吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (10): 2419-2427.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210278
• 计算机科学与技术 • 上一篇
基于Mask R⁃CNN和上下文卷积神经网络的肺结节检测
- 1.西安邮电大学 计算机学院,西安 710121
2.陕西省网络数据分析与智能处理重点实验室,西安 710121
3.西北大学 信息科学与技术学院,西安 710029
Detecetion of lung nodule based on mask R-CNN and contextual convolutional neural network
Xiao-ying PAN1,2( ),De WEI1,2,Yi-zhe ZHAO1,3
),De WEI1,2,Yi-zhe ZHAO1,3
- 1.School of Computer Science and Technology,Xi'an University of Posts and Telecommunications,Xi'an 710121,China
2.Key Laboratory of Network Data Analysis and Intelligent Processing of Shaanxi Province,Xi'an 710121,China
3.School of Information Science and Technology,Northwest University,Xi'an 710129,China
摘要:
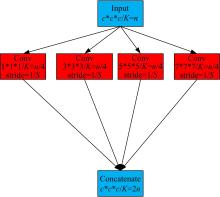
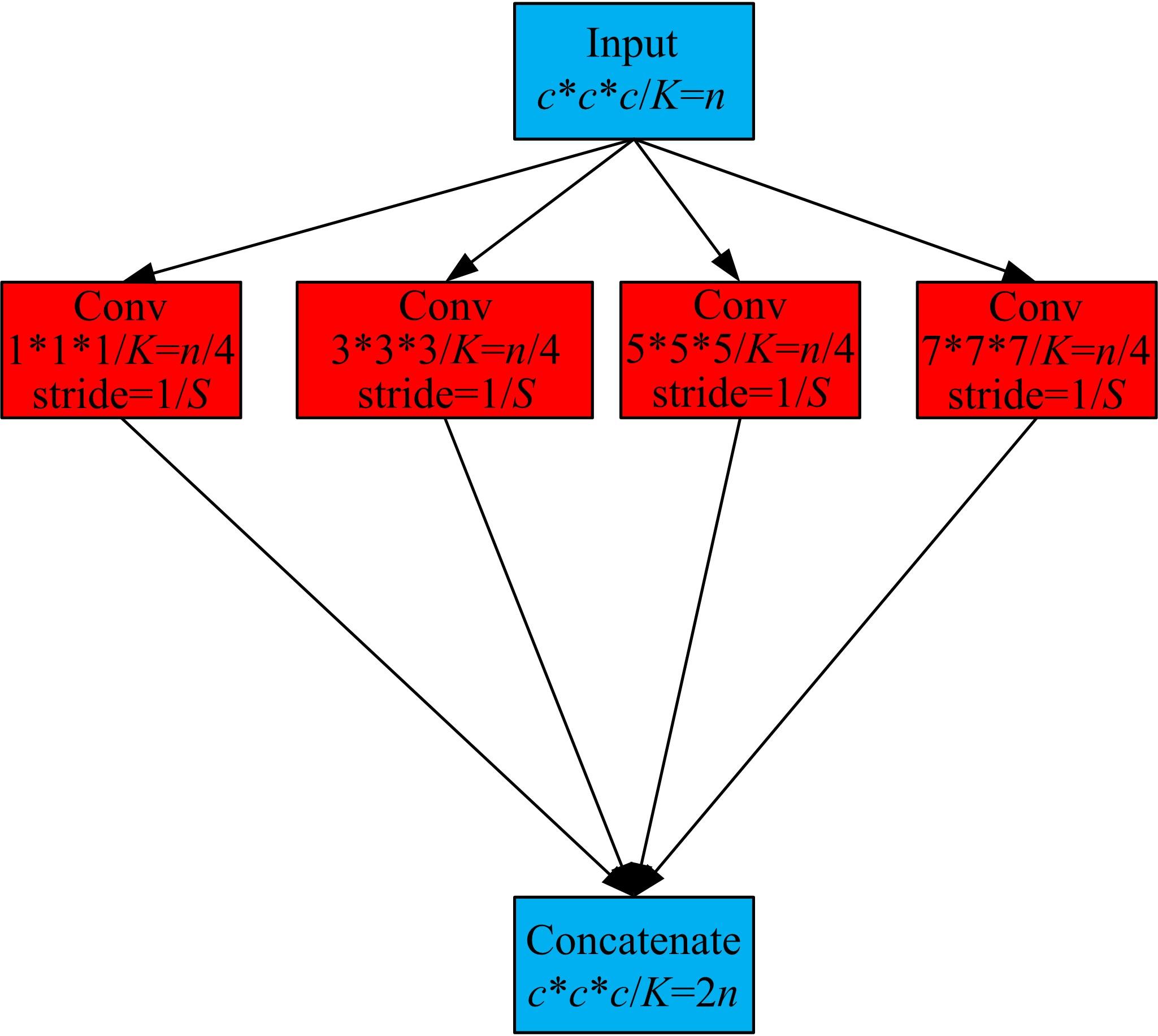
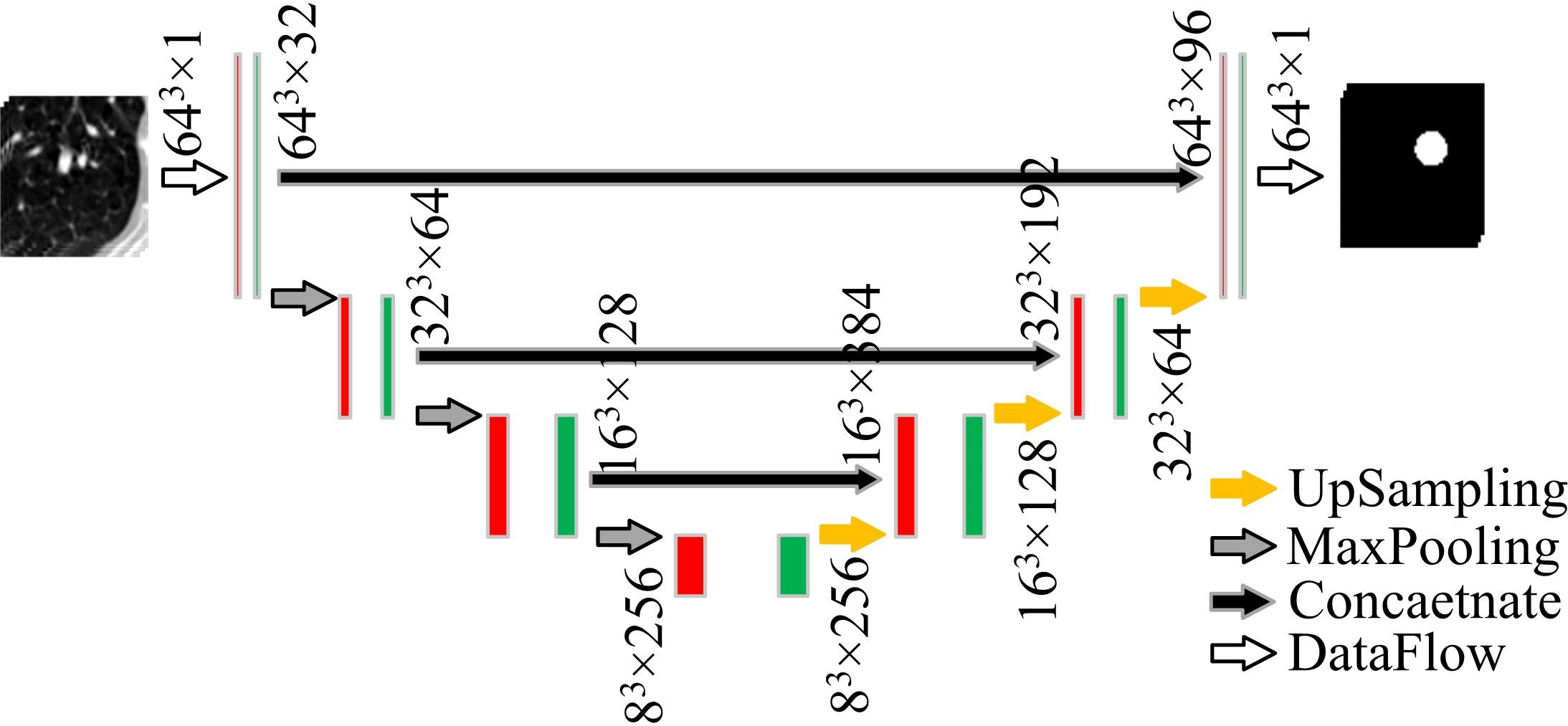
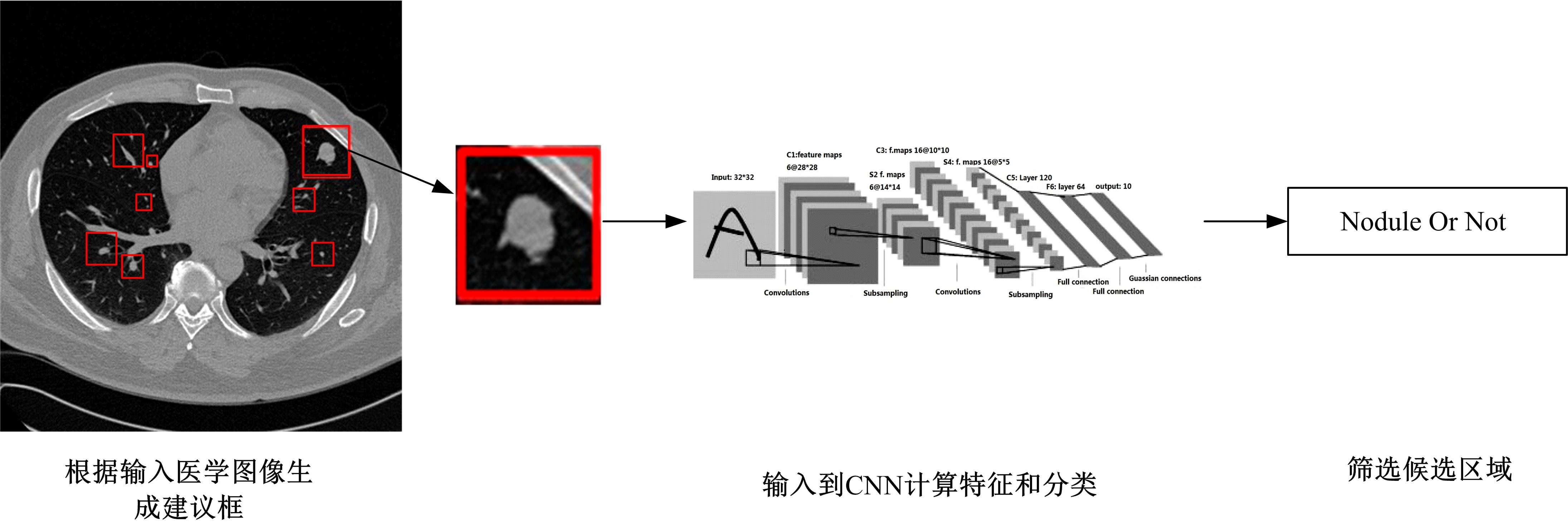
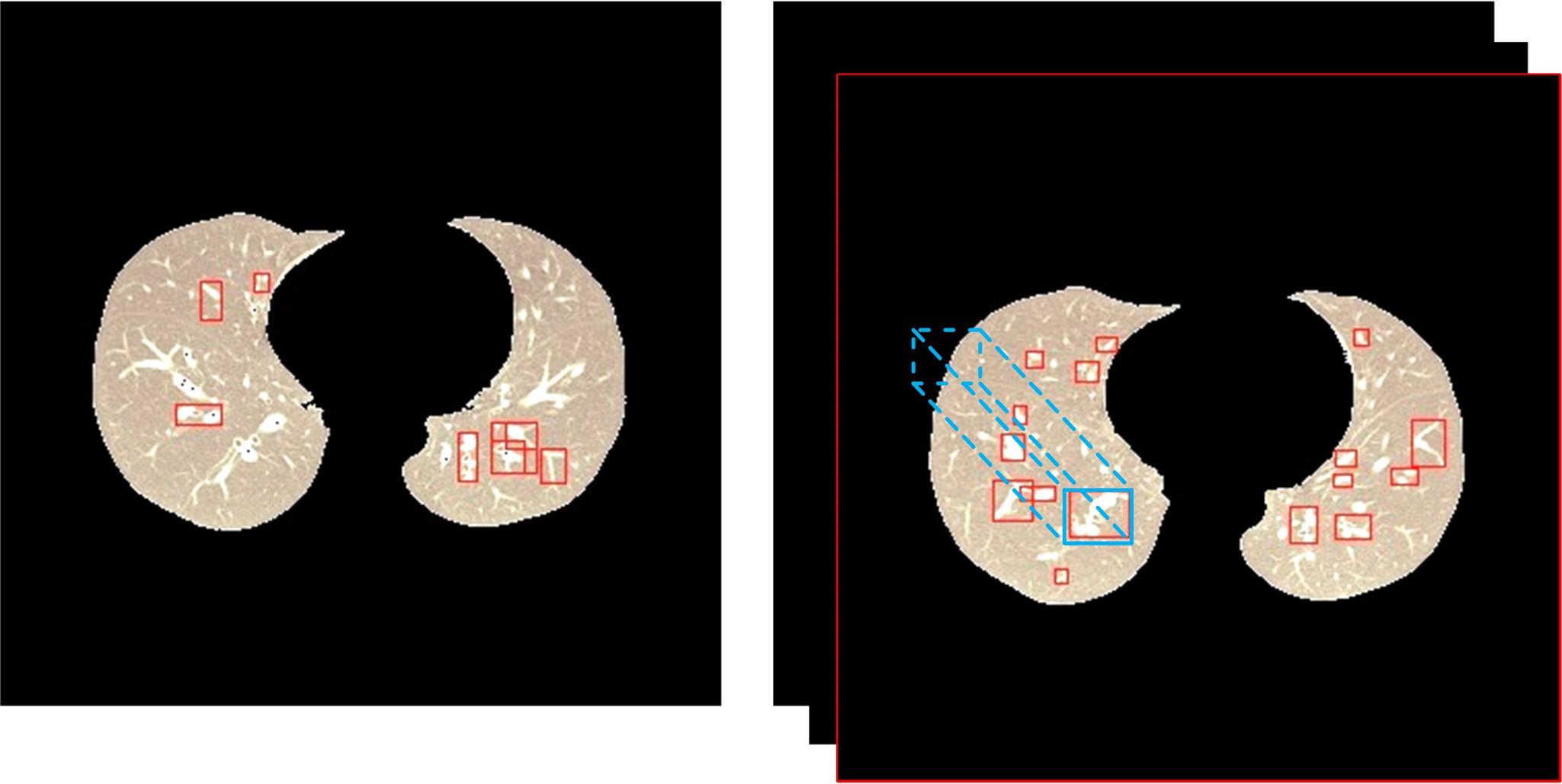
