吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1896-1903.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210194
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法
- 1.中国科学院国家空间科学中心 复杂航天系统电子信息技术重点实验室,北京 100190
2.中国科学院大学,北京 100049
Vessel search method by earth observation satellite based on time⁃varying grid
- 1.Key Laboratory of Electronics and Information Technology for Space Systems,National Space Science Center,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100190,China
2.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100049,China
摘要:
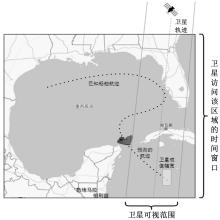
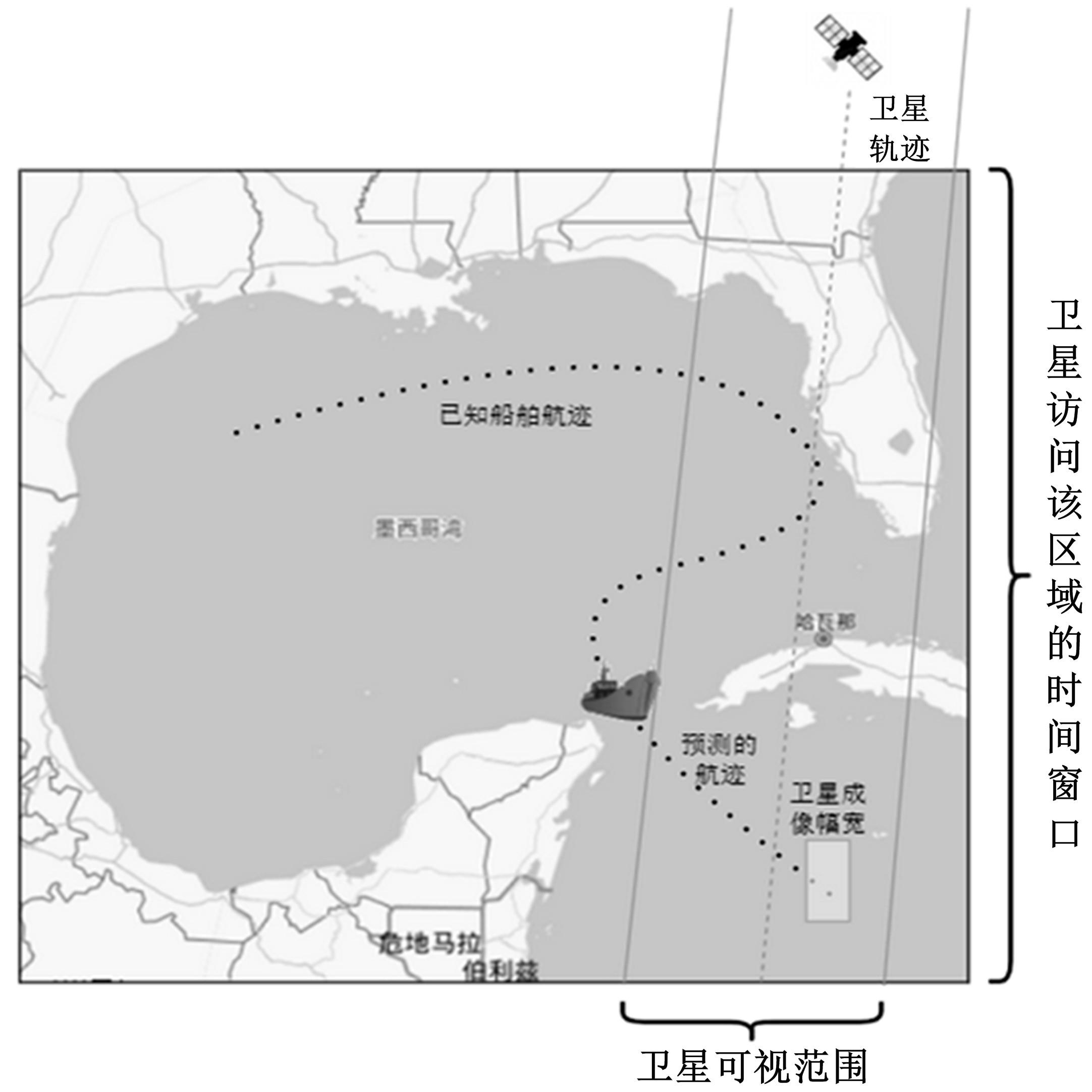
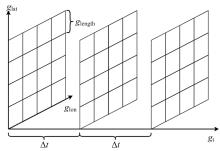
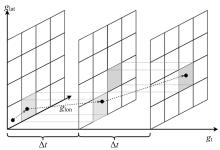
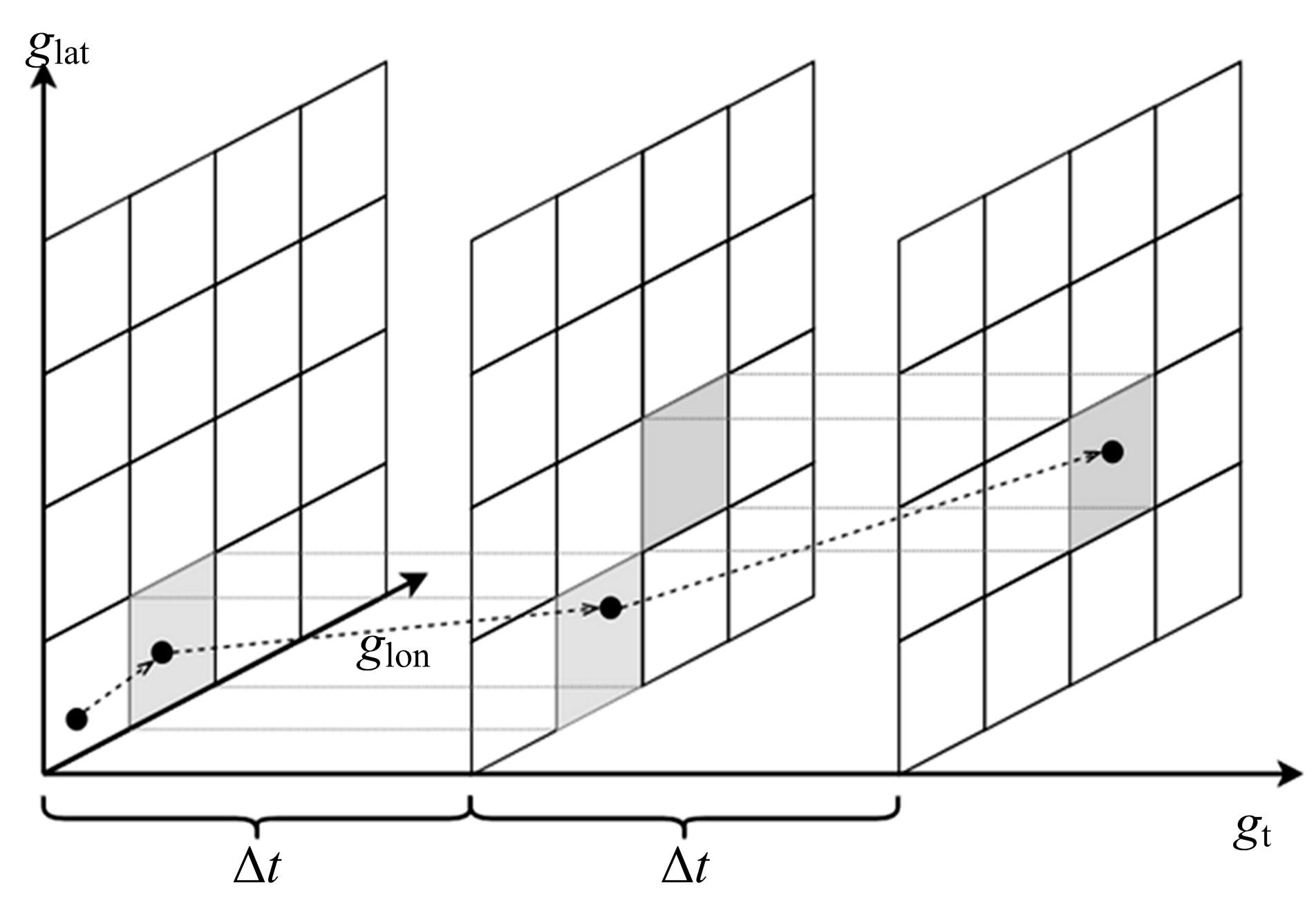
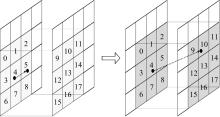
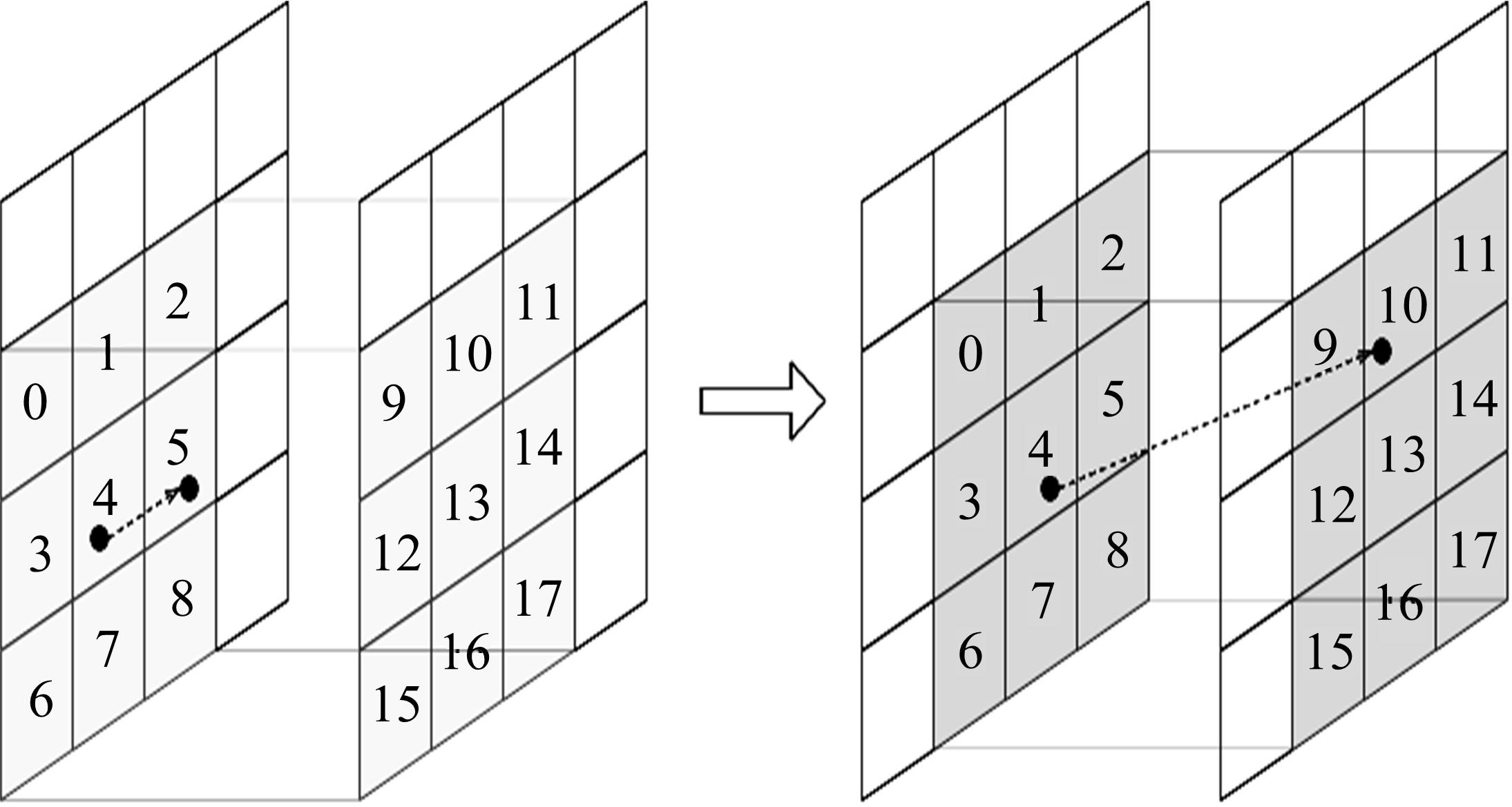
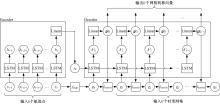
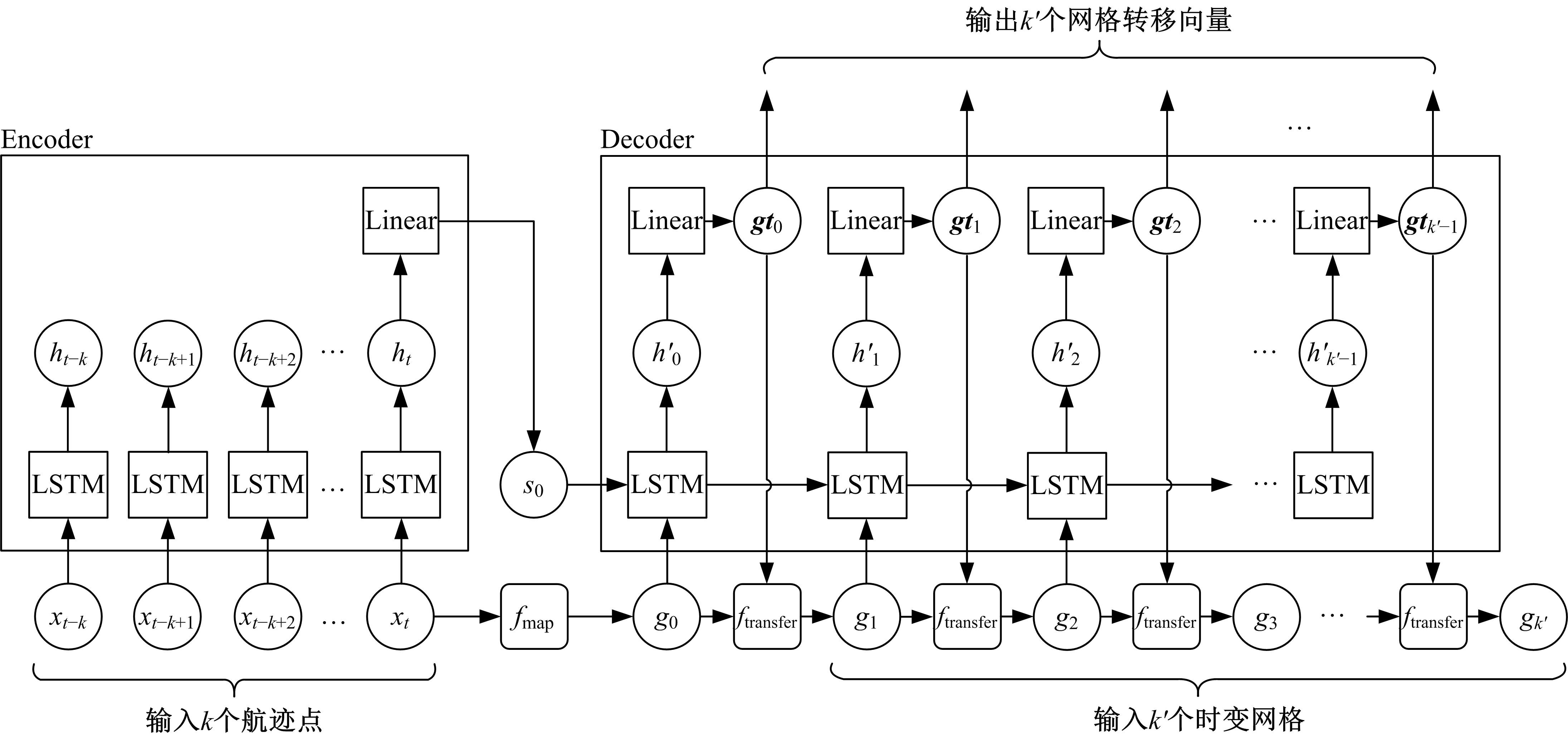
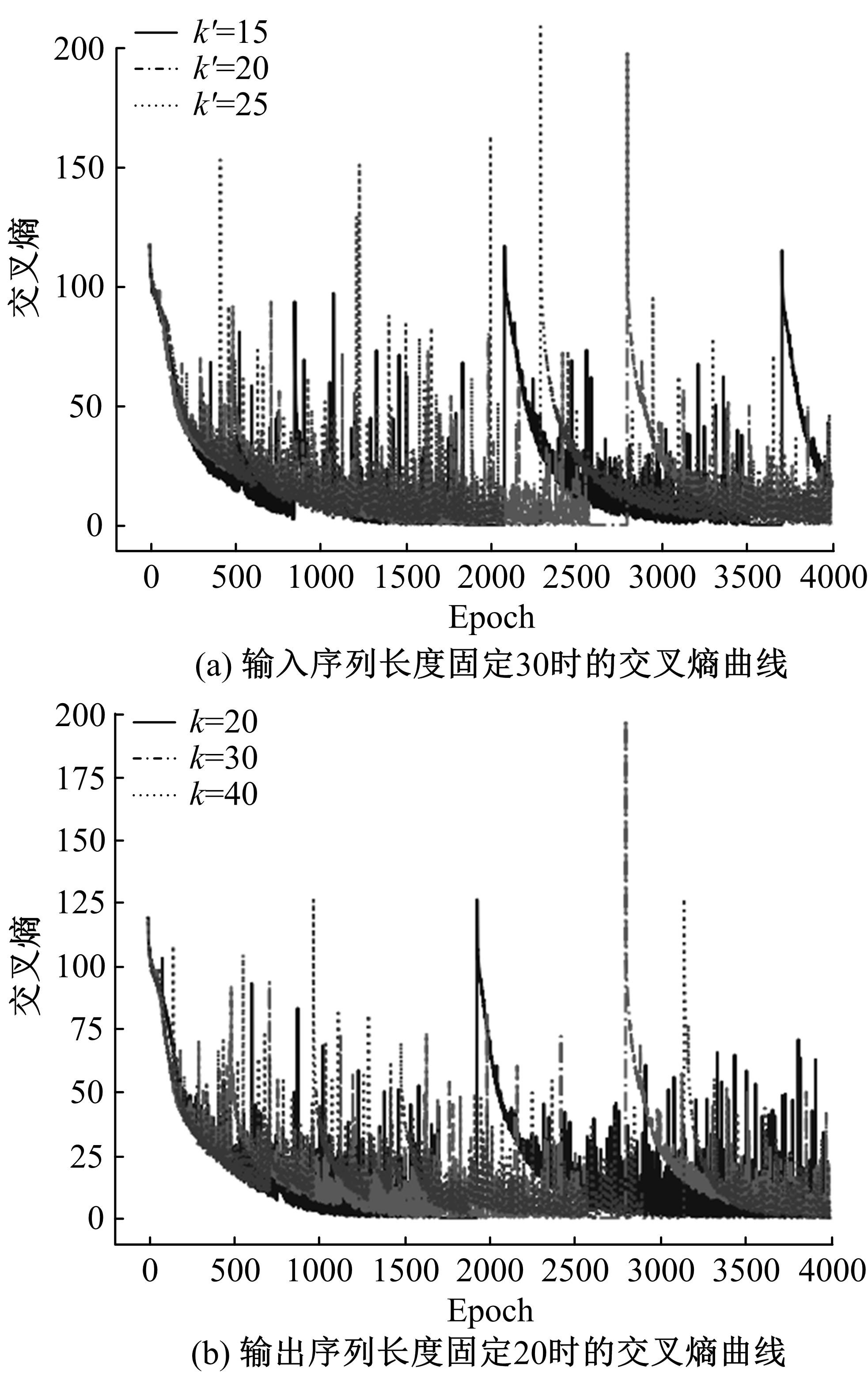
