吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 1826-1833.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210330
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
下击暴流作用下圆形马鞍面屋盖风压特性
- 1.西南科技大学 土木工程与建筑学院,四川 绵阳 621010
2.中国空气动力研究与发展中心,四川 绵阳 621010
Wind pressures on a circular hyperbolic⁃paraboloid roof subjected to a simulated downburst
Yun-peng CHU1( ),Xin-hui SUN1(
),Xin-hui SUN1( ),Ming LI2,Yong YAO1,Han-jie HUANG2
),Ming LI2,Yong YAO1,Han-jie HUANG2
- 1.College of Civil Engineering and Architecture,Southwest University of Science and Technology,Mianyang 621010,China
2.China Aerodynamics Research and Development Center,Mianyang 621010,China
摘要:
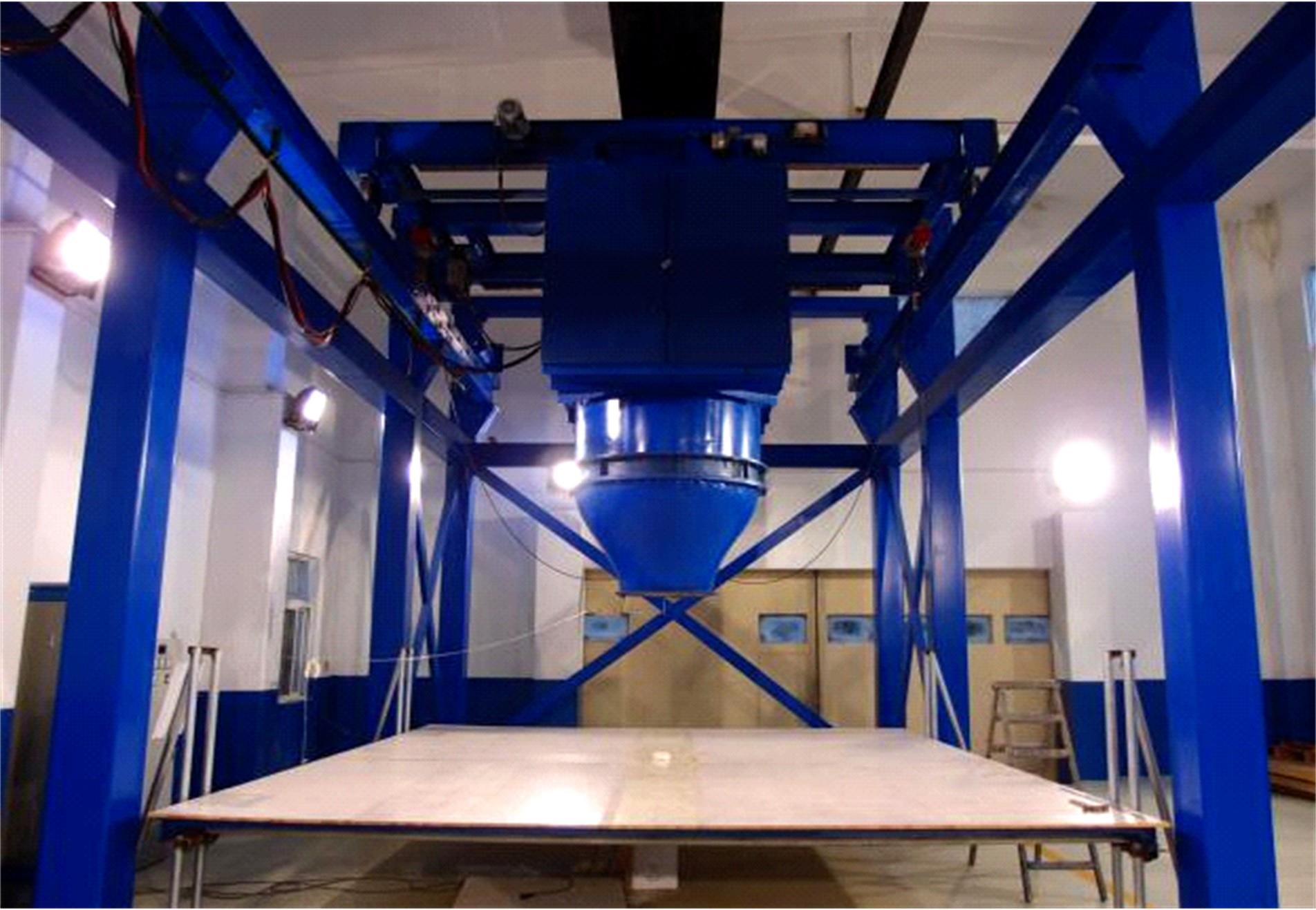
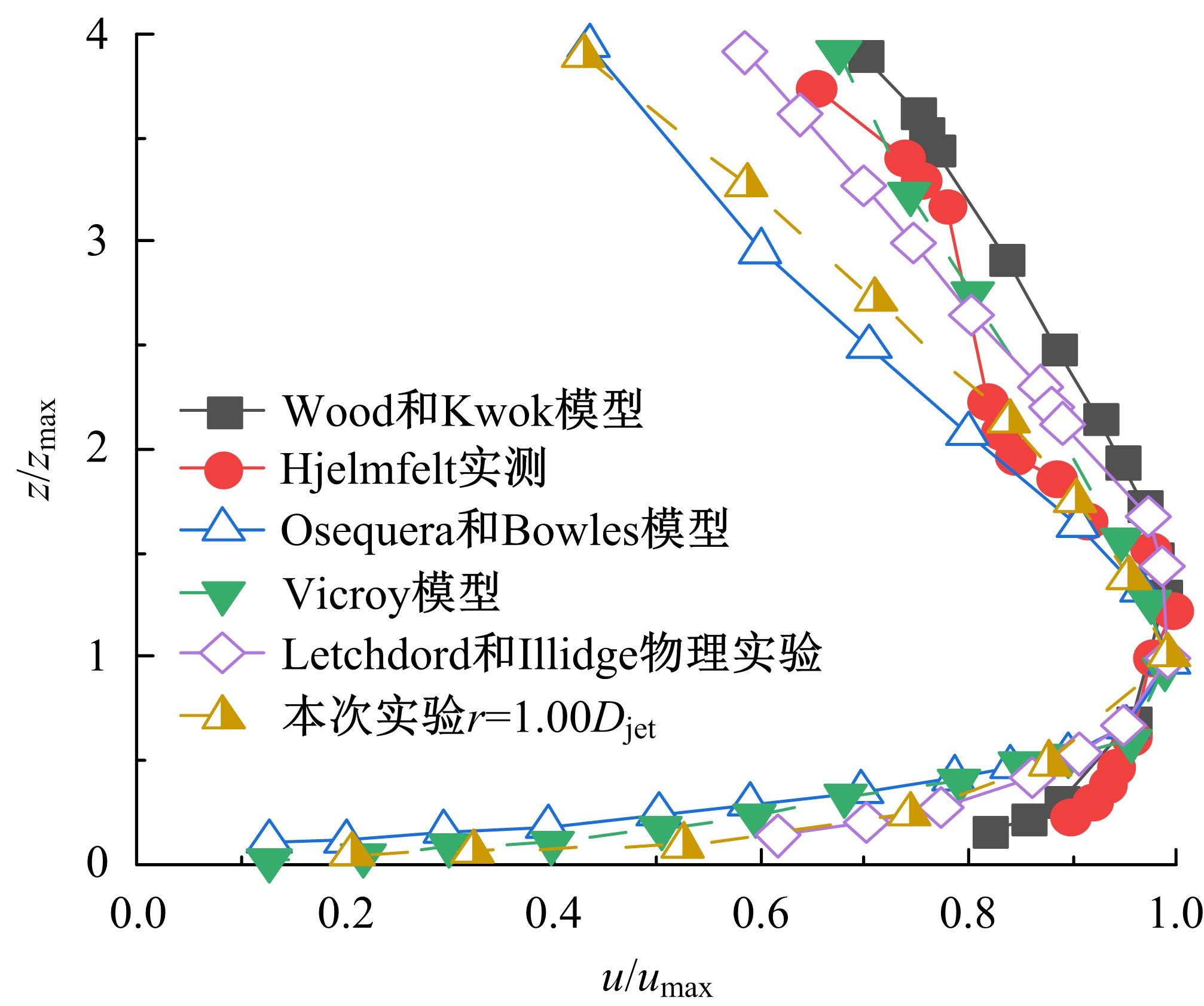
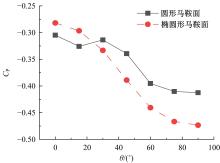
