吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (12): 2827-2838.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210415
基于优化堆叠降噪自编码器的滚动轴承故障诊断
- 1.兰州理工大学 电气工程与信息工程学院,兰州 730050
2.兰州理工大学 甘肃省工业过程先进控制重点实验室,兰州 730050
3.兰州理工大学 国家级电气与控制工程实验教学中心,兰州 730050
Fault diagnosis of rolling bearing based on optimized stacked denoising auto encoders
Xian-jun DU1,2,3( ),Liang-liang JIA1
),Liang-liang JIA1
- 1.College of Electrical and Information Engineering,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
2.Key Laboratory of Gansu Advanced Control for Industrial Processes,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
3.National Demonstration Center for Experimental Electrical and Control Engineering Education,Lanzhou University of Technology,Lanzhou 730050,China
摘要:
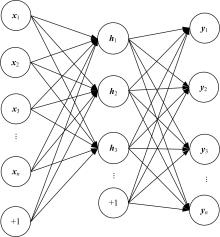
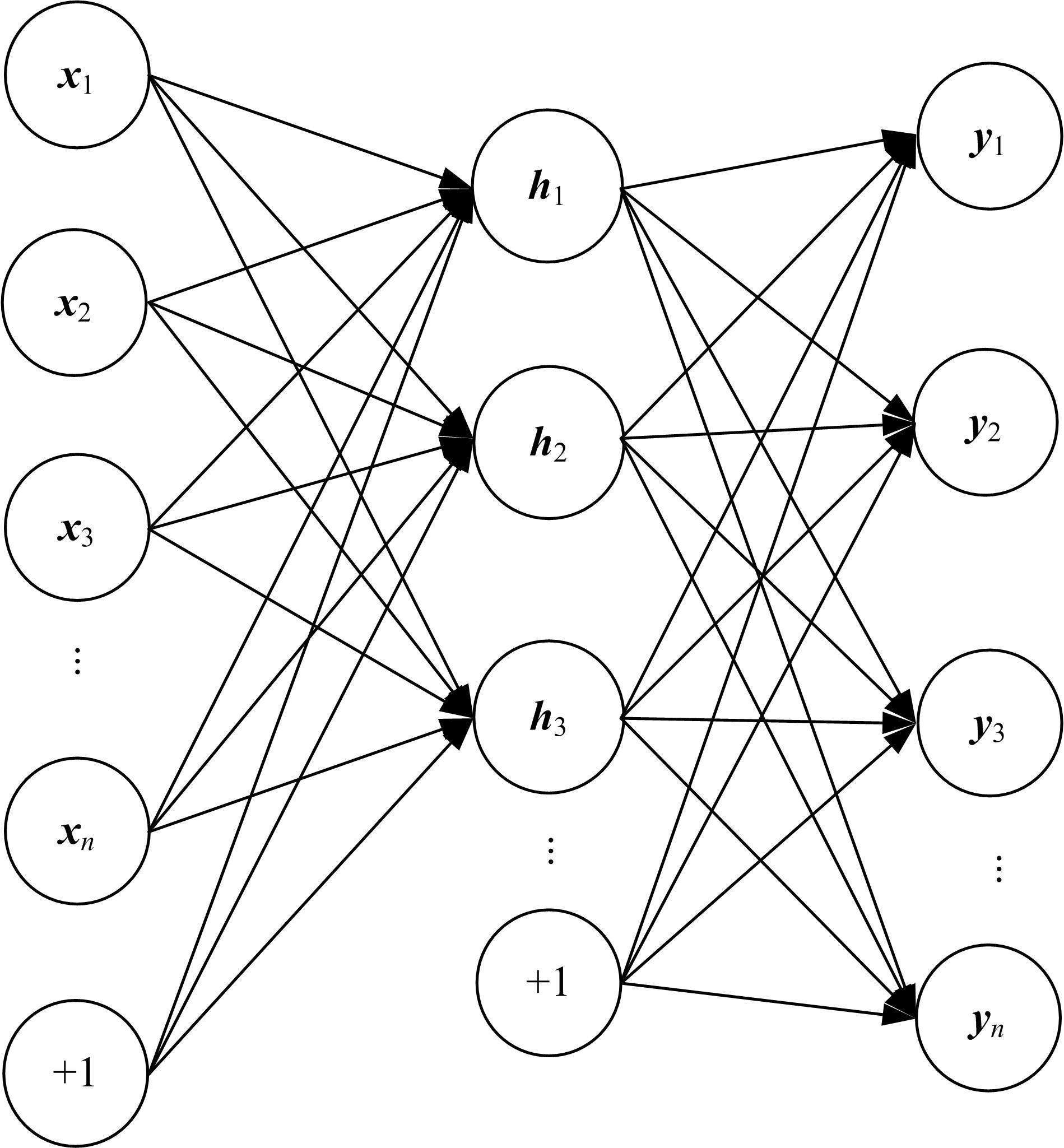
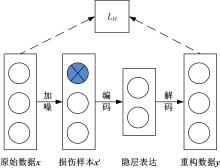
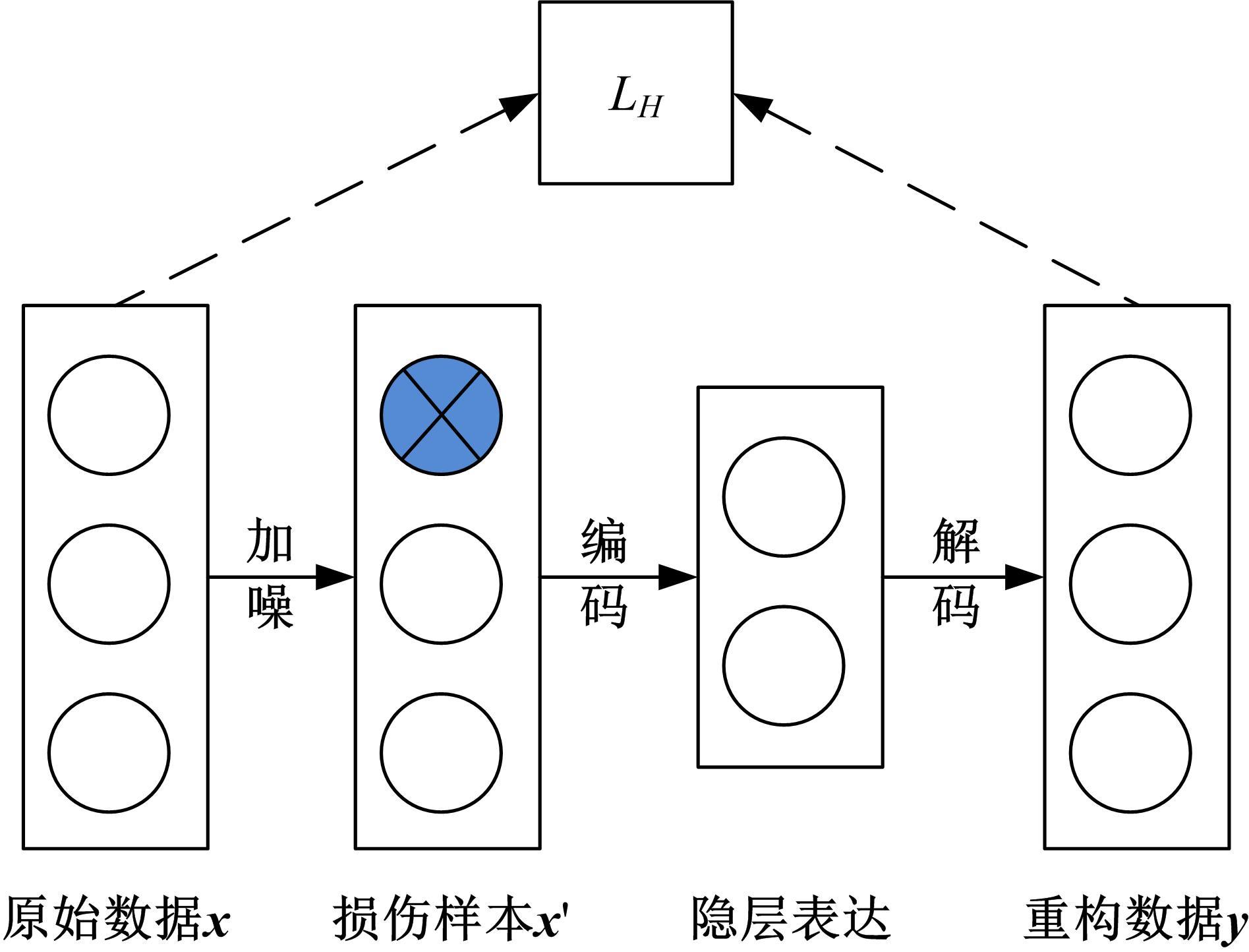
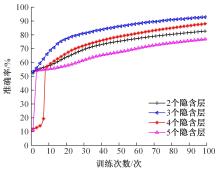
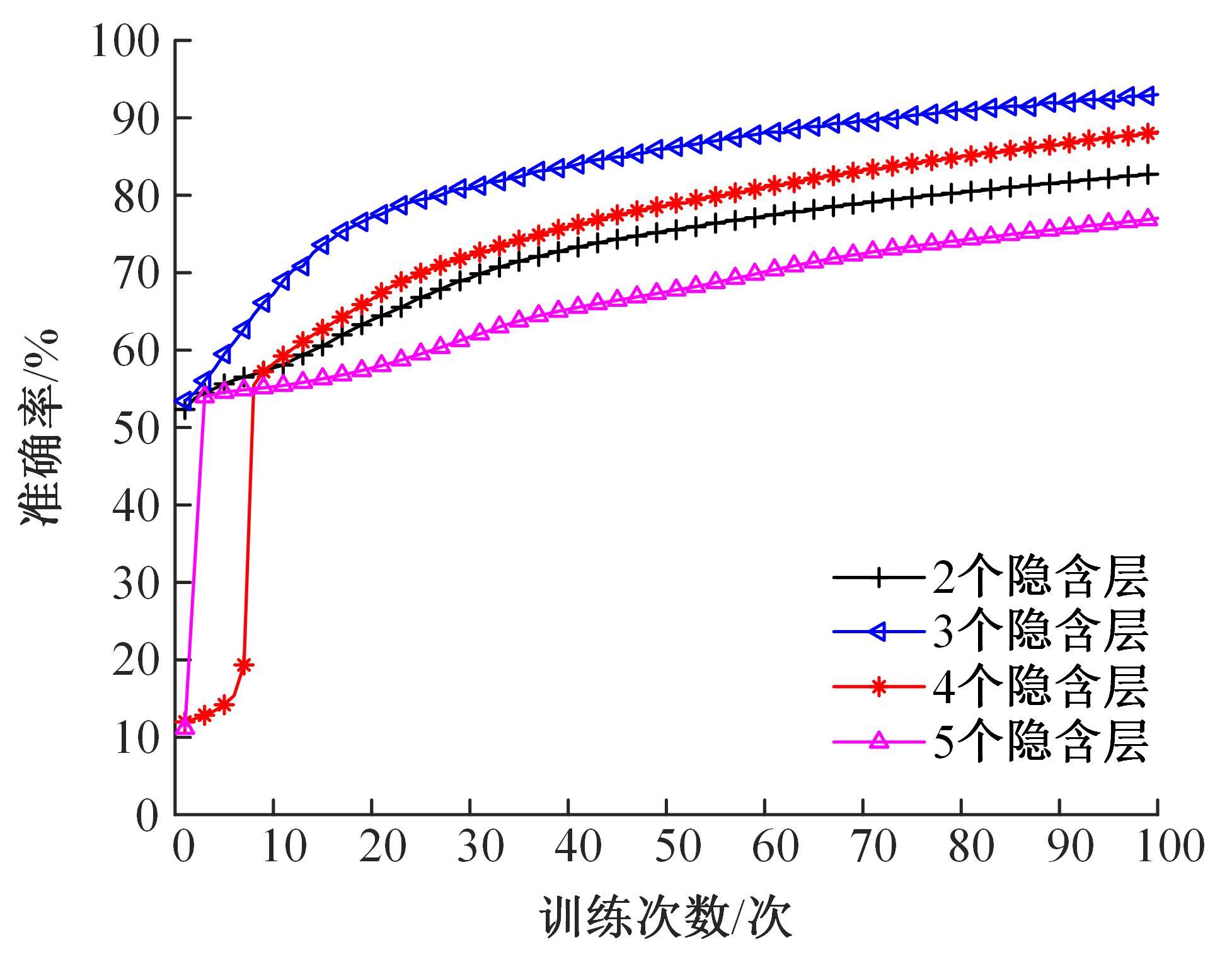
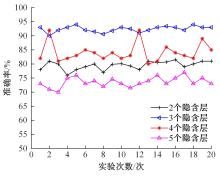
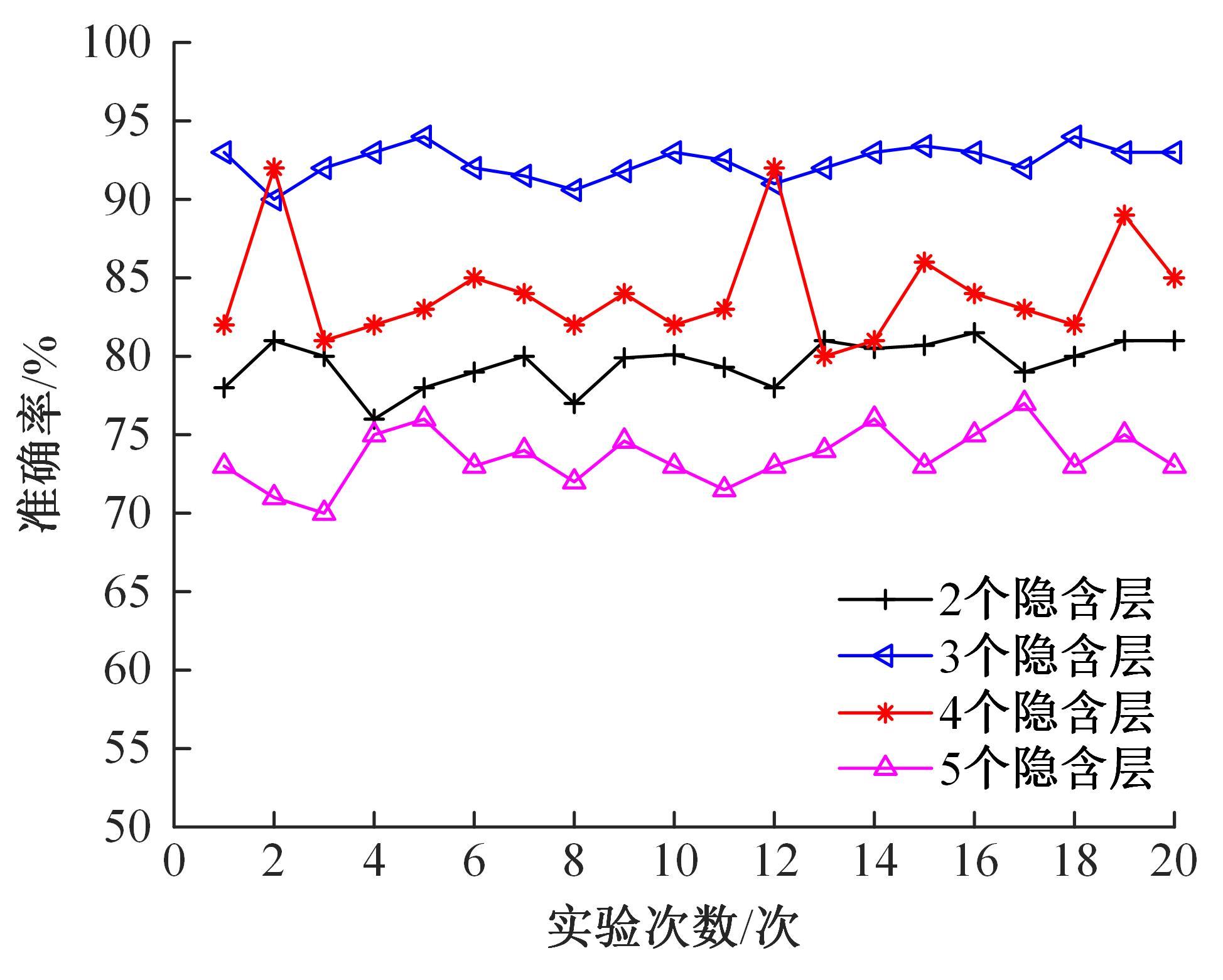
