吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 709-721.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230543
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于多尺度候选融合与优化的三维目标检测算法
- 1.长春理工大学 电子信息工程学院,长春 130022
2.长春理工大学 空间光电技术研究所,长春 130022
3.吉林大学第一医院 泌尿外二科,长春 130061
Three-dimensional object detection algorithm based on multi-scale candidate fusion and optimization
Hua CAI1( ),Yan-yang ZHENG1,Qiang FU2,Sheng-yu WANG1,Wei-gang WANG3,Zhi-yong MA3
),Yan-yang ZHENG1,Qiang FU2,Sheng-yu WANG1,Wei-gang WANG3,Zhi-yong MA3
- 1.School of Electronic Information Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
2.School of Opto-Electronic Engineer,Changchun University of Science and Technology,Changchun 130022,China
3.No. 2 Department of Urology,The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
摘要:
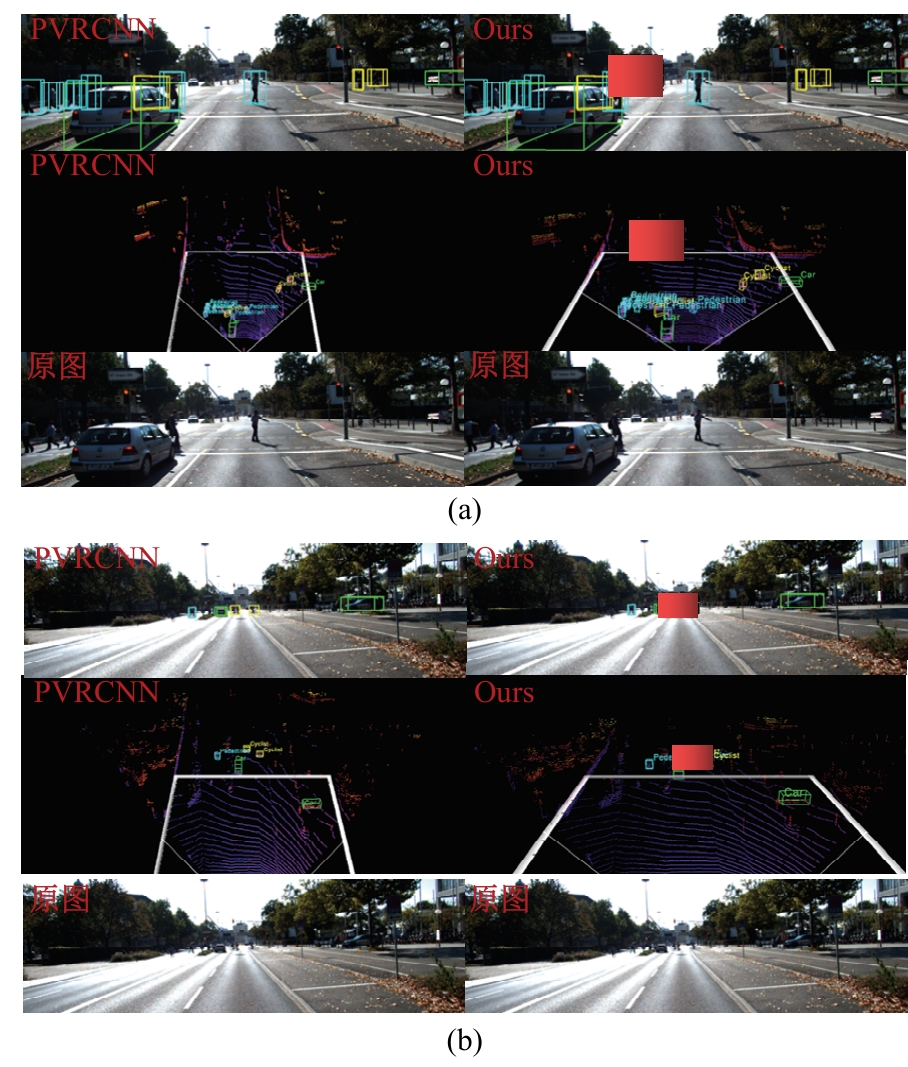
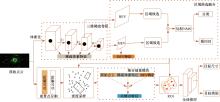
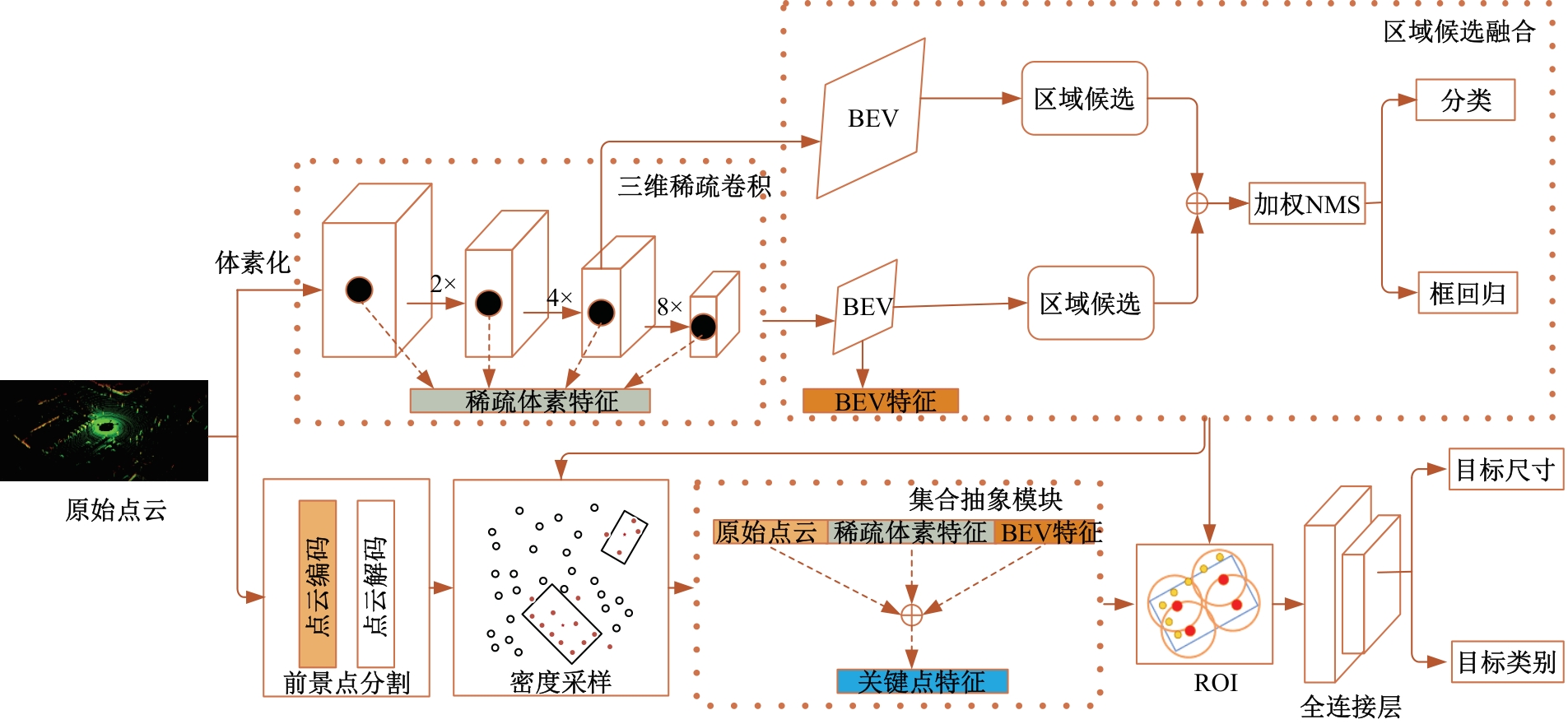
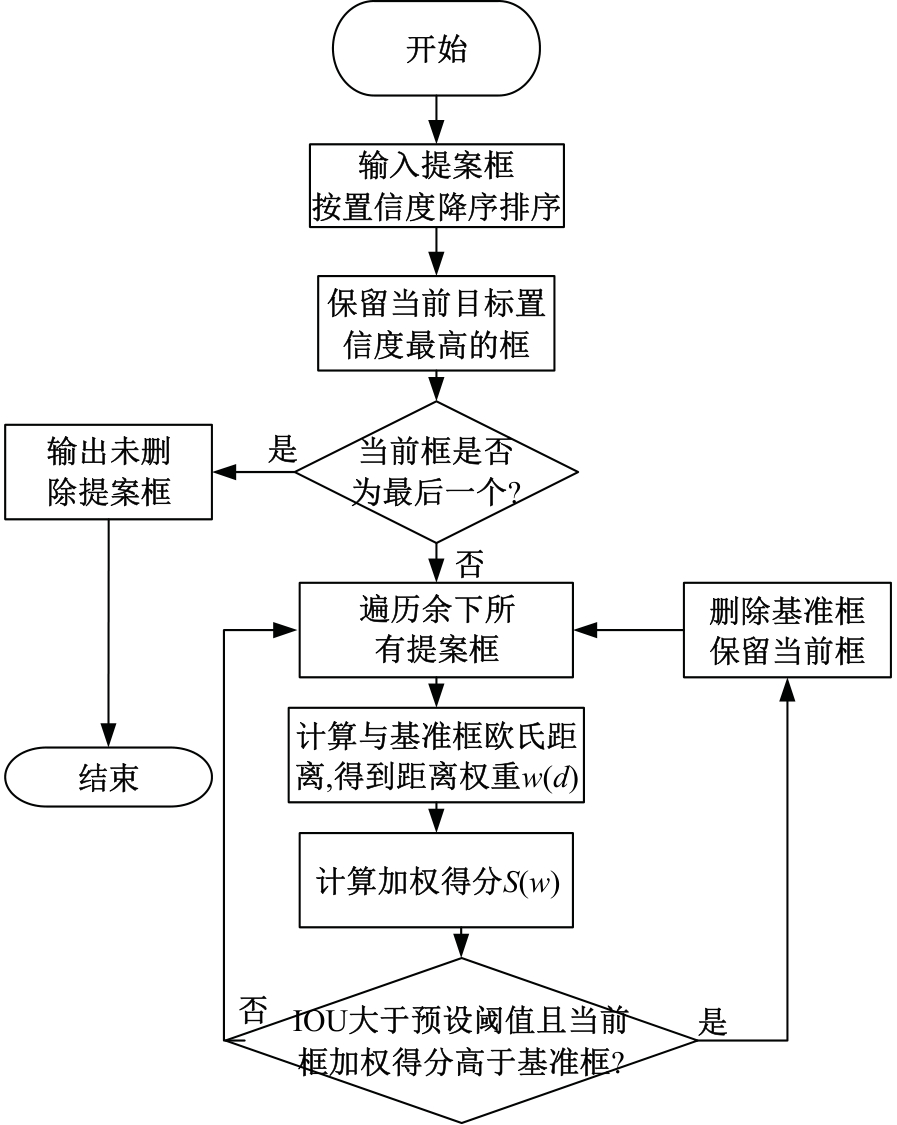
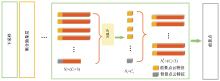
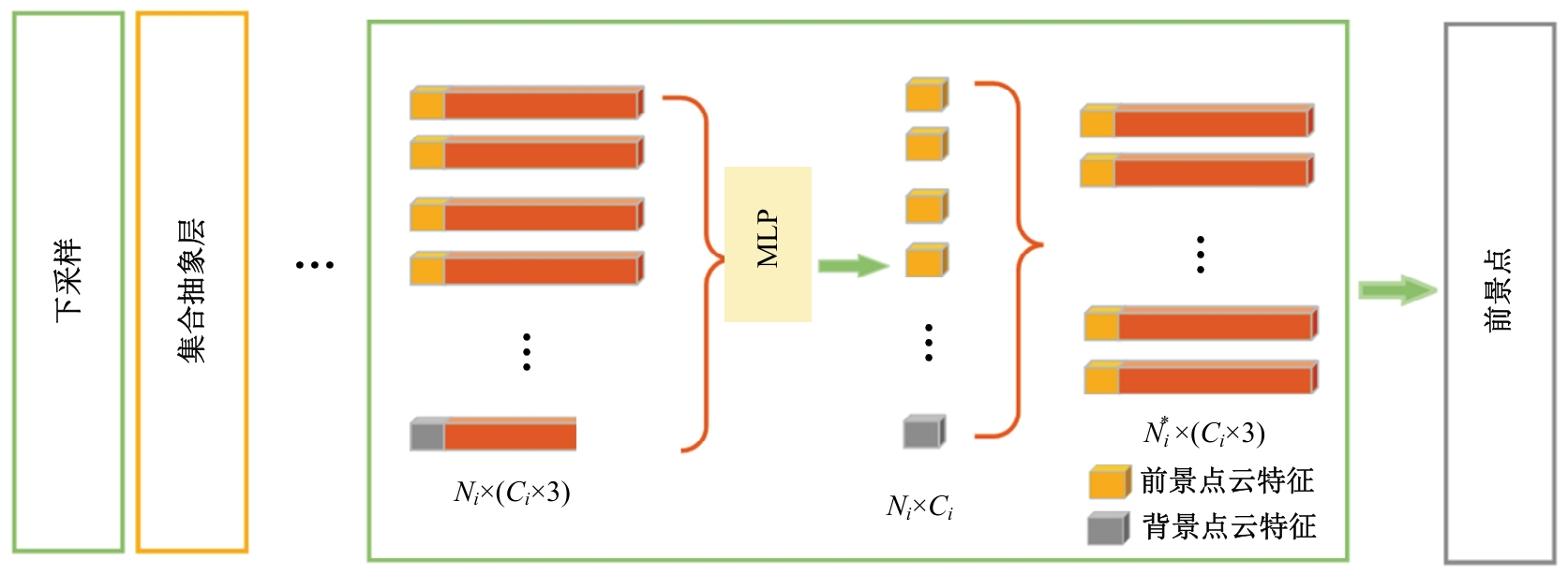
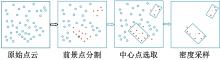
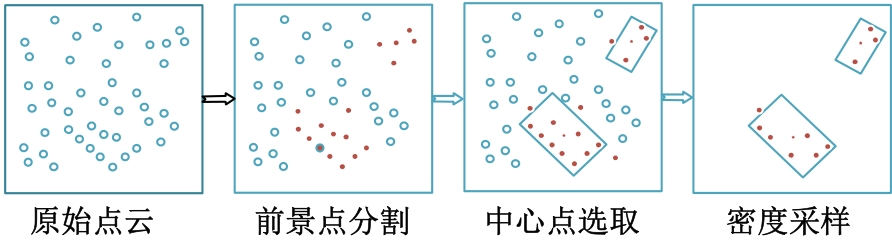
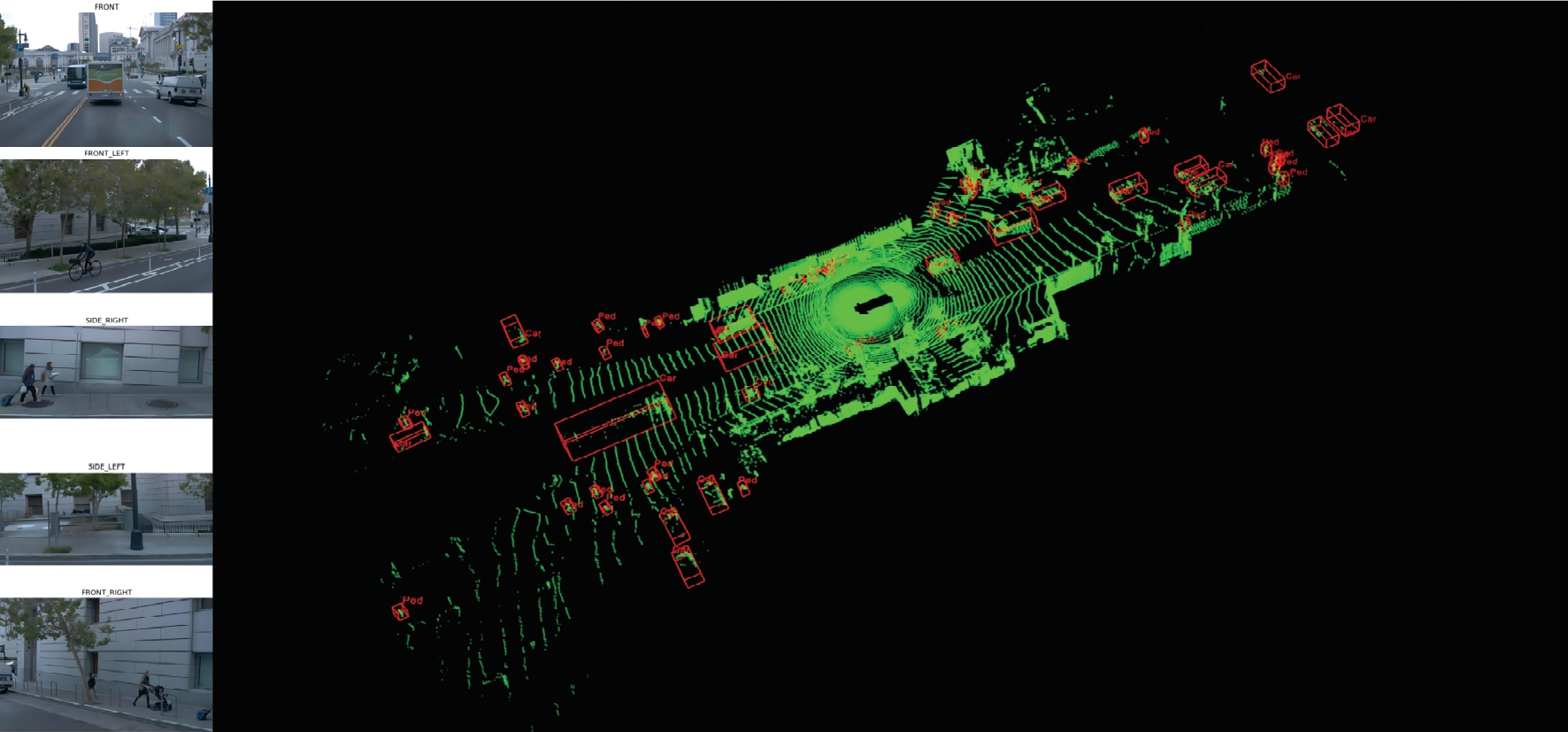
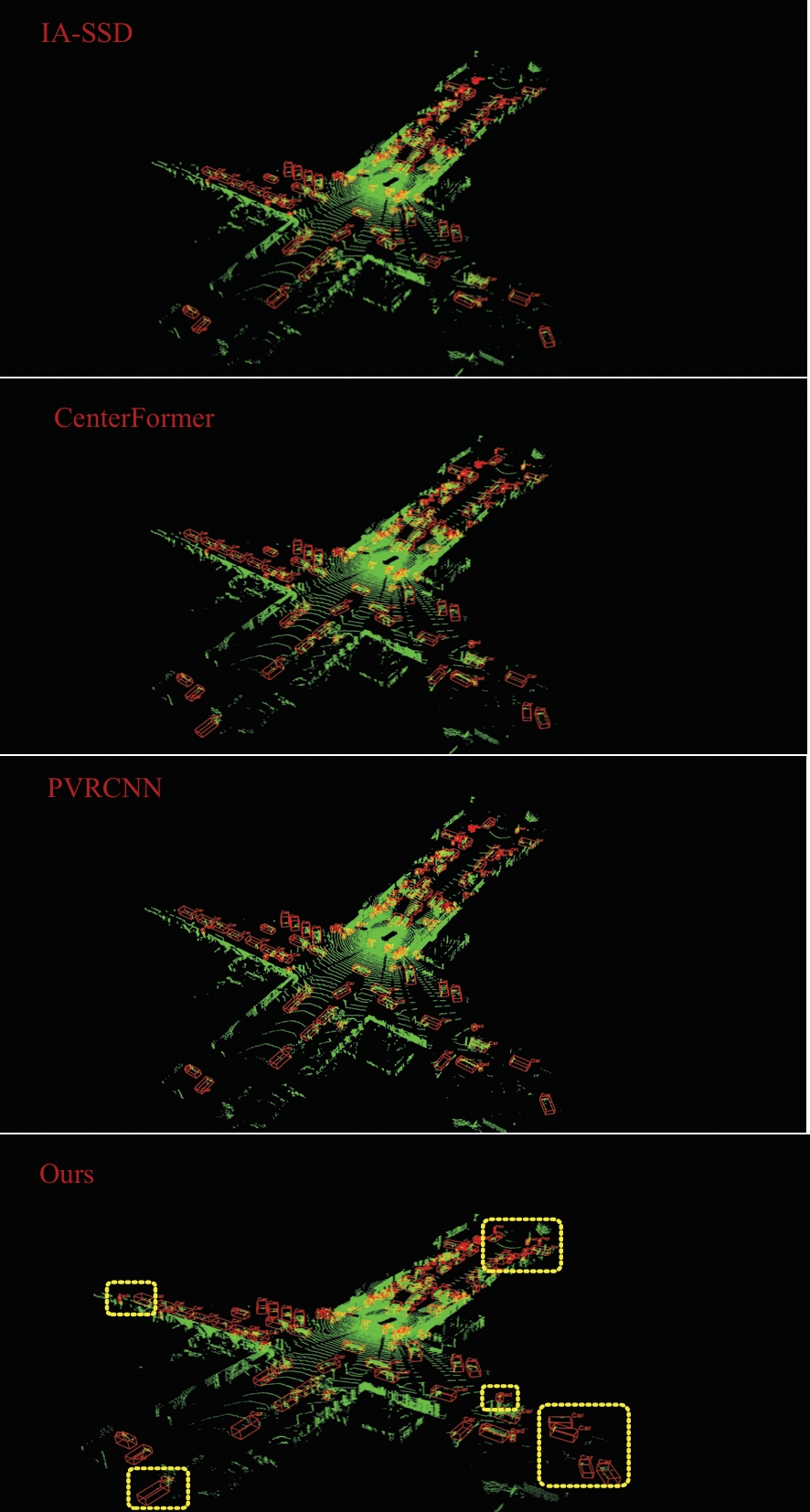
