吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (4): 938-946.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220628
(Mg2Si+Si)/Al复合材料的组织和耐磨性
- 1.北华大学 机械工程学院,吉林省 吉林市 132021
2.北华大学 工程训练中心,吉林省 吉林市 132021
Microstructure and wear resistance of (Mg2Si+Si)/Al composites
Xiao-bo LIU1( ),Miao YANG2(
),Miao YANG2( ),De-kun ZHOU1
),De-kun ZHOU1
- 1.College of Mechanical Engineering,Beihua University,Jilin 132021,China
2.Engineering Training Center,Beihua University,Jilin 132021,China
摘要:
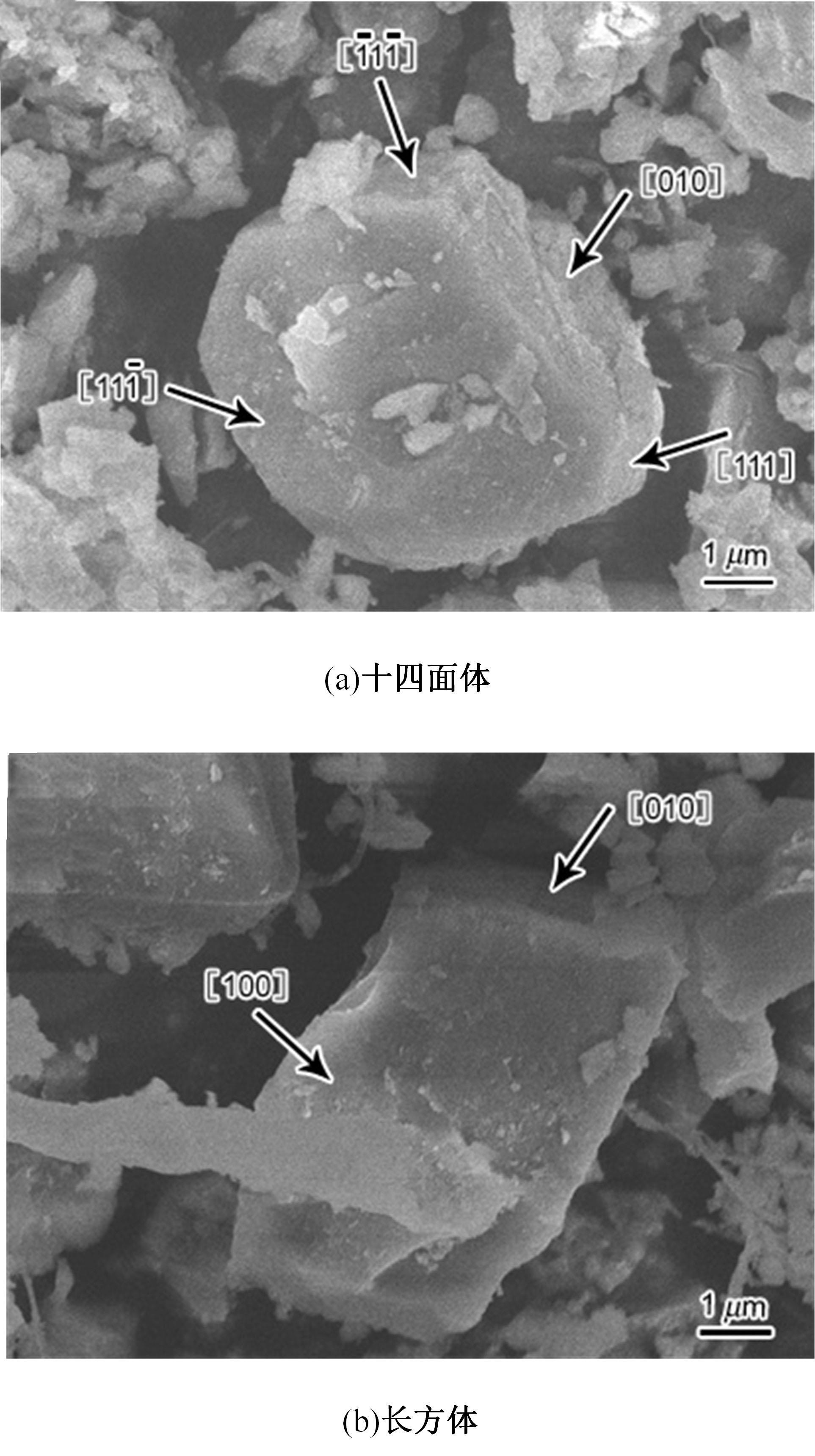
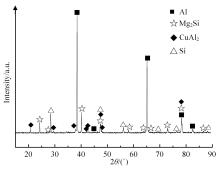
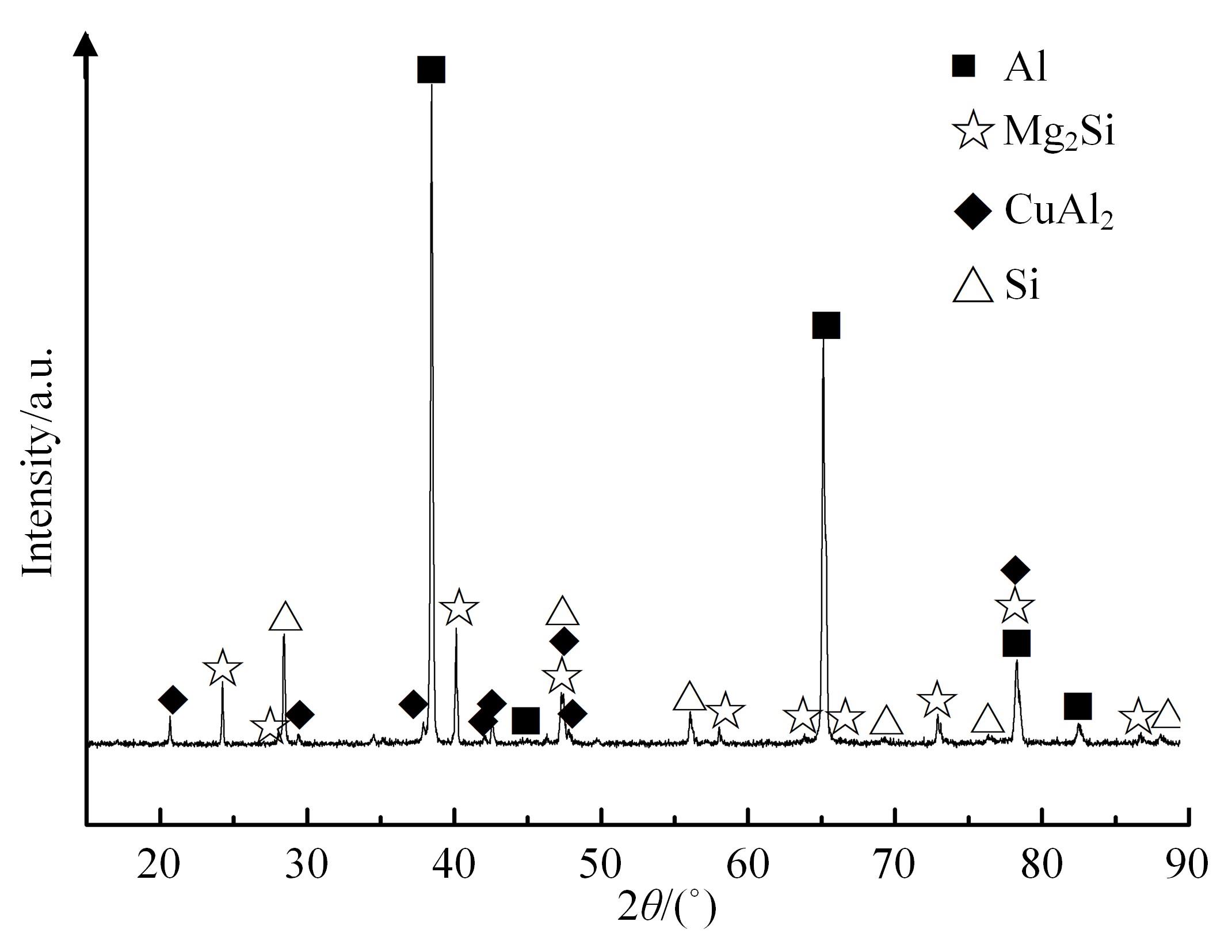
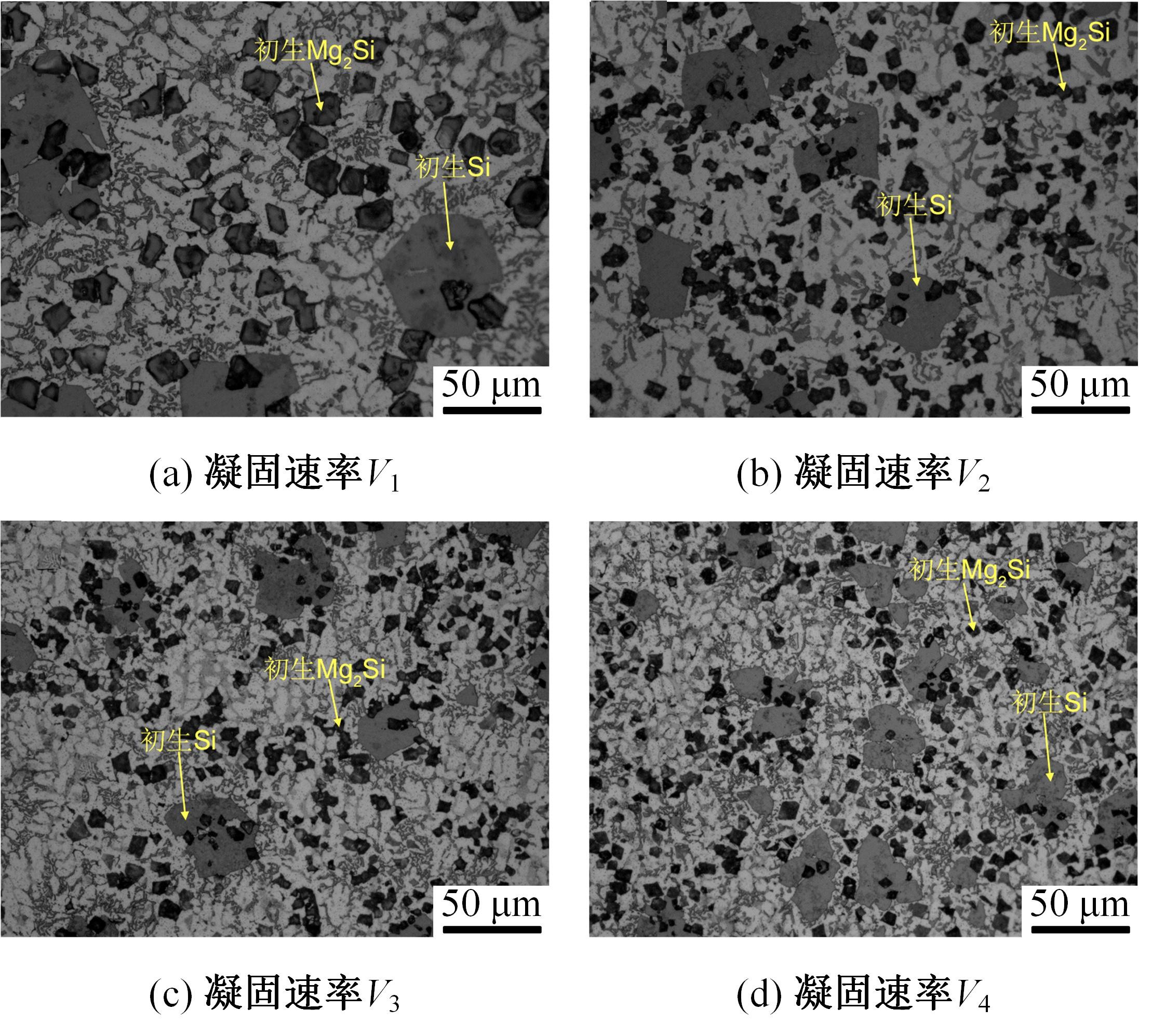
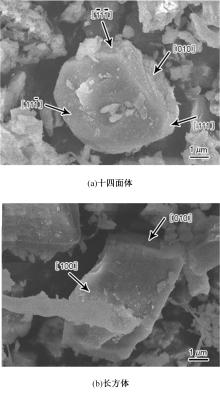
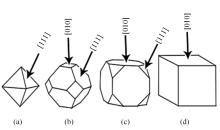
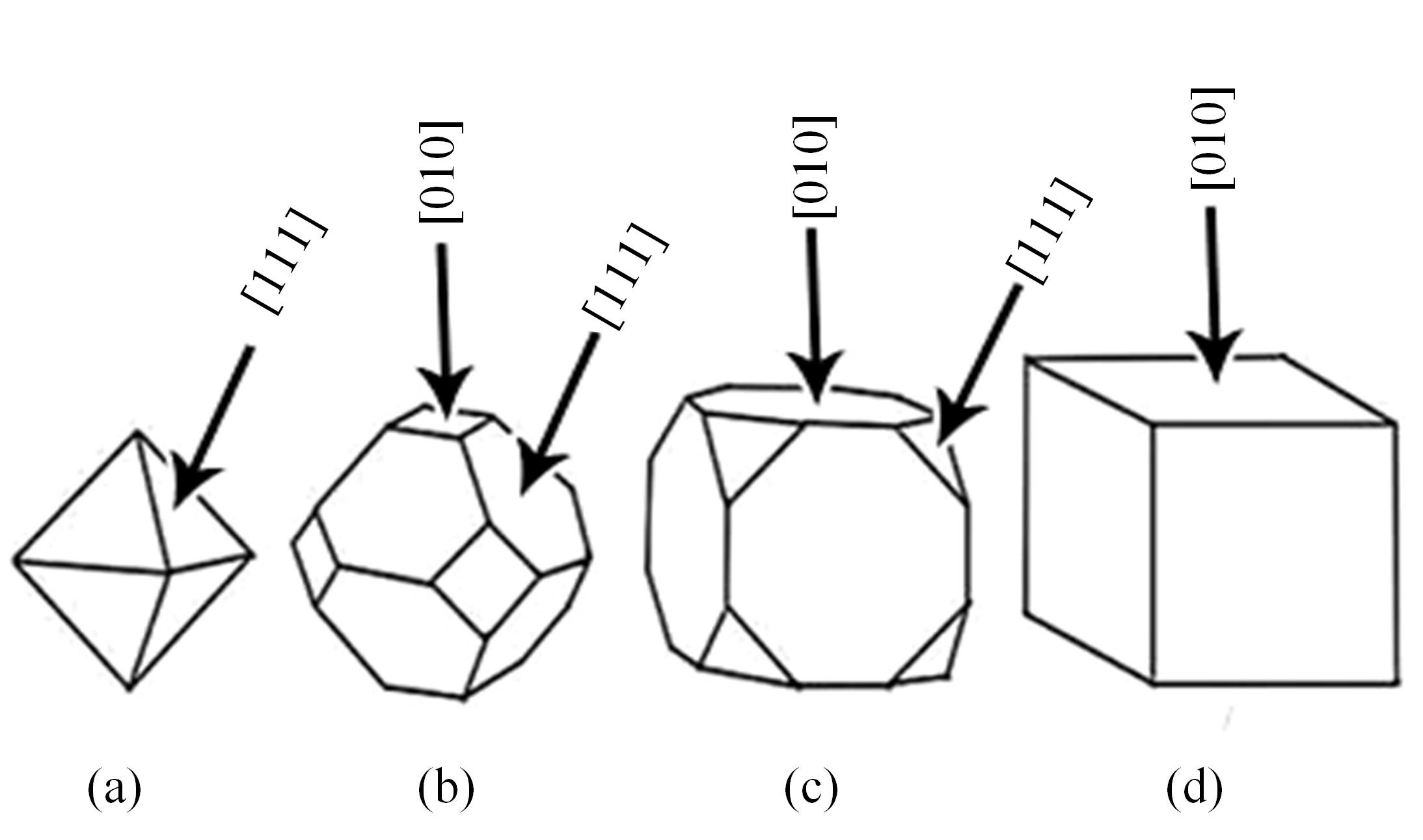
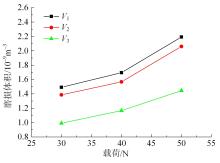
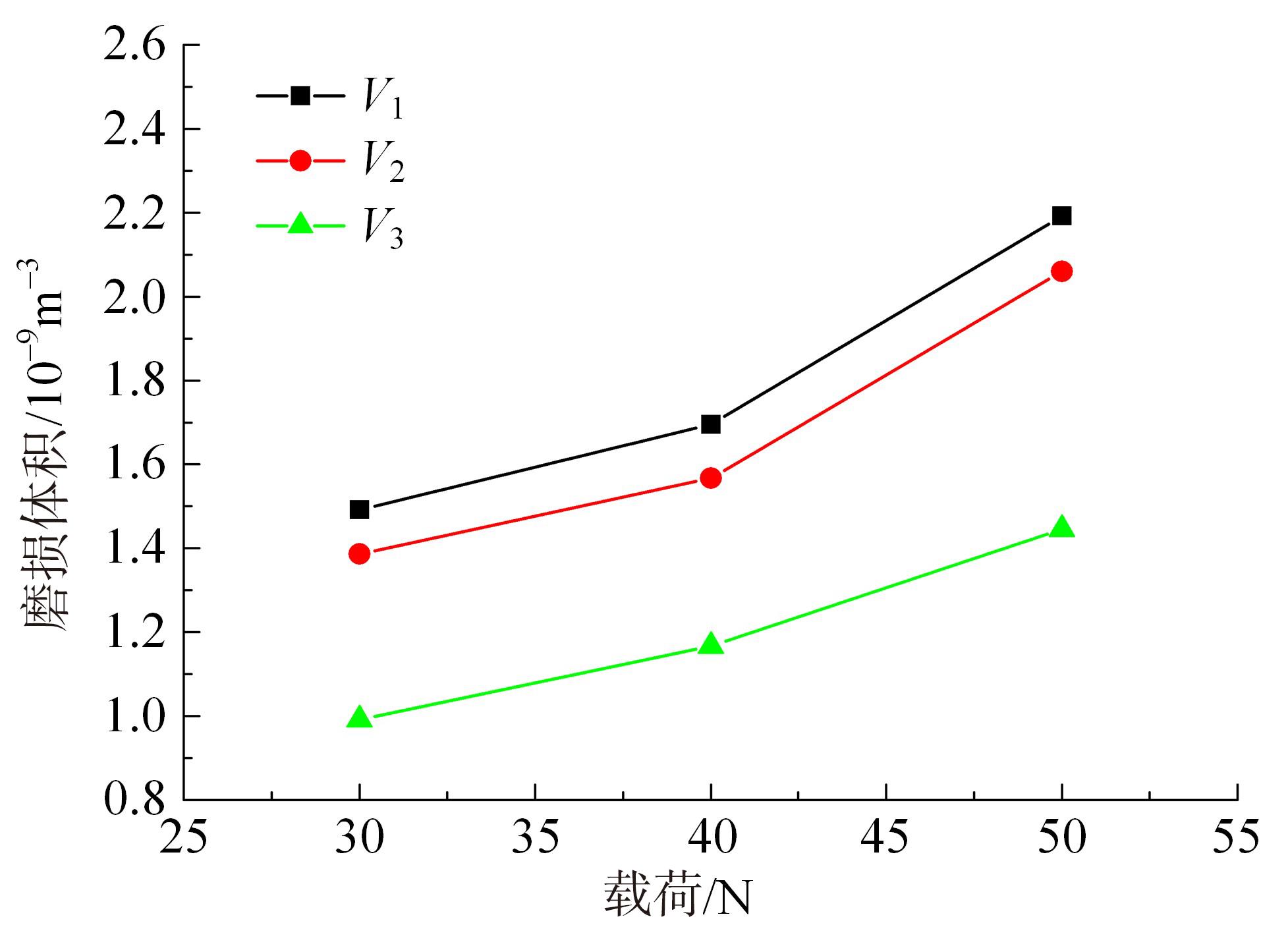
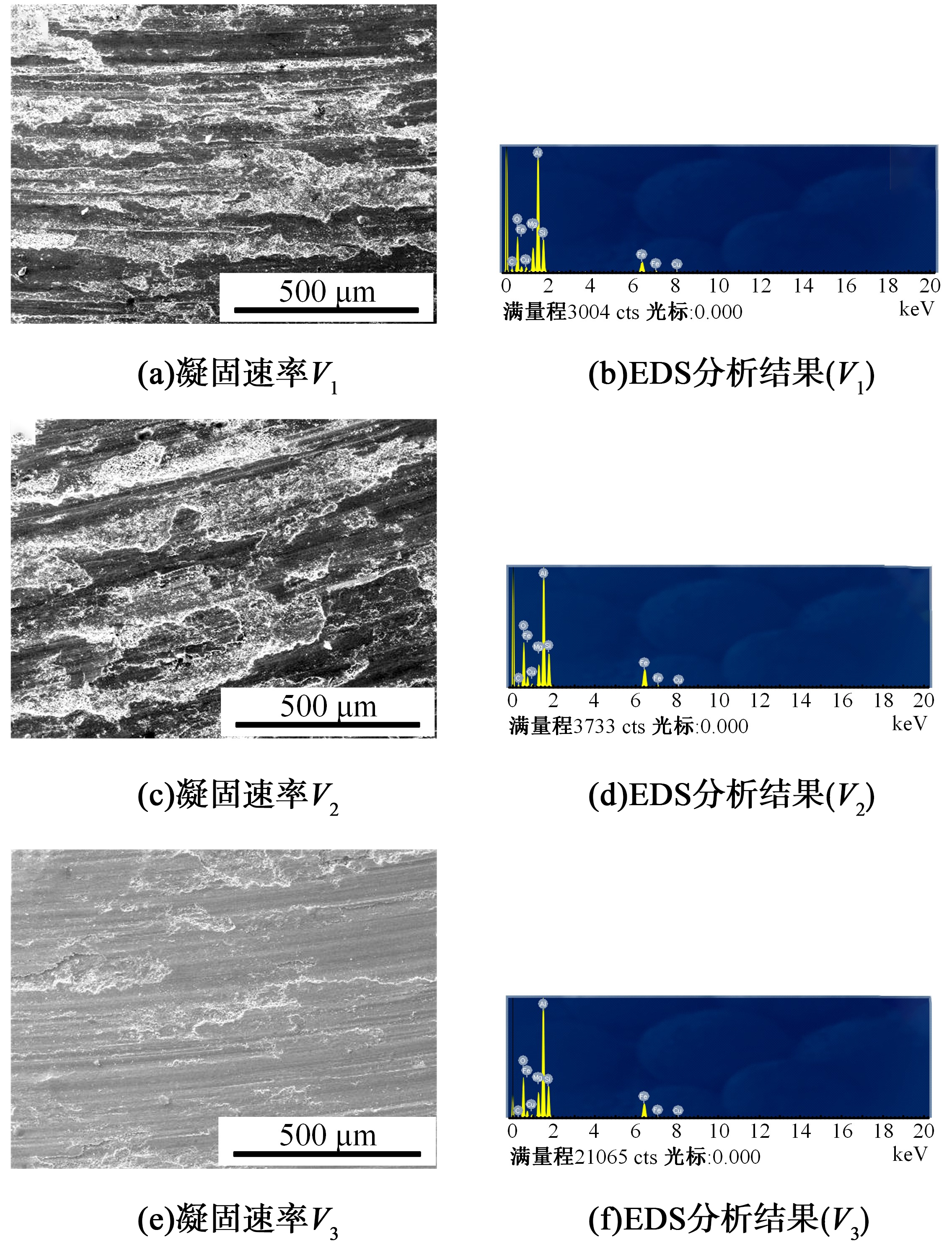
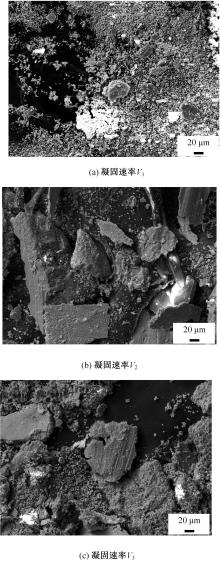
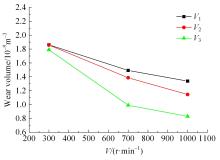
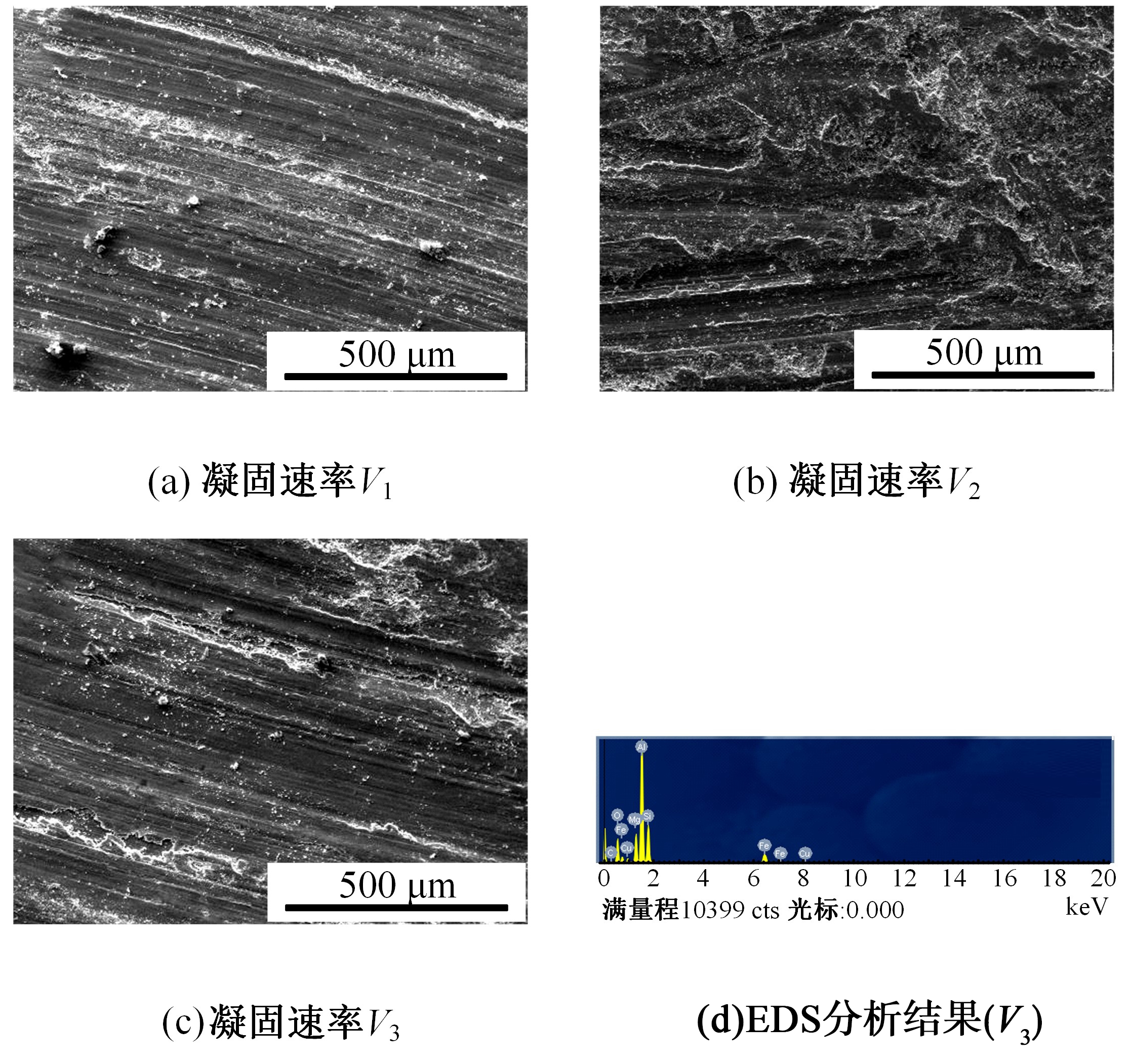
采用熔铸法制备了不同凝固速率的原位(Mg2Si+Si)/Al复合材料,研究了其组织和耐磨性。结果表明,磷改性后,初生Mg2Si为多边形块状,初生Si仍为复杂形貌。随着凝固速率的提高,初生Mg2Si和初生Si的数量随之增加,尺寸随之减小。萃取试验表明,Mg2Si晶体具有十四面体和六面体形貌。研究了不同滑动速度和载荷条件下复合材料对45#钢的干滑动磨损行为。结果表明,复合材料的耐磨性随着凝固速率的提高而提高,(Mg2Si+Si)/Al复合材料的失效机制主要是黏着磨损和磨粒磨损。
