吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (9): 2588-2599.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221413
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于时空序列相似性的城轨乘客出行模式识别
- 1.西安建筑科技大学 资源工程学院,西安 710055
2.北京交通大学 土木建筑工程学院,北京 100044
3.长安大学 运输工程学院,西安 710064
Recognition of travel patterns for urban rail transit passengers based on spatiotemporal sequence similarity
Na ZHANG1( ),Feng CHEN2(
),Feng CHEN2( ),Jian-po WANG3,Ya-di ZHU2
),Jian-po WANG3,Ya-di ZHU2
- 1.School of Resources Engineering,Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology,Xi'an 710055,China
2.School of Civil Engineering,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
3.School of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
摘要:
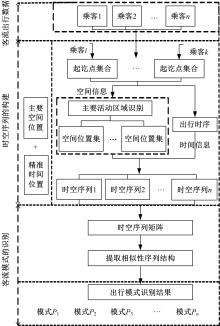
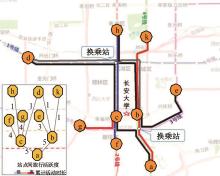
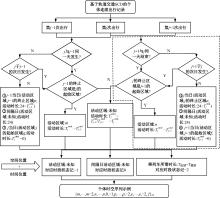
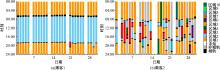
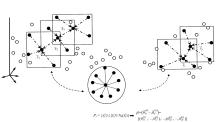
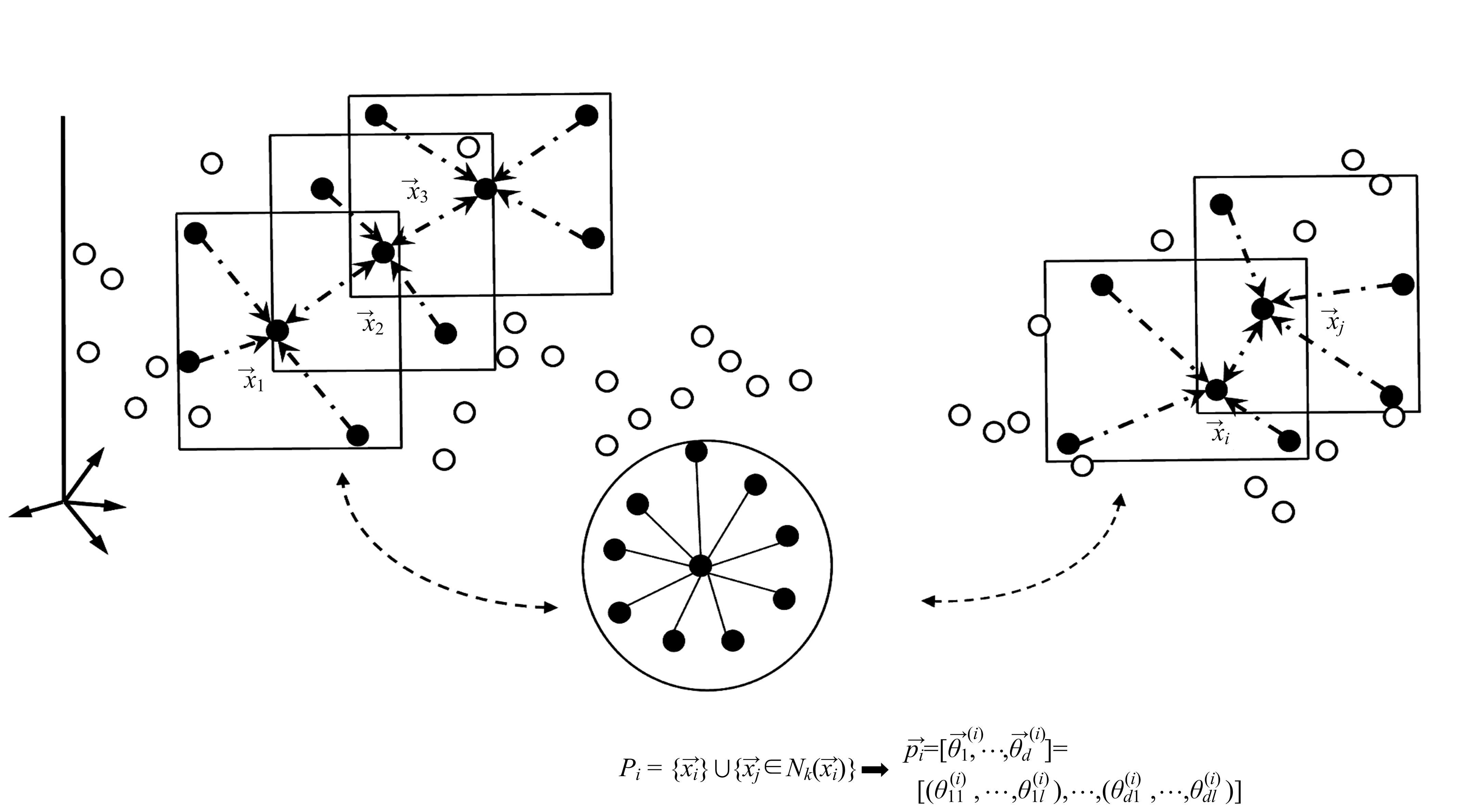
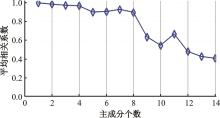
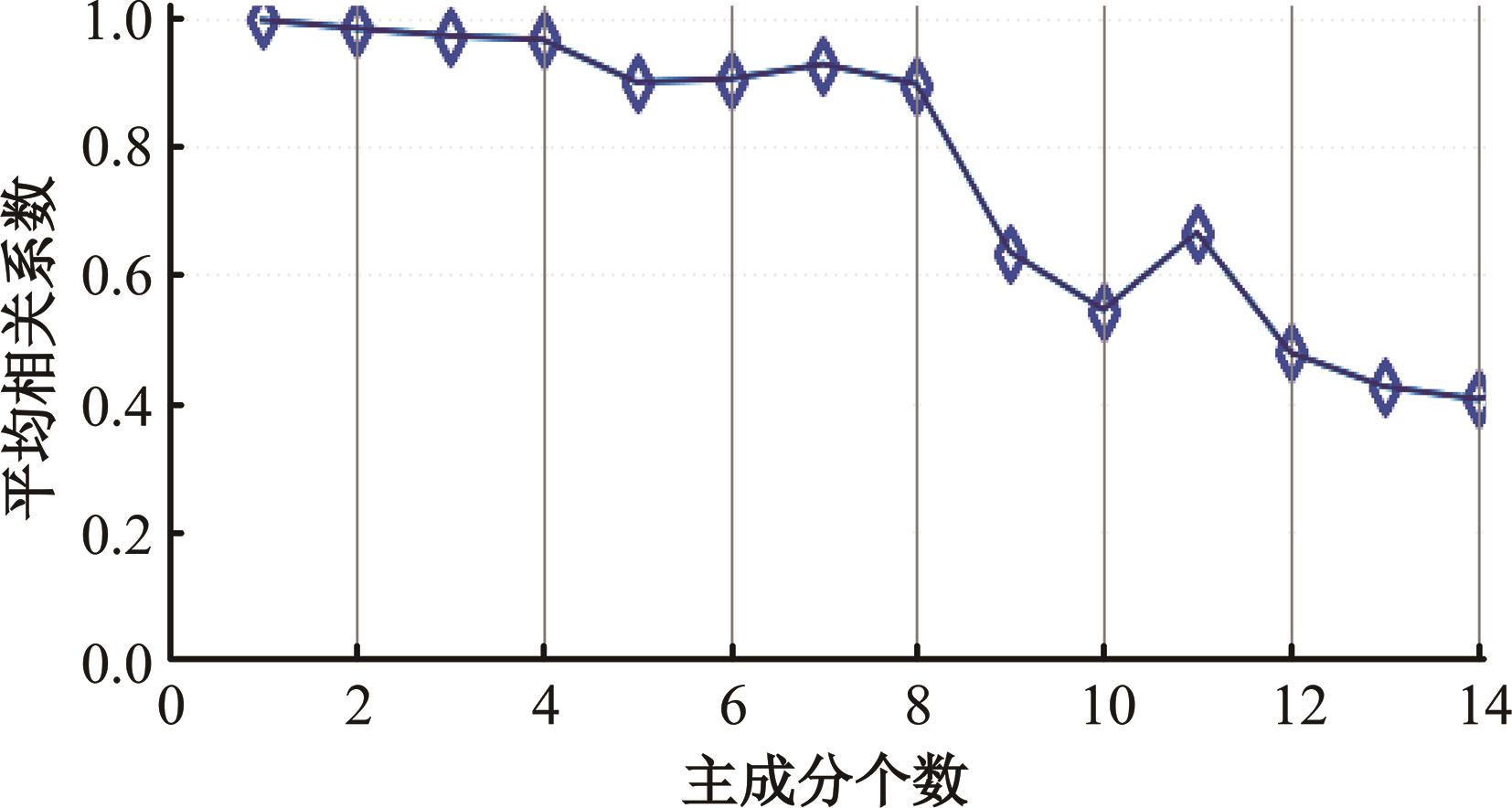
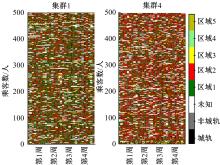
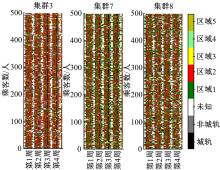
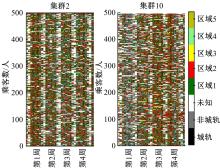
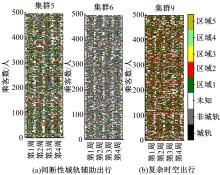
基于轨道交通智能卡数据,提出一种通过建模个体的时空序列识别出行模式的方法。首先,提取乘客个体访问的所有站点,以站间出行频次、站间距离和站点活动时长计算站点的相似性,利用层次聚类算法划分该个体的主要空间活动区域。其次,基于个体的出行次序推断时空序列,该序列为一组表征时空状态的离散值,依次采用PCA-KL和K-Means++提取相似性序列结构以识别乘客出行模式。最后,以西安某月的轨道交通智能卡数据为例,识别其乘客出行模式。结果表明,复杂的客流具有5种出行模式,其中3种典型模式宏观上属通勤出行,客流占比79%。可见,本文基于个体时空序列相似性的模式识别充分体现了研究方法的特殊性和通用性,针对不同城市操作性强。
中图分类号:
- U491.1
| 1 | 赵娟娟. 城市轨道交通乘客时空出行模式挖掘及动态客流分析[D].深圳:中国科学院大学深圳先进技术研究院,2017. |
| Zhao Juan-juan. Spatio-temporal travel pattern mining and dynamic passenger flow analysis in urban rail transit system[D]. Shenzhen: Shenzhen Institutes of Advance Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2017. | |
| 2 | 朱亚迪,陈峰,王子甲,等.基于概率图模型的乘客出行链提取方法[J].吉林大学学报:工学版,2019,49(1):60-65. |