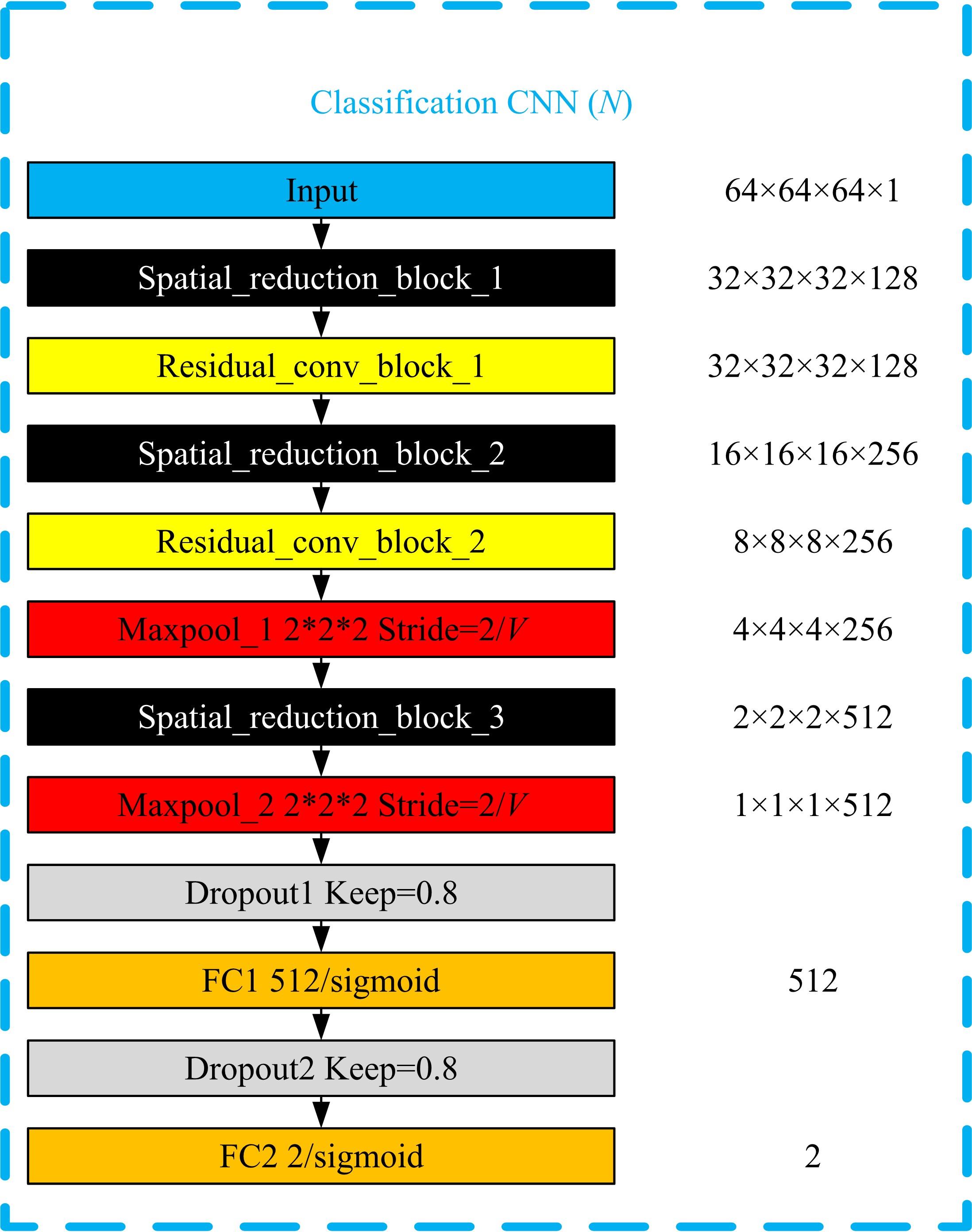
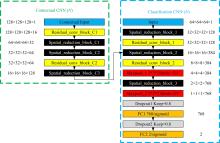
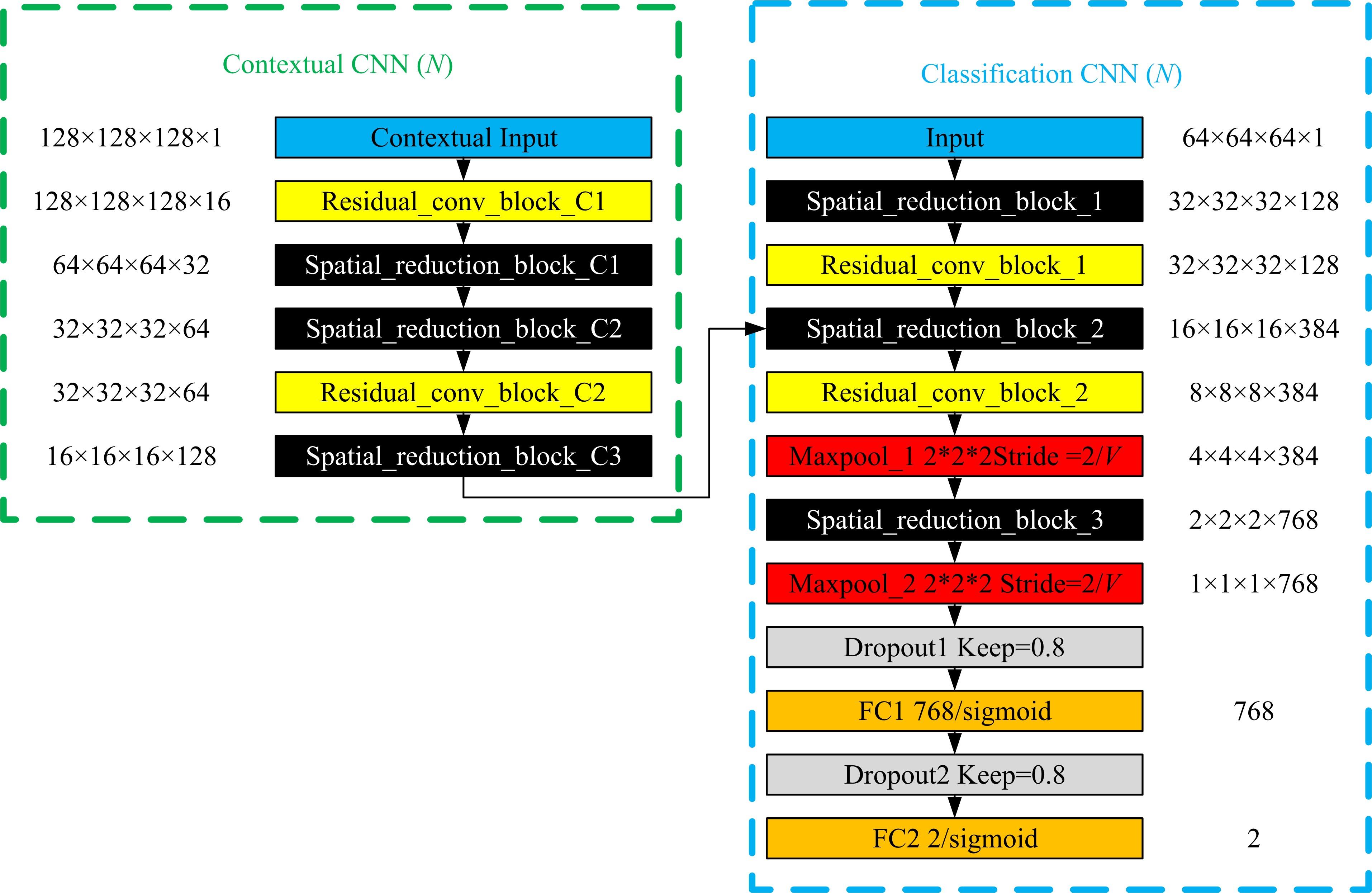
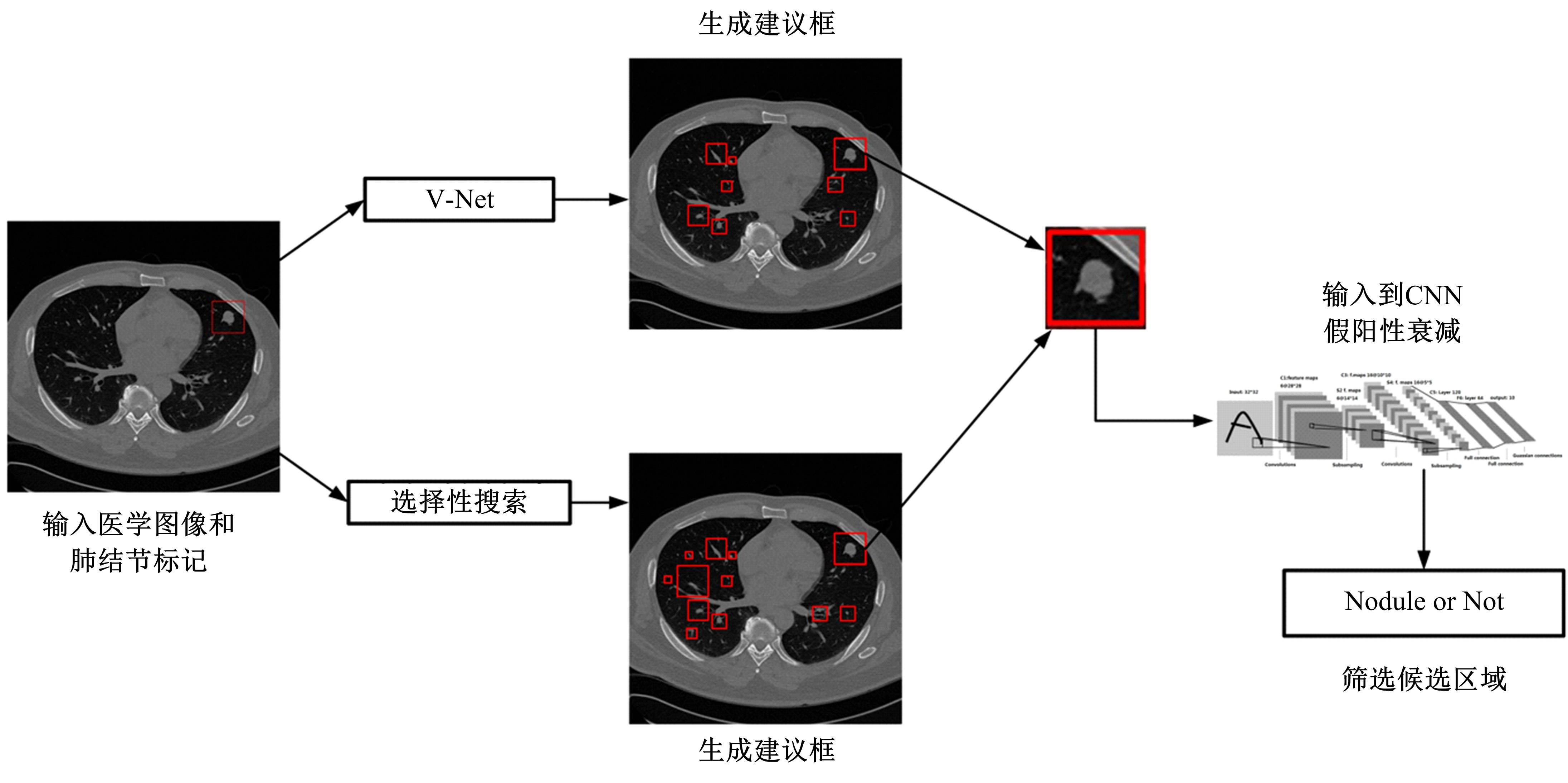
