吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2018, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1677-1684.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20170543
共享单车故障车辆回收模型
- 北京交通大学 城市交通复杂系统理论与技术教育部重点实验室,北京 100044
Recycling model of faulty bike sharing
CHANG Shan( ),SONG Rui(
),SONG Rui( ),HE Shi-wei,LI Hao-dong,YIN Wei-chuan
),HE Shi-wei,LI Hao-dong,YIN Wei-chuan
- MOE Key Laboratory for Urban Transportation Complex Systems Theory and Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
摘要:
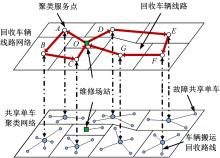
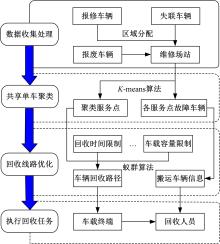
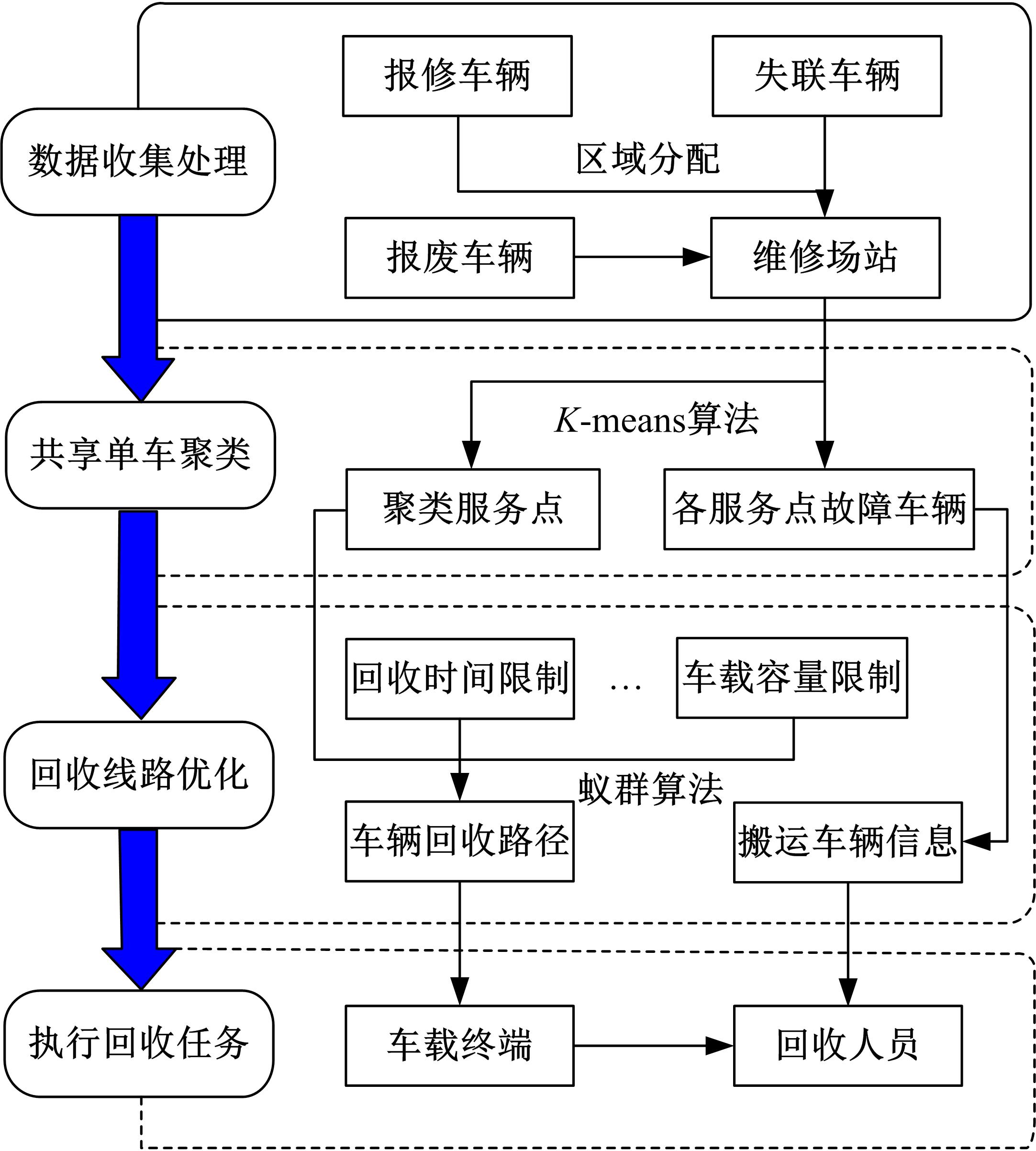
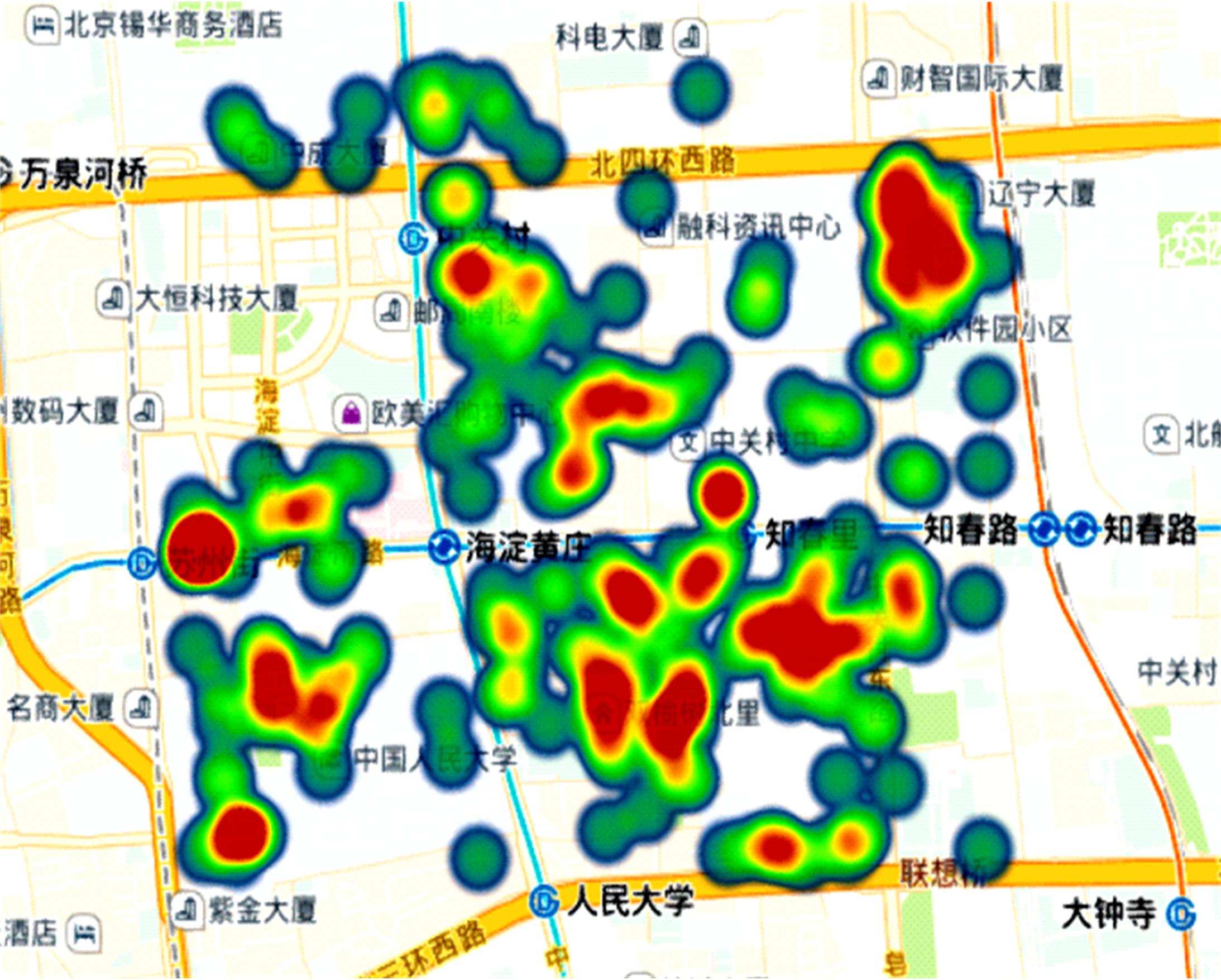
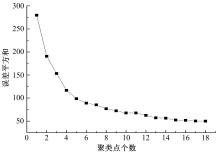