为了改善点云场景下的检测任务中,基于单一低分辨特征图生成的候选框容易造成目标丢失和关键点采样过程中引入大量背景点的问题,本文提出了一种基于PV-RCNN网络的改进算法。通过区域候选融合网络和加权非极大值抑制融合不同尺度下的候选框并消除冗余。利用分割网络对原始点云进行前景点分割,并根据候选框确定目标中心点位置,利用高斯密度函数进行区域密度估计得到不同的采样权重以解决稀疏区域采样困难的问题。本文使用KITTI数据集进行实验评估,在汽车、行人和骑行者中等难度下的平均精度分别较基线算法提升0.39%、1.31%和0.63%,并同样在Waymo open数据集上进行泛化实验。实验结果证明本文算法与目前大部分三维目标检测算法相比取得更高的检测精度。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Qian R, Garg D, Wang Y, et al. End-to-end pseudo-lidar for image-based 3d object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 5881-5890. |
| 2 | Wang Z, Huang Z, Fu J, et al. Object as query: equipping any 2D object detector with 3D detection ability[J]. Arxiv Preprint, 2023, 1: No.230102364. |
| 3 | 陶博, 颜伏伍, 尹智帅, 等. 基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2023, 53(3): 802-809. |
| Tao Bo, Yan Fu-wu, Yin Zhi-shuai, et al. 3D object detection algorithm based on high-precision map enhancement[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 802-809. | |
| 4 | Yang Z, Zhou Y, Chen Z, et al. 3D-man: 3D multi-frame attention network for object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1863-1872 |
| 5 | Li Y, Yu A W, Meng T, et al. Deepfusion: lidar-camera deep fusion for multi-modal 3d object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 17182-17191. |
