吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2391-2398.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210891
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
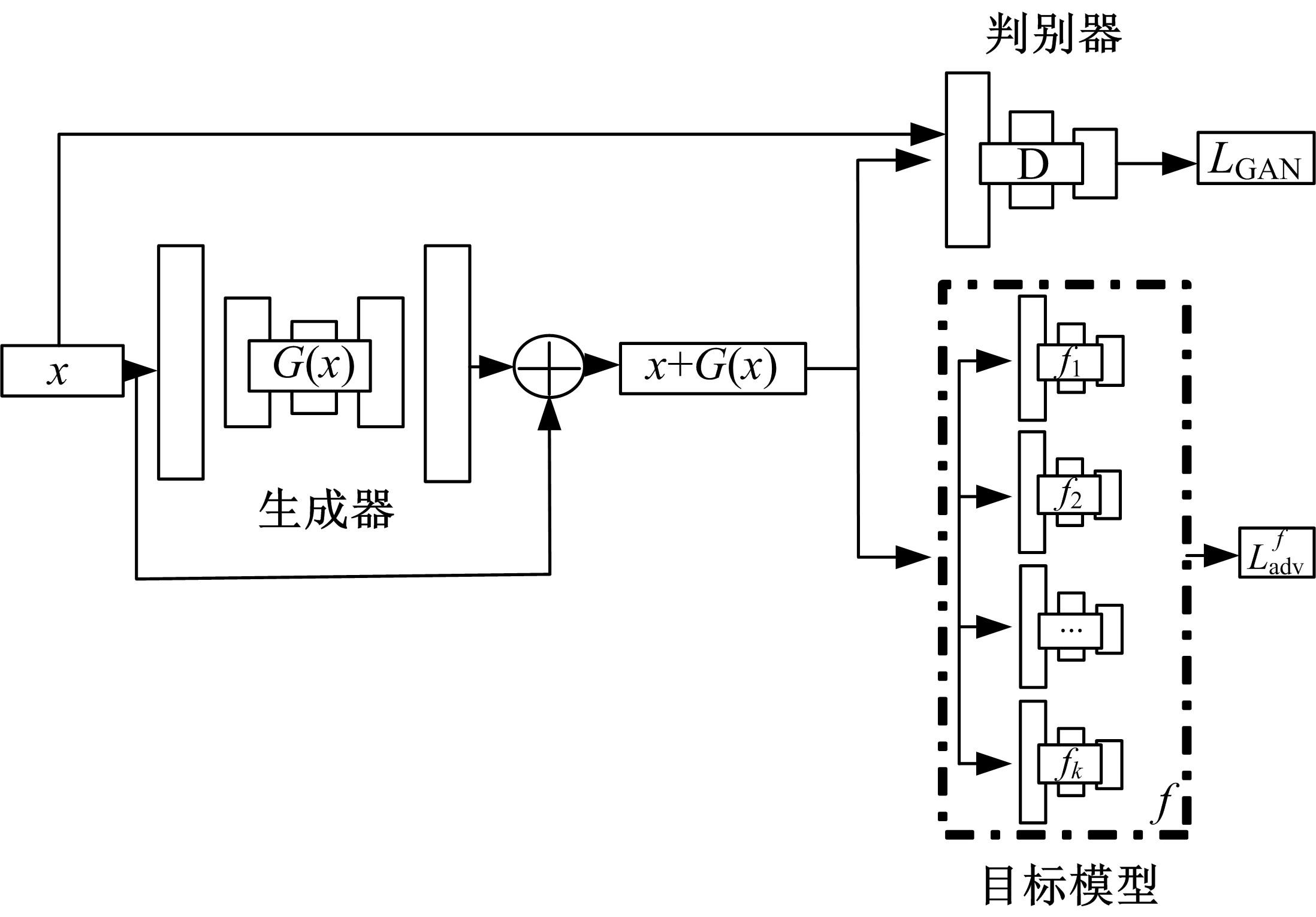
基于集成advGAN的黑盒迁移对抗攻击
黄帅娜1,2( ),李玉祥1,2,毛岳恒1,2,班爱莹1,2,张志勇1,2(
),李玉祥1,2,毛岳恒1,2,班爱莹1,2,张志勇1,2( )
)
- 1.河南科技大学 信息工程学院,河南 洛阳 471023
2.河南科技大学 河南省网络空间安全应用国际联合实验室,河南 洛阳 471023
Black-box transferable adversarial attacks based on ensemble advGAN
Shuai-na HUANG1,2( ),Yu-xiang LI1,2,Yue-heng MAO1,2,Ai-ying BAN1,2,Zhi-yong ZHANG1,2(
),Yu-xiang LI1,2,Yue-heng MAO1,2,Ai-ying BAN1,2,Zhi-yong ZHANG1,2( )
)
- 1.School of Information Engineering,Henan University of Science and Technology,Luoyang 471023,China
2.Henan International Joint Laboratory for Cyberspace Security Applications,Henan University of Science and Technology,Luoyang 471023,China
摘要:
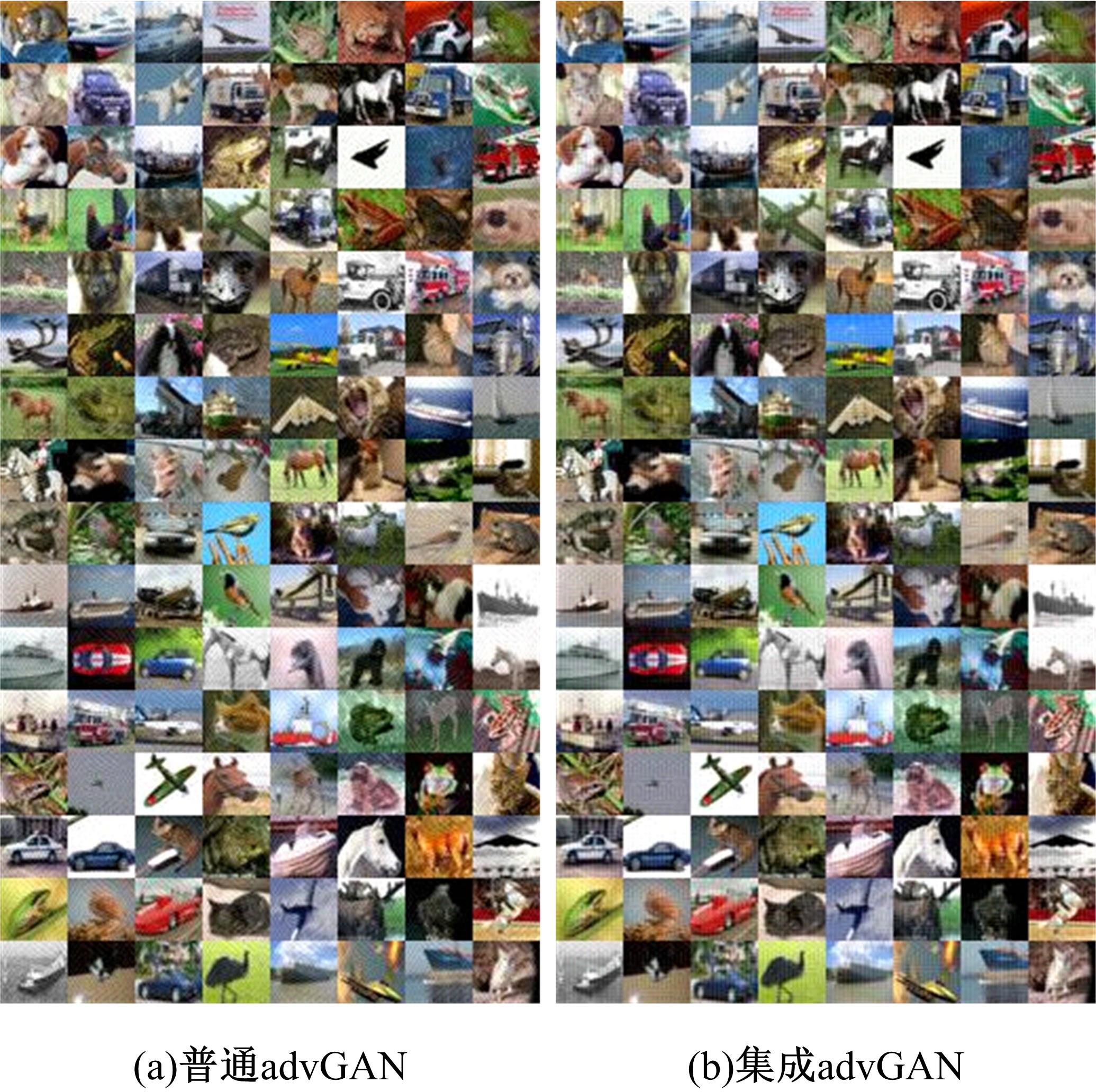
针对传统advGAN方法可高效地生成高保真度的对抗样本,但advGAN容易过拟合于原始样本空间流形导致迁移性变差的问题,,提出了一种集成advGAN的方法。在生成对抗网络中添加由多个分类模型的logits集成构成目标分类模型,汇聚所有模型输出的期望,着力降低过拟合现象,使得生成的对抗样本迁移性强且保真度高。在MNIST数据集上,使用集成advGAN方法生成的对抗样本迁移攻击成功率平均提高了6%,最高可达43.9%,在CIFAR-10数据集上,对抗样本迁移攻击成功率平均提高了7.6%,最高可达75.62%,且PSNR比起传统advGAN有提升。实验结果表明:集成advGAN方法可以生成具备更高对抗迁移性的高保真对抗样本。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | Guo J Z, Zhu X Y, Zhao C X, et al. Learning meta face recognition in unseen domains[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 6163-6172. |
| 2 | Tang T A, Mhamdi L, Mclernon D, et al. Deep learning approach for network intrusion detection in software defined networking[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Networks & Mobile Communications, Fez, Morocco, 2016: 258-263. |
| 3 | Yurtsever E, Lambert J, Carballo A, et al. A survey of autonomous driving:common practices and emerging technologies[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 8: 58443- 58469. |
