吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (3): 842-849.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180112
激光冲击强化层数对6061⁃T6铝合金抗腐蚀性能的影响
- 江苏大学 机械工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
Effect of coverage layer on corrosion resistance of 6061⁃T6 aluminum alloy subjected to laser shock peening
Jin⁃zhong LU( ),Wan⁃ting ZHOU,Sheng⁃yang ZHANG,Yi⁃kai SHAO,Chang⁃yu WANG,Kai⁃yu LUO
),Wan⁃ting ZHOU,Sheng⁃yang ZHANG,Yi⁃kai SHAO,Chang⁃yu WANG,Kai⁃yu LUO
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China
摘要:
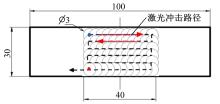
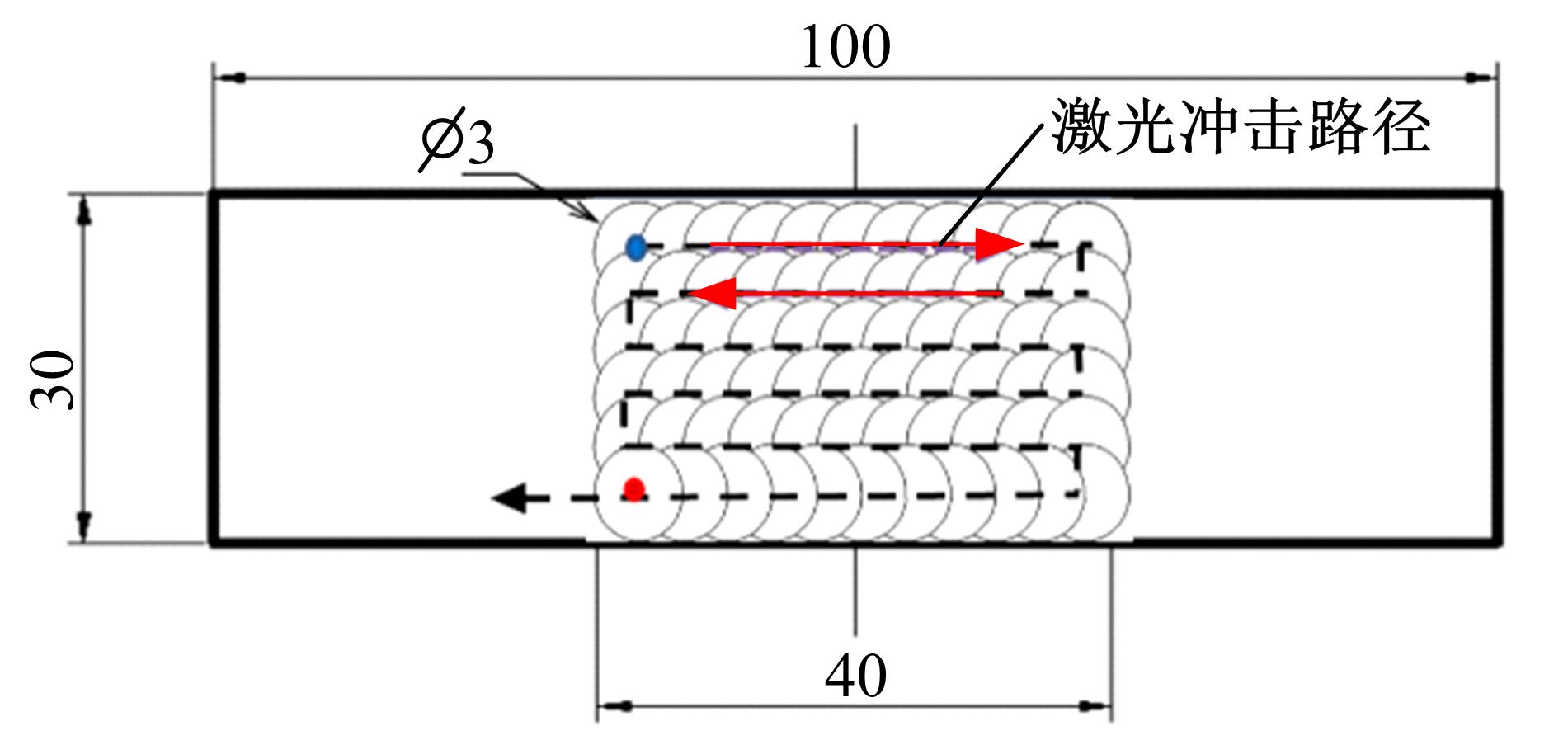
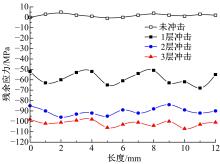
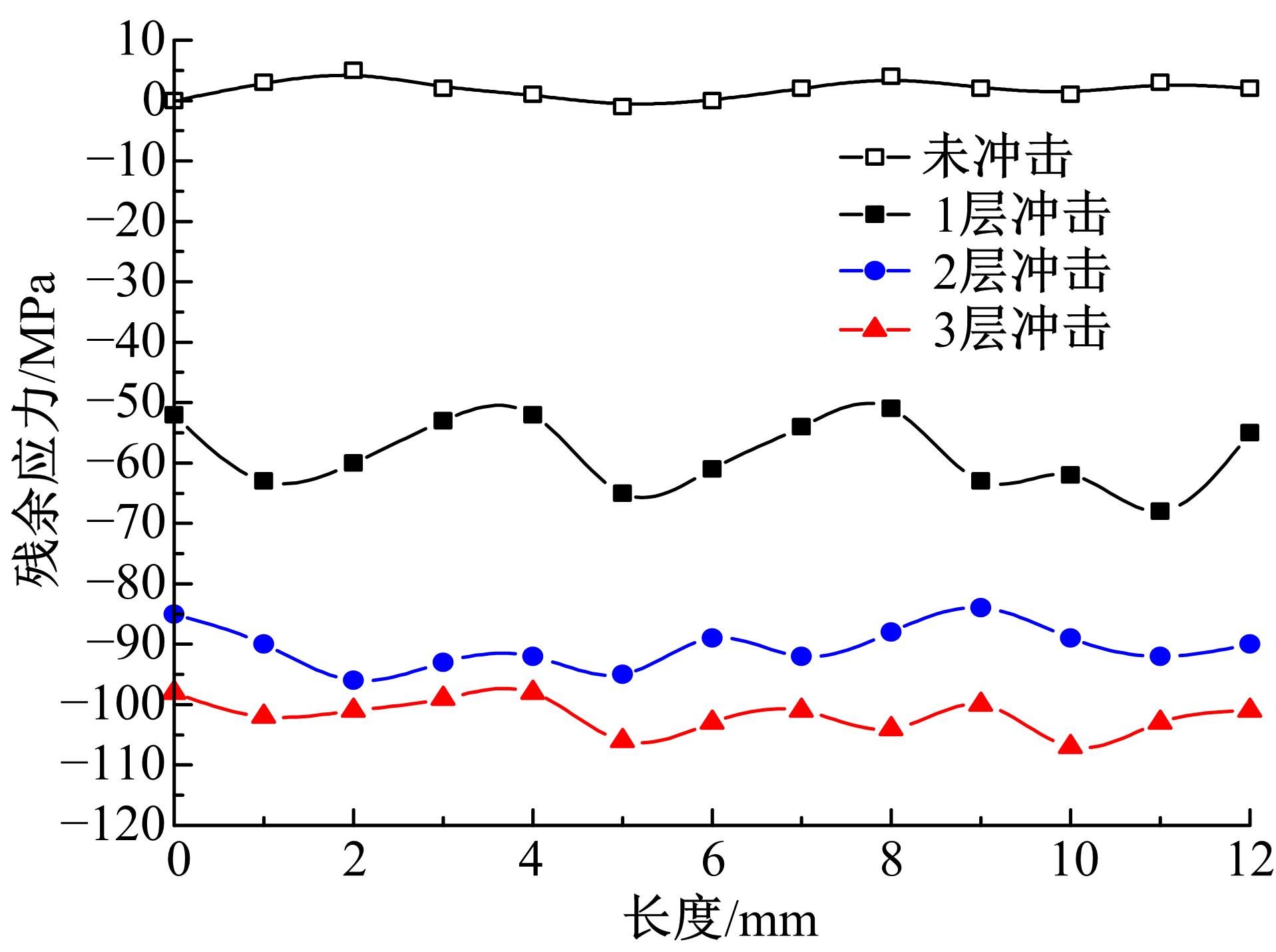
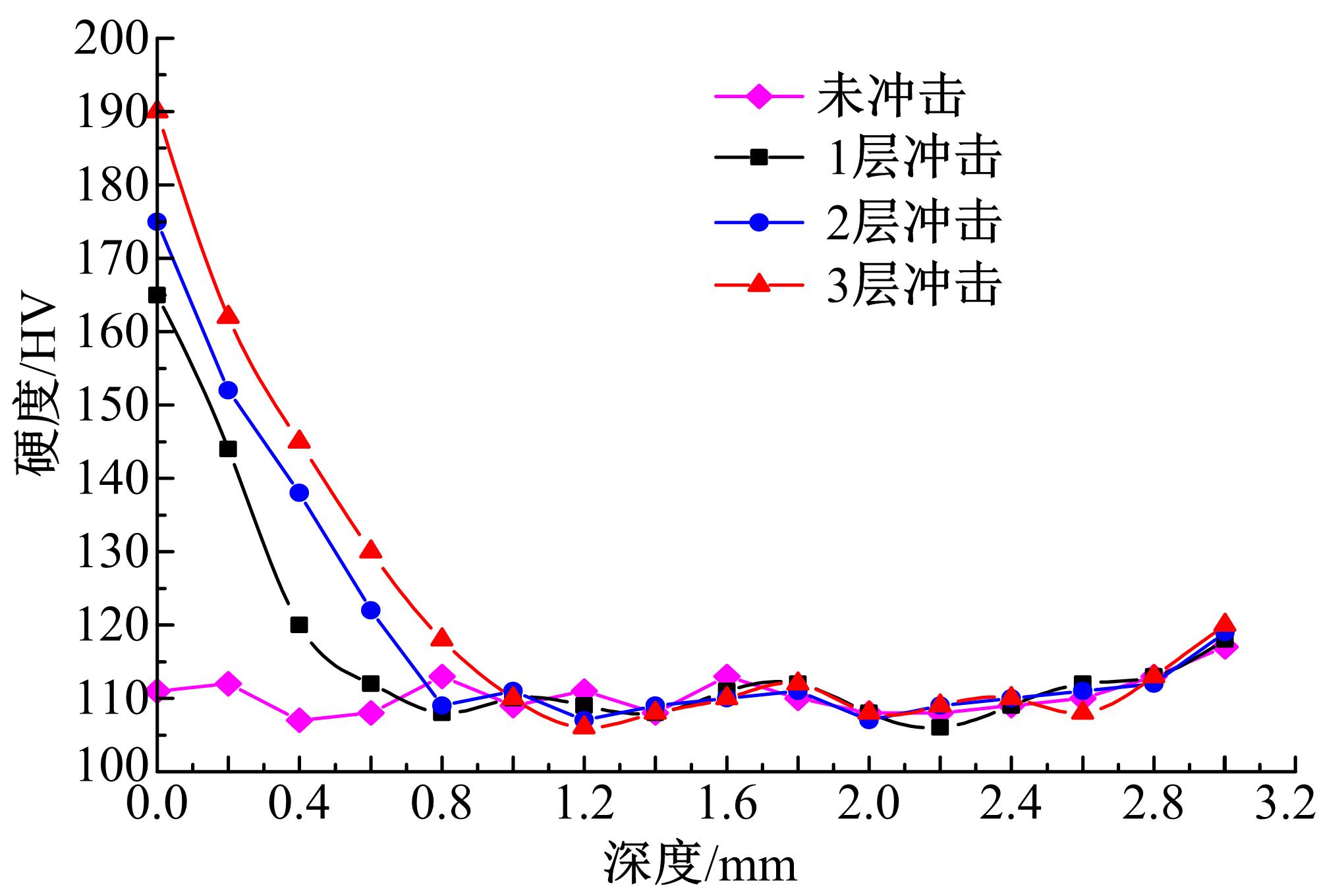
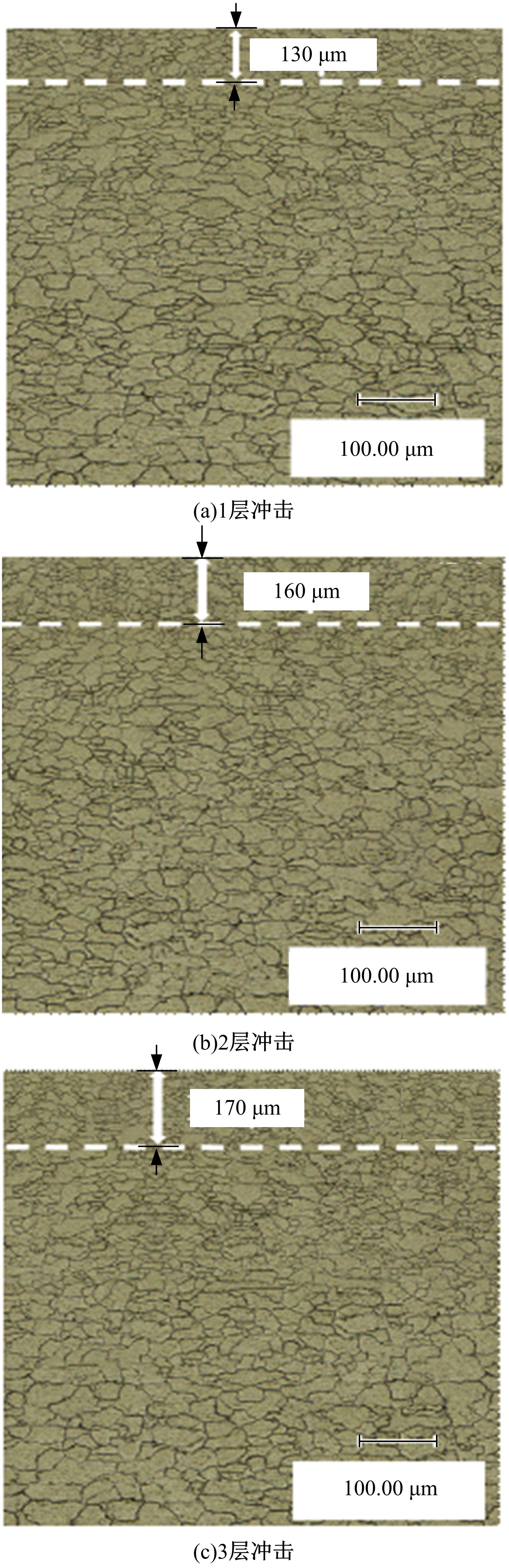
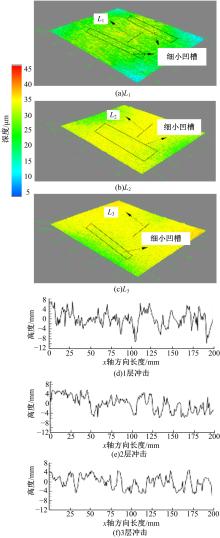
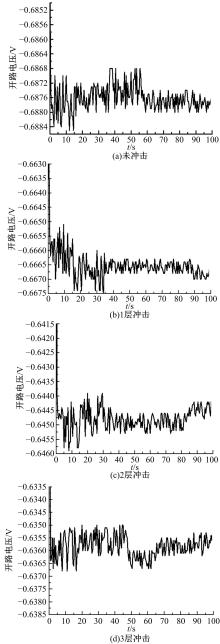
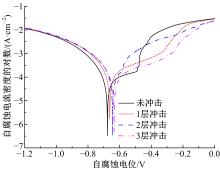
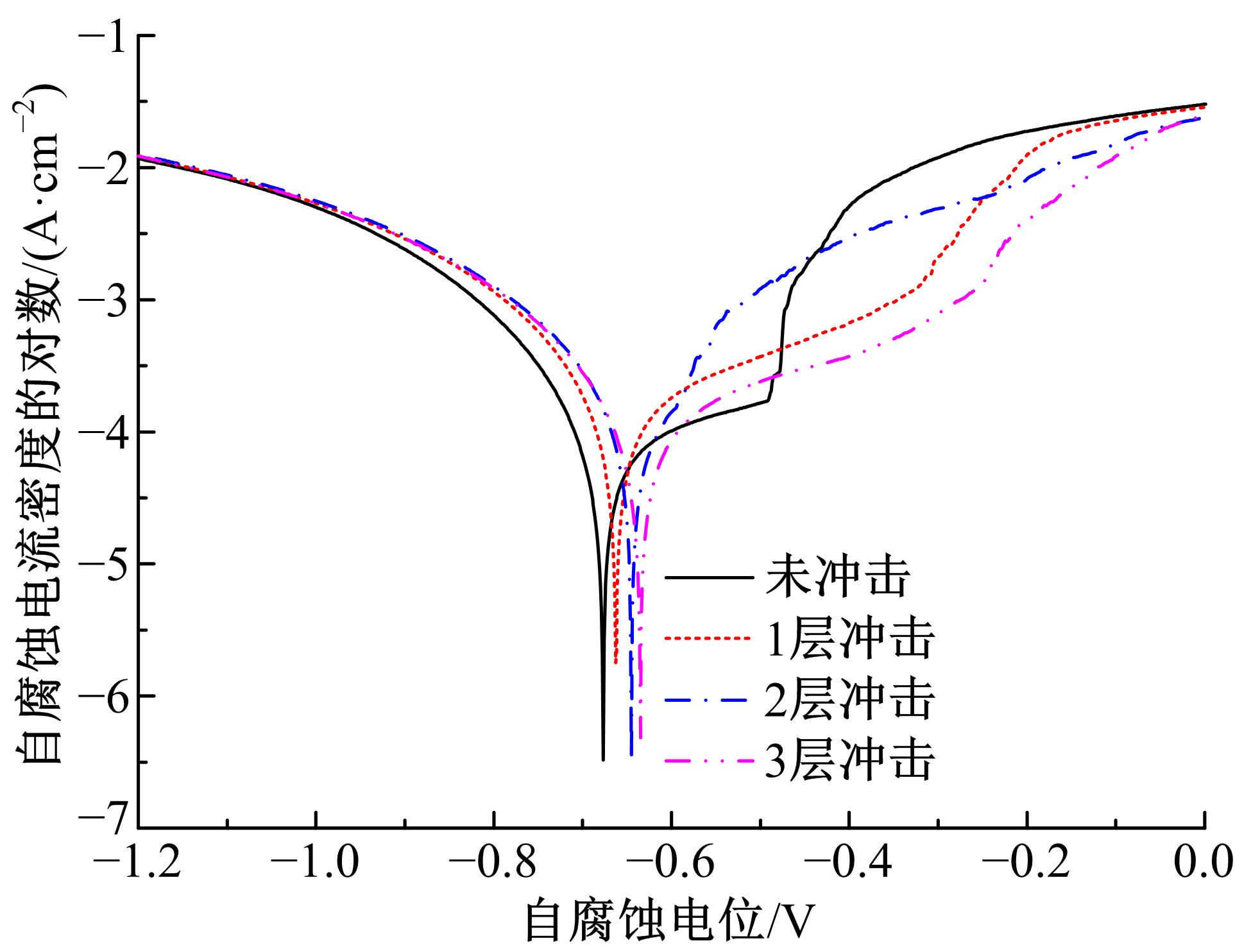
