吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (3): 640-647.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20211274
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法
- 1.吉林大学 计算机科学与技术学院,长春 130012
2.吉林大学 符号计算与知识工程教育部重点实验室,长春 130012
3.吉林大学 公共计算机教学与研究中心,长春 130012
Medical image segmentation based on multi⁃scale context⁃aware and semantic adaptor
Xue WANG1,2( ),Zhan-shan LI1,2,Ying-da LYU3(
),Zhan-shan LI1,2,Ying-da LYU3( )
)
- 1.College of Computer Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
2.Key Laboratory of Symbolic Computation and Knowledge Engineering of Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
3.Center for Computer Fundamental Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130012,China
摘要:
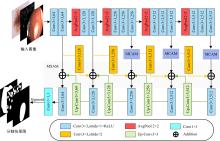
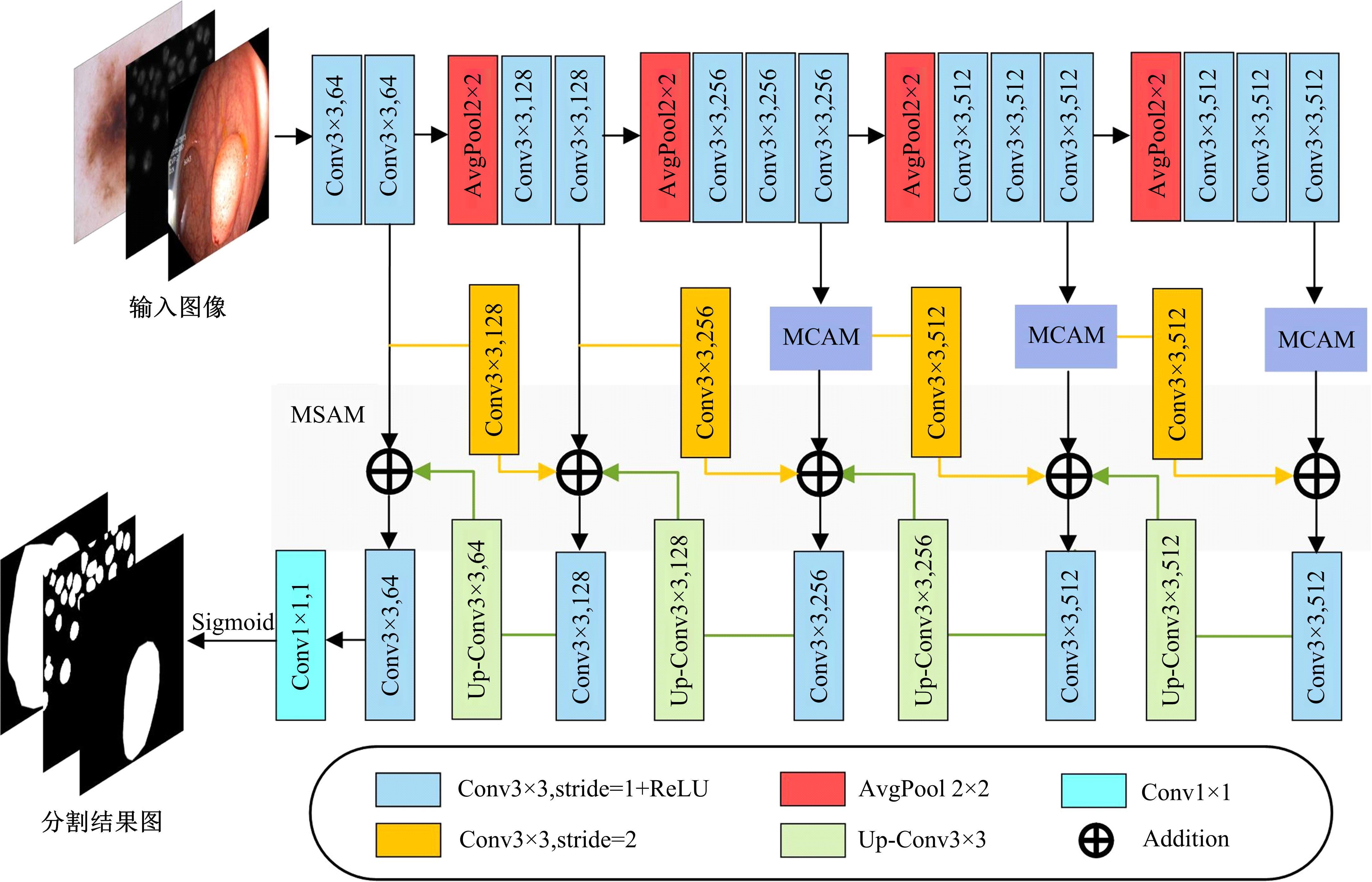
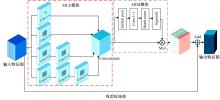
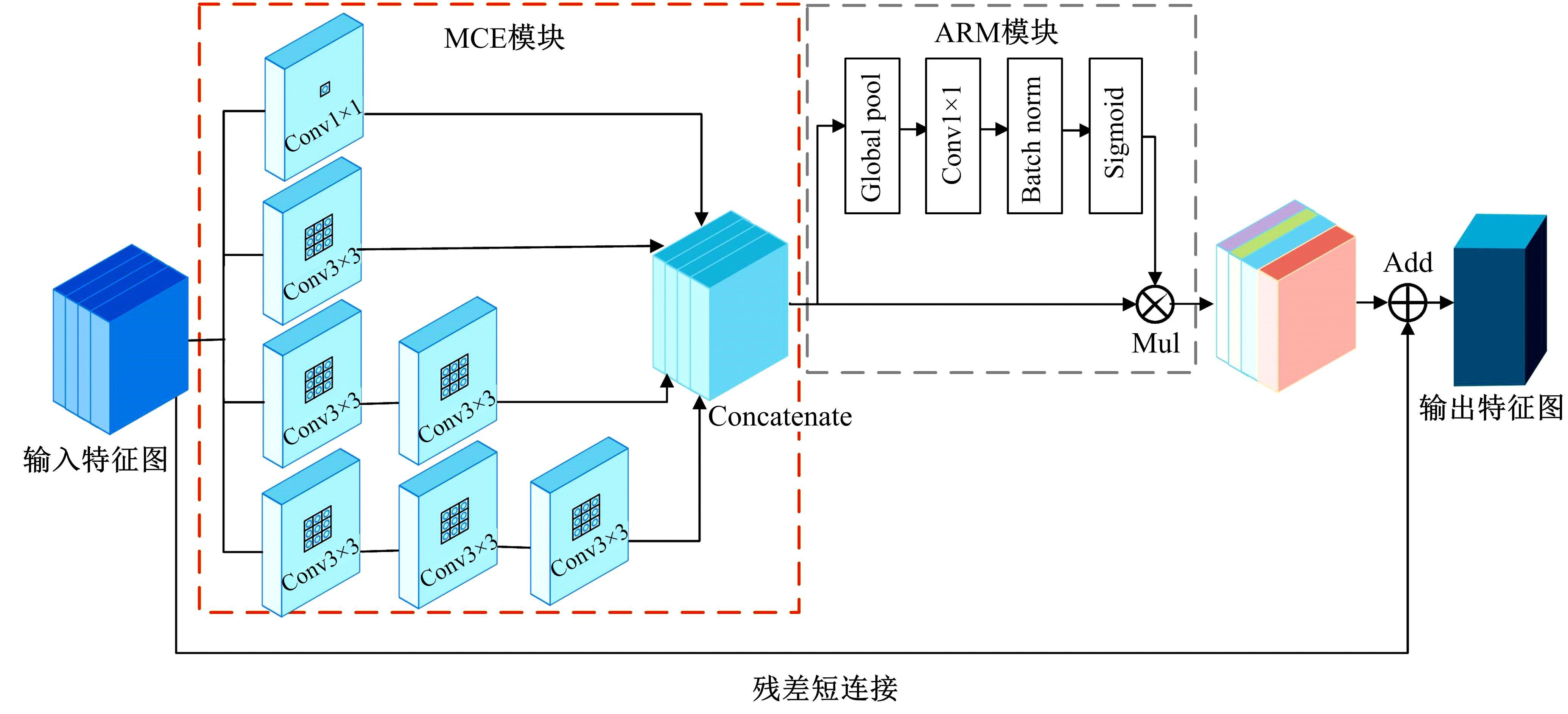
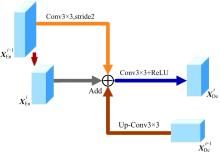
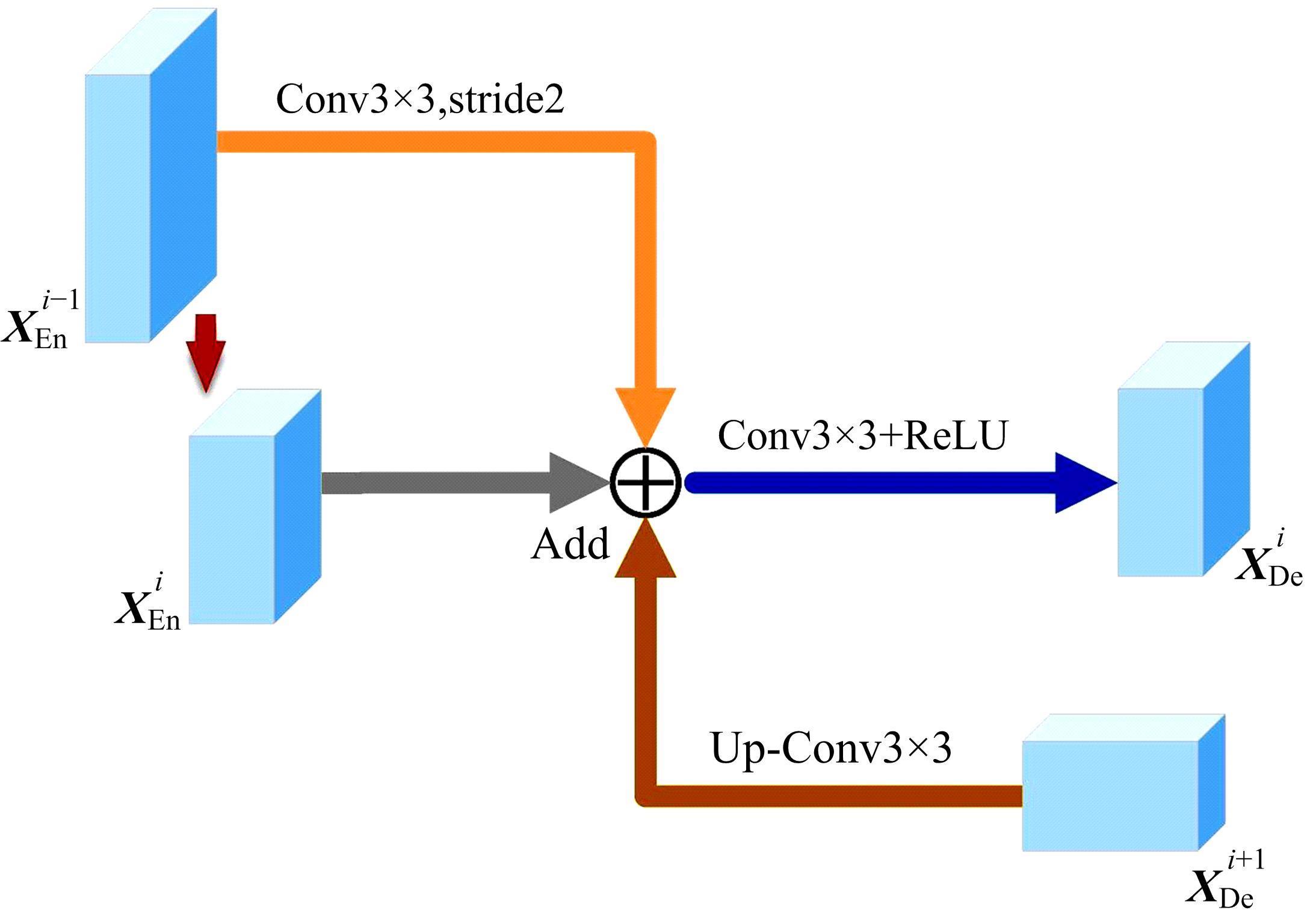
