吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2019, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (5): 1492-1499.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20180451
• • 上一篇
基于转运延误风险的多方式协同货运载运工具配置优化
- 1. 武汉理工大学 交通学院,武汉430063
2. 湖北第二师范学院 管理学院,武汉 430205
Optimizing vehicles allocation of multimodal coordinated freight transport based on transshipment delay risks
Hai-bo LONG1( ),Jia-qi YANG1,Xue-yu ZHAO2(
),Jia-qi YANG1,Xue-yu ZHAO2( )
)
- 1. School of Transportation, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430063, China
2. School of Management, Hubei University of Education, Wuhan 430205, China
摘要:
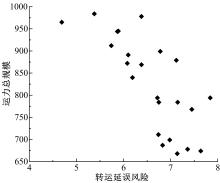
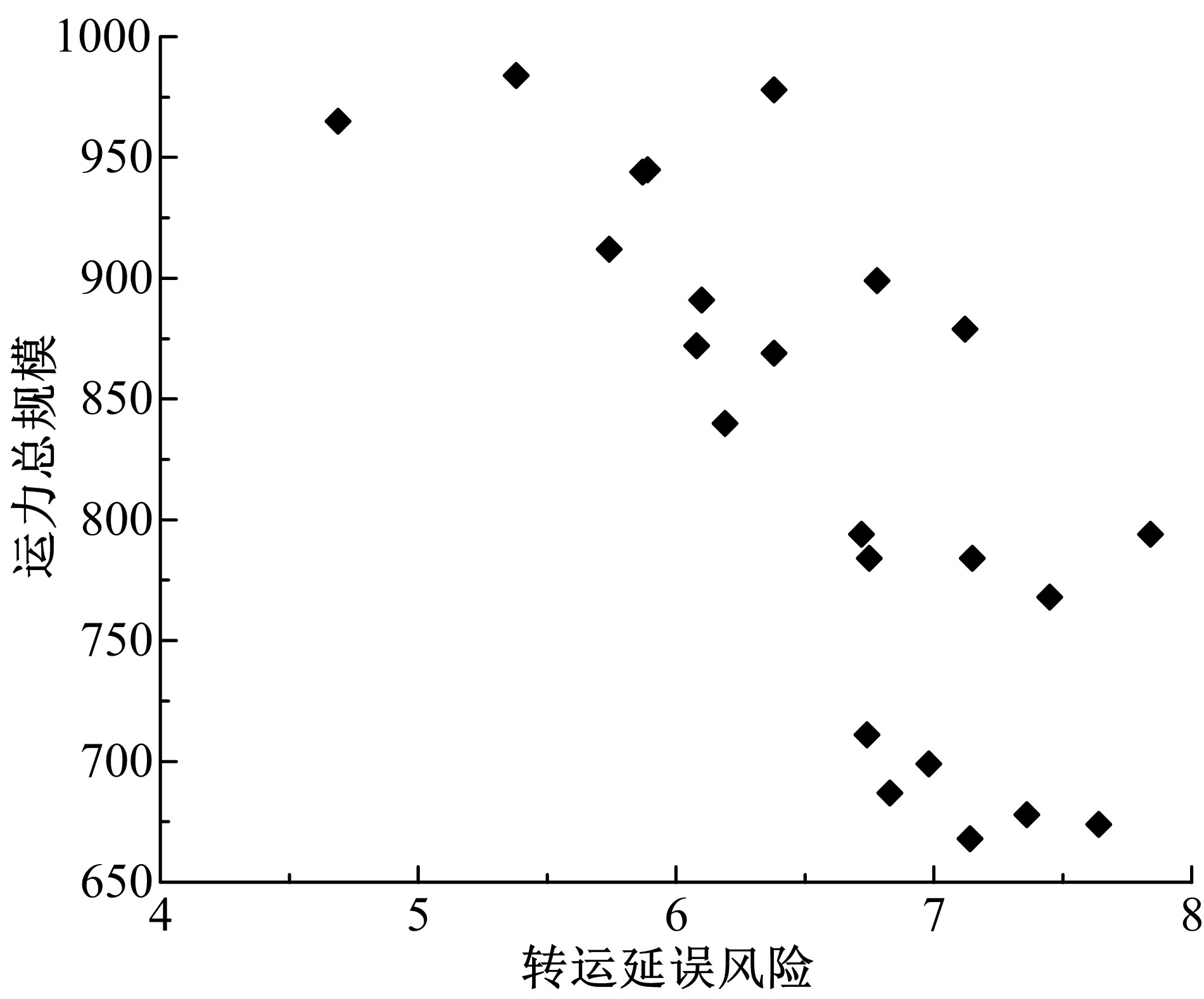
从货运节点转运延误风险的视角研究了多方式协同货运运力资源分配协调优化问题。在综合分析转运风险因素的基础上,运用熵权法对多方式协同货运节点转运延误风险程度进行了评价,并构建了考虑转运延误风险的分区段多方式协同货运运力资源配置优化模型,提出NSGA-II算法思路对模型进行求解。最后,通过算例验证分析了基于转运延误风险的多方式协同货运载运工具配置优化效果。
中图分类号:
- U12
| 1 | VilkoJ P P, HallikasJ M. Risk assessment in multimodal supply chains[J]. International Working Seminar on Production Economics, 2012, 140(2): 586-595. |
| 2 | MohammadiM, JulaP, Tavakkoli-MoghaddamR. Design of a reliable multi-modal multi-commodity model for hazardous materials transportation under uncertainty[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 257(3): 792-809. |
| 3 | TalaricoL, ReniersG, SörensenK, et al. MISTRAL: a game-theoretical model to allocate security measures in a multi-modal chemical transportation network with adaptive adversaries[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2015, 138: 105-114. |
| 4 | JansenB, SwinkelsP C J, TeeuwenG J A, et al. Operational planning of a large-scale multi-modal transportation system[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2004, 156(1): 41-53. |
| 5 | 帅斌, 黄丽霞. 危险货物运输风险评估研究动态[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2014, 24(7): 50-56. |
| BinShuai, HuangLi-xia. Developments in research on assessment of risk in hazardous materials transportation[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2014, 24(7): 50-56. | |
| 6 | XieY, LuW, WangW, et al. A multimodal location and routing model for hazardous materials transportation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012(227/228): 135-141. |
| 7 | 郭丰润, 韩文涛, 魏毓. 危险品运输方式优化研究[J].中国安全生产科学技术, 2013, 9(2): 126-129. |
| GuoFeng-run, HanWen-tao, WeiYu. Research on optimization for transportation way of hazardous materials[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2013, 9(2): 126-129. | |
| 8 | GuimarãesA G, MaiaA D G. Challenges and innovation opportunities in load multimodal transport-LMT in brazil: cluster technique application as a support tool for decision making[J]. Transportation Research Procedia, 2017, 25: 870-887. |
