吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (2): 685-691.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20191050
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于移动最小二乘法的稳健重构方法
- 福州大学 机械工程及自动化学院,福州 350116
Robust reconstruction method based on moving least squares algorithm
Tian-qi GU( ),Chen-jie HU,Yi TU,Shu-wen LIN
),Chen-jie HU,Yi TU,Shu-wen LIN
- College of Mechanical Engineering and Automation,Fuzhou University,Fuzhou 350116,China
摘要:
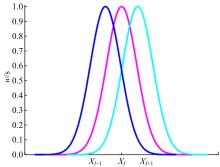
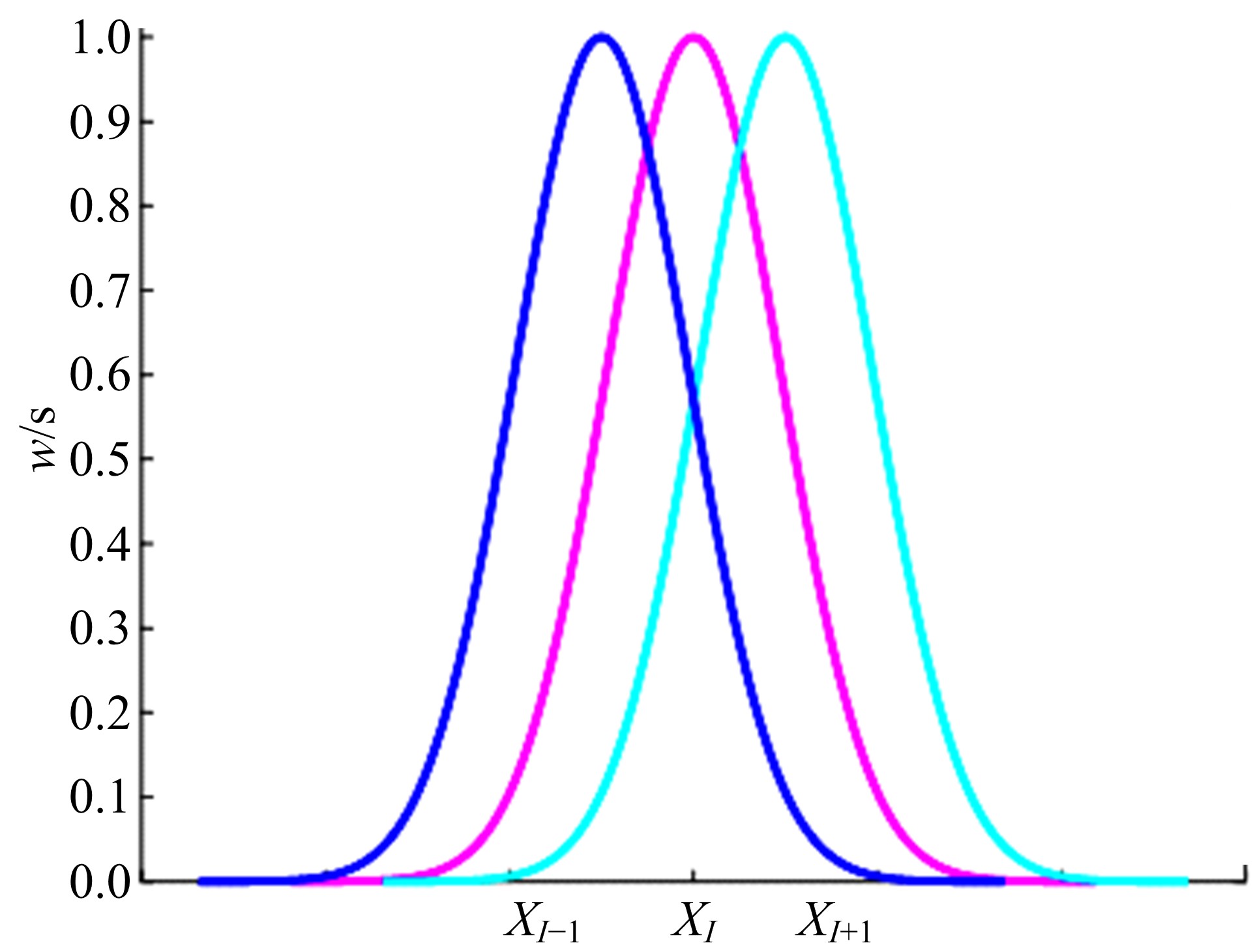
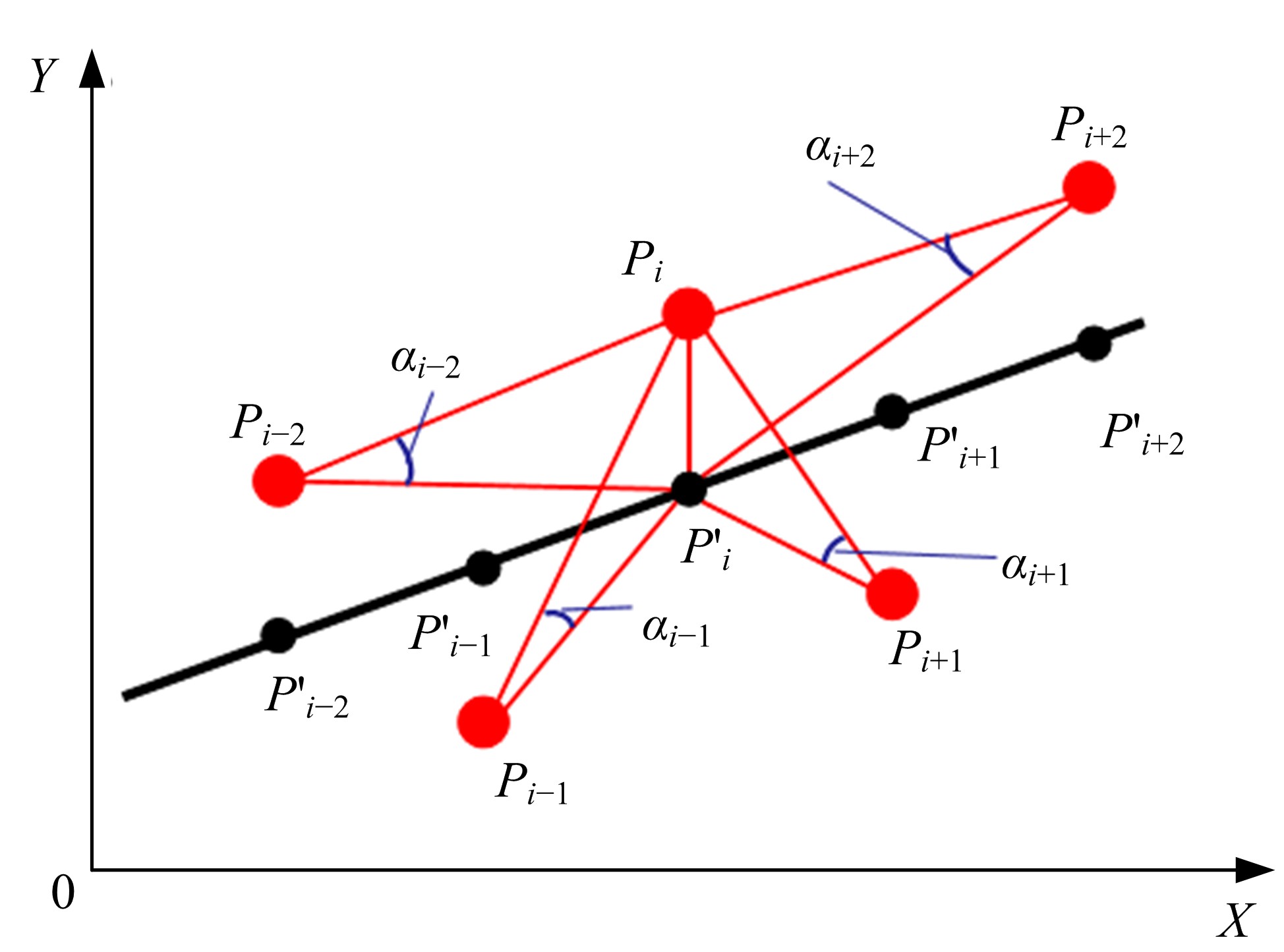
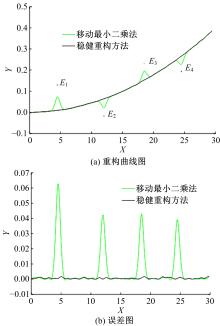
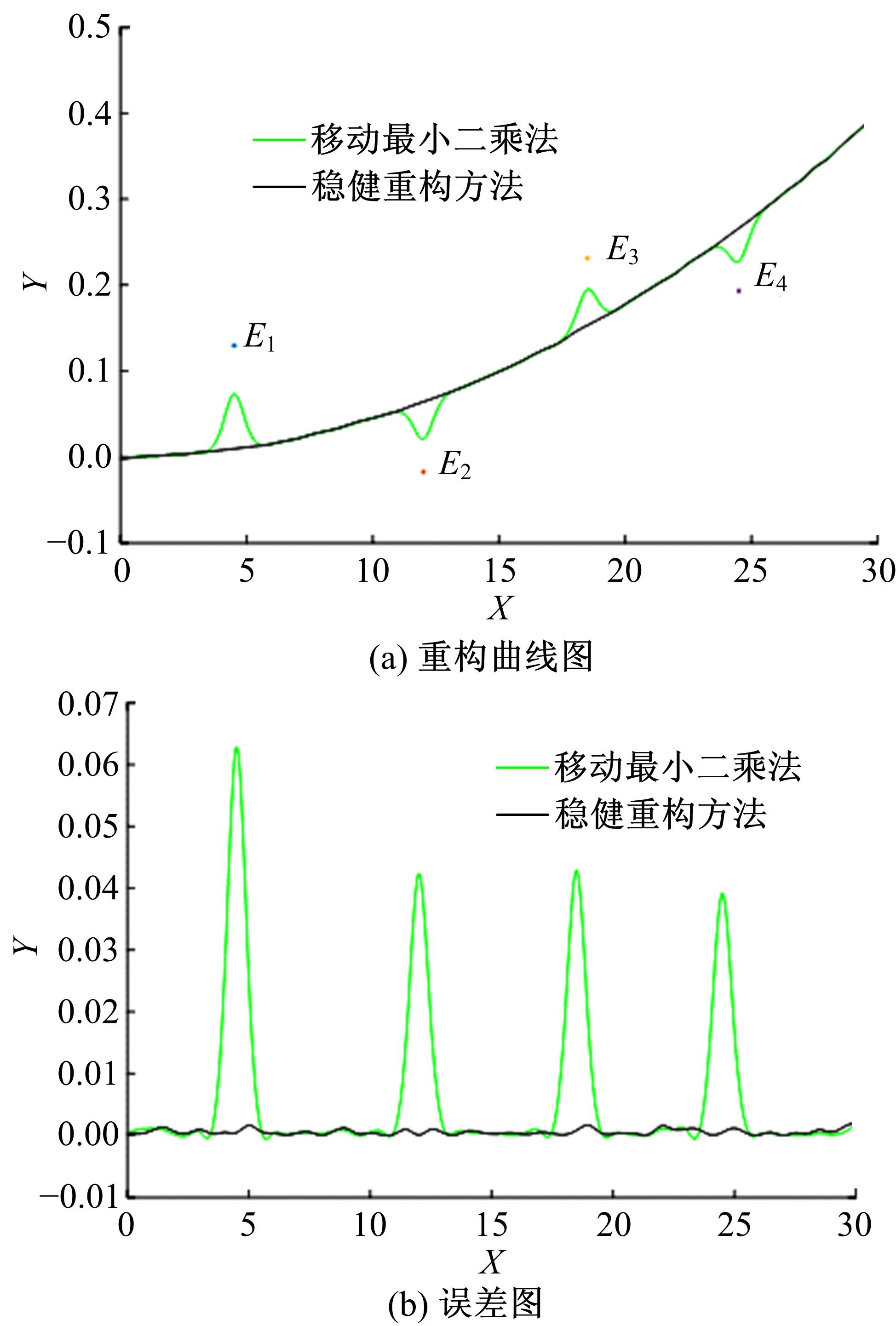
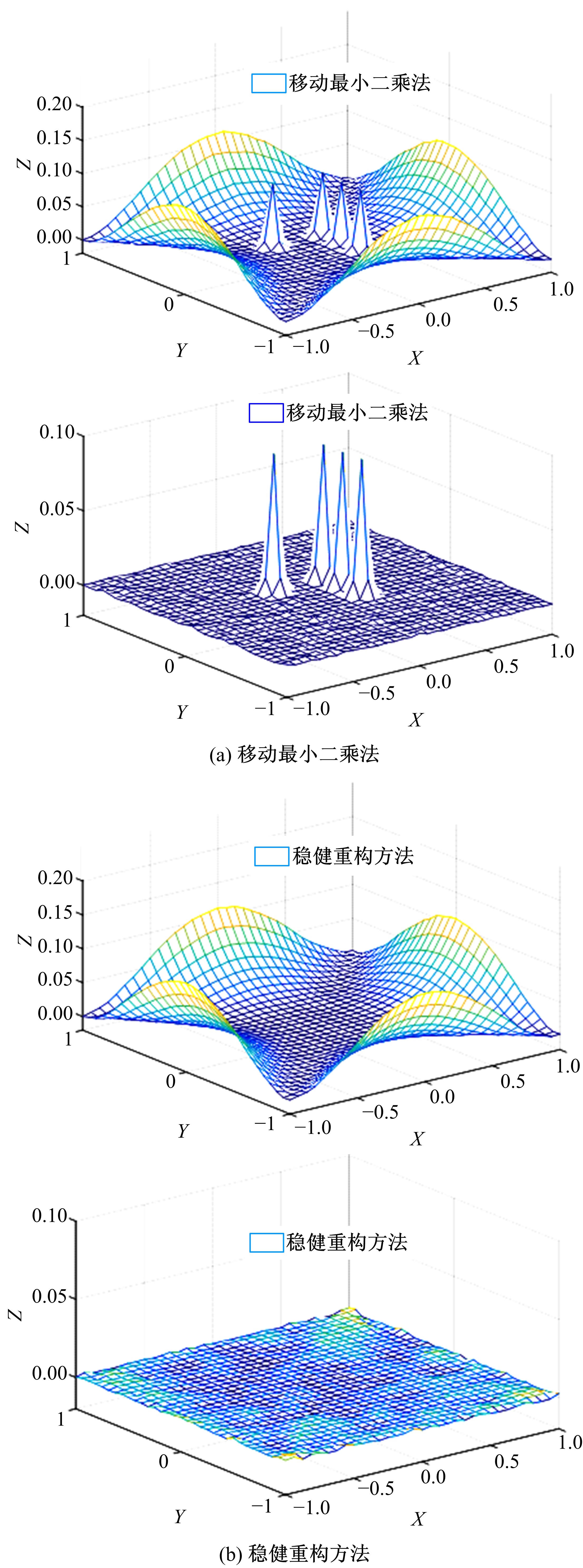
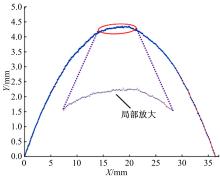
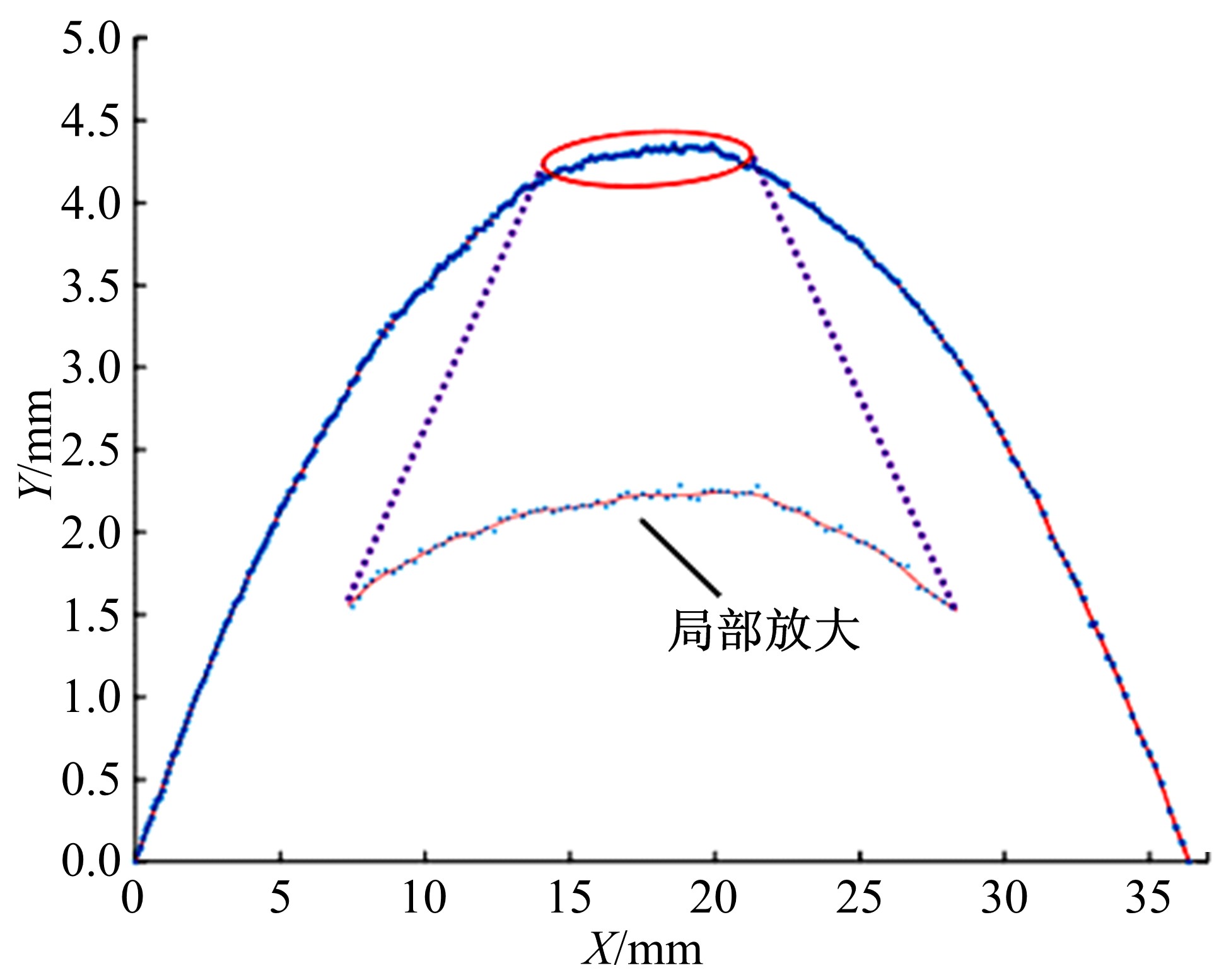
在实际工程问题中,由于人为或环境等外界因素的影响,通过仪器测量获得的数据,不可避免地会存在粗大误差,以某种方式偏离测量数据,导致数据重构的精度不稳定。针对包含粗大误差的测量数据,本文提出一种基于移动最小二乘法的稳健重构方法,该方法对支持域内节点采用最小二乘法进行拟合,将生成的拟合点根据引入的几何特征参数α,量化各节点的异常程度并剔除异常值。对支持域内的剩余节点采用加权最小二乘法确定局部拟合系数,移动支持域完成全域的曲线曲面重构。在每个支持域内仅剔除一个点,就能有效地处理多个粗大误差,且剔除过程无需主观地设定阈值或分配权重。数值模拟与测量实验结果表明:本文方法可有效剔除测量数据中的粗大误差,与传统移动最小二乘法相比,本文数值案例精度能提高60%以上,具有良好的重构稳健性。