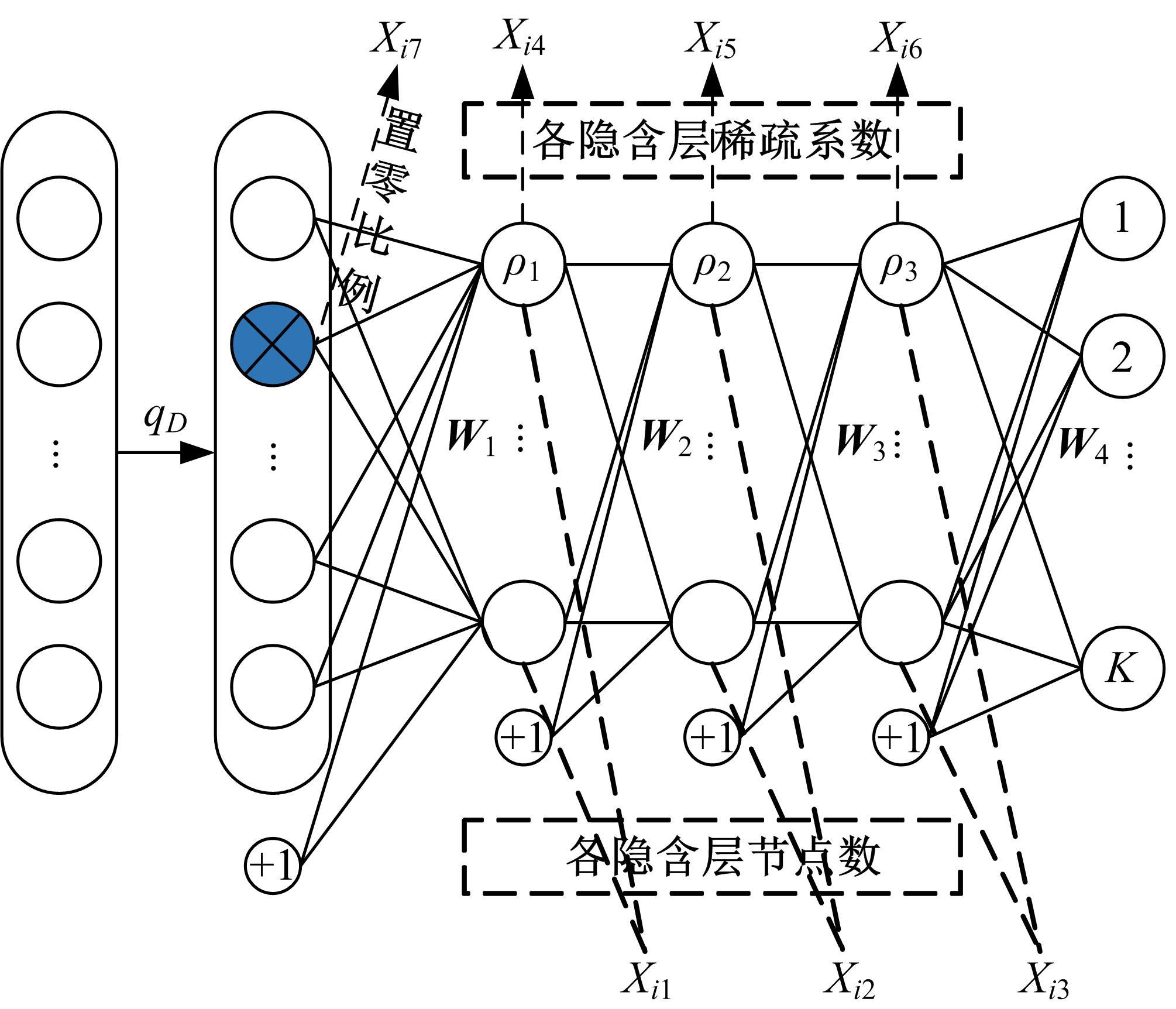
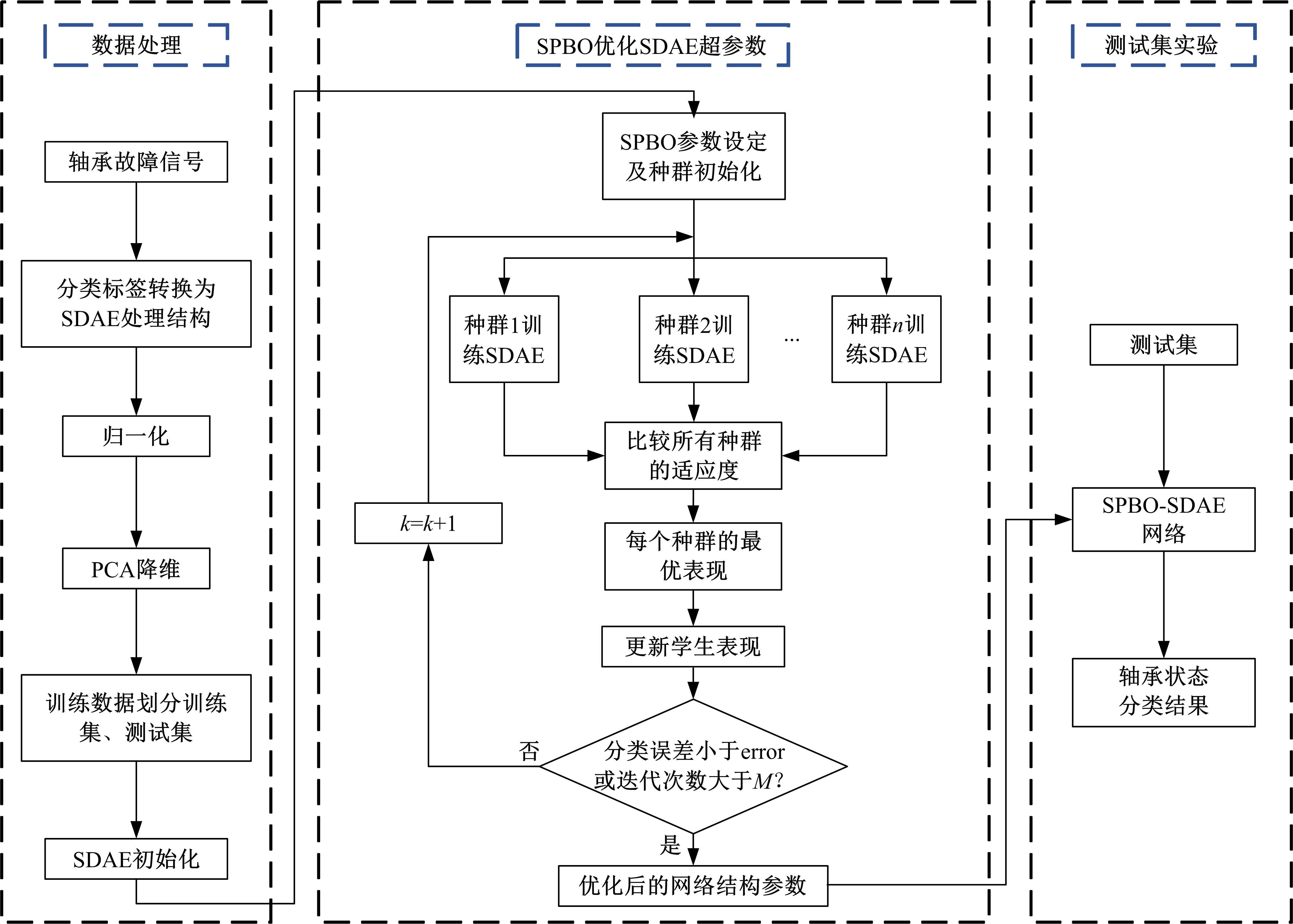
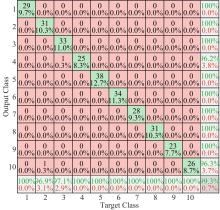
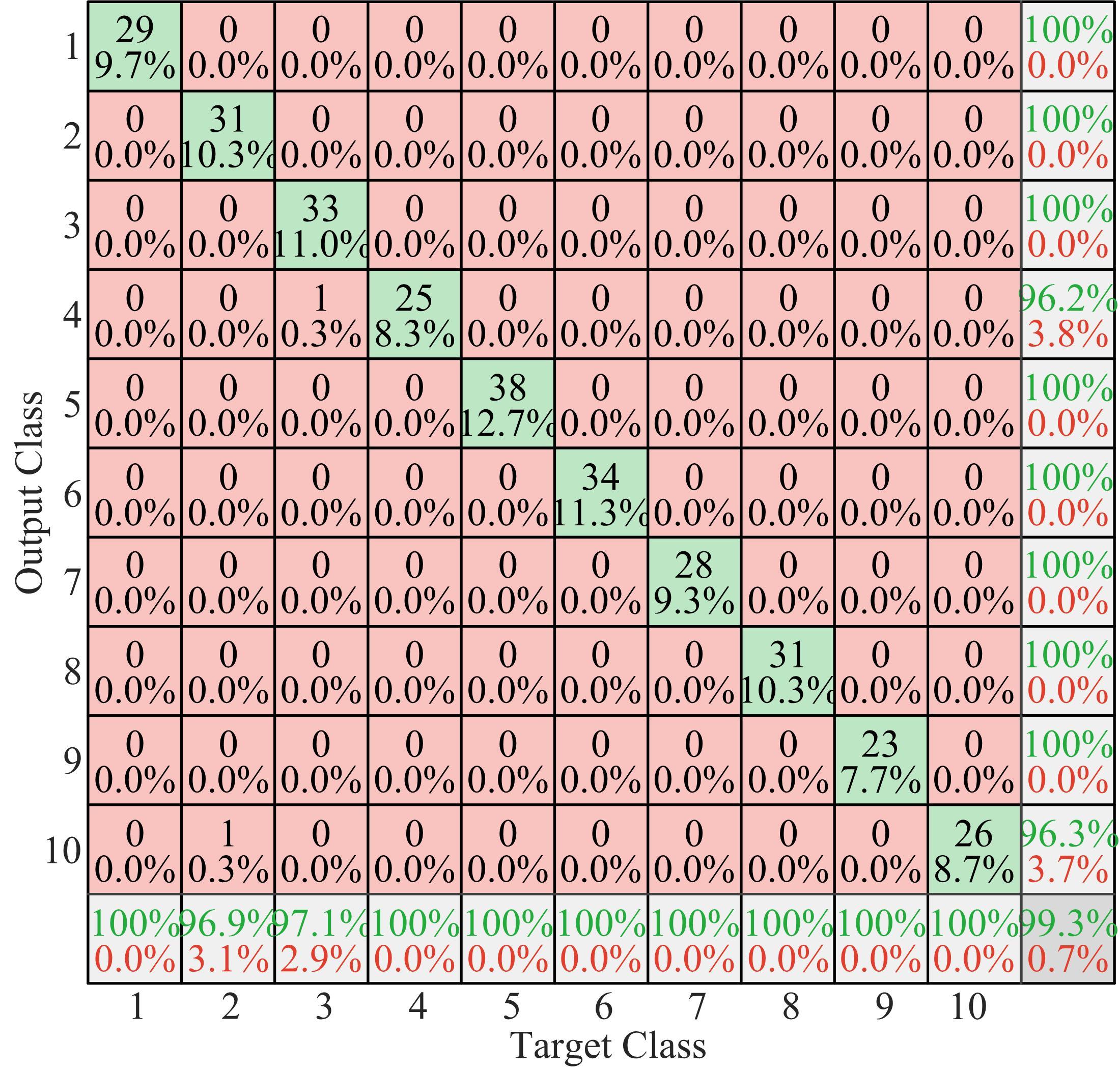
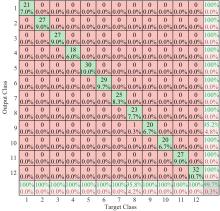
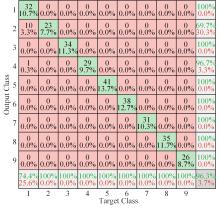
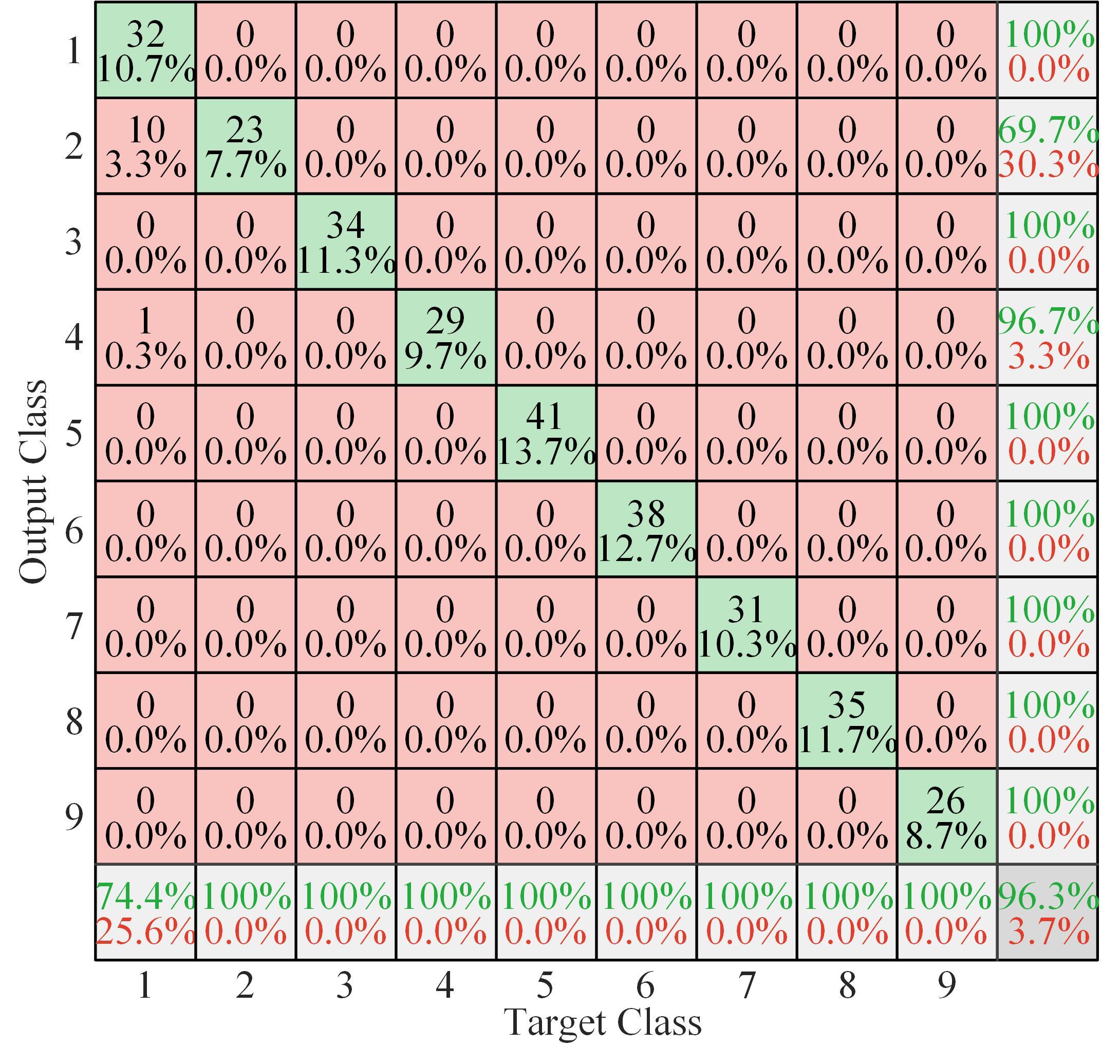
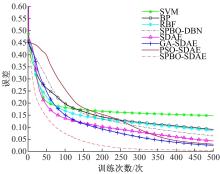
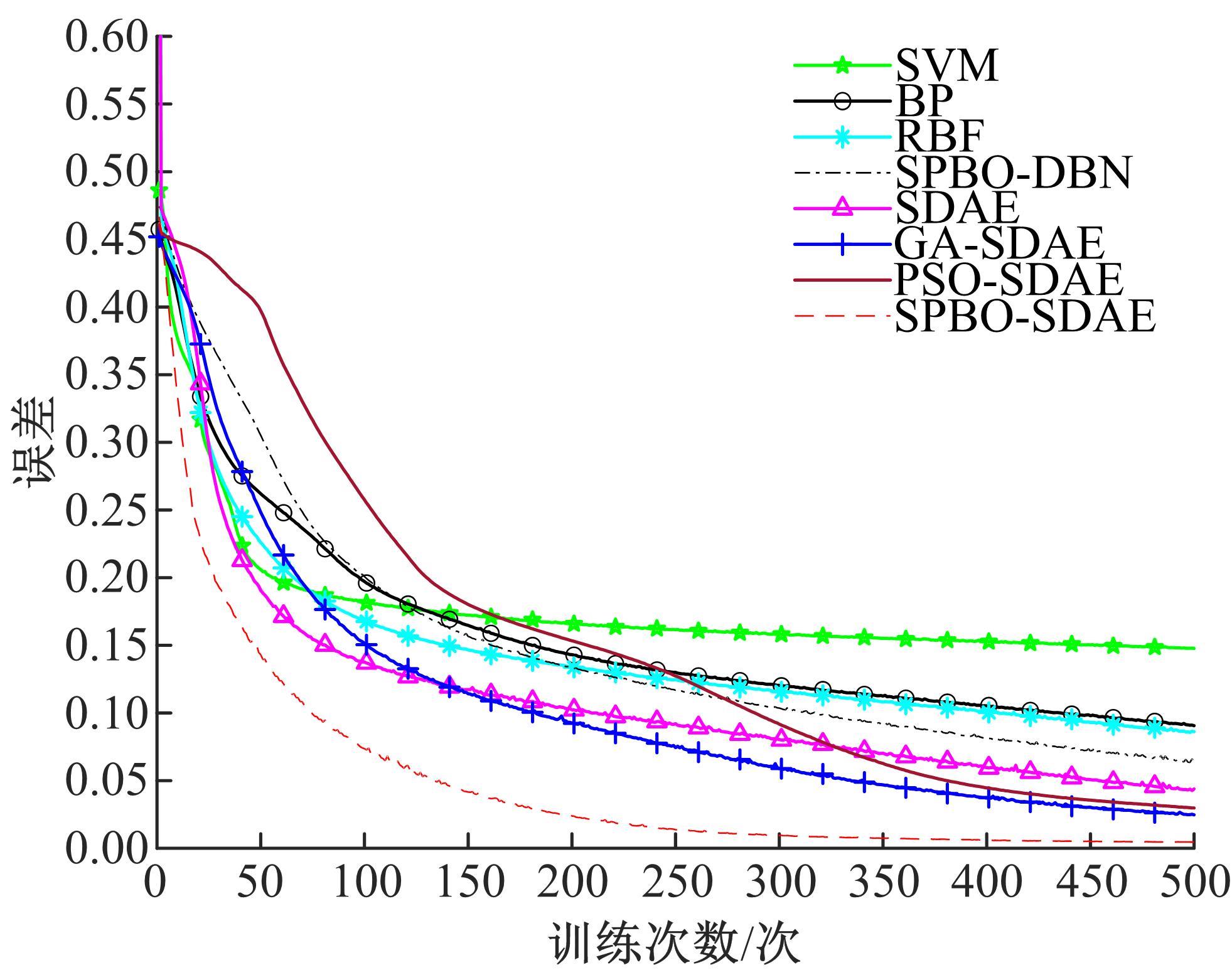
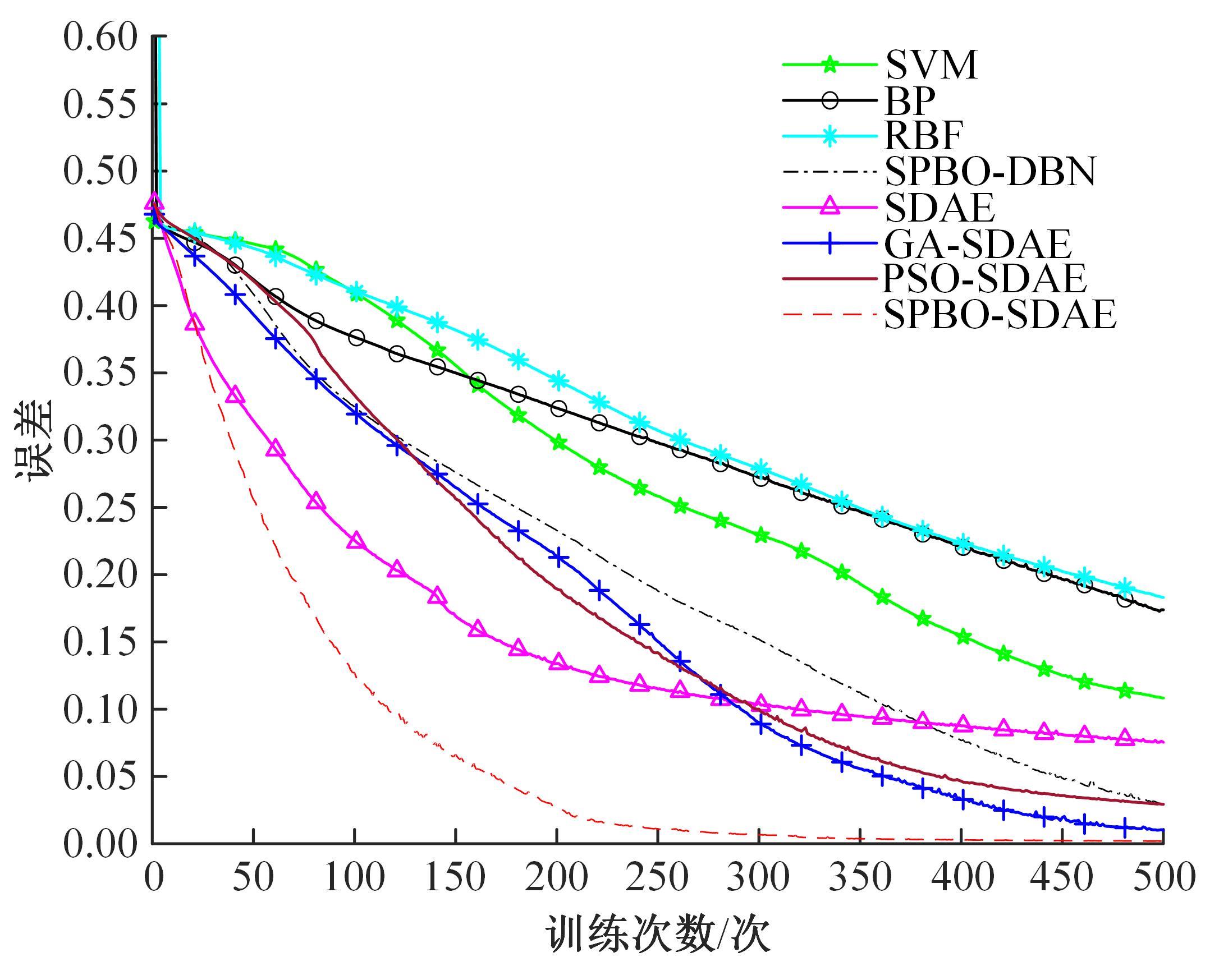
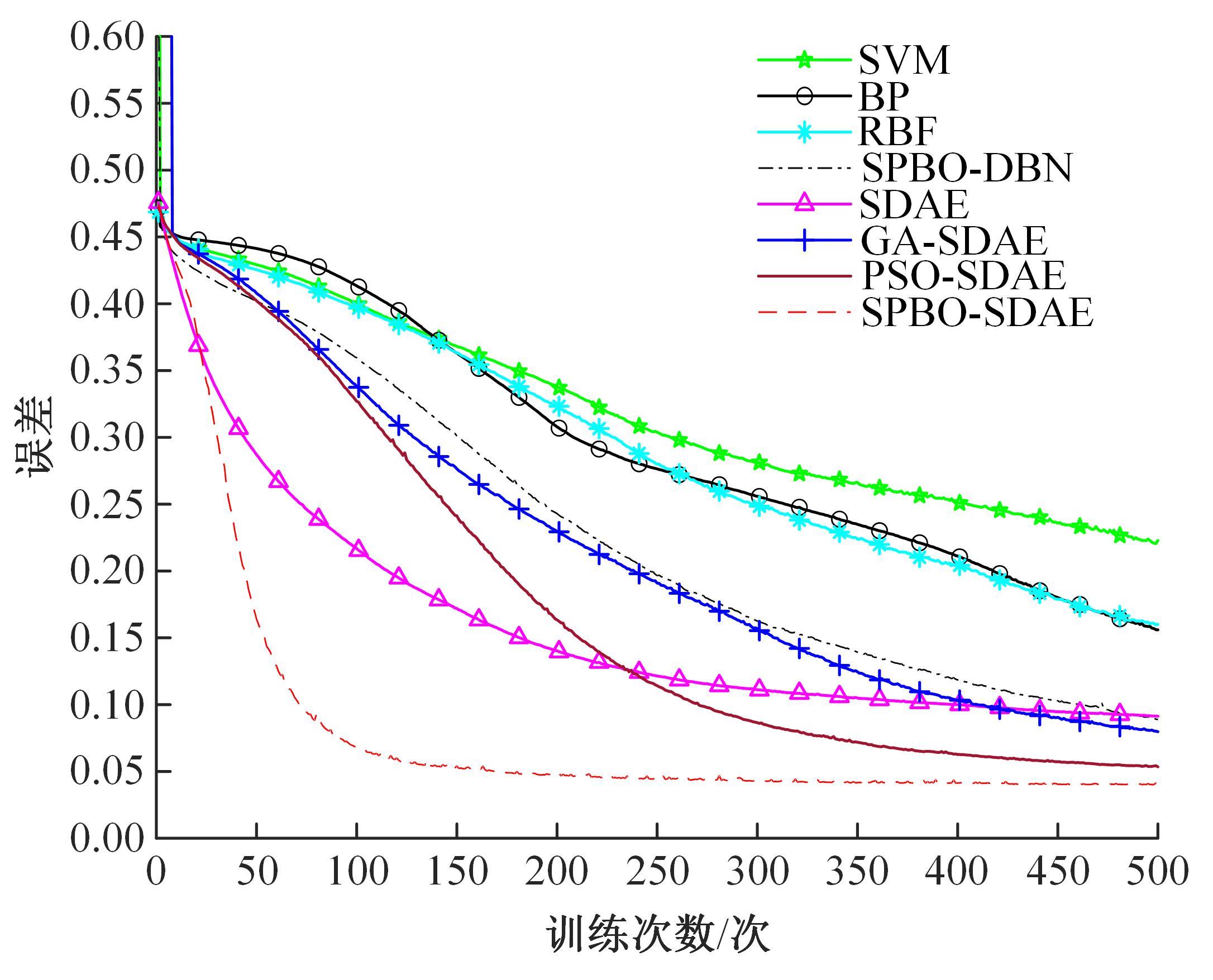
针对深度神经网络用于滚动轴承故障诊断时,网络隐含层层数、各隐含层节点数、稀疏系数以及输入数据置零比例等超参数会直接影响网络诊断性能的问题,提出了一种优化改进堆叠降噪自编码器(SDAE)的滚动轴承故障智能诊断方法。使用学生心理优化算法(SPBO)对降噪自编码器(DAE)网络的超参数进行自适应选取来确定SDAE网络的最优结构和参数,据此提取具有更强表征力的故障状态特征表示,输入到soft-max分类器实现滚动轴承运行工况的精确诊断。使用3个开源数据集对所提网络的性能进行验证,实验结果表明,基于SPBO-SDAE网络的诊断方法在特征有效提取、诊断速度以及故障诊断准确率方面均优于支持向量机(SVM)、反向传播(BP)神经网络、径向基(RBF)神经网络、SDAE网络、SPBO优化后的深度置信网络(DBN)、遗传算法(GA)优化后的SDAE网络以及粒子群算法(PSO)优化后的SDAE网络。
中图分类号:
- TP277
| 1 | Shifat T A, Hur J W. ANN assisted multi sensor information fusion for BLDC motor fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 9429-9441. |
| 2 | Li J, Yao X, Wang X, et al. Multiscale local features learning based on BP neural network for rolling bearing intelligent fault diagnosis[J]. Measurement, 2019, 153: No.107419. |
