吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (2): 430-438.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210720
基于循环神经网络的城市轨道交通短时客流预测
张惠臻1( ),高正凯1,2,李建强2,王晨曦1,潘玉彪1,3,王成1,王靖1
),高正凯1,2,李建强2,王晨曦1,潘玉彪1,3,王成1,王靖1
- 1.华侨大学 计算机科学与技术学院,福建 厦门 361021
2.北京工业大学 信息学部软件学院,北京 100124
3.南威软件股份有限公司,福建 泉州 362000
Short⁃term passenger flow forecasting of urban rail transit based on recurrent neural network
Hui-zhen ZHANG1( ),Zheng-kai GAO1,2,Jian-qiang LI2,Chen-xi WANG1,Yu-biao PAN1,3,Cheng WANG1,Jing WANG1
),Zheng-kai GAO1,2,Jian-qiang LI2,Chen-xi WANG1,Yu-biao PAN1,3,Cheng WANG1,Jing WANG1
- 1.School of Computer Science and Technology,Huaqiao University,Xiamen 361021,China
2.School of Software Engineering,Faculty of Information Technology,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China
3.Linewell Software Co. ,Ltd. ,Quanzhou 362000,China
摘要:
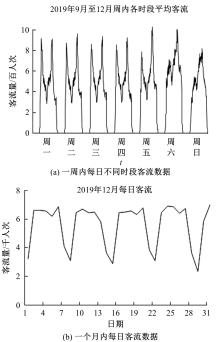
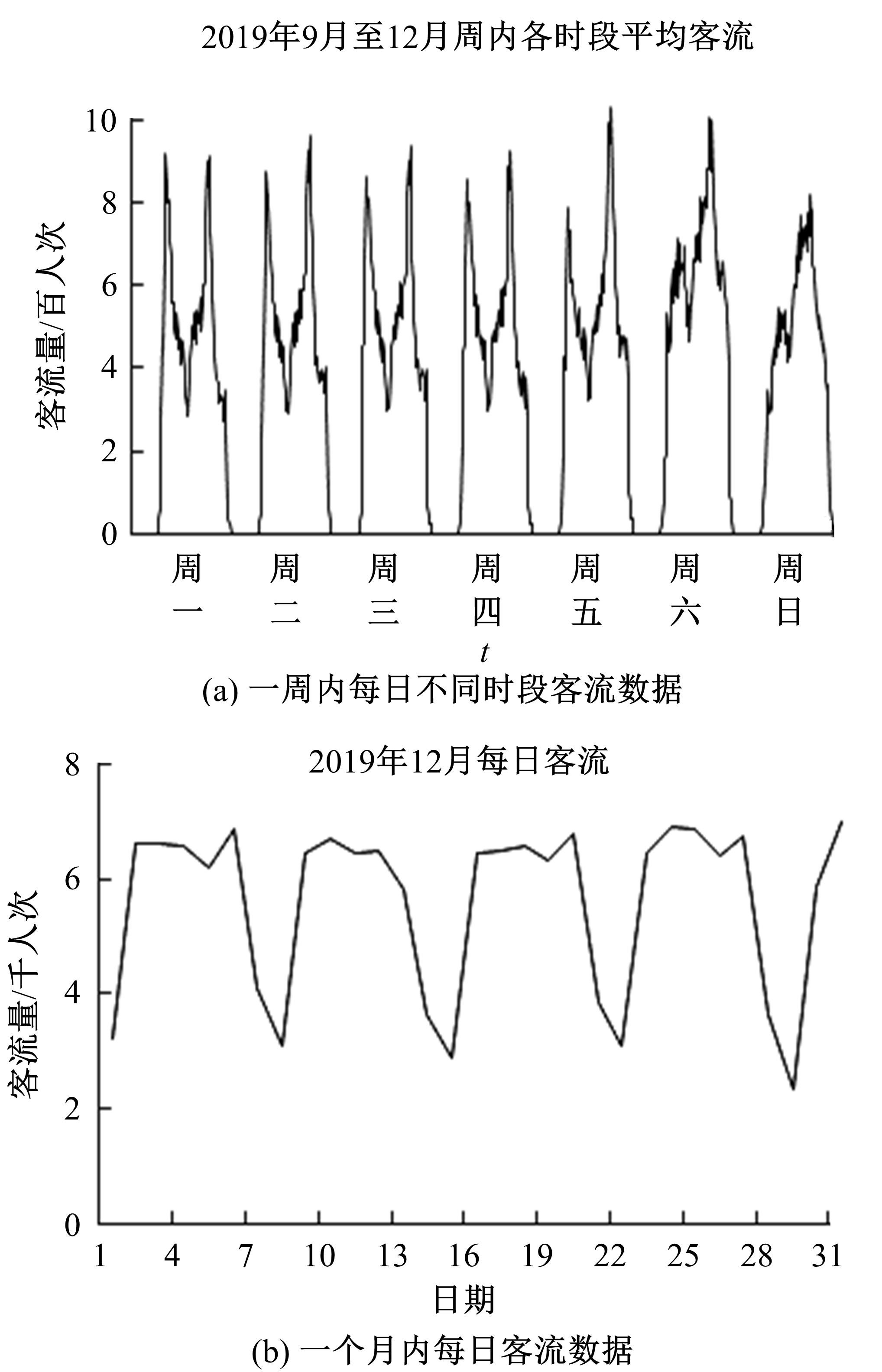
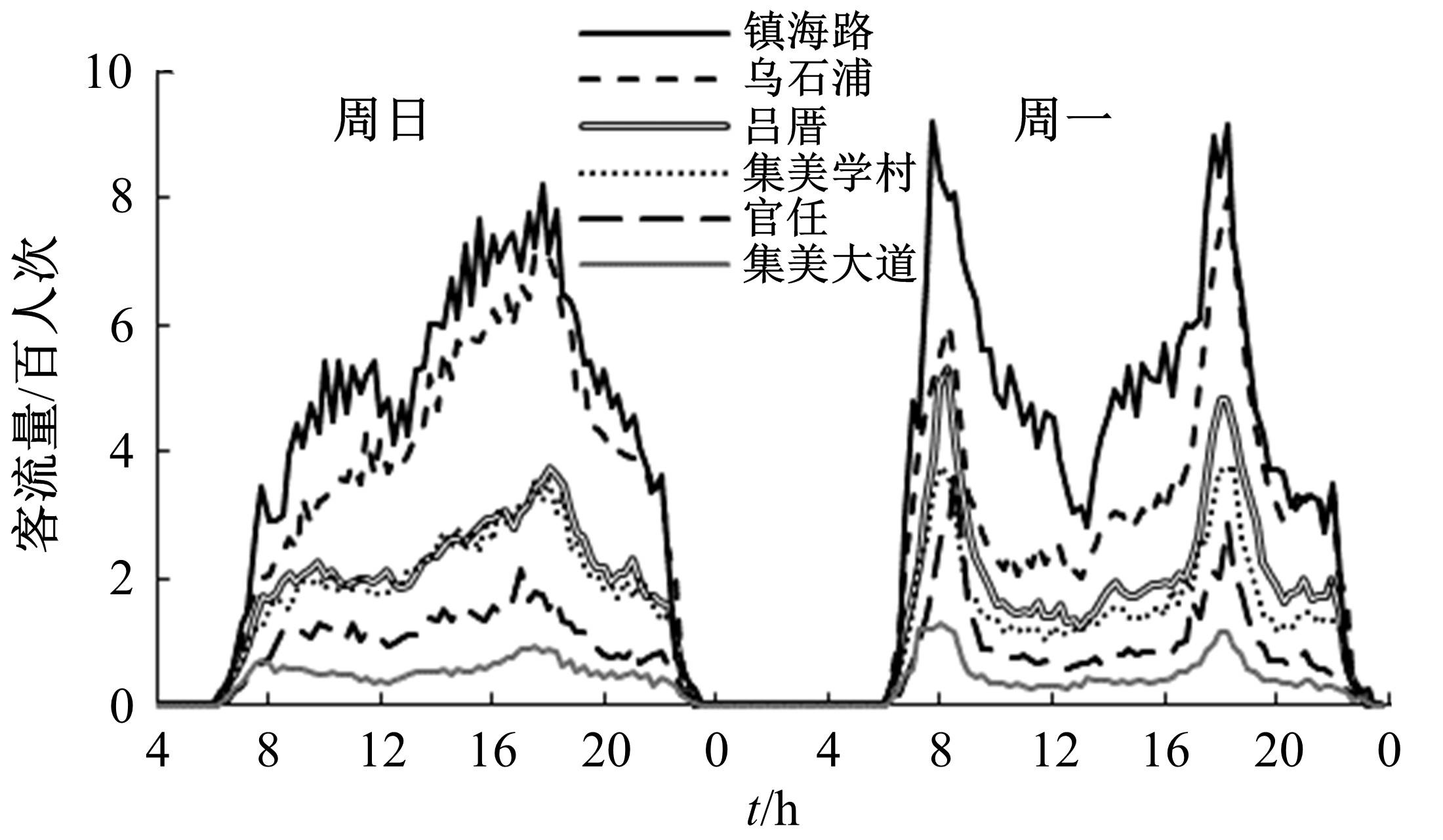
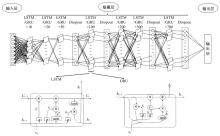
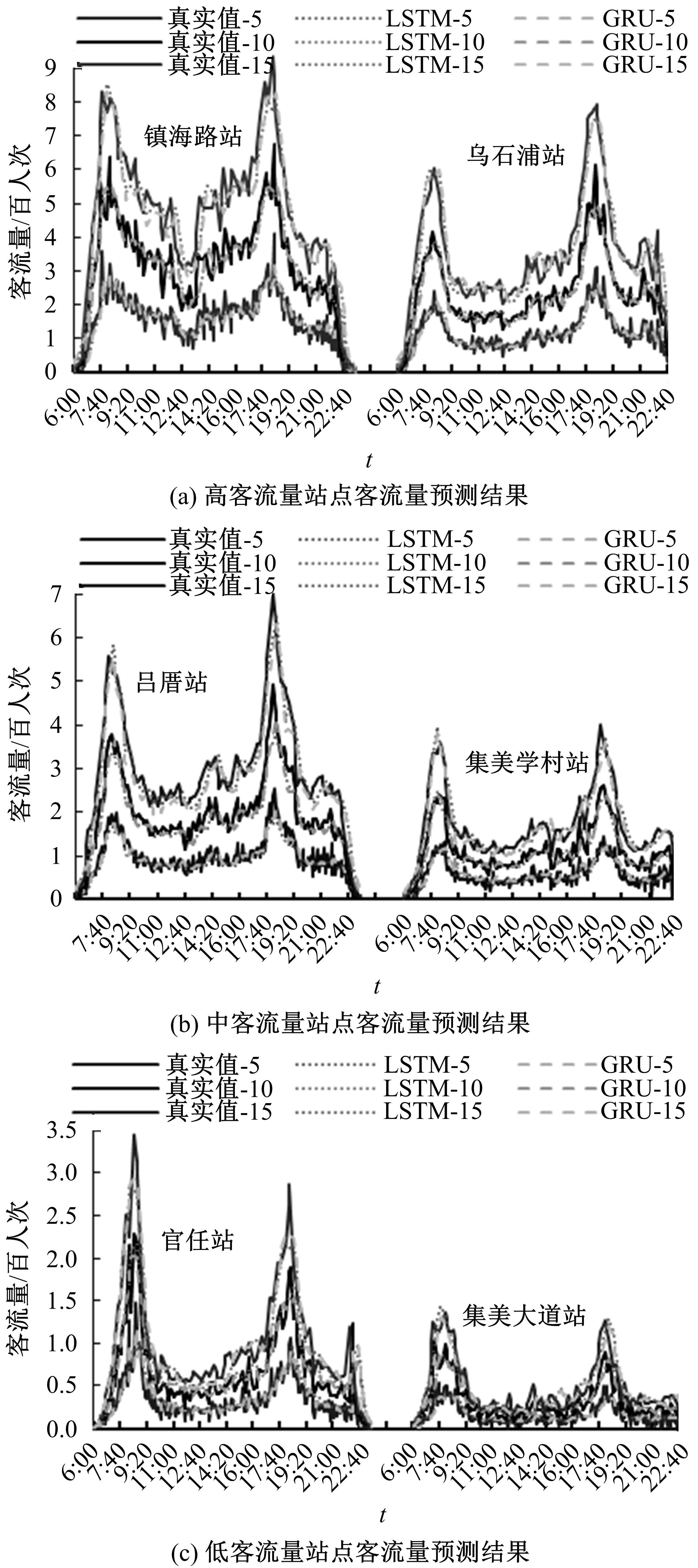
为更好地预测城市轨道交通的短时客流情况,提出了基于循环神经网络模型的预测方法。首先,针对轨道交通进出站客流数据,利用Pearson相关系数确定短时客流影响因素;然后,改进K-means聚类算法划分高、中、低客流量三类轨道站点,分析客流时空分布规律及高峰时间段;最后,采用分别基于长短时记忆神经网络(LSTM)与门控循环单元(GRU)的短时客流预测方法,预测不同类型站点在不同时段的客流。实验结果表明:5 min为预测的最佳时间粒度,在此时间粒度下GRU模型整体性能优于LSTM模型。
中图分类号:
- U121
| 1 | 中国城市轨道交通协会. 城市轨道交通2020年度统计和分析报告[J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2021, 41(4): 691. |
| China Association of Metros. Statistics and analysis Report of urban rail transit in 2020[J]. Tunnel Construction(English and Chinese), 2021, 41(4): 691. | |