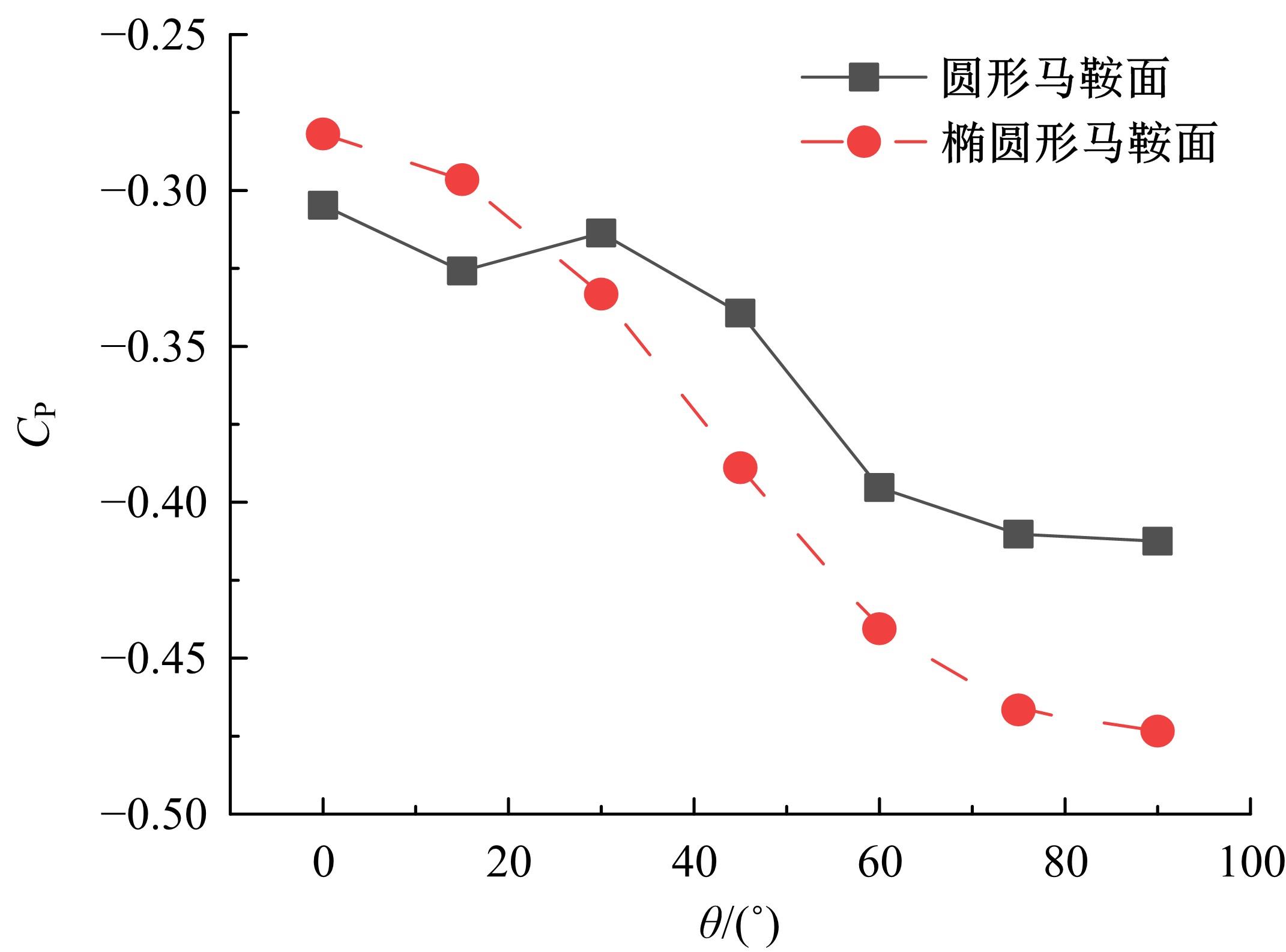
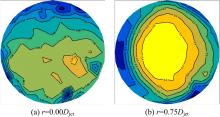
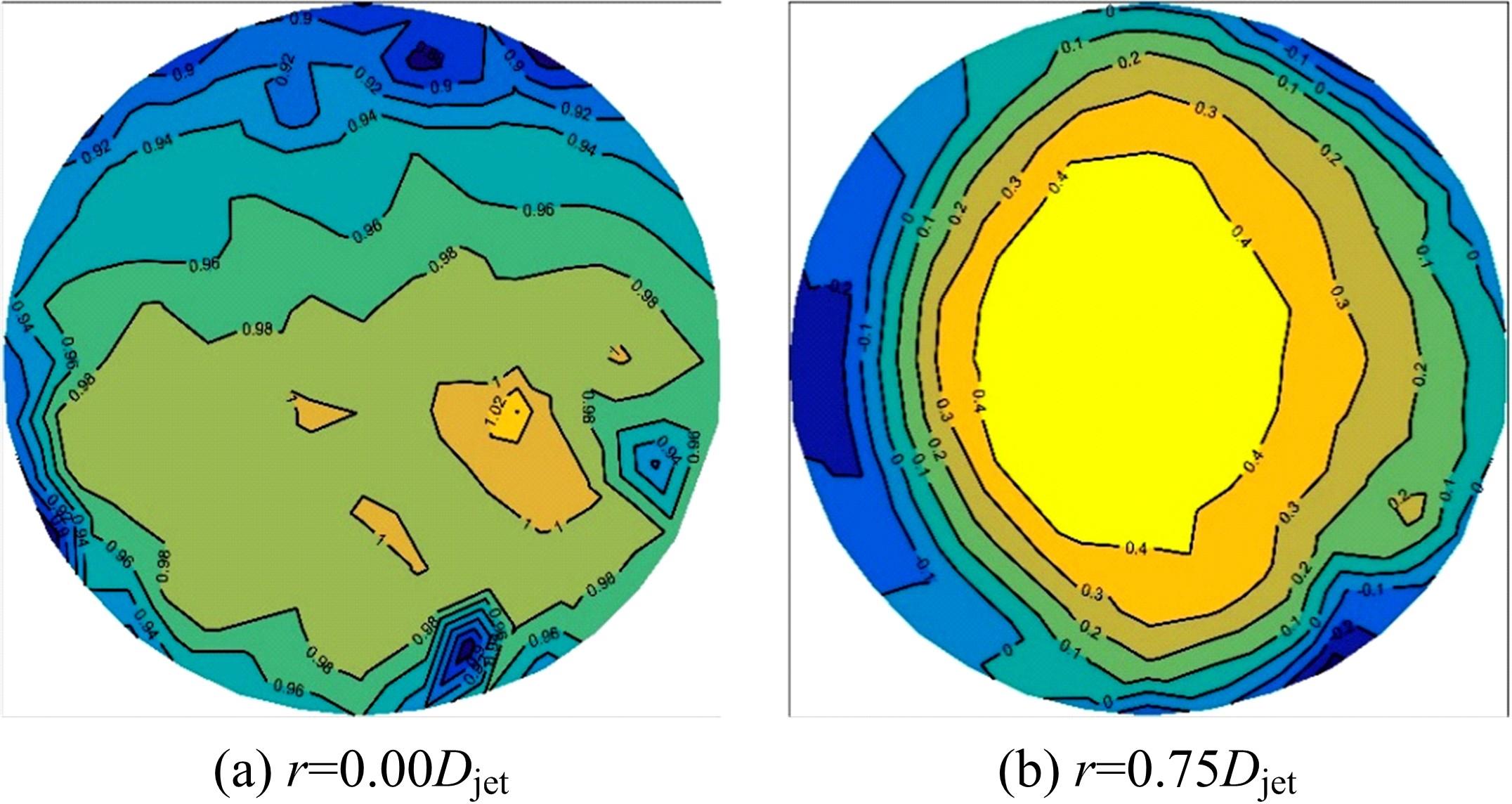
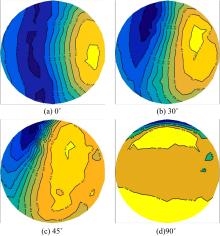
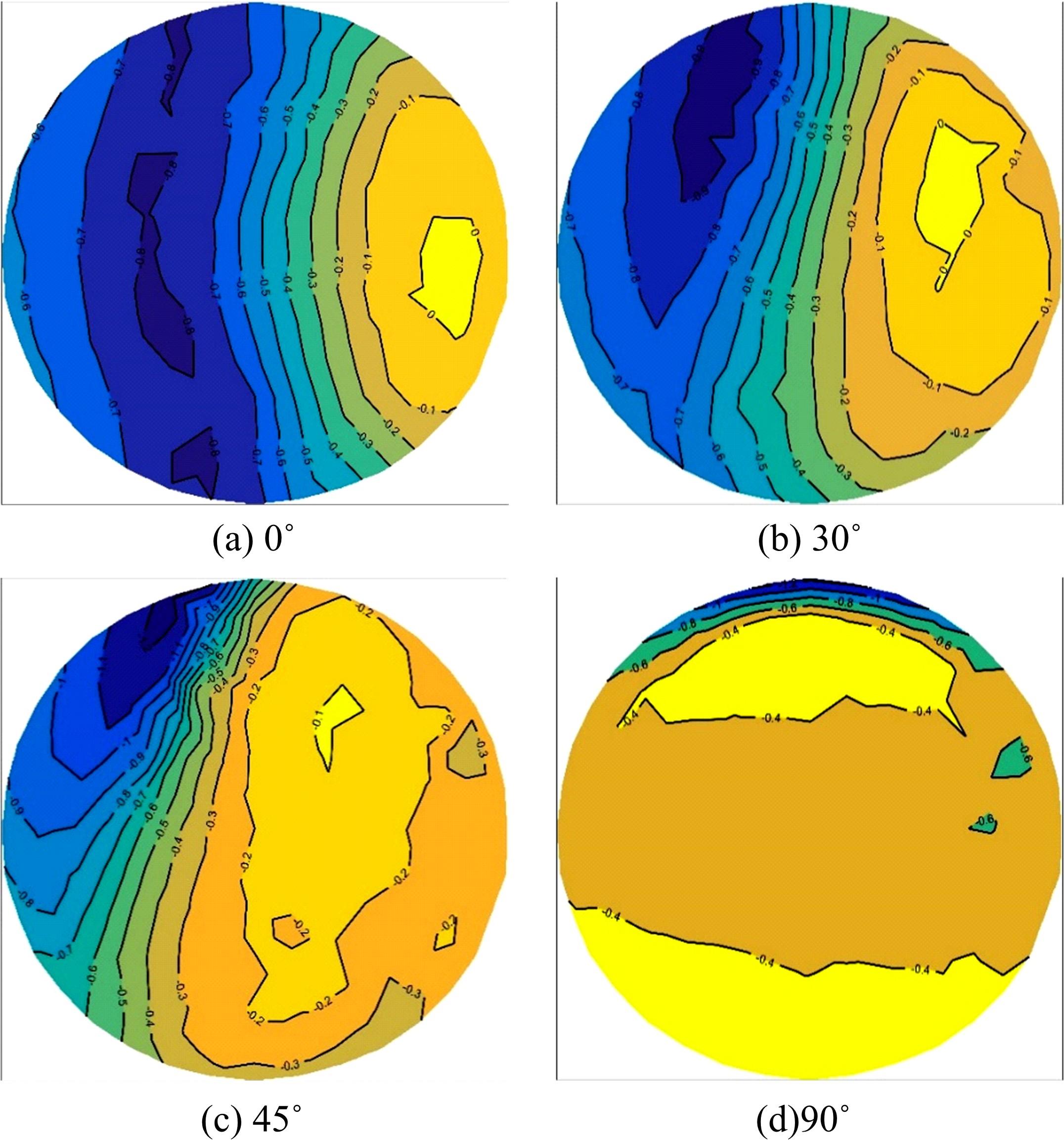
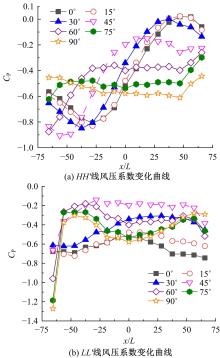
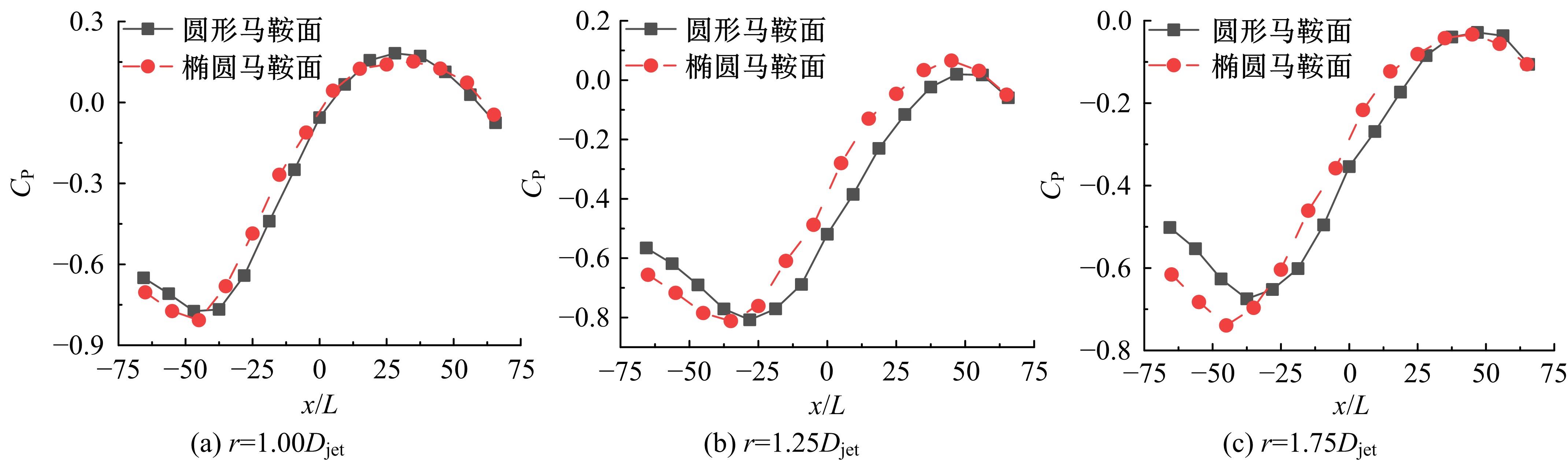
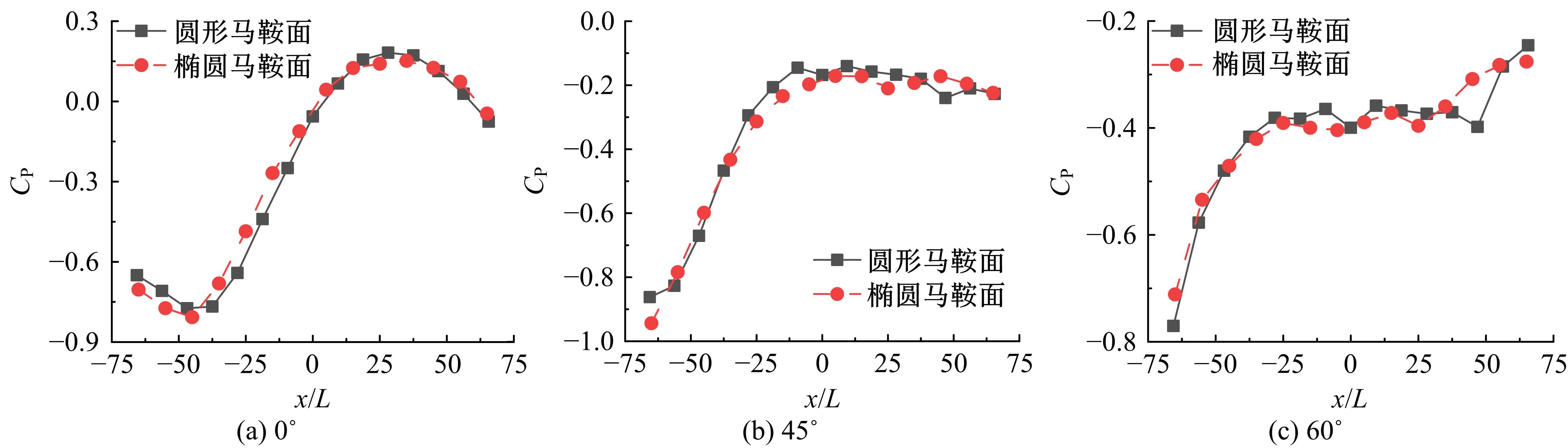
设计并制作了圆形马鞍面大跨屋盖结构缩尺模型,利用冲击射流装置展开下击暴流模拟试验,根据不同径向距离和风向角设计试验工况,得出屋盖风压系数,探究了不同径向距离和风向角下圆形马鞍面屋盖的风压分布规律。通过改变建筑宽度设计椭圆形马鞍面屋盖,并分析了两种屋盖风压的异同点。得出结论如下:①圆形马鞍面屋盖的高点连线上的最大风压随径向距离的增加先增加后减小,在1.25Djet时达最大,其风压系数为-0.81;②风向角对圆形马鞍面低点区域的风压影响很大,当来流正对低点区域时,迎风面风压增长较快,且变化梯度很大;③椭圆形马鞍面屋盖受建筑物狭长形态的影响,其高点连线上距屋盖中心1/3L处及低点迎风区的测点风压略大于圆形,结构设计时需对这些区域进行加强。
中图分类号:
- TU312
| 1 | 孔锋, 郭君, 王一飞, 等. 近56年来中国雷暴日数的时空分异特征[J]. 灾害学, 2018, 33(3) :87-95. |