| Zhu Ya-di, Chen Feng, Wang Zi-jia, et al. Passengers' trip chains extraction method based on probabilistic graph model[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019,49(1):60-65. | |
| 3 | Ma X L, Wu Y J, Wang Y H, et al. Mining smart card data for transit riders' travel patterns[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2013, 36: 1-12. |
| 4 | Cui Z Y, Long Y. Perspectives on stability and mobility of transit passenger's travel behavior through smart card data[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2019, 13(12):1761-1769. |
| 5 | 彭飞,宋国华,朱珊.城市公共交通常乘客通勤出行提取方法[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2021,21(2):158-165, 172. |
| Peng Fei, Song Guo-hua, Zhu Shan. A method for extracting commuting trips of frequent passengers in urban public transportation[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2021,21(2):158-165, 172. | |
| 6 | 周航,陈学武.集时空聚类和指标筛选的公共交通通勤者识别[J].交通运输工程与信息学报,2022,20(1):89-97. |
| Zhou Hang, Chen Xue-wu. Public transportation commuter identification based on spatiotemporal clustering and index screening[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2022,20(1):89-97. | |
| 7 | Hagerstraand T. What about people in regional science [J]. Papers in Regional Science,1970, 24(1): 7-24. |
| 8 | Langlois G G, Koutsopoulos H N, Zhao J. Inferring patterns in the multi-week activity sequences of public transport users[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2016, 64:1-16. |
| 9 | 刘永鑫.基于多源数据融合的城市公交系统乘客出行模式挖掘及其应用研究[D].广州: 华南理工大学土木与交通学院, 2018. |
| Liu Yong-xin. Study on key technologies of transit passengers' travel pattern mining and applications based on multiple sources of data[D]. Guangzhou: School of Civil Engineering & Transportation, South China University of Technology, 2018. | |
| 10 | Kieu L M, Bhaskar A, Chung E. Passenger segmentation using smart card data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(3):1537-1548. |