| 2 | Schimbinschi F, Moreira-Matias L, Nguyen V X, et al. Topology-regularized universal vector autoregression for traffic forecasting in large urban areas[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 82: 301-316. |
| 3 | Guo J H, Huang W, Williams B M. Adaptive kalman filter approach for stochastic short-term traffic flow rate prediction and uncertainty quantification[J]. Transportation Research Part C, 2014, 43(2): 50-64. |
| 4 | 张淑玉. 基于贝叶斯理论的铁路短期客流预测方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2018. |
| Zhang Shu-yu. Research on forecasting method of short term passenger flow based on Bayesian theory[D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2018. | |
| 5 | 孟品超,李学源,贾洪飞,等.基于滑动平均法的轨道交通短时客流实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2018, 48(2): 448-453. |
| Meng Pin-chao, Li Xue-yuan, Jia Hong-fei, et al. Short-time rail transit passenger flow real-time prediction based on moving average[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering ang Technology Edition), 2018, 48(2): 448-453. | |
| 6 | Zhang Y R, Zhang Y L, Haghani A. A hybrid short-term traffic flow forecasting method based on spectral analysis and statistical volatility model[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2014, 43: 65-78. |
| 7 | 刁文君. 基于灰色模型的城市轨道交通客流预测研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学管理与经济学部, 2016. |
| Diao Wen-jun. Study on the forecast of urban rail transit passenger flow based on Grey Model[D]. Tianjin: College of Management and Economy, Tianjin University, 2016. | |
| 8 | 杨兆升,王媛,管青.基于支持向量机方法的短时交通流量预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2006, 36(6): 881-884. |
| Yang Zhao-sheng, Wang Yuan, Guan Qing. Short-term traffic flow prediction method based on SVM[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering ang Technology Edition), 2006, 36(6): 881-884. | |