为提高对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶效能,提出了一种根据卫星对地观测幅宽和船舶最大航速划分区域时空维度的时变网格模型,将船舶航迹预测问题转化为时变网格转移概率预测问题,有效降低了多步预测的复杂度。改进了序列到序列(Seq2Seq)模型,通过对搜索区域内大量历史航迹的学习,实现了较高精确度的多步时变网格转移预测。设计了面向时变网格的卫星观测任务规划算法,以实际AIS数据和卫星信息开展了仿真实验,实验结果表明:基于深度学习的Seq2Seq模型多步预测时变网格具有较高的精确度,有效提升了对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶的效能。
中图分类号:
- TP301.6
| 1 | Paul E B, Carmine P, David A B F. Optimal search,location and tracking of surface maritime targets by a constellation of surveillance satellites[R]. Edinburgh:DSTO Information Sciences Laboratory, 2002. |
| 2 | 王慧林,邱涤珊,马满好,等.基于先验信息的海洋移动目标卫星成像侦测任务规划[J].火力与指挥控制,2011, 36(3): 105-110. |
| Wang Hui-lin, Qiu Di-shan, Ma Man-hao, et al. Research on mission-planning of satellite imaging reconnaissance for ocean moving targets based on the prior information[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2011, 36(3): 105-110. | |
| 3 | 陈杰,邢利菊. 面向海洋移动目标成像侦察方法研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2014, 42(3): 395-398. |
| Cheng Jie, Xing Li-ju. Imaging reconnaissance method facing ocean motion target[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2014, 42(3): 395-398. | |