中图分类号:
- TP391.9
| 1 | 张雄, 刘岩, 马上. 无网格法的理论及应用[J]. 力学进展, 2009, 39(1): 1-36. |
| Zhang Xiong, Liu Yan, Ma Shang. Theory and application of meshless method[J]. Progress in Mechanics, 2009, 39(1): 1-36. | |
| 2 | Lancaster P,Salkauskas K. Surfaces generated by moving least squares methods[J]. Mathematics Computation, 1981, 37: 141-158. |
| 3 | 韩加坤. 无网格法中MLS参数的选取[J]. 数学学习与研究, 2016(23): 145,147. |
| Han Jia-kun. Selection of MLS parameters in meshless method[J]. Mathematics Learning and Research, 2016(23): 145,147. | |
| 4 | 王青青, 李小林. 基于比例移动最小二乘近似的误差分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2017, 38(11): 1289-1299. |
| Wang Qing-qing, Li Xiao-lin. Error analysis based on proportional moving least square approximation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2017, 38(11): 1289-1299. | |
| 5 | Carlos Z. Good quality point sets and error estimates for moving least square approximations[J]. Applied Numerical Mathematics, 2003, 47(3): 575-585. |
| 6 | 袁占斌, 聂玉峰, 欧阳洁. 基于泰勒基函数的移动最小二乘法及误差分析[J]. 数值计算与计算机应用, 2012, 33(1): 25-31. |
| Yuan Zhan-bin, Nie Yu-feng, Jie Ou-yang. Moving least square method and error analysis based on taylor basis function[J]. Numerical Computing and Computer Applications, 2012, 33(1): 25-31. | |
| 7 | 顾天奇, 张雷, 冀世军, 等. 封闭离散点的曲线拟合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(2): 437-441. |
| Gu Tian-qi, Zhang Lei, Ji Shi-jun, et al. Curve fitting method for closed discrete points[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2015, 45(2): 437-441. | |
| 8 | 李世飞, 王平, 沈振康. 利用移动最小二乘法进行深度图像曲面拟合[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2010, 40(1): 229-233. |
| Li Shi-fei, Wang Ping, Shen Zhen-kang. Range image surface fitting via moving least squares methods[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2010, 40(1): 229-233. | |
