吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2021, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (5): 1857-1865.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210436
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于MEA⁃BP神经网络的建筑能耗预测模型
- 1.吉林大学第一医院,长春 130021
2.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130021
Modeling of building energy consumption prediction based on MEA⁃BP neural network
Wen-long TENG1( ),Bing-hu CONG1,Yun-kun SHANG1,Yu-chen ZHANG1,Tian BAI2(
),Bing-hu CONG1,Yun-kun SHANG1,Yu-chen ZHANG1,Tian BAI2( )
)
- 1.The First Hospital of Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
摘要:
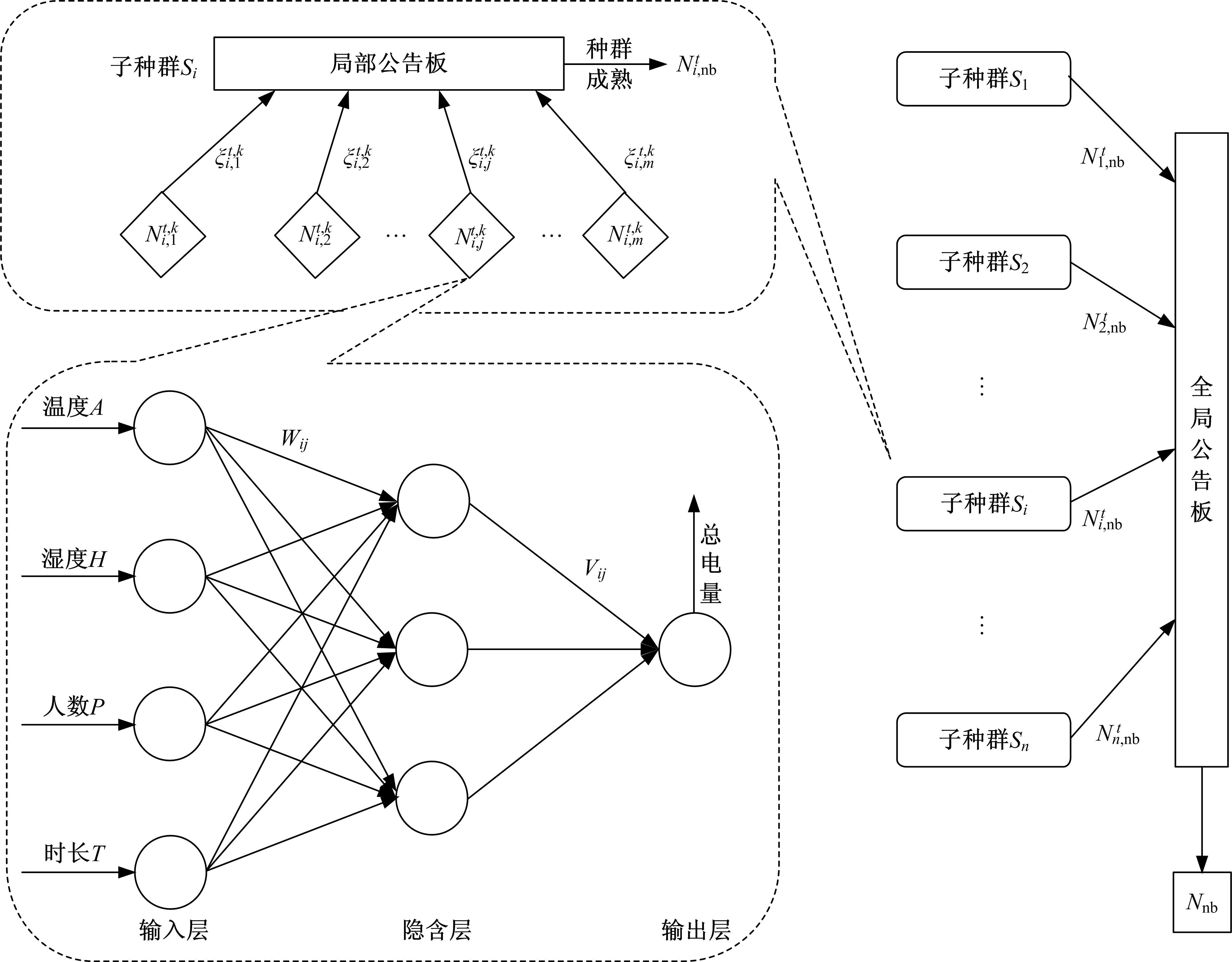
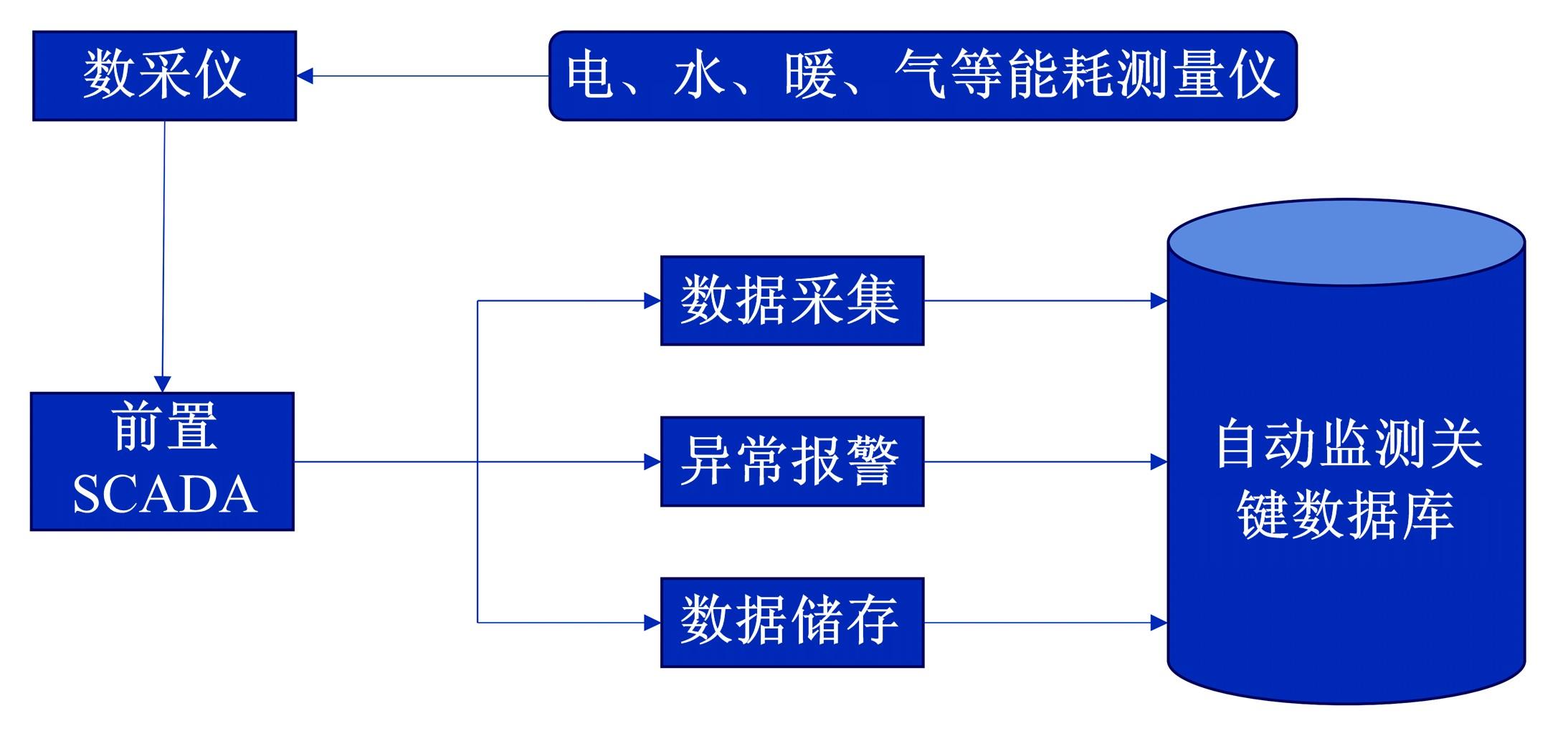
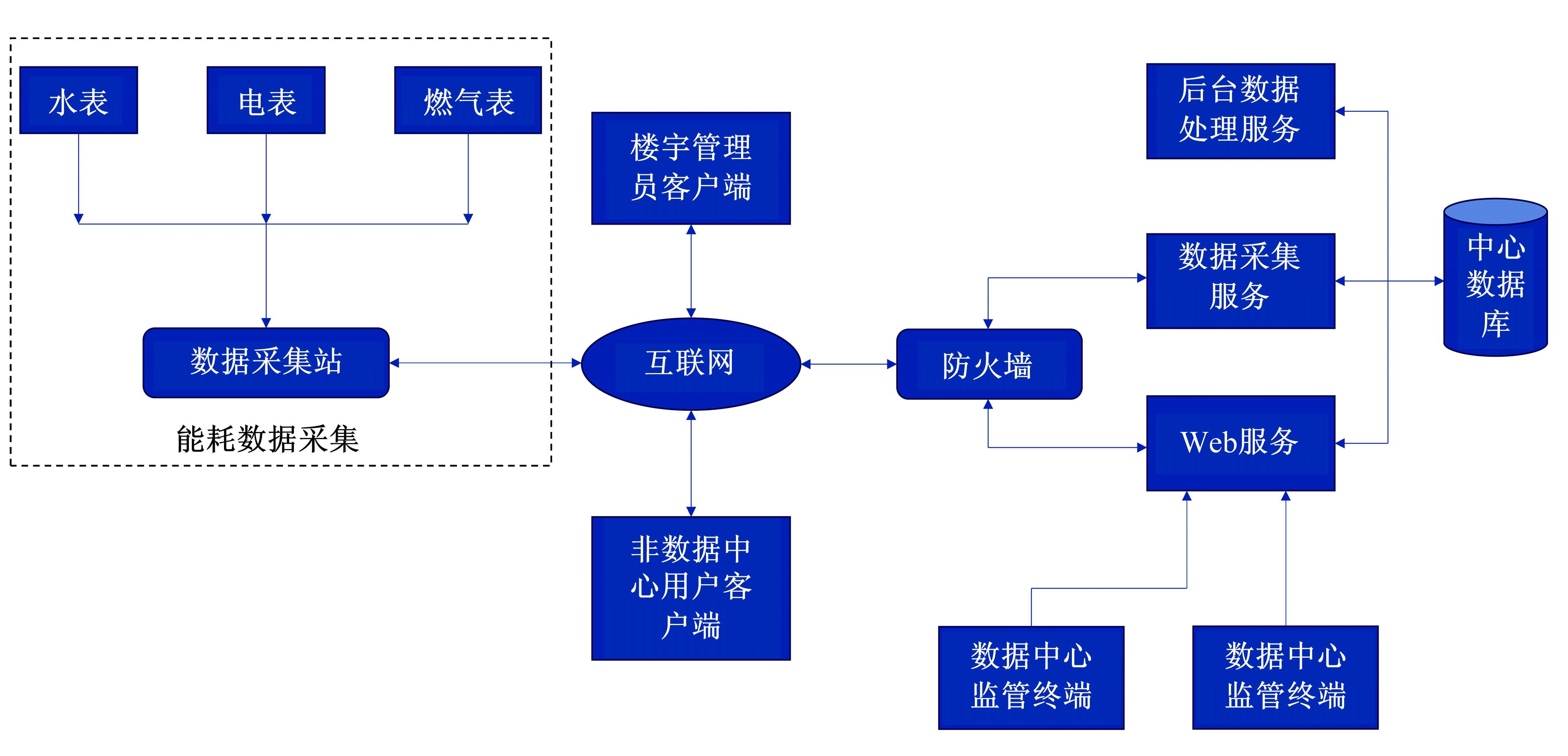
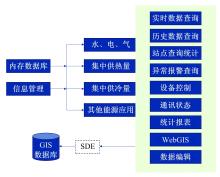
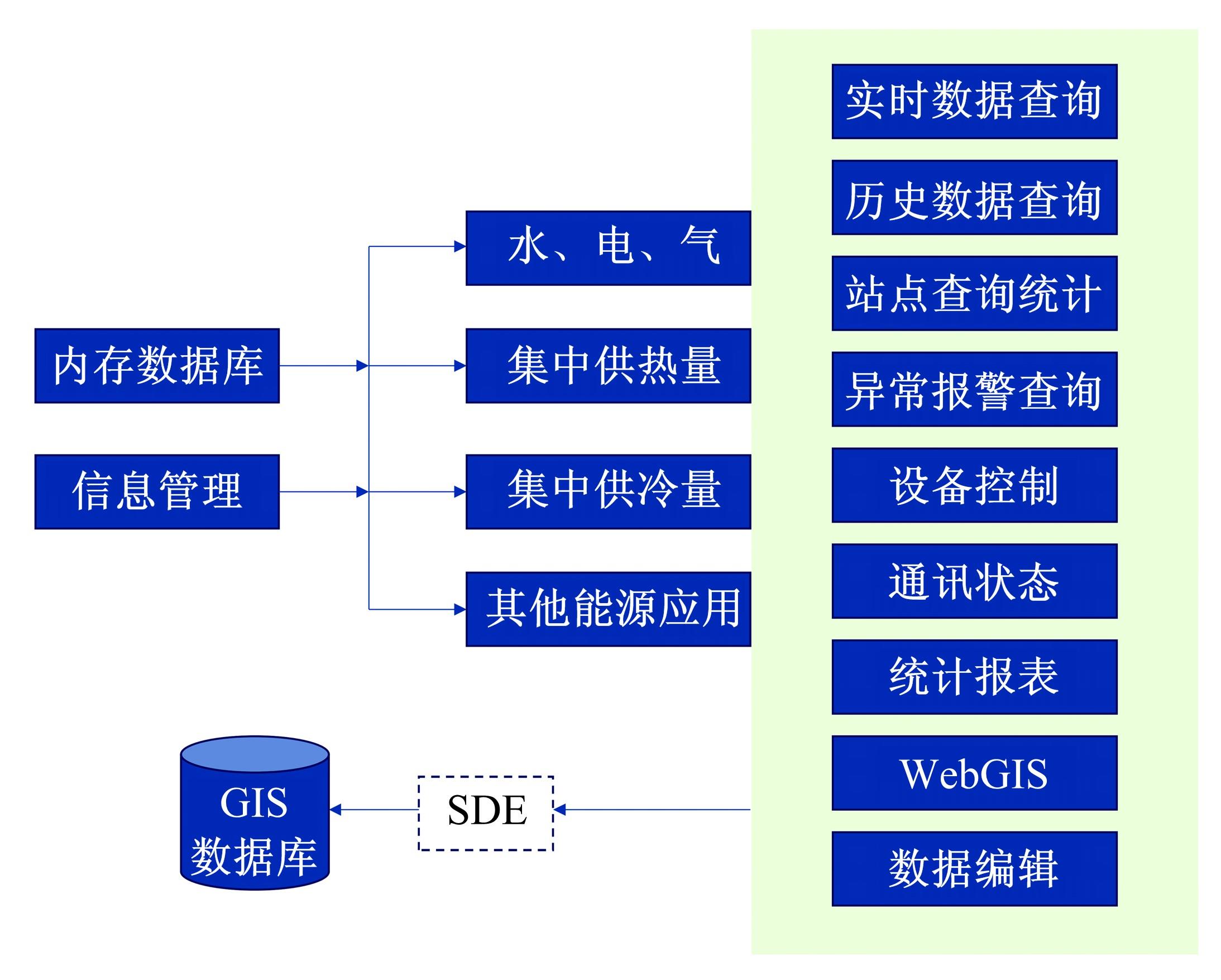
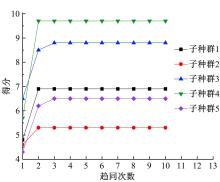
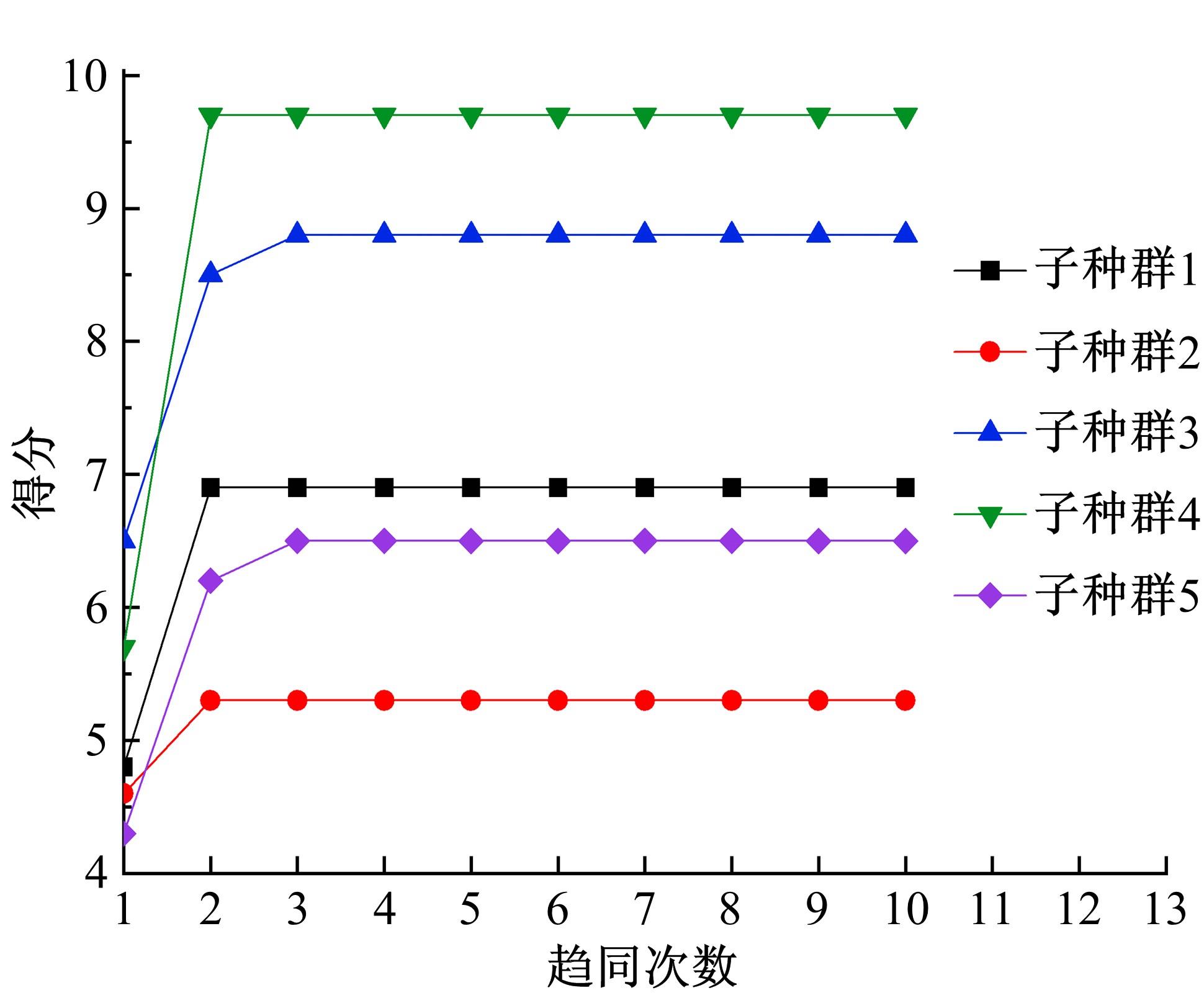
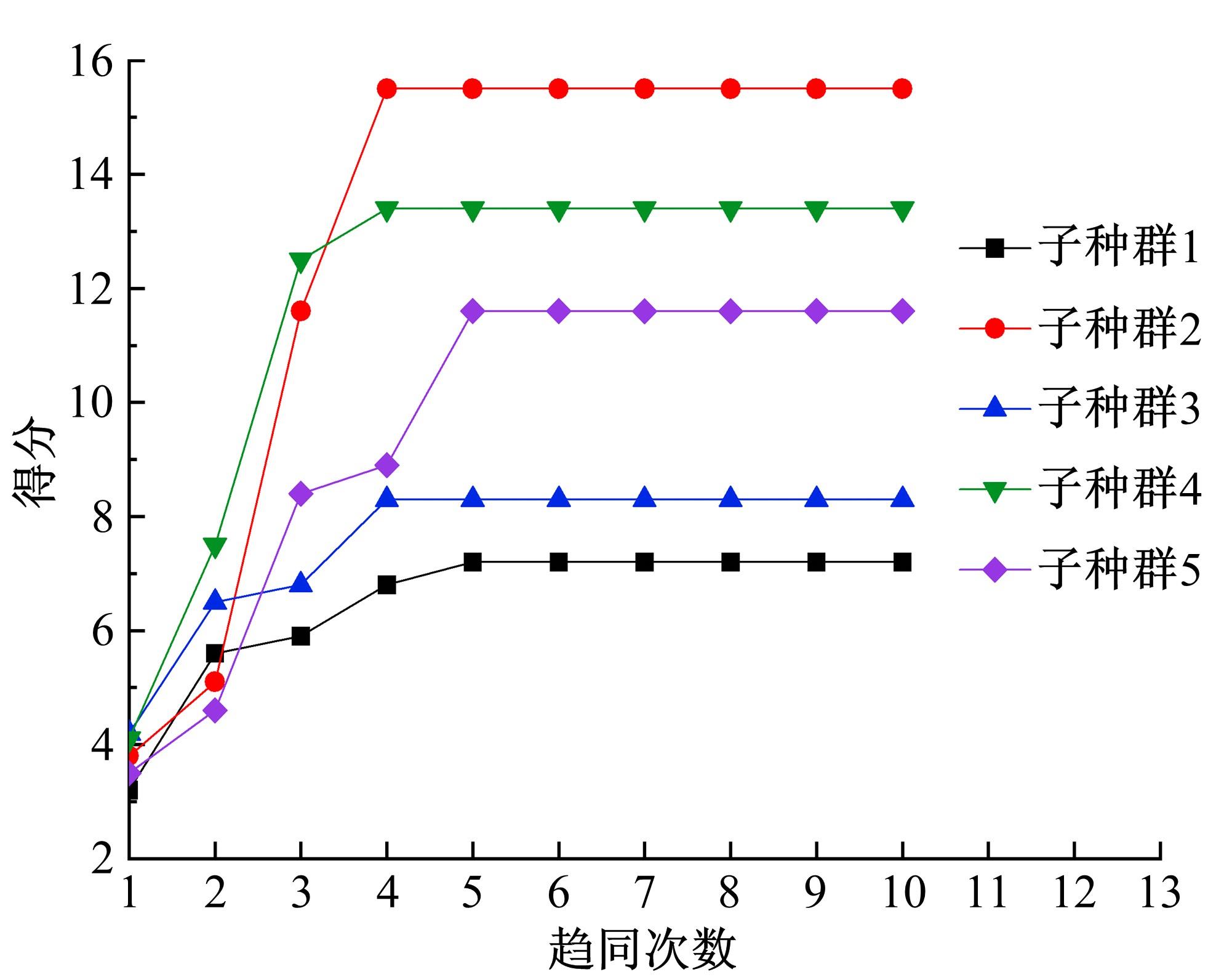
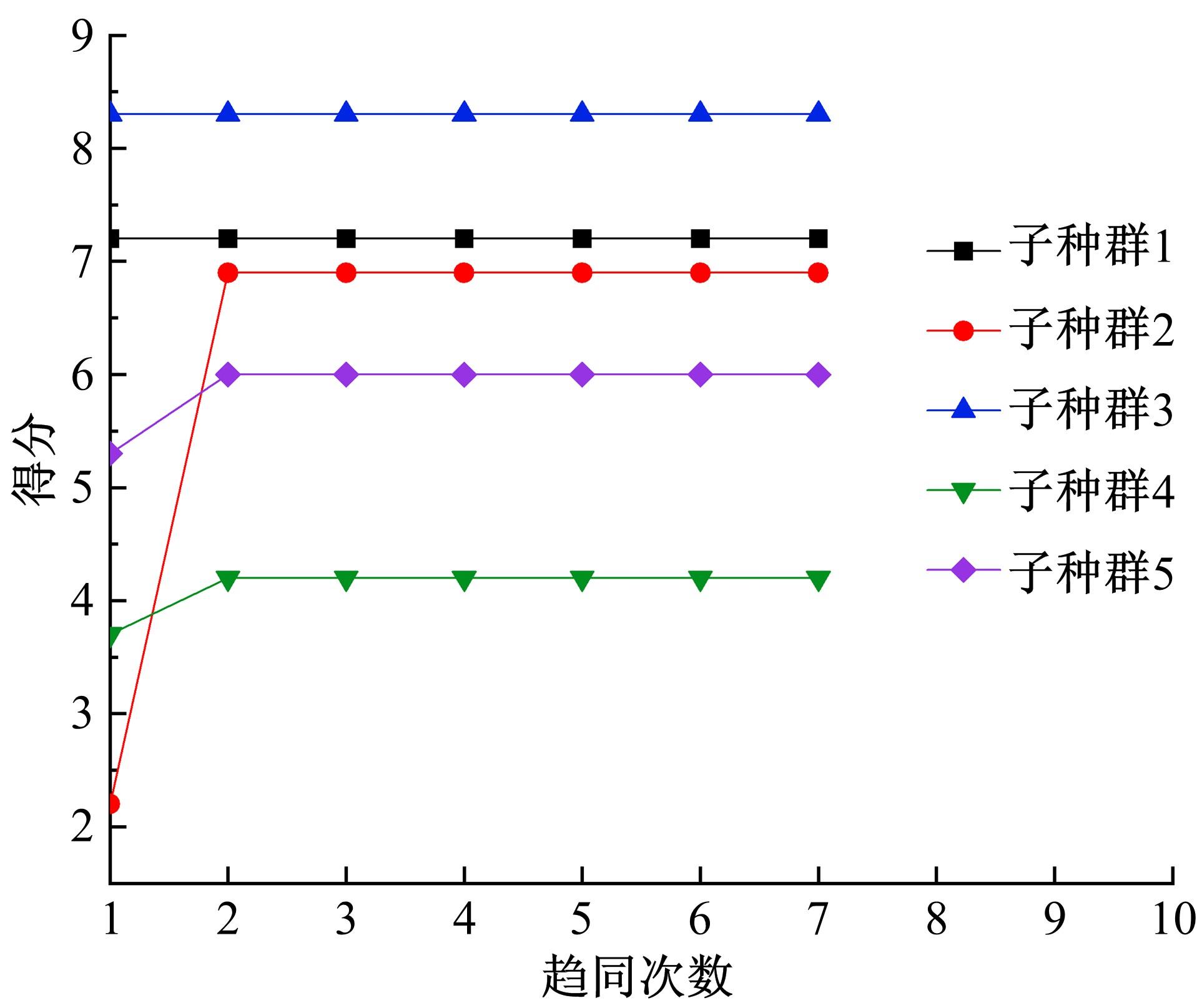
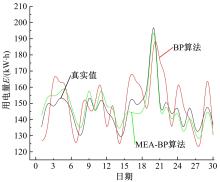
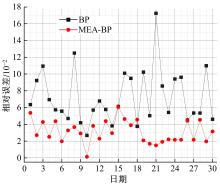
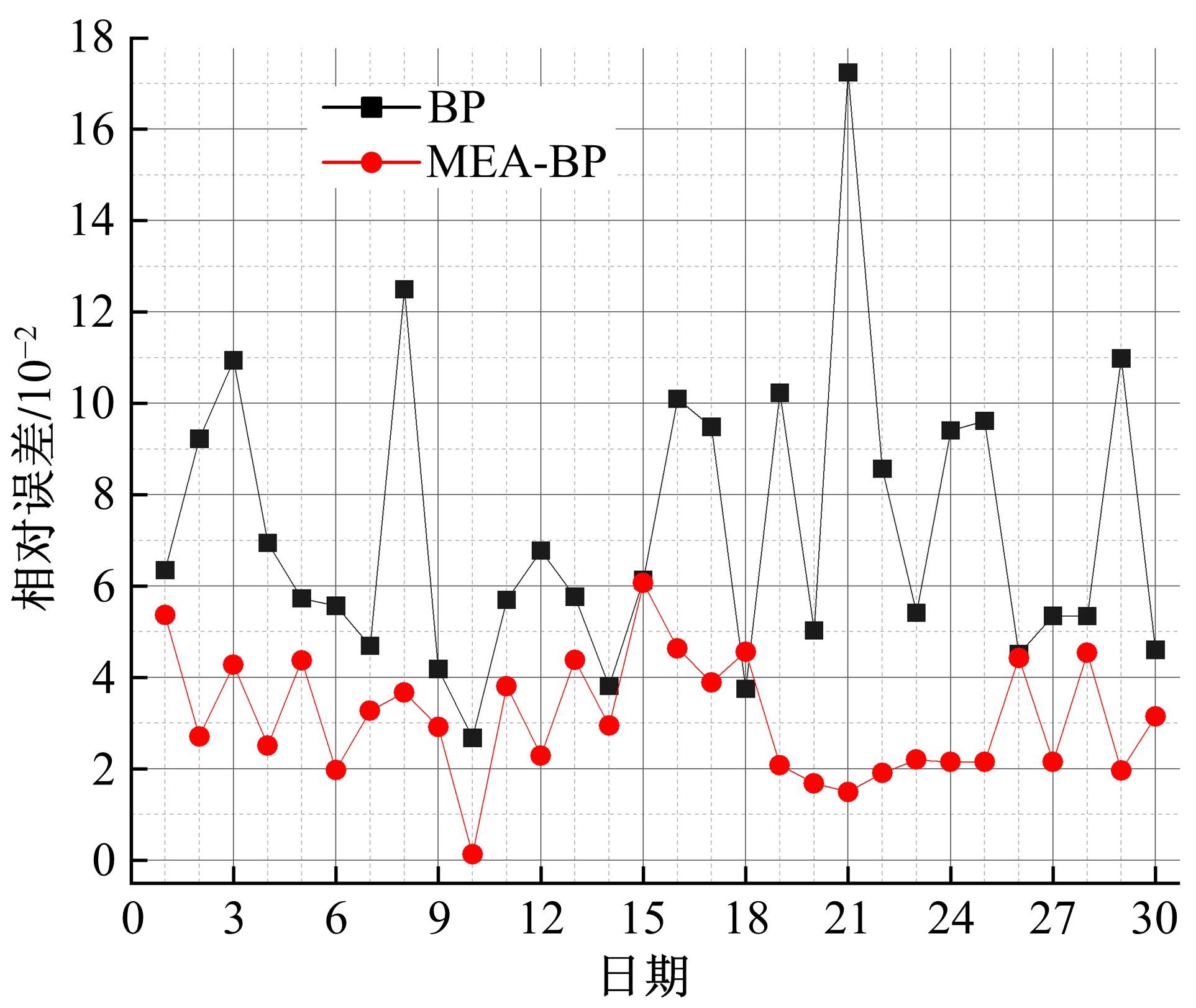