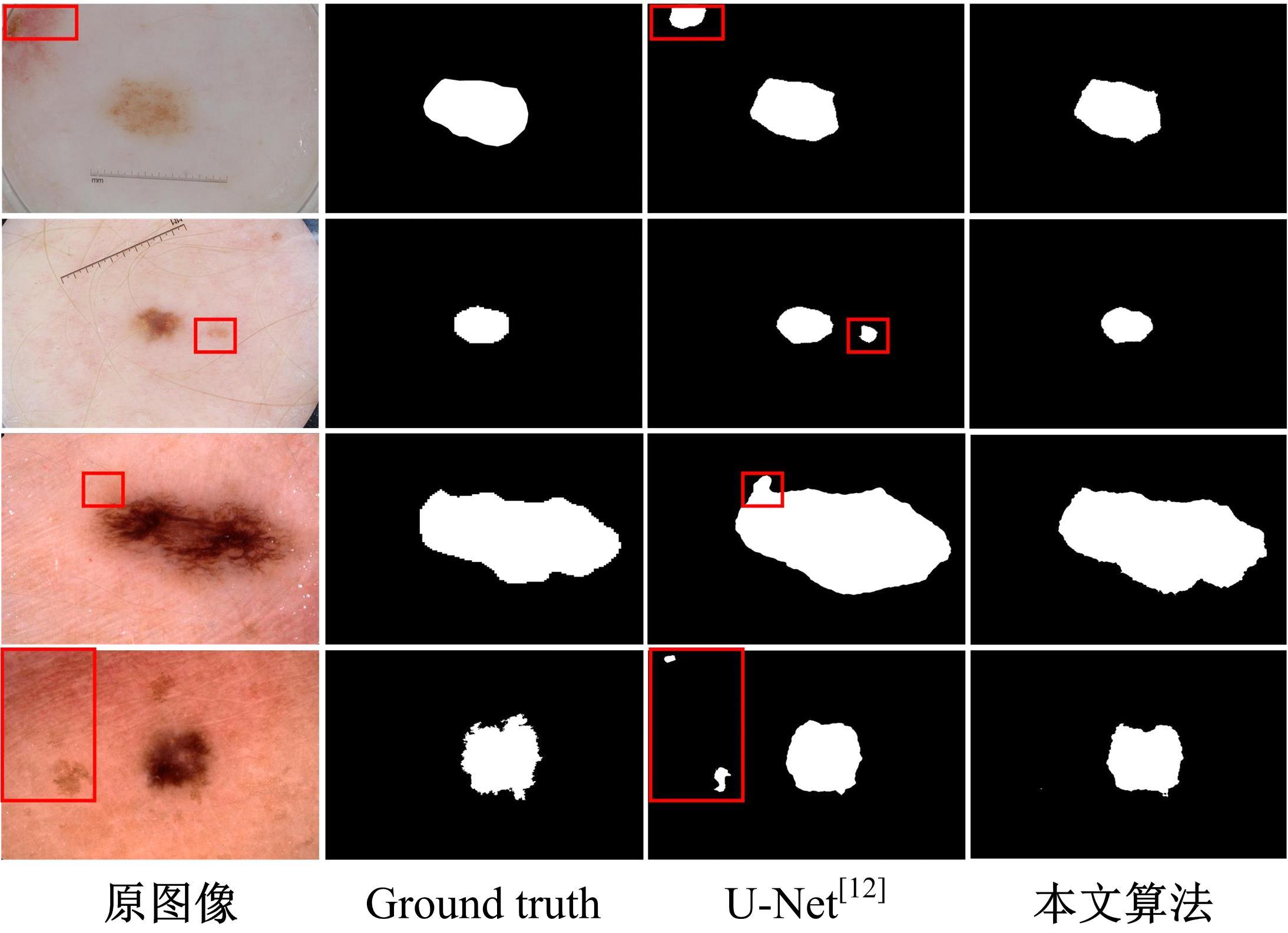
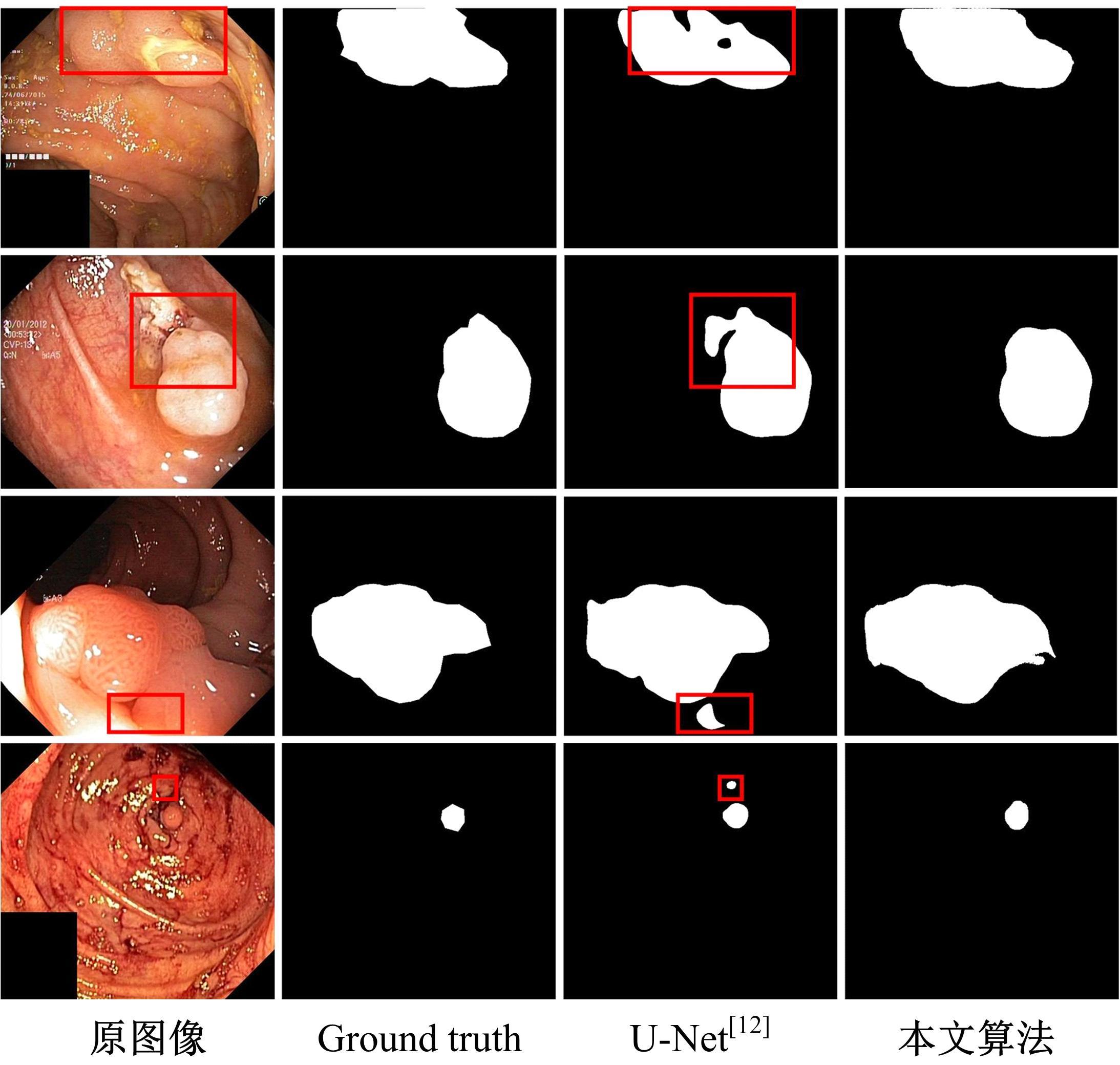
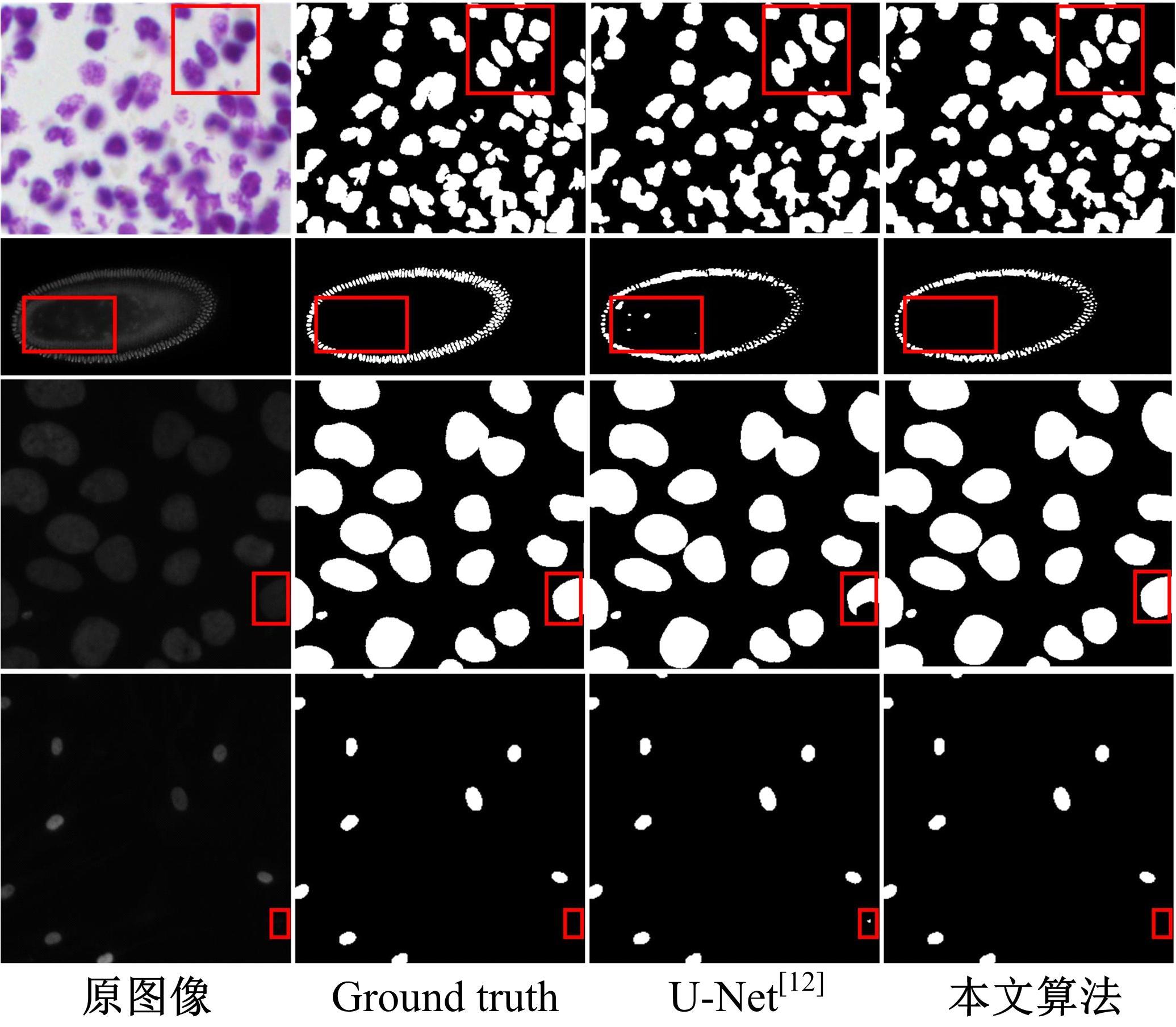
针对医学图像中病灶区域的形状不规则、尺度变化大、强度不均匀和边界模糊等复杂特点导致医学图像分割精度下降的问题,本文提出了一种基于多尺度感知和语义适配的医学图像分割算法。通过多尺度上下文感知模块,从多个感受野学习目标区域丰富的上下文信息,并根据目标区域大小动态分配不同尺度语义特征的权重,以提高特征学习的表征能力。通过多层语义适配模块聚合多级抽象语义特征和空间细节信息,细化目标区域的边界,同时减少编解码器间的特征差异。将本文算法在3个不同模态的公开医学图像数据集上进行定量和定性对比,实验结果表明,本文算法在多个医学图像复杂场景分割中均优于其他算法。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | 宋杰,肖亮,练智超,等. 基于深度学习的数字病理图像分割综述与展望[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(5): 1427-1460. |
| Song Jie, Xiao Liang, Lian Zhi-chao, et al. Overview and prospect of deep learning for image segmentation in digital pathology[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(5): 1427-1460. | |
| 2 | Mahmud T, Paul B, Fattah S A. PolypSegNet: a modified encoder-decoder architecture for automated polyp segmentation from colonoscopy images[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2021, 128:No.104119. |