| 6 | 才华, 寇婷婷, 杨依宁, 等. 基于轨迹优化的三维车辆多目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2024, 54(8): 2338-2347. |
| Cai Hua, Kou Ting-ting, Yang Yi-ning, et al. Three-dimensional vehicle multiple target tracking based on trajectory optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2338-2347. | |
| 7 | Zheng A, Zhang Y, Zhang X, et al. Progressive end-to-end object detection in crowded scenes[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 857-866. |
| 8 | Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]∥ 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779-788. |
| 9 | Waleed A, Sherif A, Mahmoud Z, et al. Yolo3D: end-to-end real-time 3D oriented object bounding box detection from lidar point cloud[C]∥Computer Vision-ECCV 2018 Workshops, Munichi, Germany, 2018: 716-728. |
| 10 | Zhou Y, Sun P, Zhang Y, et al. End-to-end multi-view fusion for 3D object detection in lidar point clouds[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, Cambridge, USA, 2020: 923–932. |
| 11 | Zhou Y, Tuzel O. Voxelnet: end-to-end learning for point cloud based 3d object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4490-4499. |
| 12 | Yan Y, Mao Y, Li B. Second: sparsely embedded convolutional detection[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): No.18103337. |
| 13 | Qi C R, Su H, Mo K, et al. Pointnet: deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 652-660. |
| 14 | Qi C R, Yi L, Su H, et al. Pointnet++: deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]∥Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 5105-5114. |
| 15 | Qi C R, Liu W, Wu C, et al. Frustum pointnets for 3d object detection from rgb-d data[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 918-927. |
| 16 | Yang Z, Sun Y, Liu S, et al. Std: sparse-to-dense 3d object detector for point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 1951-1960. |
| 17 | Shi S, Guo C, Jiang L, et al. PV-RCNN: point-voxel feature set abstraction for 3d object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10529-10538. |
| 18 | Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? the kitti vision benchmark suite[C]∥2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, Rhode Island,USA, 2012: 3354-3361. |
| 19 | Sun P, Kretzschmar H, Dotiwalla X, et al. Scalability in perception for autonomous driving: Waymo open dataset[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 2446-2454. |
| 20 | Ye M, Xu S, Cao T. Hvnet: hybrid voxel network for lidar based 3D object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1631-1640. |