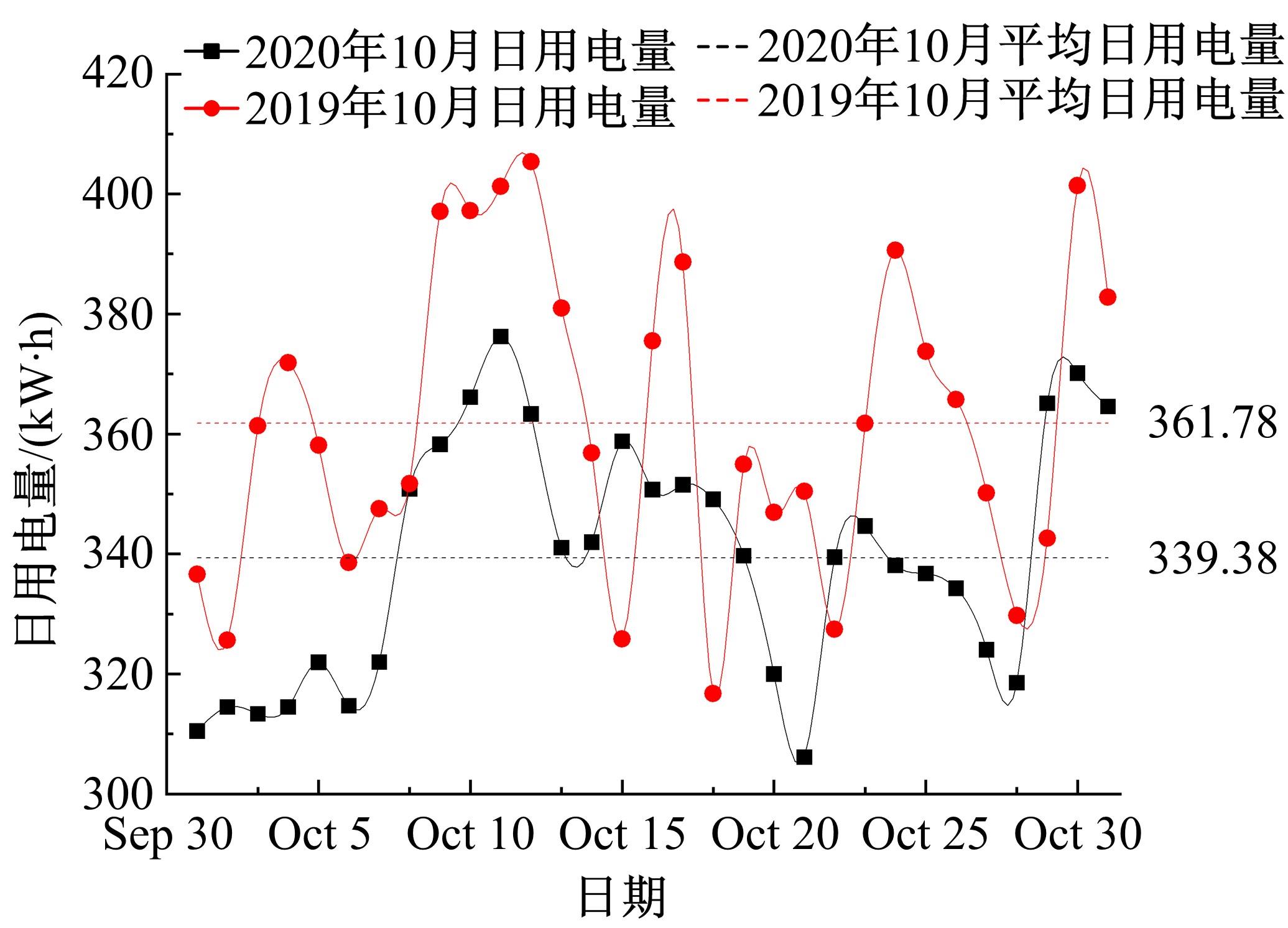
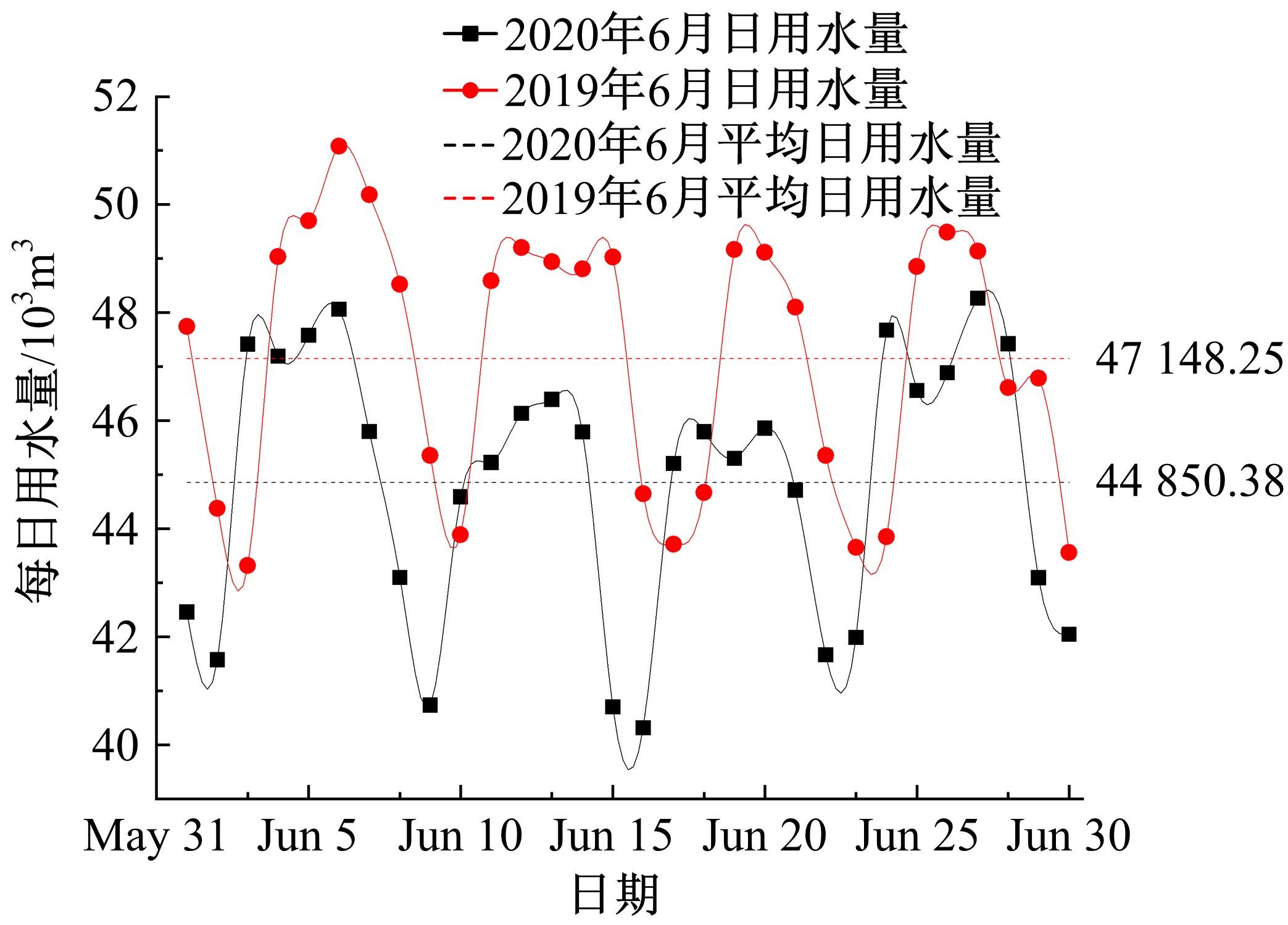
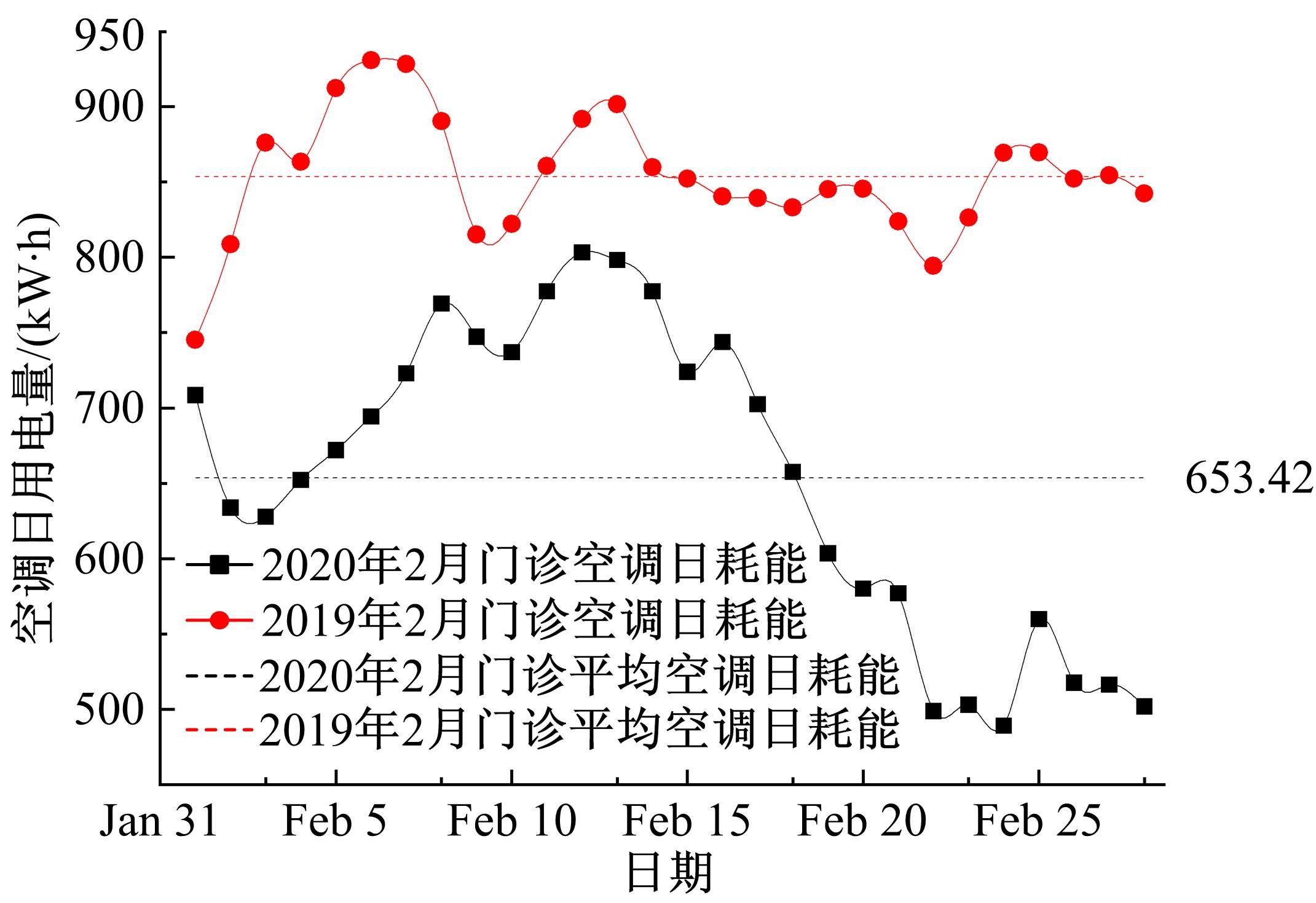
针对节能管理方面面临内部能耗状况无法准确计量、缺乏科学的能耗指标和评价标准、能耗管理考虑不够等问题,本文建立了MEA-BP神经网络能耗预测模型。基于能耗监管平台输出的历史能耗数据,对BP神经网络与MEA-BP神经网络进行训练,使用训练后的模型对建筑能耗进行预测,对比能耗预测值与能耗真实值,发现MEA-BP模型的能耗预测结果精度较高,有实际应用价值。根据能耗预测值,通过能耗监测平台对用能设施、用能方式进行相应控制与改善,提升了水、电、暖、气的节能效率,实现了最优的能耗控制和能源有效利用。
中图分类号:
- U491.1
| 1 | Parvin K, Lipu M S H, Hannan M A, et al. Intelligent controllers and optimization algorithms for building energy management towards achieving sustainable development: challenges and prospects[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 41577-41602. |
| 2 | Dun M, Wu L. Forecasting the building energy consumption in China using grey model[J]. Environmental Processes—an International Journal, 2020, 7(3): 1009-1022. |
| 3 | Daut M M, Hassan M Y, Abdullah H, et al. Building electrical energy consumption forecasting analysis using conventional and artificial intelligence methods: a review[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 70: 1108-1118. |
| 4 | Amber K P, Ahmad R, Aslam M W, et al. Intelligent techniques for forecasting electricity consumption of buildings[J]. Energy, 2018, 157: 886-893. |
