吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (12): 3342-3350.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220173
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
基于自然驾驶数据的电动公交踏板误操作辨识方法
袁伟1( ),袁小慧1,2,高岩3,李坤宸1,赵登峰4,刘朝辉4
),袁小慧1,2,高岩3,李坤宸1,赵登峰4,刘朝辉4
- 1.长安大学 汽车学院,西安 710064
2.西安航空学院 车辆工程学院,西安 710077
3.道路交通安全公安部重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214000
4.郑州宇通客车股份有限公司,郑州 450016
Identification method for electric bus pedal misoperation based on natural driving data
Wei YUAN1( ),Xiao-hui YUAN1,2,Yan GAO3,Kun-chen LI1,Deng-feng ZHAO4,Zhao-hui LIU4
),Xiao-hui YUAN1,2,Yan GAO3,Kun-chen LI1,Deng-feng ZHAO4,Zhao-hui LIU4
- 1.School of Automobile,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
2.School of Vehicle Engineering,Xi'an Aeronautical Institute,Xi'an 710077,China
3.Key Laboratory of Ministry of Public Security for Road Traffic Safety,Wuxi 214000,China
4.Zhengzhou Yutong Bus Company Ltd. ,Zhengzhou 450016,China
摘要:
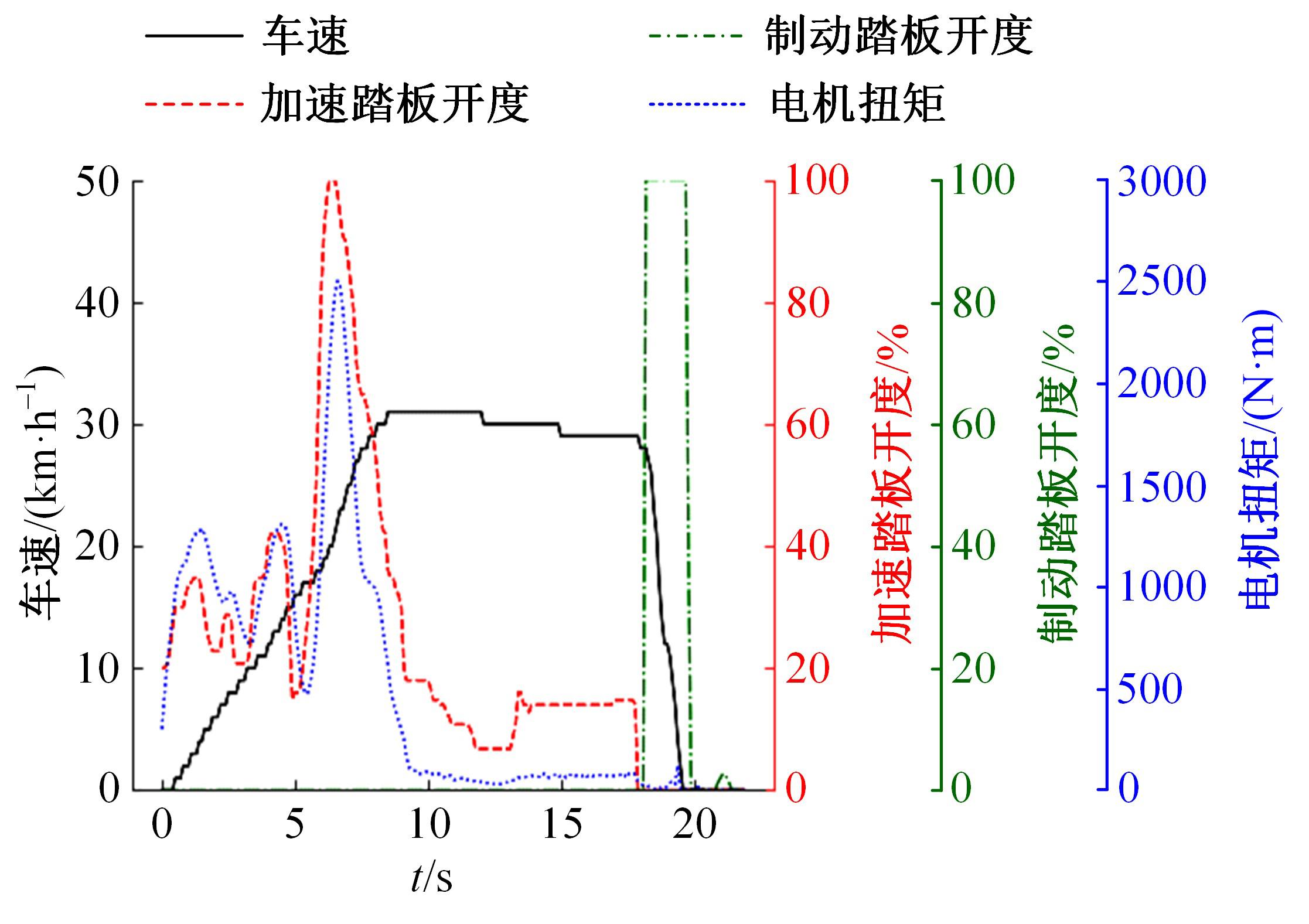
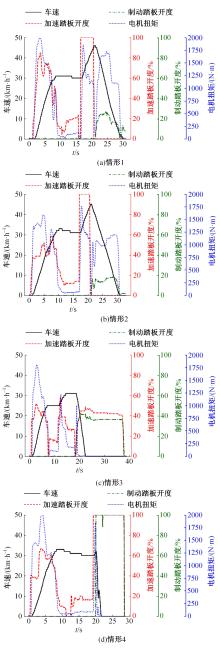
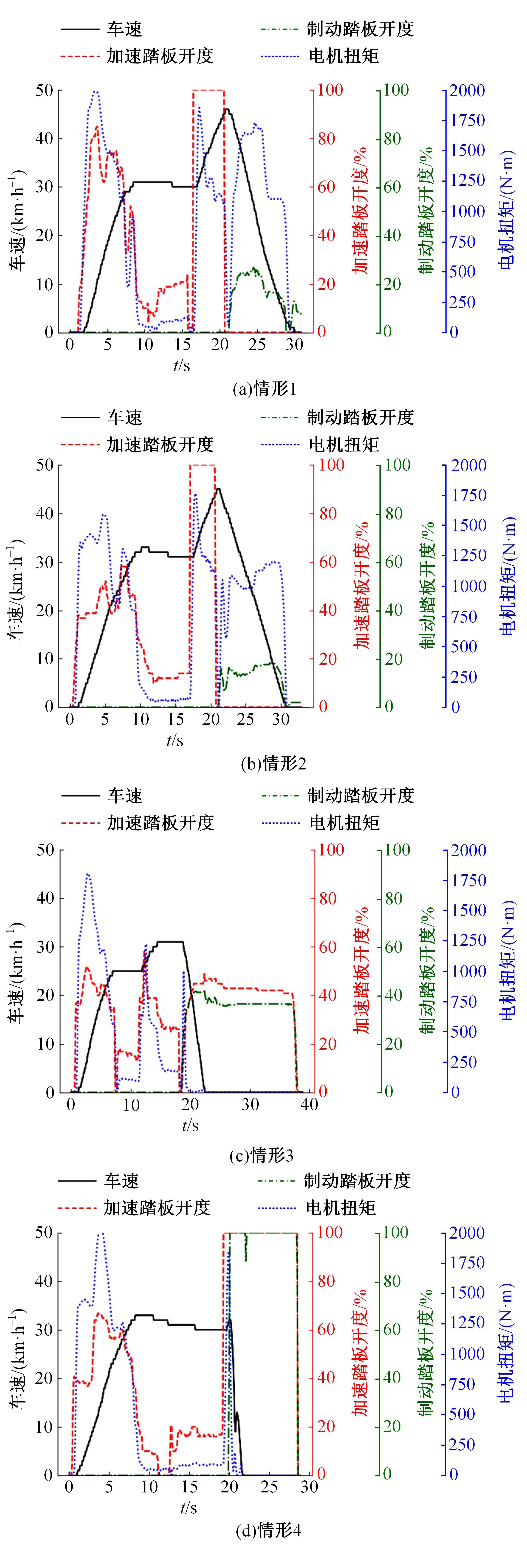
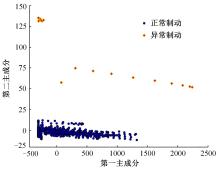
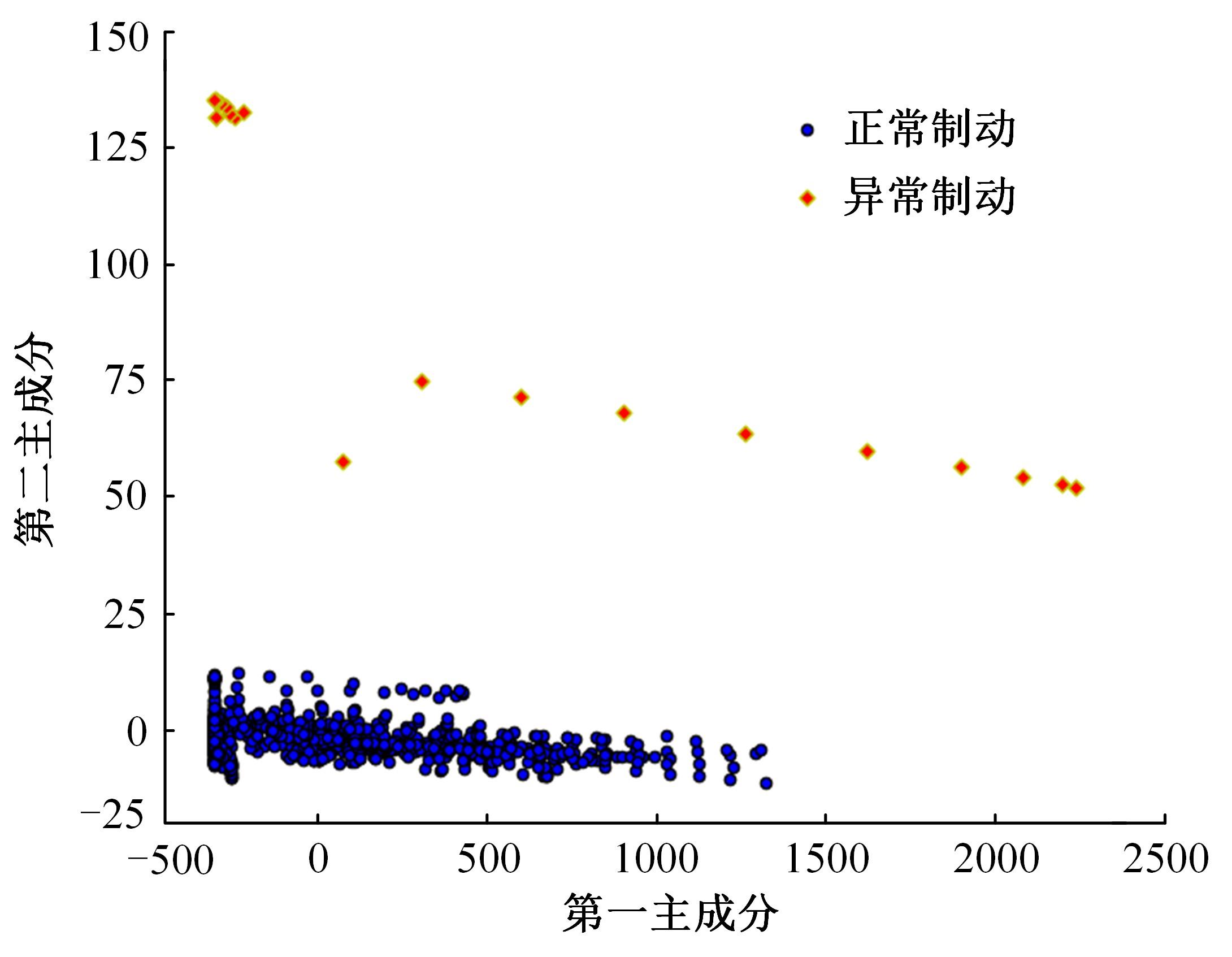
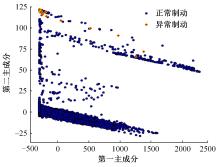