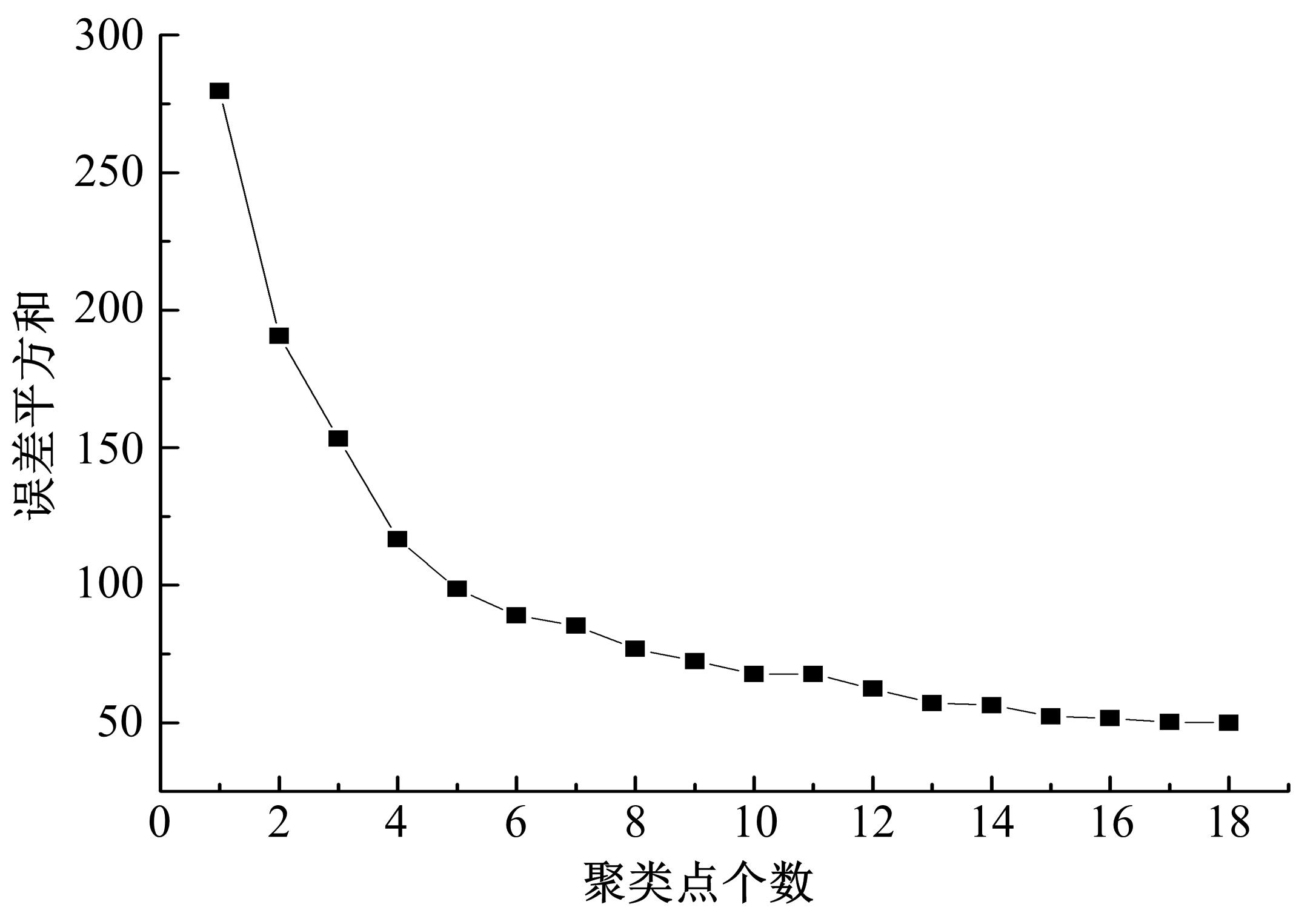
提出了共享单车故障车辆回收的流程,采用K-means算法对共享单车故障车辆进行聚类,形成聚类服务点,在此基础上构建了以车辆回收工作总成本最小为目标的共享单车故障车辆回收模型,并使用Cplex优化软件求解。以北京市某片区共享单车为例,验证了模型和方法的有效性。结果表明:装载容量的取值对回收任务产生较大影响,本文模型和算法可较好地应用于共享单车故障车辆回收任务中。
中图分类号:
- U491
| [1] |
Fishman E, Washington S, Haworth N , et al. Factors influencing bike share membership: an analysis of Melbourne and Brisbane[J]. Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice, 2015,71:17-30.
doi: 10.1016/j.tra.2014.10.021 |
| [2] |
Fishman E . Bikeshare: a review of recent literature[J]. Transport Reviews, 2016,36(1):92-113.
doi: 10.1080/01441647.2015.1033036 |
| [3] | Shaheen S A, Guzman S, Zhang H . Bikesharing in Europe, the Americas, and Asia: past, present, and future[J]. Transportation Research Record, 2010(2143):159-167. |
| [4] |
Chemla D, Meunier F, Calvo R W . Bike sharing systems: Solving the static rebalancing problem[J]. Discrete Optimization, 2013,10(2):120-146.
doi: 10.1016/j.disopt.2012.11.005 |
| [5] |
Schuijbroek J, Hampshire R C, Hoeve W J V . Inventory rebalancing and vehicle routing in bike sharing systems[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017,257(3):992-1004.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2016.08.029 |
| [6] |
Ghosh S, Varakantham P, Adulyasak Y , et al. Dynamic repositioning to reduce lost demand in bike sharing systems[J] Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2017,58:387-430.