中图分类号:
- TB331
| 1 | Seth P P, Parkash O, Kumar D. Structure and mechanical behavior of in situ developed Mg2Si phase in magnesium and aluminum alloys-a review[J]. Royal Society of Chemistry, 2020, 10: 37327-37345. |
| 2 | Qin Q D, Li W X, Zhao K W, et al. Effect of modification and aging treatment on mechanical properties of Mg2Si/Al composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(9): 2253-2257. |
| 3 | Qin Q D, Zhao Y G, Zhou W. Dry sliding wear behavior of Mg2Si/Al composites against automobile friction material[J]. Wear, 2008, 264(7,8): 654-661. |
| 4 | 周琦, 李延荣, 胡永辉, 等. 球磨时间对Mg2Si组织和 性能的影响[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2014, 40(4): 9-12. |
| Zhou Qi, Li Yan-Rong, Hu Yong-Hui, et al.Influence of ball milling time on microstructures and properties of Mg2Si[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2014, 40(4): 9-12. | |
| 5 | Song C J, Xu Z M, Liang G F, et al.Study of in situ Al/Mg2Si functional graded materials by electronmagnetic separation method[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 424(1-2): 6-16. |
| 6 | 周琦, 李福祥, 南雪丽, 等. 自蔓延高温合成Al/Mg2Si 复合材料的淬熄试验[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2009,35(3): 1-3. |
| Zhou Qi, Li Fu-Xiang, Xue-Li Nan, et al. Quenching experiment of Al/Mg2Si composite synthesized with high-temperature self-propagation[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2009, 35(3): 1-3. | |
| 7 | Qin Q D, Zhao Y G. Nonfaceted growth of intermetallic Mg2Si in Al melt during rapid solidification[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 462(1-2): 28-31. |
| 8 | Zhai Y B, Ma X T, Mei Z. Centrifugal forming mechanism of Al gradient composites reinforced with complementary primary Si and Mg2Si particles[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43(4): 769-774. |
| 9 | 刘政, 谢敏, 封志芳,等. 熔体过热处理对过共晶 Al-Si-Mg合金中Mg2Si相的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2010, 35(10): 63-66. |
| Liu Zheng, Xie Min, Feng Zhi-Fang, et al.Influence of melt superheating on Mg2Si phase of hypereutectic Al-Si-Mg casting alloy[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2010, 35(10): 63-66. | |
| 10 | 刘晓波, 周德坤, 赵宇光. 不同等温热处理条件下半固态挤压Mg2Si/Al复合材料的组织和性能[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2016, 46(5): 1577-1582. |