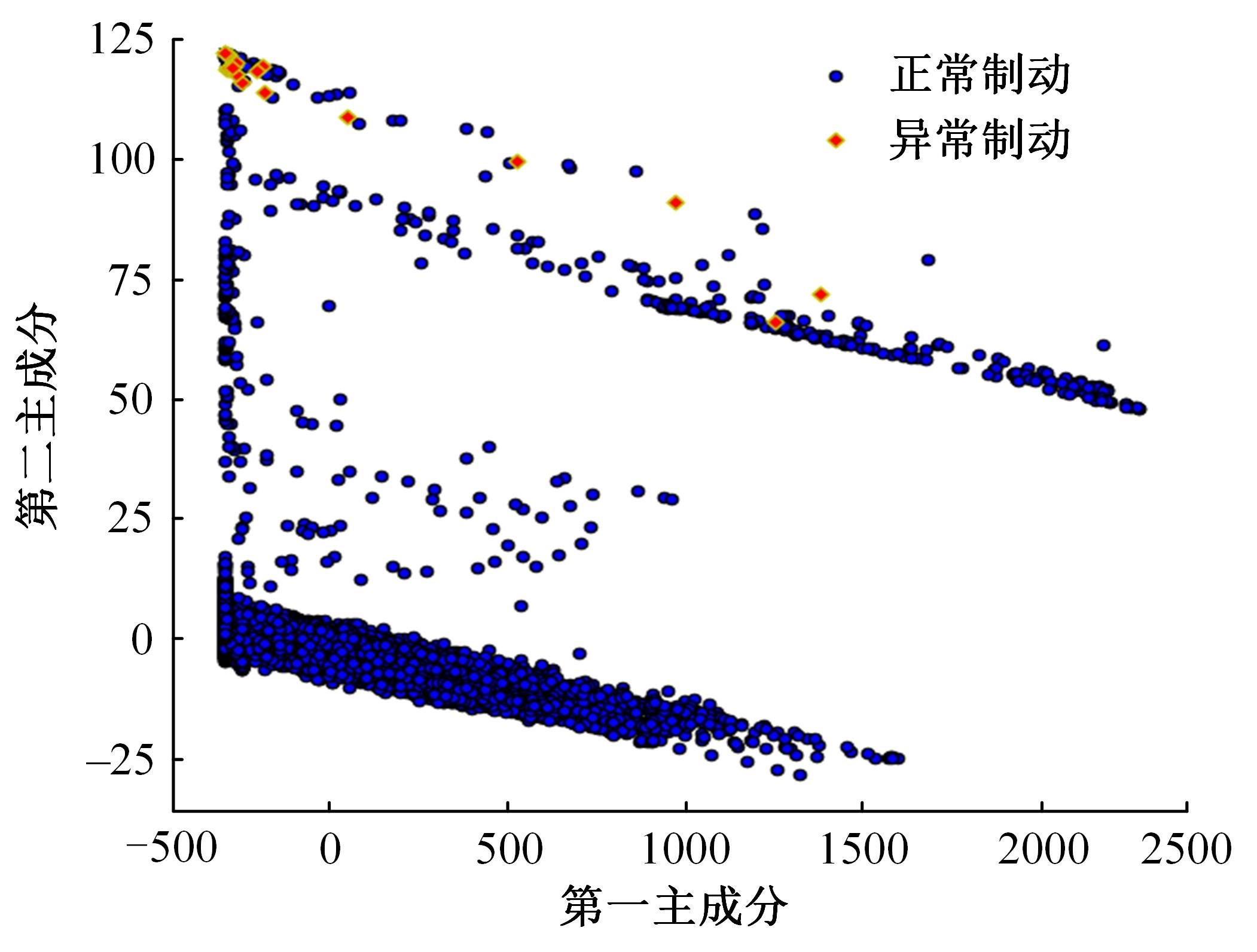
针对驾驶人误踩踏板引发电动公交失控问题,开展了自然驾驶试验和误踩踏板的模拟驾驶试验,采用One-Class SVM和iForest方法建立了踏板误操作辨识方法。试验结果表明:车速、电机转矩、加速踏板开度和制动踏板开度可作为反映踏板误操作行为的特征参数;One-Class SVM和iForest辨识方法识别准确率分别为94.9%和99.5%,但iForest辨识方法在踏板误操作行为的识别精确率方面具有突出优势。利用iForest辨识方法对电动公交运行数据进行辨识,可为降低误踩踏板相关事故发生提供理论支持。
中图分类号:
- U471.3
| 1 | Zhang C, Gong B, He H, et al. Special investigation and countermeasure suggestions on electric vehicle out-of-control accidents[C]∥IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Dalian, China, 2020: 1-8. |
| 2 | Tran C, Doshi A, Trivedi M M. Pedal error prediction by driver foot gesture analysis: a vision-based inquiry[C]∥2011 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Baden, Germany, 2011: 577-582. |
| 3 | Lococo K, Staplin L, Martell C, et al. Pedal application errors[R]. Washington DC: Department of Transportation, 2014. |
| 4 | Wu Y, Boyle L N, Mcgehee D V. Evaluating variability in foot to pedal movements using functional principal components analysis[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2018, 118: 146-153. |
| 5 | Wang X, Liu Y, Wang J, et al. Study on influencing factors selection of drive's propensity[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2019, 66: 35-48. |