| 21 | Shi S, Wang X, Li H. Pointrcnn: 3D object proposal generation and detection from point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 770-779. |
| 22 | Liu Z, Tang H, Lin Y, et al. Point-voxel CNN for efficient 3D deep learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 965-975. |
| 23 | 田枫, 姜文文, 刘芳, 等. 混合体素与原始点云的三维目标检测方法[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学, 2022, 36(11): 108-117. |
| Tian Feng, Jiang Wen-wen, Liu Fang, et al. Hybrid element and original point cloud 3D target detection method [J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2022, 36(11):108-117. | |
| 24 | Shi S, Jiang L, Deng J, et al. PV-RCNN++: point-voxel feature set abstraction with local vector representation for 3D object detection[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2023, 131(2): 531-551. |
| 25 | 车运龙, 袁亮, 孙丽慧. 基于强语义关键点采样的三维目标检测方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2024, 60(9): 254-260. |
| Che Yun-long, Yuan Liang, Sun Li-hui, et al. 3D object detection method based on strong semantic key point sampling[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2024, 60(9): 254-260. | |
| 26 | He C, Zeng H, Huang J, et al. Structure aware single-stage 3D object detection from point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 11873-11882. |
| 27 | Zhang Y, Hu Q, Xu G, et al. Not all points are equal: learning highly efficient point-based detectors for 3D lidar point clouds[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 18953-18962. |
| 28 | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980-2988. |
| 29 | Lang A H, Vora S, Caesar H, et al. Pointpillars: fast encoders for object detection from point clouds [C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seoul, South Korea, 2019: 12697-12705. |
| 30 | Shi W, Rajkumar R. Point-GNN: graph neural network for 3d object detection in a point cloud[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1711-1719. |
| 31 | Liu Z, Zhao X, Huang T, et al. Tanet: robust 3D object detection from point clouds with triple attention[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 11677-11684. |
| 32 | Shi S, Wang Z, Shi J, et al. From points to parts: 3D object detection from point cloud with part-aware and part-aggregation network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 43(8): 2647-2664. |
| 33 | Deng J, Shi S, Li P, et al. Voxel R-Cnn: towards high performance voxel-based 3d object detection[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(2): 1201-1209. |