| 3 | Zhou J, Wang F, Zhang C, et al. Evaluation of rolling bearing performance degradation using wavelet packet energy entropy and RBF neural network[J]. Symmetry, 2019, 11(8): 1064-1074. |
| 4 | 张鑫, 郭顺生, 李益兵, 等. 基于拉普拉斯特征映射和深度置信网络的半监督故障识别[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(1): 83-95. |
| Zhang Xin, Guo Shun-sheng, Li Yi-bing, et al. Semi-supervised fault identification based on laplacian feature map and deep confidence network[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(1): 83-95. | |
| 5 | 文成林, 吕菲亚. 基于深度学习的故障诊断方法综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 234-248. |
| Wen Cheng-lin, Fei-ya Lü. Review of fault diagnosis methods based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 234-248. | |
| 6 | Han S, Oh S, Jeong J. Bearing fault diagnosis based on multiscale convolutional neural network using data augmentation[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2021, 2021(1): 1-14. |
| 7 | Feng J, Yao Y, Lu S, et al. Domain knowledge-based deep-broad learning framework for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 68(4): 3454-3464. |
| 8 | Xing S, Lei Y, Wang S, et al. Distribution-invariant deep belief network for intelligent fault diagnosis of machines under new working conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 68(3): 2617-2625. |
| 9 | He J, Ouyang M, Yong C, et al. A novel intelligent fault diagnosis method for rolling bearing based on integrated weight strategy features learning[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(6): No.1774. |
| 10 | Liu S, Jiang H, Wu Z, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis using variational autoencoding generative adversarial networks with deep regret analysis[J]. Measurement, 2021, 168: No.108371. |
| 11 | Xu F, Tse P W. Automatic roller bearings fault diagnosis using DSAE in deep learning and CFS algorithm[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23(13): 5117-5128. |
| 12 | Shao Hai-dong, Jiang Hong-kai, Li Xing-qiu, et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis of rolling bearing using deep wavelet auto-encoder with extreme learning machine[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 140(15): 1-14. |