| 6 | 尹怡欣, 徐令仪, 徐雅璠, 等. 基于旋转编码器的汽车油门误踩检测[J]. 控制工程, 2013, 20(4): 611-613, 622. |
| Yin Yi-xin, Xu Ling-yi, Xu Ya-bo, et al. Detection of the mistaken pressing accelerator pedal based on encoder[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2013, 20(4): 611-613, 622. | |
| 7 | 曹菁, 孟宪皆. 基于联合判别参数的防误踩油门制动控制系统设计[J]. 广西大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 41(2): 470-479. |
| Cao Jing, Meng Xian-jie. Brake control system design against mistakenly stepping on accelerator based on joint discriminate parameter[J]. Journal of Guangxi University (Nat Sci Ed), 2016, 41(2): 470-479. | |
| 8 | 苑警支. 基于多传感器融合的误踩油门辅助系统控制方法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学交通学院, 2019. |
| Yuan Jing-zhi. Research on control strategy of assistance system for misoperation of accelerator pedal based on multi-sensor data fusion[D]. Changchun: College of Transportation, Jilin University, 2019. | |
| 9 | 王力斌, 刘树伟. 基于模糊推理的油门防误踩系统控制研究[J]. 控制工程, 2020, 27(8): 1462-1467. |
| Wang Li-bin, Liu Shu-wei. Research on the control system of preventing false stepping the accelerating pedal based on the fuzzy theory[J]. Control Engineering of China, 2020, 27(8): 1462-1467. | |