doi: 10.1613/jair.5308 |
| [7] | 刘臻 . 城市公共自行车运营中的多车场车辆调配优化研究[D]. 北京:北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2014. |
| Liu Zhen . Study on multiple-depot scheduling optimization in urban public bicycle operation[D]. Beijing:School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2014. | |
| [8] |
何流, 李旭宏, 陈大伟 , 等. 公共自行车动态调度系统需求预测模型研究[J]. 武汉理工大学学报:交通科学与工程版, 2013,37(2):278-282.
doi: 10.3963/j.issn.2095-3844.2013.02.014 |
|
He Liu, Li Xu-hong, Chen Da-wei , et al. Research on the demand forecast model of public bike dynamic scheduling system[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology(Transportation Science & Engineering), 2013,37(2):278-282.
doi: 10.3963/j.issn.2095-3844.2013.02.014 |
|
| [9] |
Baldacci R, Christofides N, Mingozzi A . An exact algorithm for the vehicle routing problem based on the set partitioning formulation with additional cuts[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2008,115(2):351-385.
doi: 10.1007/s10107-007-0178-5 |
| [10] |
Subramanian A, Penna P H V, Uchoa E , et al. A hybrid algorithm for the heterogeneous fleet vehicle routing problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2012,221(2):285-295.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2012.03.016 |
| [11] | Wang S, Liu X. Energy minimization vehicle routing problem with heterogeneous vehicles [C]//International Conference on Service Systems and Service Management, Kunming, China, 2016: 7538462. |
| [12] | 潘述亮, 卢小林, 邹难 . 灵活型接驳公交路径优化及协同调度模型[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2016,46(6):1827-1835. |
| Pan Shu-liang, Lu Xiao-lin, Zou Nan . Route planning and coordinated scheduling model for flexible feeder transit service[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2016,46(6):1827-1835. | |
| [13] |
Sterzik S, Wang X, Kopfer H . A case study for a location-routing problem[J]. Operations Research Proceedings, 2012,208(2):275-280.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-20009-0_44 |
| [14] | Farham M S, Süral H, Iyigun C . A column generation approach for the location-routing problem with time windows[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2018,90:249-263. |
| [15] | 冯超 . K-means聚类算法的研究[D]. 大连:大连理工大学软件学院, 2007. |
| Feng Chao . Research of K-means clustering algorithm[D]. Dalian:School of Software Technology, Dalian University of Technology, 2007. |
| [1] | 白乔文,曲昭伟,陈永恒,熊帅,陶楚青. 非严格优先权下无左转专用相位直行车辆轨迹模型建立[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 673-679. |
| [2] | 李志慧,钟涛,赵永华,胡永利,李海涛,赵景伟. 面向车辆自主驾驶的行人跟踪算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 680-687. |
| [3] | 曹宁博,赵利英,曲昭伟,陈永恒,白乔文,邓晓磊. 考虑双向行人跟随行为的社会力模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 688-694. |
| [4] | 罗小芹,王殿海,金盛. 面向混合交通的感应式交通信号控制方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 695-704. |
| [5] | 陈磊,王江锋,谷远利,闫学东. 基于思维进化优化的多源交通数据融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
| [6] | 尹超英,邵春福,王晓全. 考虑停车可用性的建成环境对小汽车通勤出行的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 714-719. |
| [7] | 凃强,程琳,林芬,孙超. 考虑出行者风险态度的最优路径搜索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 720-726. |
| [8] | 陈永恒,刘芳宏,曹宁博. 信控交叉口行人与提前右转机动车冲突影响因素[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1669-1676. |
| [9] | 曲大义,杨晶茹,邴其春,王五林,周警春. 基于干线车流排队特性的相位差优化模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(6): 1685-1693. |
| [10] | 宗芳, 齐厚成, 唐明, 吕建宇, 于萍. 基于GPS数据的日出行模式-出行目的识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1374-1379. |
| [11] | 刘翔宇, 杨庆芳, 隗海林. 基于随机游走算法的交通诱导小区划分方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1380-1386. |
| [12] | 钟伟, 隽志才, 孙宝凤. 不完全网络的城乡公交一体化枢纽层级选址模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1387-1397. |
| [13] | 刘兆惠, 王超, 吕文红, 管欣. 基于非线性动力学分析的车辆运行状态参数数据特征辨识[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(5): 1405-1410. |
| [14] | 宗芳, 路峰瑞, 唐明, 吕建宇, 吴挺. 习惯和路况对小汽车出行路径选择的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1023-1028. |
| [15] | 栾鑫, 邓卫, 程琳, 陈新元. 特大城市居民出行方式选择行为的混合Logit模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1029-1036. |
|