| 13 | Shin H C, Orton M R, Collins D J, et al. Stacked autoencoders for unsupervised feature learning and multiple organ detection in a pilot study using 4D patient data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 35(8): 1930-1943. |
| 14 | 雷亚国, 贾峰, 周昕, 等. 基于深度学习理论的机械装备大数据健康监测方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2015, 51(21): 49-56. |
| Lei Ya-guo, Jia Feng, Zhou Xin, et al. Big data health monitoring method of mechanical equipment based on deep learning theory[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(21): 49-56. | |
| 15 | Suk H I, Lee S W, Shen D. Latent feature representation with stacked auto-encoder for AD/MCI diagnosis[J]. Brain Structure and Function, 2015, 220(2): 841-859. |
| 16 | Hong C, Yu J, Wan J, et al. Multimodal deep autoencoder for human pose recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 5659-5670. |
| 17 | Vincent P, Larochelle H, Lajoie I, et al. Stacked denoising autoencoders:learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11(12): 3371-3408. |
| 18 | Arablouei R, Werner S, Doğançay K. Analysis of the gradient-descent total least-squares adaptive filtering algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(5): 1256-1264. |
| 19 | Das B, Mukherjee V, Das D. Student psychology based optimization algorithm: a new population based optimization algorithm for solving optimization problems[J]. Advances in Engineering Software, 2020, 146: No.102804. |
| 20 | Ranaee V, Ebrahimzadeh A, Ghaderi R. Application of the PSO–SVM model for recognition of control chart patterns[J]. ISA Transactions, 2010, 49(4): 577-586. |
| 21 | Al-Faisal H R, Ahmad I, Salman A A, et al. Adaptation of population size in sine cosine algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 25258-25277. |
| 22 | Smith W A, Randall R B. Rolling element bearing diagnostics using the case western reserve university data: a benchmark study[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 64: 100-131. |
| 23 | Hasan B M. Current based condition monitoring of electromechanical systems. Model-free drive system current monitoring: faults detection and diagnosis through statistical features extraction and support vector machines classification[D]. Bradford: School of Engineering Design and Technology, University of Bradford, 2013. |