| 4 | Devlin J, Chang M W, Lee K, et al. BERT: pretraining of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[C]∥Proceedings of Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis,USA, 2019: 4171-4186. |
| 5 | Kurakin A, Goodfellow I J, Bengio S. Adversarial machine learning at scale[C]∥Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017: 1-17. |
| 6 | Moosavi-Dezfooli S M, Fawzi A, Frossard P. DeepFool: a simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2574-2582. |
| 7 | Moosavi-Dezfooli S M, Fawzi A, Fawzi O, et al. Universal adversarial perturbations[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 86-94. |
| 8 | 陈阳, 王勇. 绿色云计算环境中基于温度感知的虚拟机迁移策略[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 32(2): 192-199. |
| Chen Yang, Wang Yong. Temperature-aware virtual machine migration strategy for green cloud computing environments[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 32(2): 192-199. | |
| 9 | Dong Y, Pang T, Su H, et al. Evading defenses to transferable adversarial examples by translation invariant attacks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4307-4316. |
| 10 | Xiao C, Li B, Zhu J Y, et al. Generating adversarial examples with adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 3905-3911. |
| 11 | Szegedy C, Zaremba W, Sutskever I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks[C]∥ Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, Canada, 2014. |
| 12 | Carlini N, Wagner D. Towards evaluating the robustness of neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Jose, USA, 2017: 39-57. |
| 13 | Goodfellow I J, Shlens J, Szegedy C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples[C]∥Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, DiegoSan, USA, 2015: 1-11. |
| 14 | Kurakin A, Goodfellow I J, Bengio S. Adversarial examples in the physical world[C]∥Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2016: 1-14. |
| 15 | Baluja S, Fischer I. Adversarial transformation networks: Learning to generate adversarial examples[C]∥Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. |