| 5 | 吴炜洪, 许巧玲, 严哲钦, 等. GM-LSSVM模型在建筑能耗预测中的应用[J]. 福州大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 45(2): 238-245. |
| Wu Wei-hong, Xu Qiao-ling, Yan Zhe-qin, et al. Forecasting of building energy consumption based on grey theory and least squares support vector machine[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(2): 238-245. | |
| 6 | 陈彦熹, 刘建华, 李旭东, 等. 基于ANN的绿色办公建筑HVAC系统运行能耗预测[J]. 建筑节能, 2017, 45(10): 1-5. |
| Chen Yan-xi, Liu Jian-hua, Li Xu-dong, et al. HVAC system energy consumption prediction of green office building based on ANN method[J]. Building Energy Efficiency, 2017, 45(10): 1-5. | |
| 7 | 丁飞鸿, 刘鹏, 卢暾, 等. 基于遗传优化决策树的建筑能耗短期预测模型[J]. 计算机工程, 2019, 45(6): 280-289, 296. |
| Ding Fei-hong, Liu Peng, Lu Tun, et al. Short-term prediction model of building energy consumption based on genetically optimized decision tree[J]. Computer Engineering, 2019, 45(6): 280-289, 296. | |
| 8 | 汪君, 吴利瑞. 基于BP神经网络模型的上海高校能耗预测研究[J]. 建筑节能, 2015, 43(1): 92-97. |
| Wang Jun, Wu Li-rui. Forecast of the energy consumpt ion in universit ies at Shanghai based on BP neural networks[J]. Building Energy Efficiency, 2015, 43(1): 92-97. | |