| Liu Xiao-Bo, Zhou De-Kun, Zhao Yu-Guang. Microstructure and mechanical property of Mg2Si/Al composites fabricated by semi-solid extrusion under different isothermal heat treatments[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016, 46(5): 1577-1582. | |
| 11 | 任玉艳. 原位Mg2Si/Al复合材料强韧化及其机理的研究[D].沈阳: 沈阳工业大学材料科学与工程学院, 2012: 12-13. |
| Ren Yu-Yan. Study on strengthening and toughening mechanisms of in-situ Mg2Si/Al composite[D]. Shengyang: College of Material Science and Engineering,Shengyang University of Technology, 2012: 12-13. | |
| 12 | Zhao Y G, Qin Q D, Zhao Y Q, et al.In situ Mg2Si/Al-Si composite modified by K2TiF6 [J]. Materials Letters, 2004, 58(16): 2192-2194. |
| 13 | Qin Q D, Zhao Y G, Zhou W, et al.Effect of phosphorus on microstructure and growth manner of primary Mg2Si crystal in Mg2Si/Al composite[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2007, 447(1,2): 186-191. |
| 14 | Wu X F, Zhang G A, Wu F F. Influence of Bi addition on microstructure and dry sliding wear behaviors of cast Al-Mg2Si metal matrix composite[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(6): 1532-1542. |
| 15 | Wu X F, Zhang G A, Wu F F. Microstructure and dry sliding wear behavior of cast Al-Mg2Si in-situ metal matrix composite modified by Nd[J]. Rare metals, 2013, 32(3): 284-289. |