| 16 | Peng X, Xian H, Lu Q, et al. Semantics aware adversarial malware examples generation for black-box attacks[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 109: No. 107506 |
| 17 | Papernot N, Mcdaniel P, Goodfellow I, et al. Practical Black-Box attacks against machine learning[C]∥Proceedings of the ACM on Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2017: 506-519. |
| 18 | Dong Y, Liao F, Pang T, et al. Boosting adversarial attacks with momentum[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 9185-9193. |
| 19 | Xie C, Zhang Z, Zhou Y, et al. Improving transferability of adversarial examples with input diversity[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2725-2734. |
| 20 | 王超, 魏祥麟, 田青, 等. 基于特征梯度的调制识别深度网络对抗攻击方法[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(7): 25-32. |
| Wang Chao, Wei Xiang-lin, Tian Qing, et al. Feature gradient-based adversarial attack on modulation recognition oriented deep neural networks[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(7): 25-32. | |
| 21 | 陈晓楠, 胡建敏, 张本俊, 等. 基于模型间迁移性的黑盒对抗攻击起点提升方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2021, 47(8): 162-169. |
| Chen Xiao-nan, Hu Jian-min, Zhang Ben-jun, et al. Black box adversarial attack starting point promotion method based on mobility between models[J]. Computer Engineering, 2021, 47(8): 162-169. | |
| 22 | 廖俊帆, 顾益军, 张培晶, 等. 端到端说话人辨认的对抗样本应用比较研究[J]. 计算机工程, 2021, 47(6): 132-141. |
| Liao Jun-fan, Gu Yi-jun, Zhang Pei-jing, et al. Comparative research on application of adversarial samples for end-to-end speaker identification[J]. Computer Engineering, 2021, 47(6): 132-141. | |
| 23 | 宋娟, 潘欢, 马晓. 带安全检测的云数据中心虚拟机迁移策略[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 33(2): 311-318. |
| Song Juan, Pan Huan, Ma Xiao. A virtual machine migration strategy with secure checking for cloud data centers[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 33(2): 311-318. | |