| 9 | Liu D, Cheng Y M. The interpolating element-freeGalekin (IEFG) method for three-dimensional pote-ntial problems[J]. Engineering Analysis with Boun-Dary Elements, 2019, 108: 115-123. |
| 10 | Wang Q, Zhou W, Feng Y T, et al. An adaptive orthogonal improved interpolating moving least-square method and a new boundary element-free method[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2019, 353: 347-370. |
| 11 | 崔鑫, 闫秀天, 李世鹏. 保持特征的散乱点云数据去噪[J]. 光学精密工程, 2017, 25(12): 3169-3178. |
| Cui Xin, Yan Xiu-tian, Li Shi-peng. Denoising of scattered point cloud data with preserved features[J]. Optical Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(12): 3169-3178. | |
| 12 | Liu D L, Shi Y, Tian Y J, et al. Ramp loss least squares support vector machine[J]. Journal of Computation Science, 2016, 14: 61-68. |
| 13 | Suykens J A K, Brabanter J D, Lukas L, et al. Weighted least squares support vector m-achines: robustness and sparse approximation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2002, 48(1-4): 85-105. |
| 14 | Lin Y L, Hsieh J G, Jeng J H, et al. On least trimmed squares neural networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 161: 107-112. |
| 15 | Yang B, Shao Q M, Pan L, et al. A study on regularized weighted least square support vector classifier[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2018, 108: 48-55. |
| 16 | Chen C F, Yan C Q, Li Y Y. A robust weighted least squares support vector regression based on least trimmed squares[J]. Neurocomputing, 2015, 168: 941-946. |
| 17 | Wen W, Hao Z F, Yang X W. Robust least squares support vector machine based on recursive outlier elimination[J]. Soft Computing, 2010, 14(11): 1241-1251. |
| 18 | Grand R J, Habibullah A C, Adam W, et al. Modified moving least squares with polynomial bases for scattered data approximation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2015, 266: 893-902. |
| 19 | 李睿, 林海荣, 吴小燕. 基于稳健移动最小二乘法的点云数据拟合[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2017, 40(5): 122-124. |