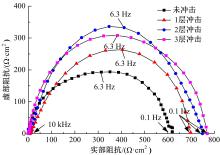
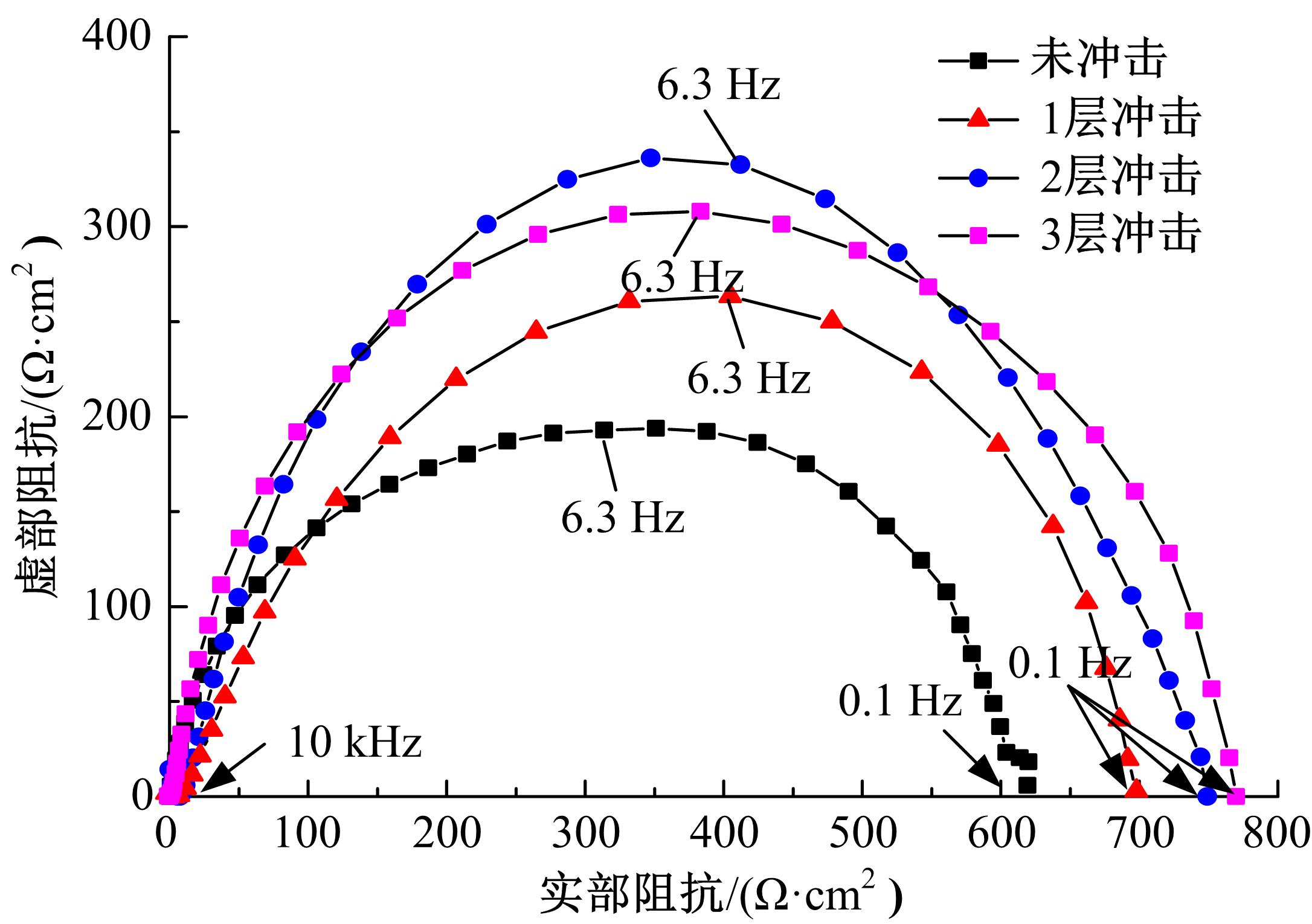
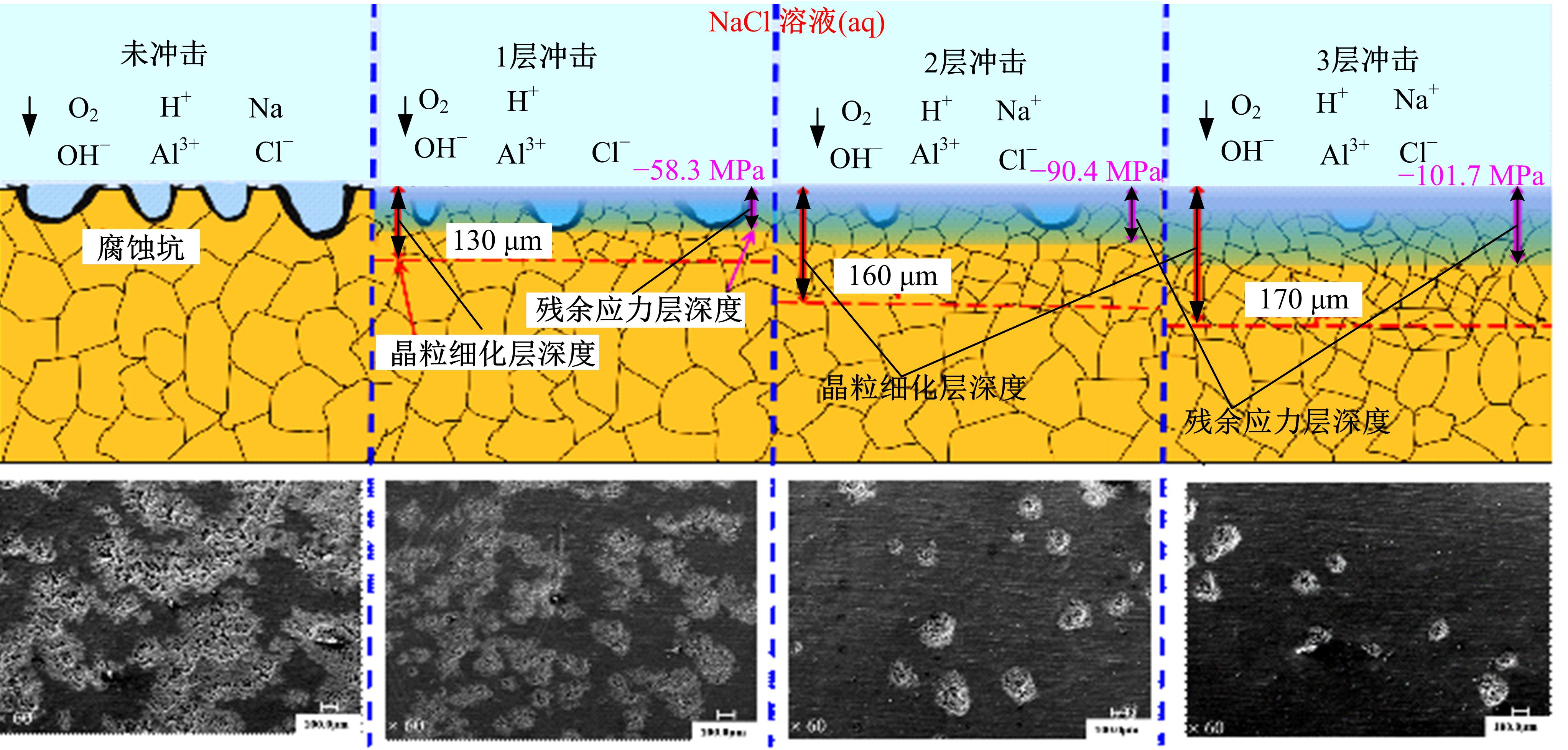
针对6061?T6铝合金在各种极端工况下抗腐蚀性较差的问题,采用激光冲击强化对6061?T6铝合金进行不同层数的冲击处理,通过测量残余应力和表面粗糙度观察了微观组织和电化学腐蚀,分析了激光冲击强化对6061?T6铝合金抗腐蚀性能的影响。结果表明:激光冲击强化后,材料表面的残余压应力、表面硬度随激光冲击层数的增加而增加;冲击区域晶粒明显细化,细化层深度随冲击层数的增加而增加;材料表面的粗糙度随冲击层数的增加而降低;激光冲击强化处理后材料的电化学腐蚀电流减小、阻抗半径增大,表面点蚀坑的生长受到明显抑制;残余应力增加、微观组织细化和表面粗糙度降低,三者共同作用提升了6061?T6铝合金的抗腐蚀性能。
中图分类号:
- TH16,TN249
| 1 | GencaldI S, SaklakogluN, AkmanE, et al. Pulsed Nd:YAG laser shock processing effects on mechanical properties of 6061⁃T6 alloy[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2014,56(1):273⁃277. |
| 2 | ZhangX C, ZhangY K, LuJ Z, et al. Improvement of fatigue life of Ti–6Al–4V alloy by laser shock peening[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A,2010,527(15):3411⁃3415. |
| 3 | 葛茂忠,张永康,项建云.AZ31B镁合金激光冲击强化及抗应力腐蚀研究[J].中国激光,2010,37(11):2925⁃2930. |