| 9 | 王定奥, 刘清惓, 戴伟, 等. 基于BP神经网络的空调能耗预测与监控系统[J]. 现代电子技术, 2019, 42(22): 140-144. |
| Wang Ding-ao, Liu Qing-quan, Dai Wei, et al. Air⁃conditioning energy consumption prediction and monitoring system based on BP neural network[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2019, 42(22): 140-144. | |
| 10 | 陈昭明, 邹劲松, 王伟, 等. 改进粒子群神经网络融合有限元分析的铸锻双控动态成型多目标优化[J/OL]. (2021-04-27). |
| GN=5CWkbd0DujMK38znX6J2h%2bLBTn4%3d | |
| 11 | 黄宝洲, 杨俊华, 卢思灵, 等. 基于改进粒子群优化神经网络算法的波浪捕获功率预测[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(2): 302-308. |
| Huang Bao-zhou, Yang Jun-hua, Lu Si-ling, et al. Wave capture power forecasting based on improved particle swarm optimization neural network algorithm[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 302-308. | |
| 12 | 倪红海, 郭献洲. 基于GA-BP神经网络的电机铸铝转子压铸工艺优化[J]. 热加工工艺, 2021(15): 61-63, 66. |
| Ni Hong-hai, Guo Xian-zhou. Optimization of die-casting process of motor casting aluminum rotor based on GA-BP neural network[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2021(15): 61-63, 66. | |
