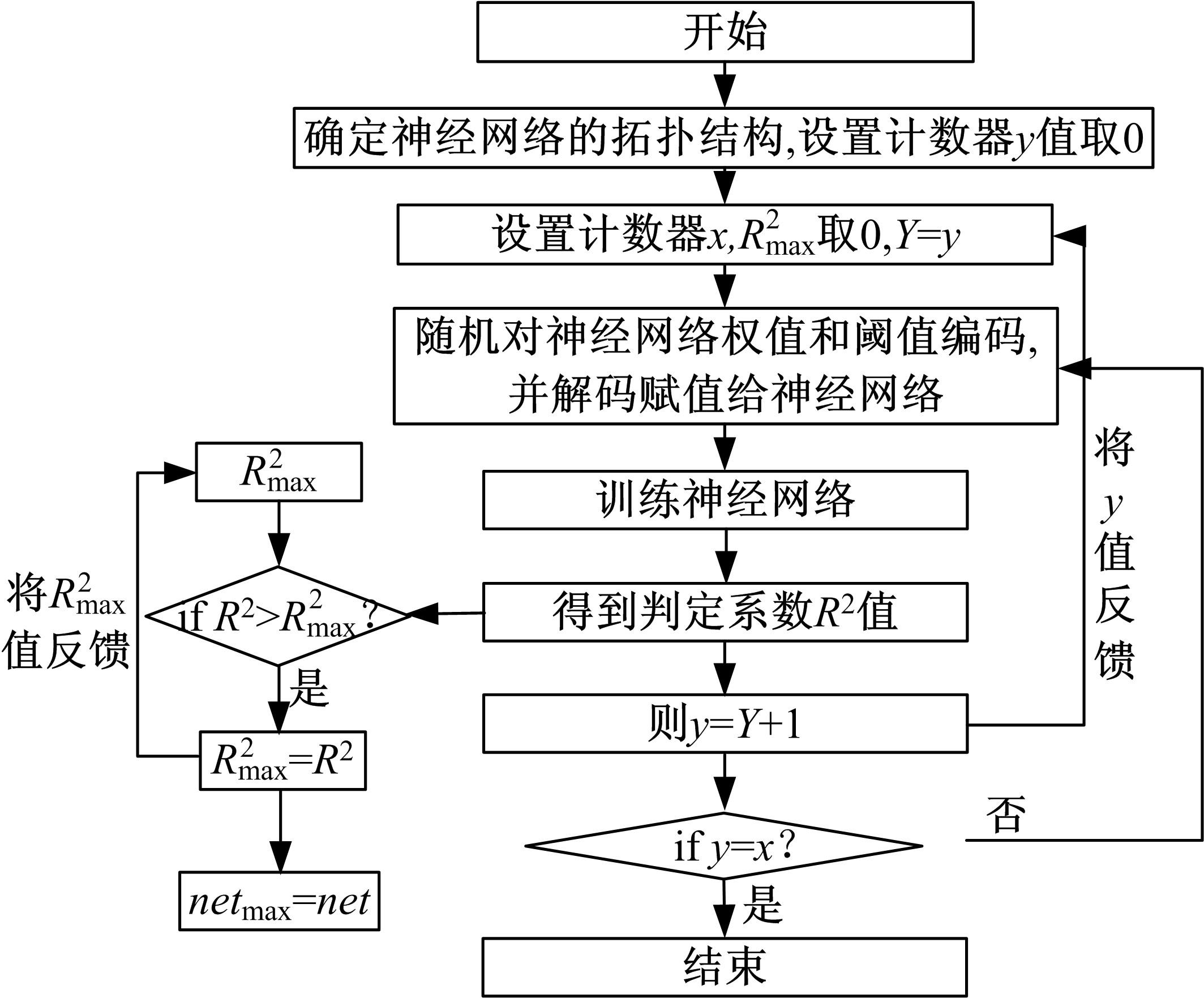
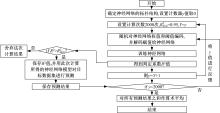
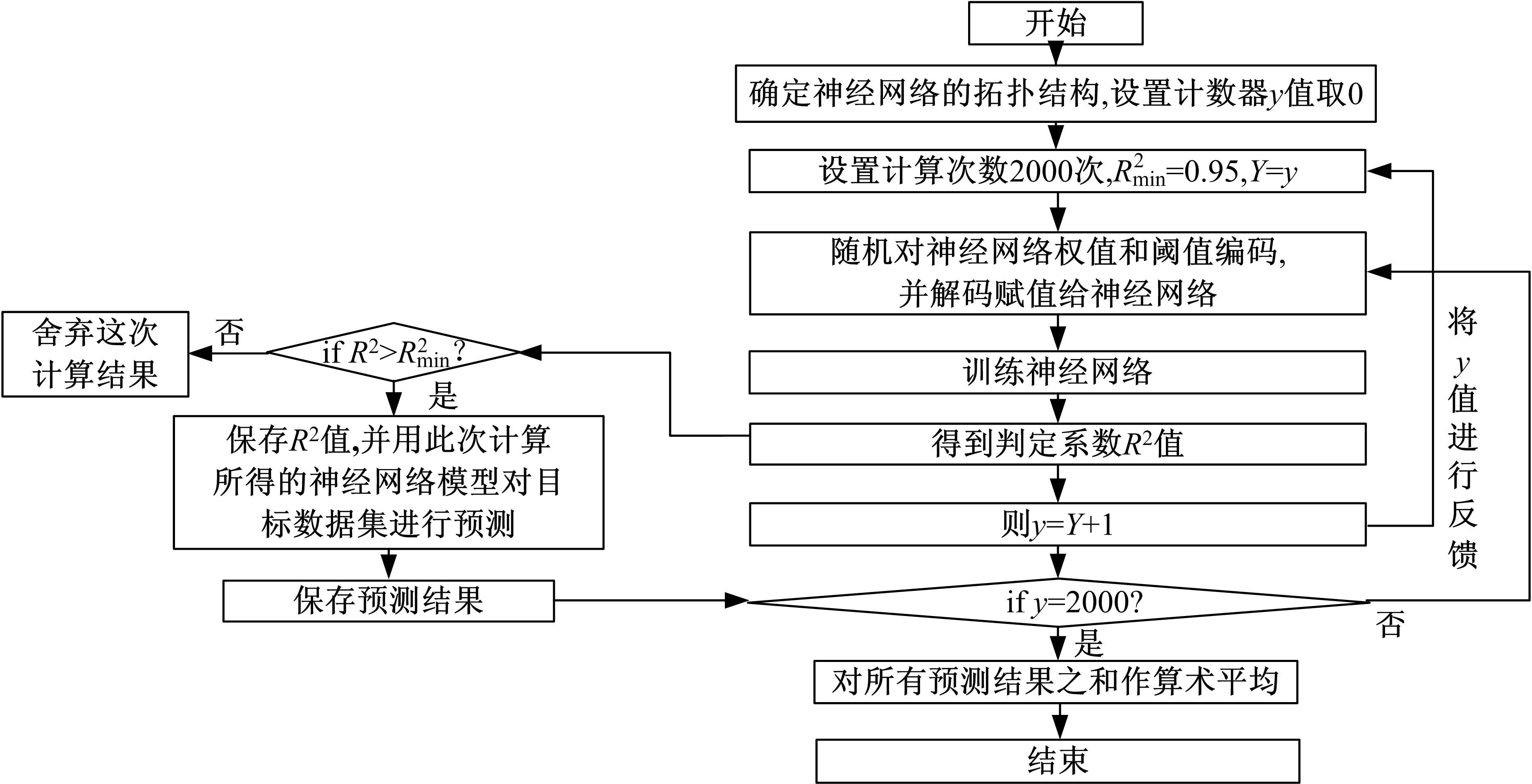
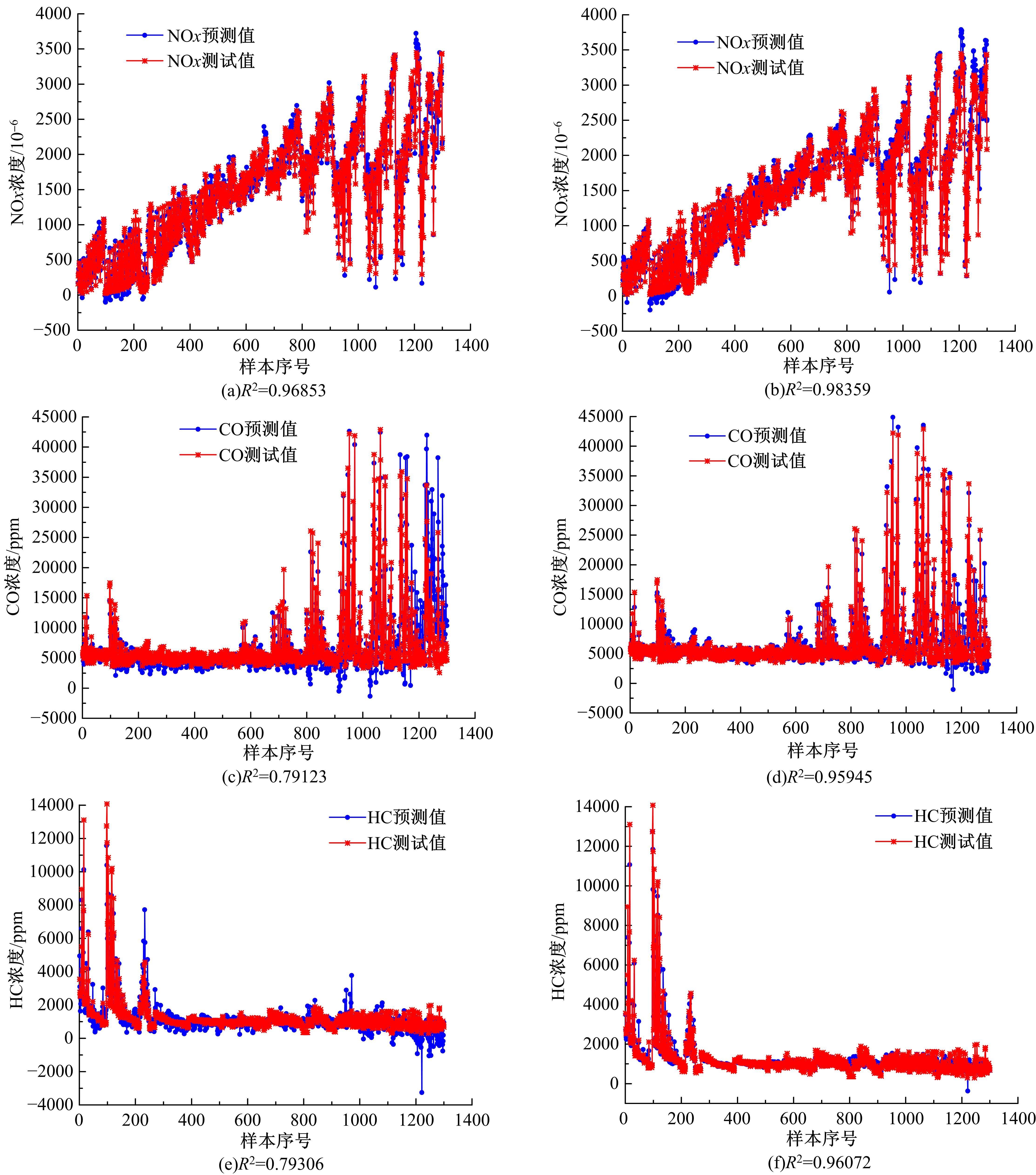
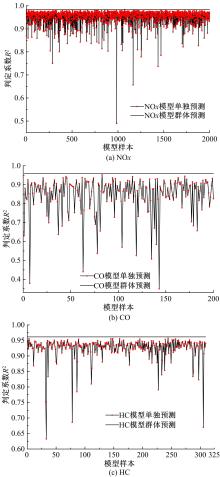
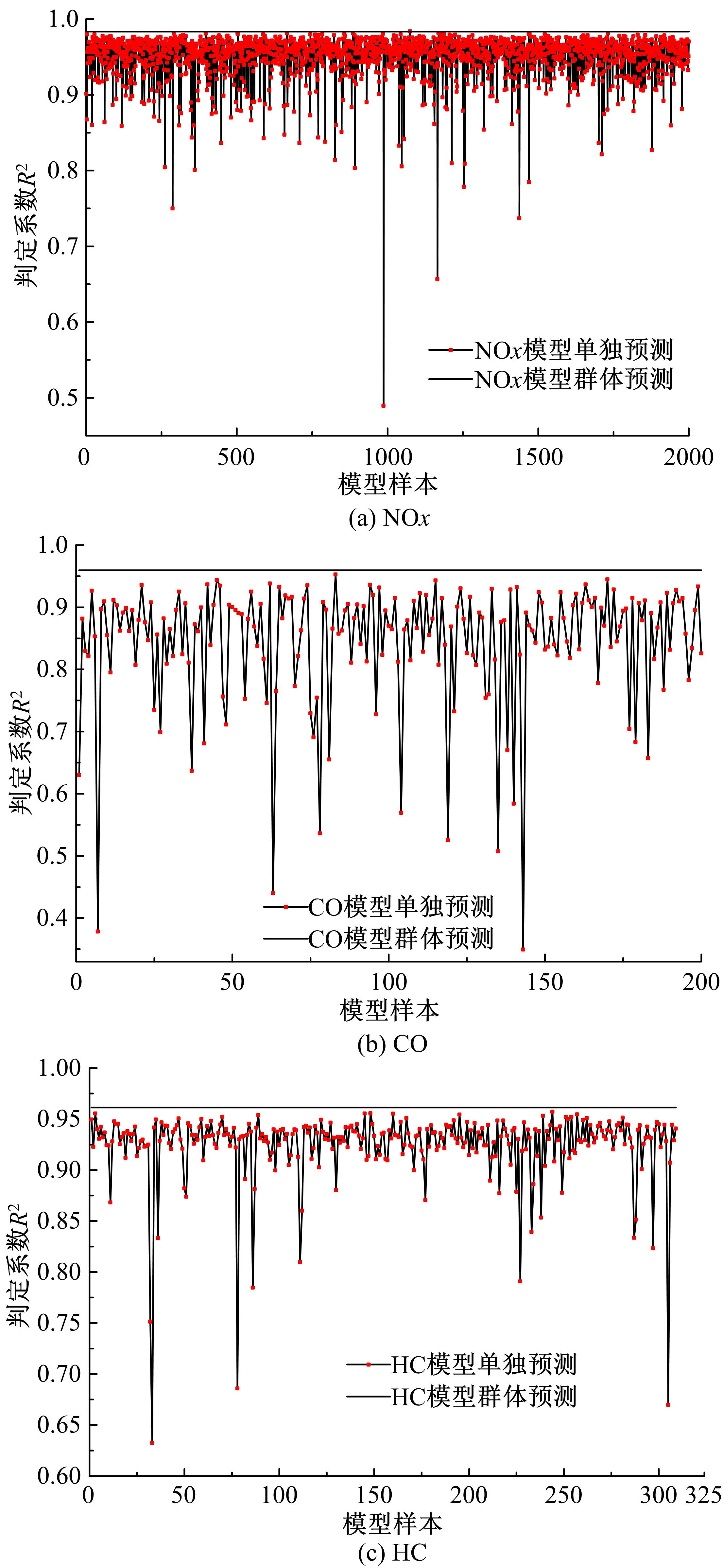
针对通过数值模拟减少汽油机台架试验环节的工作量、提高试验效率的问题,采用模型群预测法(优化后的人工神经网络方法)对汽油机台架试验过程中的NOx、CO、HC等稳态原排进行建模及预测分析。结果表明:与传统的单个模型预测方法相比较,模型群预测法具有较高的可靠性,能较好地提升预测结果的准确度。采用隔点取点法适当减少神经网络建模的训练数据集,仍能保持较好的预测能力,在项目开发过程中只需进行30%的测试量,将试验结果用于神经网络模型训练,可较好地预测剩余工况排放。通过对其他机型的验证分析,模型群预测法在内燃机稳态原排的预测过程中具有较好的普适性。
中图分类号:
- TK411
| 1 | 裴毅强, 张建业, 秦静, 等. 增压直喷汽油机起动怠速及混合气浓度对微粒排放的影响[J]. 天津大学学报: 自然科学与工程技术版, 2014, 47(10): 892-897. |
| Pei Yi-qiang, Zhang Jian-ye, Qin Jing, et al. Effect of starting idling condition and mixture concentration of a turbocharged GDI engine on particle emission [J]. Journal of Tianjin University(Science and Technology), 2014, 47(10): 892-897. | |
| 2 | 谢宗法, 付文超, 魏枫展, 等. 进气门早关对汽油机进气过程及燃烧性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(3): 850-858. |
| Xie Zong-fa, Fu Wen-chao, Wei Feng-zhan, et al. Effect of early intake valve closing on intake process and combustion performance of SI engine [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3): 850-858. | |