| Guo Feng, Guo Jun, Wang Yi-fei, et al. Spatial and temporal variation characteristics of thunderstorm days in china in recent 56 years[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2018, 33(3): 87-95. | |
| 2 | Proctor F H. Numerical simulations of an isolated microburst. Part i: dynamics and structure[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1988, 45(21): 3137-3160. |
| 3 | 陈勇, 崔碧琪, 彭志伟, 等. 球壳型屋盖在冲击风作用下的抗风设计参数及CFD分析[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2012, 30(4): 456-463. |
| Chen Yong, Cui Bi-qi, Peng Zhi-wei, et al. Wind-resistant design parameters and CFD analysis of spherical roof subjected to thunderstorm downbursts[J]. Acta Aerodynamics Sinica, 2012, 30(4): 456-463. | |
| 4 | Jesson M, Sterling M, Letchford C W, et al. Aerodynamic forces on generic buildings subject to transient, downburst-type winds[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2015, 137: 58-68. |
| 5 | 方智远, 李正良, 汪之松.下击暴流作用下不同深宽比的高层建筑风荷载[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 49(3): 488-494. |
| Fang Zhi-yuan, Li Zheng-liang, Wang Zhi-song. Wind loads of high-rise buildings with various aspect ratios in downburst wind[J]. Journal of Southeast University(Natural Science Edition), 2019, 49(3): 488-494. | |
| 6 | 汪之松, 江鹏, 武彦君, 等. 地表粗糙度对高层建筑下击暴流风荷载特性影响的试验研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2019, 38(9): 184-191, 230. |
| Wang Zhi-song, Jiang Peng, Wu Yan-jun, et al. Tests for effects of terrain roughness on wind load characteristics of a high-rise building under downburst[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2019, 38(9): 184-191, 230. | |