| 16 | Tang S Q, Zhou J X, Tian C W, et al. Morphology modification of Mg2Si by Sr addition in Mg-4%Si alloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21(9): 1932-1936. |
| 17 | Jiang Q C, Wang H Y, Wang Y, et al. Modification of Mg2Si in Mg-Si alloys with yttrium[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 392(1,2): 130-135. |
| 18 | 林继兴. 复合变质对原位Mg2Si/Al-Si复合材料组织优 化研究[J]. 轻合金加工技术, 2008, 36(11): 11-14. |
| Lin Ji-Xing. Study on optimization of complex modification on microstructure in in-situ Mg2Si/Al-Si composite[J]. Light Alloy Fabrication Technology, 2008, 36(11): 11-14. | |
| 19 | Zhang J, Fan Z, Wang Y Q, et al. Microstructural refinement in Al-Mg2Si in situ composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters, 1999, 18(2): 783-784. |
| 20 | Liu X B, Yang M, Zhou D K, et al. Microstructure and wear resistance of Mg2Si-Al composites fabricated using semi-solid extrusion[J]. Metals, 2020,10(5): No.596. |
| 21 | Kobayashi K F, Hogan L M. The crystal growth of silicon in Al-Si alloys[J]. Jourmal of Materials Science, 1985, 20(6): 1961-1975. |