| 11 | 姚志刚,杨杰,王元庆.基于个体出行模式的公交乘客活动规律性度量[J].北京交通大学学报, 2022, 46(4): 68-75. |
| Yao Zhi-gang, Yang Jie, Wang Yuan-qing. Measurement of public transport passenger behavior regularity based on individual travel pattern[J]. Journal of Beijing Jiaotong University, 2022, 46(4): 68-75. | |
| 12 | Joh C H, Arentze T, Timmermans H. Pattern recognition in complex activity travel patterns: comparison of Euclidean distance,signal-processing theoretical, and multidimensional sequence alignment methods[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2001, 1752(1):16-22. |
| 13 | Day W H E, Edelsbrunner H. Efficient algorithms for agglomerative hierarchical clustering methods[J]. Journal of Classification, 1984, 1: 7-24. |
| 14 | Ortega-Tong M A. Classification of London's public transport users using smart card data[D]. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2013. |
| 15 | Roweis S T, Saul L K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2323-2326. |
| 16 | Tenenbaum J B, Silva V, Langford J C. A global geometric framework for nonlinear dimensionality reduction[J]. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2319-2323. |
| 17 | Levada A L M. PCA-KL: a parametric dimensionality reduction approach for unsupervised metric learning[J]. Advances in Data Analysis and Classification, 2021, 15(4): 829-868. |
| 18 | Pham D T, Dimov S S, Nguyen C D. Selection of K in K-means clustering[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2005, 219(1): 103-119. |
| 19 | 2022年度中国主要城市共享单车/电单车骑行报告[R].北京: 中国城市规划设计研究院, 2022. |
| 2022 Annual report on sharing bikes/motorcycle riding in major Chinese cities[R].Beijing: China Academy of Urban Planning & Design, 2022. | |
| 20 | 周世兵,徐振源,唐旭清. K-means算法最佳聚类数确定方法[J].计算机应用, 2010, 30(8): 1995-1998. |