| 10 | 邓彪, 简晓春. 汽车误踩油门智能保护系统的设计[J]. 交通科学与工程, 2014, 30(2): 67-71. |
| Deng Biao, Jian Xiao-chun. Design of an intelligent protection system for cars stepped on the accelerator by mistakes[J]. Journal of Transport Science and Engineering, 2014, 30(2): 67-71. | |
| 11 | Rogers S B, Wierwille W W. The occurrence of accelerator and brake pedal actuation errors during simulated driving[J]. Human Factors, 1988, 30(1): 71-81. |
| 12 | Jia S, Hui F, Li S, et al. Long short-term memory and convolutional neural network for abnormal driving behaviour recognition[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020, 14(5): 306-312. |
| 13 | 佘承其, 张照生, 刘鹏, 等. 大数据分析技术在新能源汽车行业的应用综述——基于新能源汽车运行大数据[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(20): 3-16. |
| She Cheng-qi, Zhang Zhao-sheng, Liu Peng, et al. Overview of the application of big data analysis technology in new energy vehicle industry: based on operating big data of new energy vehicle[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(20): 3-16. | |
| 14 | Lattanzi E, Freschi V. Machine learning techniques to identify unsafe driving behavior by means of in-vehicle sensor data[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 176: 1-10. |
| 15 | van LY M, Martin S, Trivedi M M. Driver classification and driving style recognition using inertial sensors, 2013[C]∥2013 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Gold Coast, Australia, 2013: 1040-1045. |
| 16 | Schmidt R A. Unintended acceleration: a review of human factors contributions[J]. Human Factors, 1989, 31(3): 345-364. |
| 17 | Schölkopf B, PLATT J C, Shawe-taylor J, et al. Estimating the support of a high-dimensional distribution[J]. Neural Computation, 2001, 13(7): 1443-1471. |
| 18 | Liu F T, Ming K, Zhou Z. Isolation forest[C]∥2008 Eighth IEEE International Conference on Data Mining, Pisa, Italy, 2008: 413-422. |
| [1] | 耿庆田,刘植,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于一种深度学习模型的土壤湿度预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(8): 2430-2436. |
| [2] | 潘恒彦,张文会,梁婷婷,彭志鹏,高维,王永岗. 基于MIMIC与机器学习的出租车驾驶员交通事故诱因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 457-467. |
| [3] | 周丰丰,颜振炜. 基于混合特征的特征选择神经肽预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3238-3245. |
| [4] | 耿庆田,赵杨,李清亮,于繁华,李晓宁. 基于注意力机制的LSTM和ARIMA集成方法在土壤温度中应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(10): 2973-2981. |