| GeMao⁃zhong, ZhangYong⁃kang, XiangJian⁃yun. Research on laser shock strengthening and stress corrosion cracking resistance of AZ31B magnesium alloy [J]. Chinese Journal Lasers, 2010, 37(11): 2925⁃2930. | |
| 4 | YangJ M, HerY C, HanN, et al. Laser shock peening on fatigue behavior of 2024⁃T3 Al alloy with fastener holes and stopholes[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A,2001,298(1/2):296⁃299. |
| 5 | 邢清蒲,张凌峰,李少哲,等. 激光冲击强化对2A02铝合金电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术,2013,25(5):402⁃405. |
| XingQing⁃pu, ZhangLing⁃feng, LiShao⁃zhe, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 2A02 aluminum alloy[J]. Corrosion Science & Protection Technology, 2013,25(5):402⁃405. | |
| 6 | 王江涛,张永康,陈菊芳,等. 强激光冲击对7075铝合金等离子弧焊接头电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2015,42(12):106⁃115. |
| WangJiang⁃tao, ZhangYong⁃kang, ChenJu⁃fang, et al. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of 7075 aluminum alloy plasma arc weldments[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2015, 42(12):106⁃115. | |
| 7 | 汪诚,赖志林,何卫锋,等. 激光冲击次数对1Cr11Ni2W2MoV不锈钢高周疲劳性能的影响[J]. 中国激光,2014,41(1):46⁃51. |
| WangCheng, LaiZhi⁃lin, HeWei⁃feng, et al. Effect of multi⁃impact on high cycle fatigue properties of 1Cr11Ni2W2MoV stainless steel subject to laser shock processing[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2014,41(1):46⁃51. | |
| 8 | DiS A, KennyJ M. Grain size dependence of the fatigue behaviour of a ultrafine⁃grained AISI 304 stainless steel[J]. Materials Letters,2003,57(21):3182⁃3185. |
| 9 | ZhenL, HuH, WangX Y, et al. Distribution characterization of boundary misorientation angle of 7050 aluminum alloy after high⁃temperature compression[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2009,209(2):754⁃761. |
| 10 | LiQ, XuY B, LaiZ H, et al. Dynamic recrystallization induced by plastic deformation at high strain rate in a Monel alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A,2000,276(1/2):250⁃256. |