| 3 | Ibtehaz N, Rahman M S. MultiResUNet: rethinking the U-net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation[J]. Neural Networks, 2020, 121:74-87. |
| 4 | Zhang Yan, Lu Yao, Chen Wan-kun, et al. MSMANet: a multi-scale mesh aggregation network for brain tumor segmentation[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 110: No.107733. |
| 5 | Tang Yu-cheng, Gao Ri-qiang, Lee H, et al. Pancreas CT segmentation by predictive phenotyping[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Lima, Peru, 2021: 25-35. |
| 6 | 秦俊. 基于启发式算法的医学图像阈值分割方法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学计算机科学与技术学院, 2019. |
| Qin Jun. Research on heuristic algorithms based medical image threshold segmentation[D]. Changchun: College of Computer Science and Technology, Jilin University, 2019. | |
| 7 | 周显国, 陈大可, 苑森淼. 基于改进模糊聚类分析的医学脑部MRI图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2009, 39(2): 381-385. |
| Zhou Xian-guo, Chen Da-ke, Yuan Sen-miao. Medical brain MRI images segmentation by improved fuzzy C-means clustering analysis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2009, 39(2): 381-385. | |
| 8 | 肖晓尧, 李雄飞, 张小利, 等. 基于多尺度的区域生长的图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(5): 1591-1597. |
| Xiao Xiao-yao, Li Xiong-fei, Zhang Xiao-li, et al. Medical image segmentation algorithm based on multi-scale region growing[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(5): 1591-1597. | |
| 9 | Zhou San-ping, Wang Jin-jun, Zhang Meng-meng, et al. Correntropy-based level set method for medical image segmentation and bias correction[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 234: 216-229. |
| 10 | Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 2015: 3431-3440. |
| 11 | Brandao P, Mazomenos E B, Ciuti G, et al. Fully convolutional neural networks for polyp segmentation in colonoscopy[C]∥Medical Imaging 2017: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Orlando, Florida, USA, 2017: No.101340F. |
| 12 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234-241. |