| 9 | 姚智胜,邵春福,熊志华,等.基于主成分分析和支持向量机的道路网短时交通流量预测[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2008, 38(1): 48-52. |
| Yao Zhi-sheng, Shao Chun-fu, Xiong Zhi-hua,et al. Short-term traffic volumes forecasting of road network based on principal component analysis and support vector machine[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering ang Technology Edition), 2008, 38(1): 48-52. | |
| 10 | 陈健冲. 基于改进卡尔曼滤波算法的短时公交客流预测模型研究[D]. 大连: 大连海事大学信息科学技术学院, 2020. |
| Chen Jian-chong. Research on short-term bus passeng based on improved Kalman flow prediction model filter algorithm[D]. Dalian: College of Information Science and Technology, Dalian Maritime University, 2020. | |
| 11 | Bai Y, Sun Z Z, Zeng B, et al. A multi-pattern deep fusion model for short-term bus passenger flow forecasting[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 58: 669-680. |
| 12 | Glisovic N, Milenkovic M, Bojovic N, et al. A hybrid model for forecasting the volume of passenger flows on Serbian railways[J]. Operational Research, 2016, 16(2): 271-285. |
| 13 | 田壮壮. 城市轨道交通延伸线的进出站客流预测[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学电气与自动化工程学院, 2019. |
| Tian Zhuang-zhuang. Forecasting passenger flow of inbound and outbound for urban rail transit extension line[D].Nanchang: School of Electrical and Automation Engineering, East China Jiantong University,2019. | |
| 14 |
王秋雯, 陈彦如, 刘媛春. 基于卷积长短时记忆神经网络的城市轨道交通短时客流预测[J/OL]. [2020-09-02]. / 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.0501
doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2020.0501 |