| 13 | 吕栋, 欧吉坤, 于胜文. 基于MEA-BP神经网络的卫星钟差预报[J]. 测绘学报, 2020, 49(8): 993-1003. |
| Lv Dong, Ji-kun Ou, Yu Sheng-wen. Prediction of the satellite clock bias based on MEA-BP neural network[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartograghica Sinica, 2020, 49(8): 993-1003. | |
| 14 | 黄伟, 常俊, 孙智滨. 基于MEA-BP神经网络的压气机特性曲线预测[J]. 重庆理工大学学报: 自然科学, 2019, 33(2): 67-74. |
| Huang Wei, Chang Jun, Sun Zhi-bin. Characteristic curve prediction of compressor based on MEA-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology(Natural Science), 2019, 33(2): 67-74. | |
| 15 | 唐立力, 陈国彬. 基于MEA优化BP神经网络的农机滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 农机化研究, 2019, 41(3): 214-218. |
| Tang Li-li, Chen Guo-bin. Fault diagnosis for rolling bearing of agricultural mechanical based on BP neural network optimized by mind evolutionary algorithm[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019, 41(3): 214-218. | |
| 16 | 孙俊, 唐凯, 毛罕平, 等. 基于MEA-BP神经网络的大米水分含量高光谱技术检测[J]. 食品科学, 2017, 38(10): 272-276. |
| Sun Jun, Tang Kai, Mao Han-ping. Hyperspectral detection of moisture content in rice based on MEA-BP neural network[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(10): 272-276. | |