| 13 | Azad R, Asadi-Aghbolaghi M, Fathy M, et al. Bi-directional convLSTM U-Net with densley connected convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Korea, 2019: 406-415. |
| 14 | Gu Ran, Wang Guo-tai, Song Tao, et al. CA-Net: comprehensive attention convolutional neural networks for explainable medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2021, 40(2): 699-711. |
| 15 | Wang Cai-yong, Wang Yun-long, Liu Yun-fan, et al. ScleraSegNet: an attention assisted U-Net model for accurate sclera segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biometrics, Behavior, and Identity Science, 2020, 2(1): 40-54. |
| 16 | Gu Zai-wang, Cheng Jun, Fu Hua-zhu, et al. CE-Net: context encoder network for 2D medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(10): 2281-2292. |
| 17 | Zhou Z W, Siddiquee M M R, Tajbakhsh N, et al. UNet++:a nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation[C]∥Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support, Cham, 2018:3-11. |
| 18 | Huang Hui-min, Lin Lan-fen, Tong Ruo-feng, et al. UNet 3+: a full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 1055-1059. |
| 19 | Jha D, Riegler M A, Johansen D, et al. DoubleU-Net: a deep convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation[C]∥IEEE 33rd International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, Rochester, MN, USA, 2020: 558-564. |
| 20 | Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]∥Thirty-first AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, California, USA, 2017: 4278-4284. |
| 21 | Yu Chang-qian, Wang Jing-bo, Peng Chao, et al. BiSeNet: bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 325-341. |
| 22 | Jha D, Smedsrud P H, Riegler M A, et al. Kvasir-SEG: a segmented polyp dataset[C]∥International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Daejeon, South Korea, 2020: 451-462. |
| 23 | Tomar N K, Jha D, Riegler M A, et al. FANet: a feedback attention network for improved biomedical image segmentation[J/OL]. [2020-12-25]. . |