| 15 | 赵阳阳, 夏亮, 江欣国. 基于经验模态分解与长短时记忆神经网络的短时地铁客流预测模型[J]. 交通运输工程学报, 2020, 20(4): 194-204. |
| Zhao Yang-yang, Xia Liang, Jiang Xin-guo. Short-term metro passenger flow prediction based on EMD-LSTM[J]. Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering, 2020, 20(4): 194-204. | |
| 16 | Tsai T H, Lee C K, Wei C H.Neural network based temporal feature models for short-term railway passenger demand forecasting[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2009, 36(2): 3728-3736. |
| 17 | Pearson K. Notes on the history of correlation[J]. Biometrika, 1920, 13(1): 25-45. |
| 18 | 徐威,郑长江,马庚华,等.基于k-means聚类的城市轨道交通站点分类研究[J].贵州大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 35(6): 106-111. |
| Xu Wei, Zheng Chang-jiang, Ma Geng-hua, et al. Classification of urban rail transit stations based on k-means clustering[J]. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 2018, 35(6): 106-111. | |
| 19 | Cho K, Merrienboer B V, Gulcehre C, et al. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation[C] ∥EMNLP, Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, 2014: 1724-1734. |
| 20 | 李梅. 基于深度学习的短时公交客流预测研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学经济管理学院, 2019. |
| Li Mei. Research on short-time bus passenger flows forecasting based on deep learning[D]. Beijing: School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. | |
| 21 | 王挺. 城市轨道交通短时客流预测时间粒度选择[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学土木建筑工程学院, 2018. |
| Wang Ting. Selecting time granularity of short-term passenger flow forecast in urban rail transit[D]. Beijing: School of Civil Engineering, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2018. |