| 3 | 于秀敏, 商震, 张岳韬, 等. 废气再循环对直喷汽油机燃烧及排放影响的仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2016, 46(4): 1109-1117. |
| Yu Xiu-min, Shang Zhen, Zhang Yue-tao, et al. Simulation of EGR on combustion and emission of gasline direct-injection engine[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(4): 1109-1117. | |
| 4 | 孙平, 曹智, 于秀敏, 等. 直喷时刻对复合喷射汽油机暖机过程燃烧和排放的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2020, 50(6): 1941-1949. |
| Sun Ping, Cao Zhi, Yu Xiu-min, et al. Experimental study on effect of compound injection on cold start combustion and emission of gasoline engine[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(6): 1941-1949. | |
| 5 | 卫海桥, 裴自刚, 冯登全, 等. 压电喷油器多次喷射对GDI汽油机颗粒物排放的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 48(1): 166-173. |
| Wei Hai-qiao, Pei Zi-gang, Feng Deng-quan,et al. Effect of multi-injection piezo injector on particulate emission in gasoline direct injection engine[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(1): 166-173. | |
| 6 | Heinz-Jakob N, Jörn K, Richard D, et al. Die euro-6-motoren des modularen dieselbaukastens von volkswagen[J]. MTZ-Motortechnische Zeitschrift, 2013, 74(6): 440-447. |
| 7 | Raidt B. Local gaussian process regression in order to model air charge of turbocharged gasoline SI engines[C]∥SAE Technical Paper, 2016-01-0624. |