| 4 | 梅关林,冉晓旻,范亮,等. 面向移动目标的卫星传感器调度技术研究[J]. 信息工程大学学报, 2016, 17(5): 513-517. |
| Mei Guan-lin, Ran Xiao-min, Fan Liang, et al. Research on satellite sensor scheduling technology for moving target[J]. Journal of Information Engineering University, 2016, 17(5): 513-517. | |
| 5 | Li J F, Geng-xi Y Z, Yao F, et al.Using multiple satellites to search for maritime moving targets based on reinforcement learning[J].Journal of Donghua University(English Edition), 2016, 33(5): 749-754. |
| 6 | 张海龙,夏维,胡笑旋,等. 面向多障碍物海面卫星搜索动目标方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(10): 2256-2262. |
| Zhang Hai-long, Xia Wei, Hu Xiao-xuan, et al. Method for moving targets search by satellites on multi-obstacle sea[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(10): 2256-2262. | |
| 7 | 夏忠,张海龙,靳鹏.基于信息融合的多星搜索动目标问题[J].火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(7): 20-25, 30. |
| Xia Zhong, Zhang Hai-long, Jin Peng. Research on moving target problem of multi-satellite search based on information fusion[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2020, 45(7): 20-25, 30. | |
| 8 | Qiao S, Shen D, Wang X, et al. A self-adaptive parameter selection trajectory prediction approach via hidden markov models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(1):284-296. |
| 9 | Rong H, Teixeira A P, Soares C G. Ship trajectory uncertainty prediction based on a Gaussian process model[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 182(15): 499-511. |
| 10 | Liang Y, Zhang H. Ship track prediction based on ais data and pso optimized LSTM network[J]. International Core Journal of Engineering, 2020, 6(5): 23-33. |
| 11 | 胡玉可,夏维,胡笑旋,等.基于循环神经网络的船舶航迹预测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(4): 871-877. |
| Hu Yu-ke, Xia Wei, Hu Xiao-xuan, et al. Vessel trajectory prediction based on recurrent neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020,42(4):871-877. | |
| 12 | Duc-Duy N, Chan L V, Muhammad I A. Vessel trajectory prediction using sequence-to-sequence models over spatial grid[C]∥The 12th ACM International Conference, New Zealand, 2018: 258-261. |