| 11 | MazurinaI, SakaiT, MiuraH, et al. Grain refinement in aluminum alloy 2219 during ECAP at 250 ℃[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2008,473(1/2):297⁃305. |
| 12 | LuJ Z, HanB, CuiC Y, et al. Electrochemical and pitting corrosion resistance of AISI 4145 steel subjected to massive laser shock peening treatment with different coverage layers[J]. Optics & Laser Technology,2017,88:250⁃262. |
| 13 | 李少哲,张凌峰,邢清蒲.激光冲击强化对AZ91镁合金的电化学腐蚀行为的影响[J]. 中国激光,2013,40(5):74⁃78. |
| LiShao⁃zhe, ZhangLing⁃feng, XingQing⁃pu. Effect of laser shock processing on electrochemical corrosion behavior of AZ91 magnesium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2013,40(5):74⁃78. | |
| 14 | AmarH, VignalV, KrawiecH, et al. Influence of the microstructure and laser shock processing(LSP) on the corrosion behavior of the AA2050⁃T8 aluminium alloy[J]. Corrosion Science, 2011,53(10):3215⁃3221. |
| 15 | 陈菊芳, 张永康, 许仁军. AM50镁合金表面激光熔凝层的组织与耐蚀性能[J]. 中国激光, 2008,35(2):307⁃310. |
| ChenJu⁃fang, ZhangYong⁃kang, XuRen⁃jun. Microstructure and corrosion resistant property of laser surface melting layer of AM50 magnesium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2008,35(2):307⁃310. | |
| 16 | 罗新民,张静文,赵广志,等. 激光冲击强化对2A02铝合金疲劳行为的影响[J]. 中国激光,2009,36(12):3323⁃3328. |
| LuoXin⁃min, ZhangJing⁃wen, ZhaoGuang⁃zhi, et al. Effect of laser shock strengthening on fatigue behaviors of 2A02 aluminum alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2009,36(12):3323⁃3328. | |
| 17 | 洪晰,王声波,郭大浩,等. 激光冲击波在铝靶中衰减特性的研究[J].量子电子学报,1998,15(5):474⁃478. |
| HongXi, WangSheng⁃bo, GuoDa⁃hao, et al. Rsesearch on the attenuation property of the laser induced shock wave propagating in aluminum[J]. Chinese Joural of Quantum Electronics,1998,15(5):474⁃478. | |
| 18 | 叶作彦. 新型铝合金的腐蚀行为及表面改性的影响[D]. 西安:西北工业大学材料学院,2015. |