| 7 | 刘志文, 陈以荣, 辛亚兵, 等. 基于边界层风洞的下击暴流稳态风场特性数值模拟[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 47(7): 10-20. |
| Liu Zhi-wen, Chen Yi-rong, Xin Yan-bing, et al. Numerical simulation on steady wind field characteristics of downburst based on atmosphere boundary layer wind tunnel[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2020, 47(7): 10-20. | |
| 8 | 钟永力, 晏致涛, 游溢, 等. 平面壁面射流风场作用下建筑物表面风压数值模拟[J]. 湖南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 46(1): 47-54. |
| Zhong Yong-li, Yan Zhi-tao, You Yi, et al. Numerical simulation of mean wind pressure distribution on building surface under plane wall jet wind field[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences), 2019, 46(1): 47-54. | |
| 9 | 姚勇, 苏留锋, 李明, 等. 下击暴流作用下双面球壳型屋面风载特性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(3): 615-625. |
| Yao Yong, Su Liu-feng, Li Ming, et al. Wind load characteristics of double-sided spherical shell roof under downburst[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 615-625. | |
| 10 | 孙晓颖, 武岳, 沈世钊. 鞍形屋盖平均风压分布特性的数值模拟研究[J]. 工程力学, 2006(10): 7-14. |
| Sun Xiao-ying, Wu Yue, Shen Shi-zhao. Numerical simulation of mean wind pressure distribution on saddle roof[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2006(10): 7-14. | |
| 11 | Chen L, Letchford C W. Multi-scale correlation analysis of two lateral profiles of full scale downburst wind speeds[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2006, 94(9): 675-696. |
| [1] | 姚勇,苏留锋,李明,褚云朋,黄汉杰. 下击暴流作用下双面球壳型屋面风载特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 615-625. |