| 24 | Jha D, Smedsrud P H, Riegler M A, et al. ResUNet++: an advanced architecture for medical image segmentation[C]∥IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia, San Diego, CA, USA, 2019: 225-230. |
| 25 | Zhang Zheng-xin, Liu Qing-jie, Wang Yun-hong. Road extraction by deep residual U-Net[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(5): 749-753. |
| [1] | 康苏明,张叶娥. 基于Hadoop的跨社交网络局部时序链路预测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 626-632. |
| [2] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [3] | 赵宏伟,霍东升,王洁,李晓宁. 基于显著性检测的害虫图像分类[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2174-2181. |
| [4] | 刘洲洲,张倩昀,马新华,彭寒. 基于优化离散差分进化算法的压缩感知信号重构[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2246-2252. |
| [5] | 孙东明,胡亮,邢永恒,王峰. 基于文本融合的物联网触发动作编程模式服务推荐方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2182-2189. |
| [6] | 王生生,陈境宇,卢奕南. 基于联邦学习和区块链的新冠肺炎胸部CT图像分割[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2164-2173. |
| [7] | 林俊聪,雷钧,陈萌,郭诗辉,高星,廖明宏. 基于电影视觉特性的动态多目标实时相机规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2154-2163. |
| [8] | 任丽莉,王志军,闫冬梅. 结合黏菌觅食行为的改进多元宇宙算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2190-2197. |
| [9] | 姚引娣,贺军瑾,李杨莉,谢荡远,李英. 自构建改进型鲸鱼优化BP神经网络的ET0模拟计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1798-1807. |
| [10] | 赵宏伟,张子健,李蛟,张媛,胡黄水,臧雪柏. 基于查询树的双向分段防碰撞算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1830-1837. |
| [11] | 曹洁,屈雪,李晓旭. 基于滑动特征向量的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1785-1791. |
| [12] | 孙小雪,钟辉,陈海鹏. 基于决策树分类技术的学生考试成绩统计分析系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1866-1872. |
| [13] | 张萌谡,刘春天,李希今,黄永平. 基于K⁃means聚类算法的绩效考核模糊综合评价系统设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1851-1856. |
| [14] | 王春波,底晓强. 基于标签分类的云数据完整性验证审计方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1364-1369. |
| [15] | 欧阳丹彤,刘扬,刘杰. 故障响应指导下基于测试集的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1017-1025. |
|
||