| 22 | 周德坤, 刘晓波. 凝固速率对Mg2Si/Al复合材料组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属热处理, 2017, 42(10): 43-46. |
| Zhou De-Kun, Liu Xiao-Bo. Effect of solidification rate on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg2Si/Al composites[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2017, 42(10): 43-46. | |
| 23 | Sekhar J A, Trivedi R. Solidification microstructure evolution in the presence of inert particles[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 1991, 147: 9-12. |
| 24 | 陈磊. 变质Al-20wt.%Mg2Si合金中初生Mg2Si生长形貌演化与调控机制[D]. 长春:吉林大学材料科学与工程学院,2015: 48-53. |
| Chen Lei. The growth morphology evolution and regulation mechanism of primary Mg2Si in modified Al-20wt.%Mg2Si alloys[D]. Changchun: College of Material Science and Engineering, Jilin University, 2015: 48-53. | |
| 25 | Wang R Y, Lu W H, Hogan L M. Faceted growth of silicon crystals in Al-Si alloys[J]. Metallurgical and materials transactions A, 1997, 28(5):1233-1250. |
| 26 | Hu Y, Rao L. Effect of particulate reinforcement on wear behavior of magnesium matrix composites[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2012, 22(Sup.1): 2659-2664. |
| 27 | Somi Reddy A, Pramila Bai B N, Murthy K S S, et al. Wear and seizure of binary Al-Si alloys[J]. Wear, 1994, 171(1,2): 115-127. |
| 28 | Kwok J K M, Lim S C. High-speed tribological properties of some Al/SiCp composites: II. Wear Mechanisms[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 1999, 59: 65-75. |
| 29 | Sannino A P, Rack H J. Dry sliding wear of discontinuously reinforced aluminium composites: Review and discussion[J]. Wear, 1995, 189: 1-19. |
| 30 | Casellas D, Beltran A, Prado J M, et al. Microstructural effects on the dry wear resistance of powder metallurgy Al-Si alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2004, 257: 730-739. |
| [1] | 熙鹏,丛茜,王庆波,郭华曦. 仿生条纹形磨辊磨损试验及耐磨机理分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1787-1792. |
| [2] | 姜秋月,杨海峰,檀财旺. 22MnB5超高强钢焊接接头强化性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1806-1810. |
| [3] | 郑孝义, 孙大千, 李欣, 都桂刚, 辛伟达, 任振安. NbAl3强化Al-Nb熔覆层的组织与性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1531-1536. |
| [4] | 刘子武, 李剑峰. 叶片材料FV520B再制造熔覆层冲蚀损伤行为及评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 835-844. |
| [5] | 赵宇光, 杨雪慧, 徐晓峰, 张阳阳, 宁玉恒. Al-10Sr变质剂状态、变质温度及变质时间对ZL114A合金组织的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 212-220. |