| Zhou Shi-bing, Xu Zhen-yuan, Tang Xu-qing. Method for determining optimal number of clusters in K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2010, 30(8): 1995-1998. | |
| 21 | Day W H E, Edelsbrunner H. Efficient algorithms for agglomerative hierarchical clustering methods[J]. Journal of Classification, 1984, 1(1): 7-24. |
| [1] | 周锡浈,宫贺,李敦敦,季彦婕,严杰. 建成环境对路内停车泊位使用率的非线性影响模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [2] | 严利鑫,曾涛,贺宜,郭军华,胡鑫辉. 共驾型智能车辆人机接管行为序列编码与解析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2547-2556. |
| [3] | 曲昭伟,李霖,陈永恒,吴场建. 长区间掉头车辆特性分析及其安全评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2206-2213. |
| [4] | 何永明,权聪,魏堃,冯佳,万亚楠,陈世升. 超高速公路车路协同路侧单元感知融合方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1923-1934. |
| [5] | 马书红,廖国美,黄岩,张俊杰. 建成环境对交通小区地铁通勤客流的异质性影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1913-1922. |
| [6] | 程国柱,盛林,王浩宇,冯天军. 考虑右转车二次冲突的信号交叉口行人过街安全评价方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 1903-1912. |
| [7] | 秦雅琴,钱正富,谢济铭. 协同换道避障模型和轨迹数据驱动的车辆协同避障策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1311-1322. |
| [8] | 张明业,杨敏,黎彧,黄世玉,李清韵. 考虑有序充电策略的多车型电动公交调度优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1293-1301. |
| [9] | 马潇驰,陆建. 基于基因表达式编程的高架道路事故实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 719-726. |
| [10] | 严利鑫,冯进培,郭军华,龚毅轲. 不同险态情景下共驾型智能车辆接管行为特征分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 683-691. |
| [11] | 曲大义,张可琨,顾原,王韬,宋慧,戴守晨. 自动驾驶车辆换道决策行为分析及分子动力学建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 700-710. |
| [12] | 涂辉招,王万锦,乔鹏,郭静秋,鹿畅,吴海飞. 自动驾驶卡车路测安全员接管干预行为解析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(3): 727-740. |
| [13] | 范博松,邵春福. 城市轨道交通突发事件风险等级判别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 427-435. |
| [14] | 张健,李青扬,李丹,姜夏,雷艳红,季亚平. 基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [15] | 郑植,袁佩,金轩慧,魏思斯,耿波. 桥墩复合材料柔性防撞护舷试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2581-2590. |
|
||