| [2] | 匡亚川,宋哲轩,刘胤虎,莫小飞,伏亮明,罗时权. 新型装配式双舱综合管廊力学性能试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 596-603. |
| [3] | 樊学平,杨光红,尚志鹏,赵小雄,肖青凯,刘月飞. 考虑适用性的大跨桥梁主梁动态可靠性融合预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 144-153. |
| [4] | 刘福寿,魏琦,徐文婷,谭国金. 基于弹性波传播和谱单元法的桁架结构损伤检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2087-2095. |
| [5] | 樊学平,杨光红,肖青凯,刘月飞. 大跨桥梁主梁失效概率分析的最优R-Vine Copula[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1296-1305. |
| [6] | 于江,赵志浩,秦拥军. 基于声发射和分形的钢筋混凝土受剪梁损伤[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 620-630. |
| [7] | 熊二刚,徐涵,谭赐,王婧,丁若愚. 基于弹塑性应力场理论的钢筋混凝土梁受剪承载力[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 259-267. |
| [8] | 赖晨光,王擎宇,胡博,文凯平,陈彦宇. 静气动弹性影响下带小翼汽车尾翼的设计与优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 399-407. |
| [9] | 樊学平,屈广,刘月飞. 应用新数据同化算法的桥梁极值应力预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 572-580. |
| [10] | 杨德磊,童乐为. 支管受轴向受拉工况下CHS-CFSHS T型节点应力集中系数计算公式[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1891-1899. |
| [11] | 周华,杨志刚,朱晖. 基于整车风洞试验的MIRA车型数值计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1043-1053. |
| [12] | 戴岩, 聂少锋, 周天华. 带环梁的方钢管约束钢骨混凝土柱-钢梁节点滞回性能有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1426-1435. |
| [13] | 杨昕卉, 薛伟, 郭楠. 钢板增强胶合木梁的抗弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 468-477. |
| [14] | 王少杰, 徐赵东, 李舒, 王凯洋,Dyke Shirley J. 基于应变监测的连续梁支承差异沉降识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1090-1096. |
| [15] | 宿晓萍,王清. 复合盐浸-冻融-干湿多因素作用下的混凝土腐蚀破坏[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 112-120. |
|
||