| 24 | Lee D, Siu V, Cruz R, et al. Convolutional neural net and bearing fault analysis[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Science (ICDATA). The Steering Committee of The World Congress in Computer Science, Computer Engineering and Applied Computing, Lavasa City, Pune, 2016: 194-200. |
| 25 | Zhang X, Li J, Cai Z, et al. Over-fitting suppression training strategies for deep learning-based atrial fibrillation detection[J]. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, 2021, 59(1): 165-173. |
| [1] | 欧阳丹彤,孙睿,田新亮,高博涵. 基于集合阻塞的不确定系统中传感器选择方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 547-554. |
| [2] | 周怡娜,董宏丽,张勇,路敬祎. 基于VMD去噪和散布熵的管道信号特征提取方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 959-969. |
| [3] | 罗巍,卢博,陈菲,马腾. 基于PSO-SVM及时序环节的数控刀架故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 392-399. |
| [4] | 高文志,王彦军,王欣伟,张攀,李勇,董阳. 基于卷积神经网络的柴油机失火故障实时诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 417-424. |
| [5] | 王进花,胡佳伟,曹洁,黄涛. 基于自适应变分模态分解和集成极限学习机的滚动轴承多故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 318-328. |
| [6] | 董绍江,朱朋,裴雪武,李洋,胡小林. 基于子领域自适应的变工况下滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 288-295. |
| [7] | 李国发,王彦博,何佳龙,王继利. 机电装备健康状态评估研究进展及发展趋势[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 267-279. |
| [8] | 曹洁,马佳林,黄黛麟,余萍. 一种基于多通道马尔可夫变迁场的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 491-496. |
| [9] | 邓飞跃,吕浩洋,顾晓辉,郝如江. 基于轻量化神经网络Shuffle⁃SENet的高速动车组轴箱轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 474-482. |
| [10] | 张龙,徐天鹏,王朝兵,易剑昱,甄灿壮. 基于卷积门控循环网络的齿轮箱故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
| [11] | 陈晓雷,孙永峰,李策,林冬梅. 基于卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆的稳定抗噪声滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 296-309. |
| [12] | 曹洁,何智栋,余萍,王进花. 数据不平衡分布下轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2523-2531. |
| [13] | 戴礼灿,代翔,崔莹,魏永超. 基于深度集成学习的社交网络异常数据挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2712-2717. |
| [14] | 陈菲,杨峥,张志成,罗巍. 面向无标签数据的旋转机械故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2514-2522. |
| [15] | 欧阳宁,李祖锋,林乐平. 基于多层次空⁃谱融合网络的高光谱图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2438-2446. |
|