| 34 | Song N, Jiang T, Yao J. JPV-Net: joint point-voxel representations for accurate 3D object detection[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2022, 36(2): 2271-2279. |
| 35 | Yang Z, Jiang L, Sun Y, et al. A unified query-based paradigm for point cloud understanding[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 8541-8551. |
| 36 | Yin T, Zhou X, Krahenbuhl P. Center-based 3D object detection and tracking[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 11784-11793. |
| 37 | Zhou Z, Zhao X, Wang Y, et al. Centerformer: center-based transformer for 3D object detection[C]∥European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 2022: 496-513. |
| 38 | He C, Li R, Li S, et al. Voxel set transformer: a set-to-set approach to 3D object detection from point clouds[C]∥2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 8417-8427. |
| 39 | Sheng H, Cai S, Liu Y, et al. Improving 3D object detection with channel-wise transformer[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 2743-2752. |
| [1] | 才华,寇婷婷,杨依宁,马智勇,王伟刚,孙俊喜. 基于轨迹优化的三维车辆多目标跟踪[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2338-2347. |
| [2] | 朱圣杰,王宣,徐芳,彭佳琦,王远超. 机载广域遥感图像的尺度归一化目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(8): 2329-2337. |
| [3] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [4] | 王殿伟,张池,房杰,许志杰. 基于高分辨率孪生网络的无人机目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1426-1434. |
| [5] | 王宇,赵凯. 基于亚像素定位的人体姿态热图后处理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1385-1392. |
| [6] | 高云龙,任明,吴川,高文. 基于注意力机制改进的无锚框舰船检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1407-1416. |
| [7] | 程鑫,刘升贤,周经美,周洲,赵祥模. 融合密集连接和高斯距离的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(12): 3589-3600. |
| [8] | 孙文财,胡旭歌,杨志发,孟繁雨,孙微. 融合GPNet与图像多尺度特性的红外-可见光道路目标检测优化方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(10): 2799-2806. |
| [9] | 陶博,颜伏伍,尹智帅,武冬梅. 基于高精度地图增强的三维目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 802-809. |
| [10] | 刘晶红,邓安平,陈琪琪,彭佳琦,左羽佳. 基于多重注意力机制的无锚框目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3518-3528. |
| [11] | 王侃,苏航,曾浩,覃剑. 表观增强的深度目标跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2676-2684. |
| [12] | 曹洁,屈雪,李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [13] | 徐涛,马克,刘才华. 基于深度学习的行人多目标跟踪方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 27-38. |
| [14] | 赵宏伟,李明昭,刘静,胡黄水,王丹,臧雪柏. 基于自然性和视觉特征通道的场景分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1668-1675. |
| [15] | 车翔玖, 王利, 郭晓新. 基于多尺度特征融合的边界检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1621-1628. |
|
||