| [1] | 王菁,万峰,董春娇,邵春福. 城市轨道交通站点吸引范围及强度建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 439-447. |
| [2] | 李津,孙雨彤,魏小忠,焦玉玲. 考虑柔性车道设置的公交优先信号设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 448-456. |
| [3] | 张龙,徐天鹏,王朝兵,易剑昱,甄灿壮. 基于卷积门控循环网络的齿轮箱故障诊断[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 368-376. |
| [4] | 潘晓英,魏德,赵逸喆. 基于Mask R⁃CNN和上下文卷积神经网络的肺结节检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(10): 2419-2427. |
| [5] | 徐洪峰, 高霜霜, 郑启明, 章琨. 信号控制交叉口的复合动态车道管理方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 430-439. |
| [6] | 孟品超, 李学源, 贾洪飞, 李延忠. 基于滑动平均法的轨道交通短时客流实时预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 448-453. |
| [7] | 赵学彧, 杨家其, 彭亚美. 城市轨道交通与地面公交竞合关系演化机制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 756-764. |
| [8] | 王海玮, 温惠英, 刘敏. 夜间环境驾驶员精神负荷的生理特性评估与实验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(2): 420-428. |
| [9] | 姜桂艳, 刘彬, 隋晓艳, 马明芳. 基于IC卡收费系统的公交客流信息实时采集方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(4): 1076-1082. |
| [10] | 宗芳, 王占中, 贾洪飞, 焦玉玲, 吴杨. 基于支持向量机的通勤日活动-出行持续时间预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 406-411. |
| [11] | 李世武, 徐艺, 孙文财, 王琳虹, 郭梦竹, 柴萌. 基于瞳孔直径的撞固定物冲突自反馈识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 418-425. |
| [12] | 潘义勇, 马健霄, 孙璐. 基于可靠度的动态随机交通网络耗时最优路径[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(2): 412-417. |
| [13] | 赵淑芝, 梁士栋, 马明辉, 刘华胜, 朱永刚. 信号交叉口实时排队长度估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 85-91. |
| [14] | 姚向明, 赵鹏, 禹丹丹. 基于平均策略的城市轨道交通动态O-D矩阵估计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2016, 46(1): 92-99. |
| [15] | 刘华胜,赵淑芝,朱永刚,李晓玉. 基于有效路径的轨道交通接运线路设计模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(2): 371-378. |
|