| [5] | 李文航,倪涛,赵丁选,张泮虹,师小波. 基于集合卡尔曼滤波的高机动救援车辆主动悬挂控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2816-2826. |
| [6] | 段亮,宋春元,刘超,魏苇,吕成吉. 基于机器学习的高速列车轴承温度状态识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 53-62. |
| [7] | 李光松,李文清,李青. 基于随机性特征的加密和压缩流量分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1375-1386. |
| [8] | 朱小龙,谢忠. 基于机器学习的地理空间数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1011-1016. |
| [9] | 成耀荣,杨谦,郑国华. 考虑碳排放的大型制造企业甩挂运输牵引车调度优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 893-899. |
| [10] | 滕志军,张宇,李昊天,孙铭阳. 复杂路网的自适应D⁃S证据理论地图匹配算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 524-530. |
| [11] | 李阳,李硕,井丽巍. 基于贝叶斯模型与机器学习算法的金融风险网络评估模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1862-1869. |
| [12] | 方伟,黄羿,马新强. 基于机器学习的虚拟网络感知数据缺陷自动检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1844-1849. |
| [13] | 张云龙,郭阳阳,王静,梁东. 钢-混凝土组合梁的固有频率及其振型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 581-588. |
| [14] | 刘洲洲,尹文晓,张倩昀,彭寒. 基于离散优化算法和机器学习的传感云入侵检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 692-702. |
| [15] | 赵东, 臧雪柏, 赵宏伟. 基于果蝇优化的随机森林预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 609-614. |
|
||