| 8 | Gutjahr T, Kleinegraeber H, Huber T, et al. Commercial vehicle engineering congress[J]. SAE Technical Paper, 2015-01-2796. |
| 9 | Lasko T A. Efficient inference of gaussian process modulated renewal processes with application to medical event data[J]. Uncertain Artif Intell, 2014(2014): 469-476. |
| 10 | Bernhard S. Introduction to Gaussian Processes[M]. Massachusetts: MIT Press, 2008. |
| 11 | Mackay D J C. Bayesian interpolation[J]. Neural Computation, 1992, 4(3): 415-447. |
| 12 | Kuzin D, Yang L, Isupova O, et al. Ensemble kalman filtering for online gaussian process regression and learning[C]∥21st International Conference on Information Fusion, Cambridge, UK, 2018: 39-46. |
| 13 | Kauermann G, Bove D, Sabanes H L. Objective bayesian model selection in generalized additive models with penalized splines[J]. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2015, 24(2): 394-415. |
| 14 | Baek J, Adams A, Dolson J. Lattice-based high-dimensional gaussian filtering and the permutohedral lattice[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging & Vision, 2013, 46(2): 211-237. |
| 15 | Rot I, Daniel F P, Rinderknecht S. Investigation of black box modeling approaches for representation of transient gearshift processes in automotive powertrains with automatic transmission[C]∥SAE Technical Papers, 2015-01-1143. |