| [6] | 张志强, 刘从豪, 何东野, 李湘吉, 李纪萱. 基于性能梯度分布的硼钢热冲压工艺对形状精度的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(6): 1829-1833. |
| [7] | 张金波,佟金,马云海. 仿生肋条结构表面深松铲刃的磨料磨损特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(1): 174-180. |
| [8] | 白志范, 李桂中, 王超, 王良, 张志敏. 高速客车转向架构架焊接接头组织与力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 207-211. |
| [9] | 王素芬, 彭艳, 李志杰, 肖力子. 薄板坯连铸连轧工艺生产的低碳钢冷轧基板力学特性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2012, 42(增刊1): 221-224. |
| [10] | 白志范, 李桂中, 王超. S355J2W+N钢焊接接头显微组织与力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(增刊2): 202-204. |
| [11] | 刘晓波1,2,赵宇光1,杨雯1,张家陶1. (Mg2Si+SiCp)/Mg复合材料的耐磨性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(6): 1618-1624. |
| [12] | 李光玉,苏颖超,付宇,连建设,赵宇光. 离心铸造条件对Mg2Si/Al梯度复合材料组织与性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(05): 1295-1299. |
| [13] | 刘晓波, 赵宇光, 刘雁. Mg2Si/Al梯度复合材料的耐磨性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(02): 371-0376. |
| [14] | 卢广林,邱小明, 白杨,伦辛杰,邓宝清,任露泉. c-BN仿生耐磨复合材料的微观结构和耐磨性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(01): 73-0077. |
| [15] | 高一鹏,丁洪,金学军. CoAlW合金时效过程中γ′相析出的相场模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2011, 41(01): 84-0088. |
|
||