| 24 | Inkawhich N, Wen W, Li H H, et al. Feature space perturbations yield more transferable adversarial examples[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7059-7067. |
| 25 | 吴建, 许镜, 丁韬. 基于集成迁移学习的细粒度图像分类算法[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 32(3): 452-458. |
| Wu Jian, Xu Jing, Ding Tao. Fine-grained image classification algorithm based on ensemble methods of transfer learning[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 32(3): 452-458. |
| [1] | 高金武,贾志桓,王向阳,邢浩. 基于PSO-LSTM的质子交换膜燃料电池退化趋势预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2192-2202. |
| [2] | 李晓英,杨名,全睿,谭保华. 基于深度学习的不均衡文本分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1889-1895. |
| [3] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [4] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [5] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [6] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [7] | 宋林,王立平,吴军,关立文,刘知贵. 基于信息物理融合和数字孪生的可靠性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 439-449. |
| [8] | 曹洁,马佳林,黄黛麟,余萍. 一种基于多通道马尔可夫变迁场的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 491-496. |
| [9] | 刘桂霞,裴志尧,宋佳智. 基于深度学习的蛋白质⁃ATP结合位点预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 187-194. |
| [10] | 曲优,李文辉. 基于锚框变换的单阶段旋转目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(1): 162-173. |
| [11] | 张杰,景雯,陈富. 基于被动分簇算法的即时通信网络协议漏洞检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2253-2258. |
| [12] | 董丽丽,杨丹,张翔. 基于深度学习的大规模语义文本重叠区域检索[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(5): 1817-1822. |
| [13] | 金立生,郭柏苍,王芳荣,石健. 基于改进YOLOv3的车辆前方动态多目标检测算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1427-1436. |
| [14] | 兰凤崇,李继文,陈吉清. 面向动态场景复合深度学习与并行计算的DG-SLAM算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1437-1446. |
| [15] | 李锦青,周健,底晓强. 基于循环生成对抗网络的学习型光学图像加密方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 1060-1066. |
|
||