| 13 | 游兰,韩雪薇,何正伟,等.基于改进Seq2Seq的短时AIS轨迹序列预测模型[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(9): 169-174. |
| You Lan, Han Xue-wei, He Zheng-wei, et al. Improved sequence-to-sequence model for short-term vessel trajectory prediction using AIS data streams[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(9): 169-174. | |
| 14 | 夏永泉,黄海鹏,王兵,等.一种基于改进的无监督深度学习自编码方法[J]. 科技通报, 2018, 34(7):183-187. |
| Xia Yong-quan, Huang Hai-peng, Wang Bing, et al. Self-encoding method based on improved unsupervised deep learning[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2018, 34(7): 183-187. | |
| 15 | Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le Q V. Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks[C/OL]∥[2021-03-15]. |
| 16 | 徐谦,李颖,王刚.基于深度学习图像语义分割的机器人环境感知[J].吉林大学学报:工学版, 2019, 49(1): 248-260. |
| Xu Qian, Li Ying, Wang Gang. Robotic environment sensing based on semantic segmentation by deep learning[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(1): 248-260. | |
| 17 | Sepp Hochreiter, Technische Universität München, Fakultät für Informatik, et al. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. |
| 18 | 刘畅. 船舶自动识别系统(AIS)关键技术研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学通信与信息系统, 2013. |
| Liu Chang. Study of key technology of automatic identification system(AIS)[D].Dalian: Communication and Information Systems, Dalian Maritime University, 2013. | |
| 19 | 伊恩,约书亚,亚伦.深度学习[M].北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2017. |
| 20 | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,等.基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| Zhao Hong-wei, Liu Xiao-han, Zhang Yuan, et al. Clothing classification algorithm based on landmark attention and channel attention[J].Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. | |
| 21 | 冯荣强,赵磊,杨勇,等.计及电价和Attention机制的LSTM短期负荷预测模型[J].科技通报, 2020, 36(11): 57-62, 68. |
| Feng Rong-qiang, Zhao Lei, Yang Yong, et al. LSTM-Short-term load forecasting model considering electricity price and attention mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2020, 36(11): 57-62, 68. |
| [1] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [2] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [3] | 李晓英,杨名,全睿,谭保华. 基于深度学习的不均衡文本分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1889-1895. |
| [4] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [5] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [6] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [7] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [8] | 王军,徐彦惠,李莉. 低能耗支持完整性验证的数据融合隐私保护方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [9] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [10] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [11] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,陈富. 基于谱聚类的高维类别属性数据流离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [12] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [13] | 陈雪云,贝学宇,姚渠,金鑫. 基于G⁃UNet的多场景行人精确分割与检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
| [14] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
| [15] | 李大湘,陈梦思,刘颖. 基于STA⁃LSTM的自发微表情识别算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 897-909. |
|
||