| YeZuo⁃yan. Corrosion behavior of new aluminum alloy and the effect of surface modification[D]. Xi’an:College of Materials, Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2015. |
| [1] | 马芳武,陈实现,韩露,梁鸿宇,蒲永锋. 金属表面特征与金属⁃塑料直接连接强度的相关性[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 816-821. |
| [2] | 罗开玉,邢月华,柴卿锋,吴世凯,尹叶芳,鲁金忠. 激光冲击强化对2Cr13不锈钢腐蚀 疲劳性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 850-858. |
| [3] | 赵爽,沈继红,张刘,赵晗,陈柯帆. 微细电火花加工表面粗糙度快速高斯评定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1838-1843. |
| [4] | 郑孝义, 孙大千, 李欣, 都桂刚, 辛伟达, 任振安. NbAl3强化Al-Nb熔覆层的组织与性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1531-1536. |
| [5] | 寇淑清, 石舟. 裂解连杆接合面三维重构及其强度与刚度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1515-1523. |
| [6] | 任庆磊, 魏昕, 谢小柱, 胡伟. 硅片自旋转磨削中基于力的微接触机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 796-802. |
| [7] | 刘子武, 李剑峰. 叶片材料FV520B再制造熔覆层冲蚀损伤行为及评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(3): 835-844. |