| Li Rui, Lin Hai-rong, Wu Xiao-yan. Point cloud data fitting based on robust moving least square method[J]. Mapping and Spatial Geographic Information, 2017, 40(5): 122-124. | |
| 20 | 范晓明, 罗词金, 徐学科, 等. 光学非球面三坐标测量中的像散补偿[J]. 光学精密工程, 2016, 24(12): 3012-3019. |
| Fan Xiao-ming, Luo Ci-jin, Xu Xue-ke, et al. Astigmatic compensation in optical aspheric three-coordinate measurement[J]. Optical Precision Engineering, 2016, 24(12): 3012-3019. |
| [1] | 魏晓辉,周长宝,沈笑先,刘圆圆,童群超. 机器学习加速CALYPSO结构预测的可行性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 667-676. |
| [2] | 宋元,周丹媛,石文昌. 增强OpenStack Swift云存储系统安全功能的方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 314-322. |
| [3] | 方明,陈文强. 结合残差网络及目标掩膜的人脸微表情识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 303-313. |
| [4] | 王小玉,胡鑫豪,韩昌林. 基于生成对抗网络的人脸铅笔画算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 285-292. |
| [5] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
| [6] | 李阳,李硕,井丽巍. 基于贝叶斯模型与机器学习算法的金融风险网络评估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1862-1869. |