| 9 | ZhuL, Guner-OzbekM D, YanH. A study of liabilities of multimodal transport operators in China[J].Research in Transportation Economics, 2012, 35(1): 58-65. |
| 10 | 王清斌, 韩增霞, 计明军. 基于节点作业随机特征的集装箱多式联运路径优化[J].交通运输系统工程与信息, 2011, 11(6): 137-144. |
| WangQing-bin, HanZeng-xia, JiMing-jun. Path optimization of container multimodal transportation based on node operation randomness[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2011, 11(6): 137-144. | |
| 11 | HaoC, YueY. Optimization on combination of transport routes and modes on dynamic programming for a container multimodal transport system[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2016, 137: 382-390. |
| 12 | SeoY J, ChenF, RohS Y. Multimodal transportation: the case of laptop from chongqing in China to rotterdam in europe[J]. Asian Journal of Shipping and Logistics, 2017, 33(3): 155-165. |
| [1] | 别一鸣,汤茹茹,王运豪,文斌,冯天军,王琳虹. 信号交叉口进口车道饱和流率估计方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1459-1464. |
| [2] | 梁泉,翁剑成,周伟,荣建. 基于关联规则的公共交通通勤稳定性人群辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1484-1491. |
| [3] | 吴文静,陈润超,贾洪飞,罗清玉,孙迪. 车路协同环境下路段掉头区域车辆协同控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1100-1106. |
| [4] | 江亮,贺宜. 电动两轮车风险驾驶行为及事故影响因素分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1107-1113. |
| [5] | 曲昭伟,潘昭天,陈永恒,陶鹏飞,孙迪. 基于最优速度模型的改进安全距离跟驰模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1092-1099. |
| [6] | 秦嘉浩,李臻,光岡宗司,井上英二,宋正河,朱忠祥. 基于模型实验的拖拉机配置对稳定性的影响差异[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1236-1245. |
| [7] | 白乔文,曲昭伟,陈永恒,熊帅,陶楚青. 非严格优先权下无左转专用相位直行车辆轨迹模型建立[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 673-679. |
| [8] | 李志慧,钟涛,赵永华,胡永利,李海涛,赵景伟. 面向车辆自主驾驶的行人跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 680-687. |
| [9] | 曹宁博,赵利英,曲昭伟,陈永恒,白乔文,邓晓磊. 考虑双向行人跟随行为的社会力模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 688-694. |
| [10] | 罗小芹,王殿海,金盛. 面向混合交通的感应式交通信号控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 695-704. |
| [11] | 陈磊,王江锋,谷远利,闫学东. 基于思维进化优化的多源交通数据融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
| [12] | 凃强,程琳,林芬,孙超. 考虑出行者风险态度的最优路径搜索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 720-726. |
| [13] | 尹超英,邵春福,王晓全. 考虑停车可用性的建成环境对小汽车通勤出行的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 714-719. |
| [14] | 陈永恒,刘芳宏,曹宁博. 信控交叉口行人与提前右转机动车冲突影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1669-1676. |
| [15] | 常山,宋瑞,何世伟,黎浩东,殷玮川. 共享单车故障车辆回收模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1677-1684. |
|
||