| 17 | 李晓英, 苏志伟, 田佳乐, 等. 基于GRA-MEA-BP耦合模型的城市需水预测研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2018, 29(1): 50-54. |
| Li Xiao-ying, Su Zhi-wei, Tian Jia-le. Research on GRA-MEA-BP coupling model for water demand prediction[J]. Journal of Water Resources& Water Engineering, 2018, 29(1): 50-54. | |
| 18 | 马佩. 公共建筑能源效率分析及管理系统设计[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学土木与水利工程学院, 2017. |
| Ma Pei. Energy efficiency analysis and management system design of public buildings[D]. Wuhan: School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2017. | |
| 19 | 陈磊, 王江锋, 谷远利, 等. 基于思维进化优化的多源交通数据融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 49(3): 705-713. |
| Chen Lei, Wang Jiang-feng, Gu Yuan-li, et al. Multi-source traffic data fusion algorithm based on mind evolutionary algorithm optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 705-713. | |
| 20 | 张通鑫. 通风空调系统能耗监测管理平台研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学土木与水利工程学院, 2018. |
| Zhang Tong-xin. Study of energy consumption monitoring and management platform of ventilation and air conditioning system[D]. Wuhan: School of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2018. | |
| 21 | 吕炳霖. 基于RS-485的抄表系统硬件实现及采集成功率的数据分析[D]. 济南: 山东大学信息科学与工程学院, 2017. |
| Lv Bing-lin. Data analysis of hardware implementation and acquisition success rate of meter reading system based on RS-485[D].Ji'nan: School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong University, 2017. | |
| 22 | Kim W J, Gwak D G, Kim D H. Development of DSP-based modbus communication scheme and control module for controlling actuators in industrial equipment[J]. Transactions of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers A, 2017, 41(11): 1109-1117. |
| [1] | 钟辉,康恒,吕颖达,李振建,李红,欧阳若川. 基于注意力卷积神经网络的图像篡改定位算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1838-1844. |
| [2] | 陈涛,秦静,赵华,苏庆鹏,吕永,钟凯,王膺博,裴毅强. 基于模型群预测法对汽油机稳态原排的预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1565-1574. |
| [3] | 王德兴,吴若有,袁红春,宫鹏,王越. 基于多尺度注意力融合和卷积神经网络的水下图像恢复[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1396-1404. |
| [4] | 董延华,刘靓葳,赵靖华,李亮,解方喜. 基于BPNN在线学习预测模型的扭矩实时跟踪控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1405-1413. |