| [7] | 周炳海,何朝旭. 基于线边集成超市的混流装配线动态物料配送调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1809-1817. |
| [8] | 蒋磊,管仁初. 基于多目标进化算法的人才质量模糊综合评价系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1856-1861. |
| [9] | 赵宏伟,刘晓涵,张媛,范丽丽,龙曼丽,臧雪柏. 基于关键点注意力和通道注意力的服装分类算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1765-1770. |
| [10] | 管乃彦,郭娟利. 基于姿态估计算法的组件感知自适应模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1850-1855. |
| [11] | 刘洲洲,尹文晓,张倩昀,彭寒. 基于离散优化算法和机器学习的传感云入侵检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 692-702. |
| [12] | 王晓辉,吴禄慎,陈华伟. 基于法向量距离分类的散乱点云数据去噪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 278-288. |
| [13] | 张笑东,夏筱筠,吕海峰,公绪超,廉梦佳. 大数据网络并行计算环境中生理数据流动态负载均衡[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 247-254. |
| [14] | 陈蔓,钟勇,李振东. 隐低秩结合低秩表示的多聚焦图像融合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 297-305. |
| [15] | 金顺福,郄修尘,武海星,霍占强. 基于新型休眠模式的云虚拟机分簇调度策略及性能优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 237-246. |
|
||