| [8] | 李俊烨, 胡敬磊, 杨兆军, 张心明, 周曾炜. 离散相磨粒粒径对磨粒流研抛共轨管质量的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 492-499. |
| [9] | 陈超, 赵升吨, 崔敏超, 韩晓兰, 范淑琴, 石田徹. AL5052铝合金板平压重塑形连接试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1512-1518. |
| [10] | 郎利辉, 阚鹏, 王耀, 孙志莹, 张泉达. 铝合金板材三向应力状态下的成形性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1527-1533. |
| [11] | 李俊烨, 乔泽民, 杨兆军, 张心明. 介观尺度下磨料浓度对磨粒流加工质量的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 837-843. |
| [12] | 曲兴田, 赵永兵, 刘海忠, 王昕, 杨旭, 陈行德. 串并混联机床几何误差建模与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(1): 137-144. |
| [13] | 张鹏, 寇淑清, 赵勇, 林宝君. 装配式凸轮轴三点式轴向滚花过程[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1953-1960. |
| [14] | 任书楠, 杨向东, 王国磊, 刘志, 陈恳. 大部件喷涂中的移动机械臂站位规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(6): 1995-2002. |
| [15] | 王犇, 王晓力. 硅微球轴承关键工艺[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(3): 824-830. |
|
||