| 16 | Mao G, Zhang C, Shi K, et al. Prediction of the performance and exhaust emissions of ethanol-diesel engine using different neural network[J]. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects, 2019, 104: 1656307. |
| 17 | Nestor L S Y. Modelling the infiltration process with a multi-layer perceptron artificial neural network[J]. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2006, 51(1): 3-20. |
| 18 | 李健. 基于深度学习的变循环发动机气路故障诊断[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学电子信息与电气工程学院, 2019. |
| Li Jian. Fault diagnosis for variable cycle engine gas path: a deep learning approach[D]. Shanghai: School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2019. | |
| 19 | 肖勇, 赵云, 涂治东, 等. 基于改进的皮尔逊相关系数的低压配电网拓扑结构校验方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(11): 37-43. |
| Xiao Yong, Zhao Yun, Tu Zhi-dong, et al. Topology checking method for low voltage distribution network based on improved pearson correlation coefficient[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(11): 37-43. | |
| 20 | 龚麒鉴, 郭亚宾, 陈焕新, 等. 基于粒子群优化算法和BP神经网络的变频压缩机功率预测[J]. 制冷学报, 2020, 41(1): 89-95. |
| Gong Qi-jian, Guo Ya-bin, Chen Huan-xin, et al. Prediction of variable-speed compressor power based on particle swarm optimization and back propagation neural network[J]. Journal of Refrigeration, 2020, 41(1): 89-95. | |
| 21 | 谢岩, 廖松地, 朱曼妮, 等. 轻型汽油车稳态工况下的尾气排放特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(7): 3112-3120. |
| Xie Yan, Liao Song-di, Zhu Man-ni, et al. Emission characteristics of light-duty gasoline vehicle exhaust based on acceleration simulation mode[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(7): 3112-3120. | |
| 22 | Jeeragal R, Subramanian K A. Experimental investigation for NOx emission reduction in hydrogen fueled spark ignition engine using spark timing retardation[J]. Journal of Thermal Science, 2019, 28(4): 789-800. |
| 23 | Kosmadakis G M, Rakopoulos D C, Rakopoulos C D. Methane/hydrogen fueling a spark-ignition engine for studying NO, CO and HC emissions with a research CFD code[J]. Fuel, 2016, 185(1): 903-915. |
| [1] | 卢凯,吴蔚,林观荣,田鑫,徐建闽. 基于KNN回归的客运枢纽聚集人数组合预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1241-1250. |
| [2] | 王德兴,吴若有,袁红春,宫鹏,王越. 基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [3] | 董延华,刘靓葳,赵靖华,李亮,解方喜. 基于BPNN在线学习预测模型的扭矩实时跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1405-1413. |