| [5] | 徐卓君,杨雯婷,杨承志,田彦涛,王晓军. 雷达脉内调制识别的改进残差神经网络算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1454-1460. |
| [6] | 钱榕,张茹,张克君,金鑫,葛诗靓,江晟. 融合全局和局部特征的胶囊图神经网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1048-1054. |
| [7] | 宋大凤,杨丽丽,曾小华,王星琦,梁伟智,杨南南. 基于行驶工况合成的混合动力汽车电池寿命优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 781-791. |
| [8] | 尚福华,曹茂俊,王才志. 基于人工智能技术的局部离群数据挖掘方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 692-696. |
| [9] | 魏晓辉,孙冰怡,崔佳旭. 基于图神经网络的兴趣活动推荐算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(1): 278-284. |
| [10] | 王柯俨,王迪,赵熹,陈静怡,李云松. 基于卷积神经网络的联合估计图像去雾算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1771-1777. |
| [11] | 吴爱国,韩俊庆,董娜. 基于极局部模型的机械臂自适应滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1905-1912. |
| [12] | 李志军,杨楚皙,刘丹,孙大洋. 基于深度卷积神经网络的信息流增强图像压缩方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1788-1795. |
| [13] | 李静,石求军,洪良,刘鹏. 基于车辆状态估计的商用车ESC神经网络滑模控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1545-1555. |
| [14] | 刘国华,周文斌. 基于卷积神经网络的脉搏波时频域特征混叠分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1818-1825. |
| [15] | 车翔玖,董有政. 基于多尺度信息融合的图像识别改进算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1747-1754. |
|
||