| [4] | 徐卓君,杨雯婷,杨承志,田彦涛,王晓军. 雷达脉内调制识别的改进残差神经网络算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1454-1460. |
| [5] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [6] | 宋大凤,杨丽丽,曾小华,王星琦,梁伟智,杨南南. 基于行驶工况合成的混合动力汽车电池寿命优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 781-791. |
| [7] | 宋震,李俊良,刘贵强. 基于深度学习和限幅模糊的变转速液压动力源恒流量预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1106-1110. |
| [8] | 尚福华,曹茂俊,王才志. 基于人工智能技术的局部离群数据挖掘方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 692-696. |
| [9] | 魏晓辉,周长宝,沈笑先,刘圆圆,童群超. 机器学习加速CALYPSO结构预测的可行性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 667-676. |
| [10] | 李志军,刘浩,张立鹏,李振国,邵元凯,李智洋. 过滤壁结构对颗粒捕集器深床过滤影响的模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 422-434. |
| [11] | 刘纯国,于晓彤,岳韬,李东来,张明哲. 双曲率筋条壁板铣削回弹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 188-199. |
| [12] | 何德峰,罗捷,舒晓翔. 自主网联车辆时滞反馈预测巡航控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 349-357. |
| [13] | 慕文龙,那景新,谭伟,王广彬,申浩,栾建泽. 基于FTIR分析的CFRP-铝合金粘接接头剩余强度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 139-146. |
| [14] | 魏晓辉,孙冰怡,崔佳旭. 基于图神经网络的兴趣活动推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 278-284. |
| [15] | 王柯俨,王迪,赵熹,陈静怡,李云松. 基于卷积神经网络的联合估计图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1771-1777. |
|
||