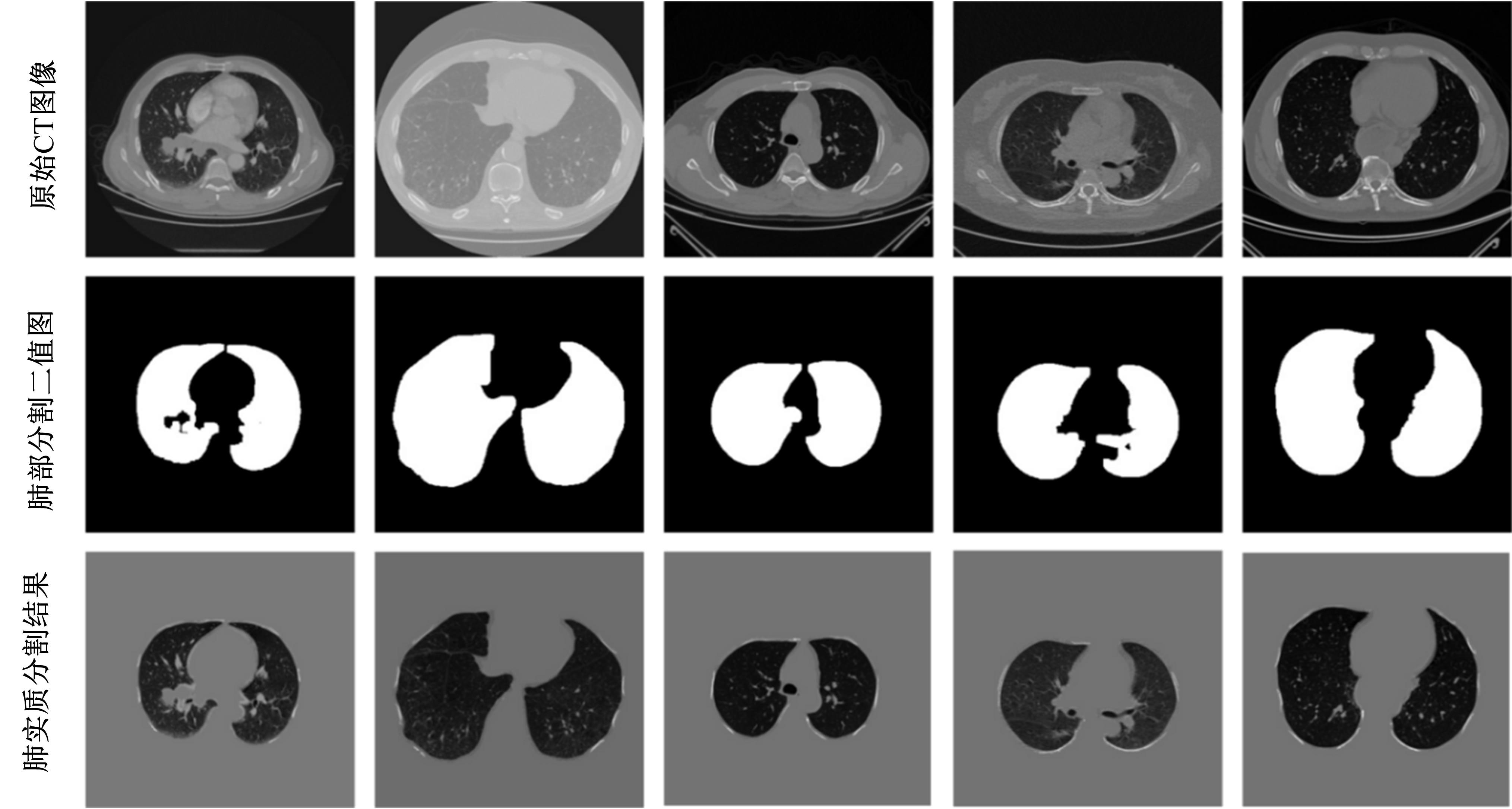
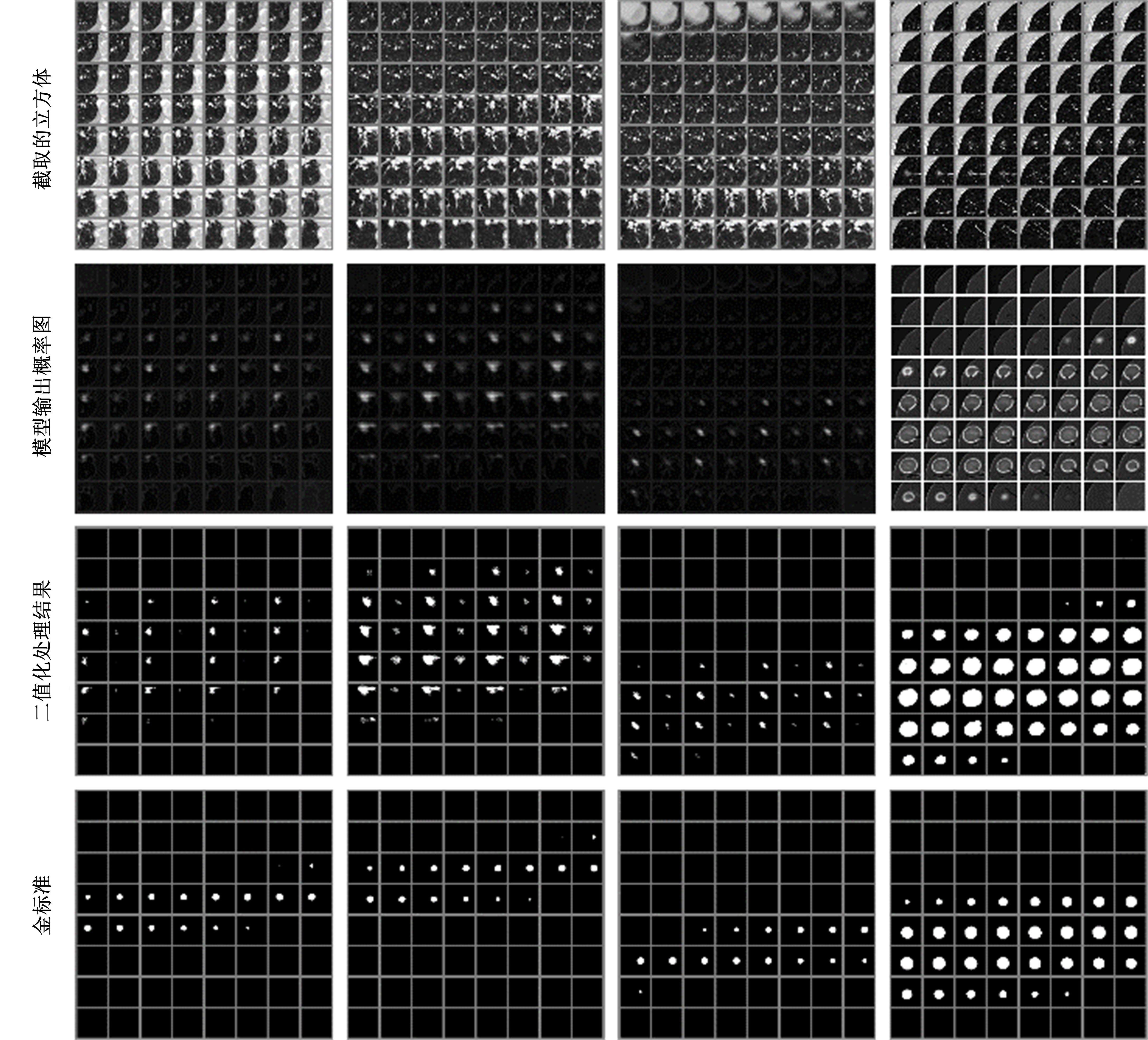
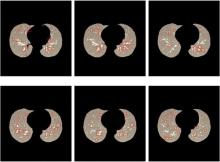
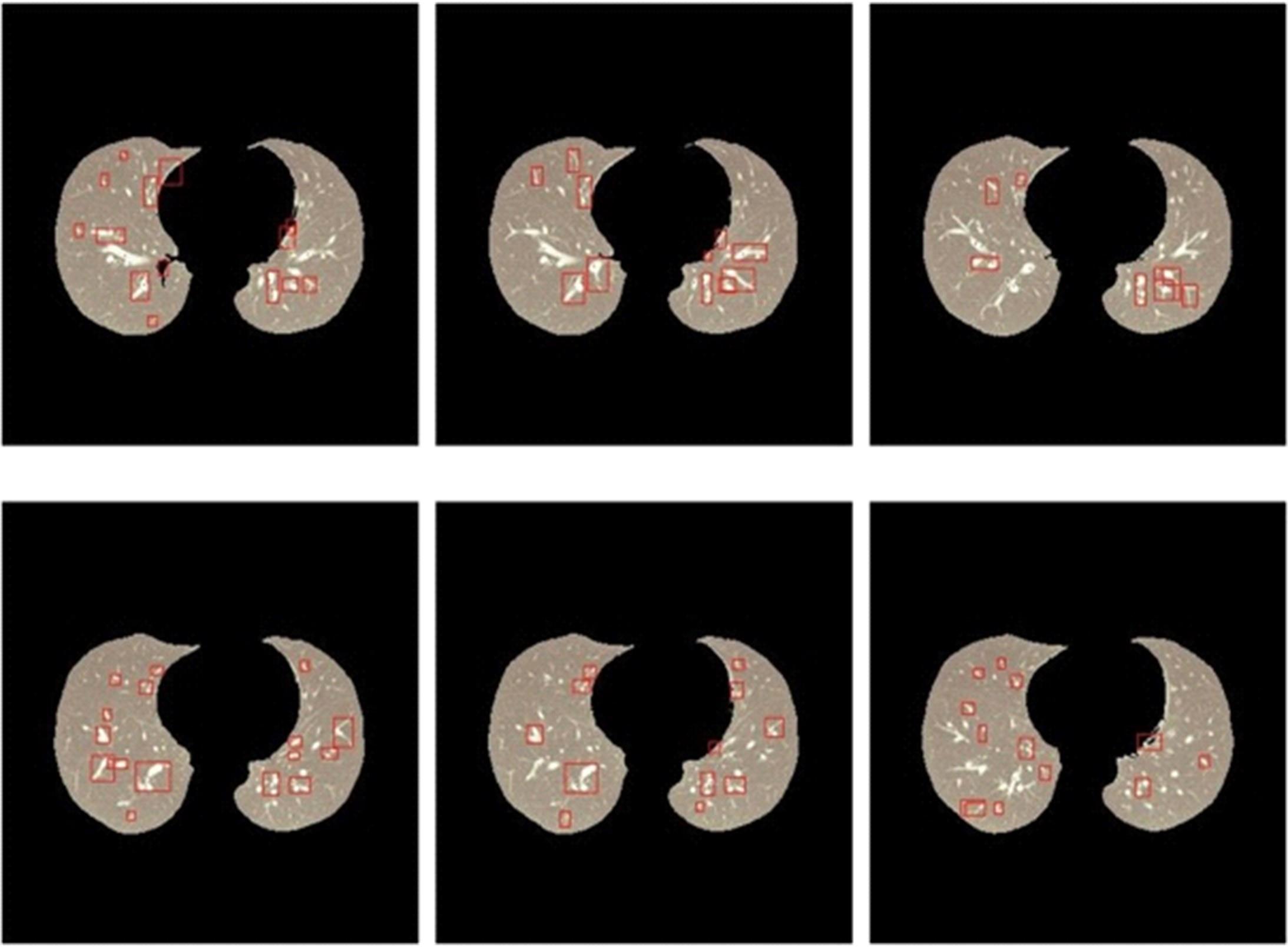
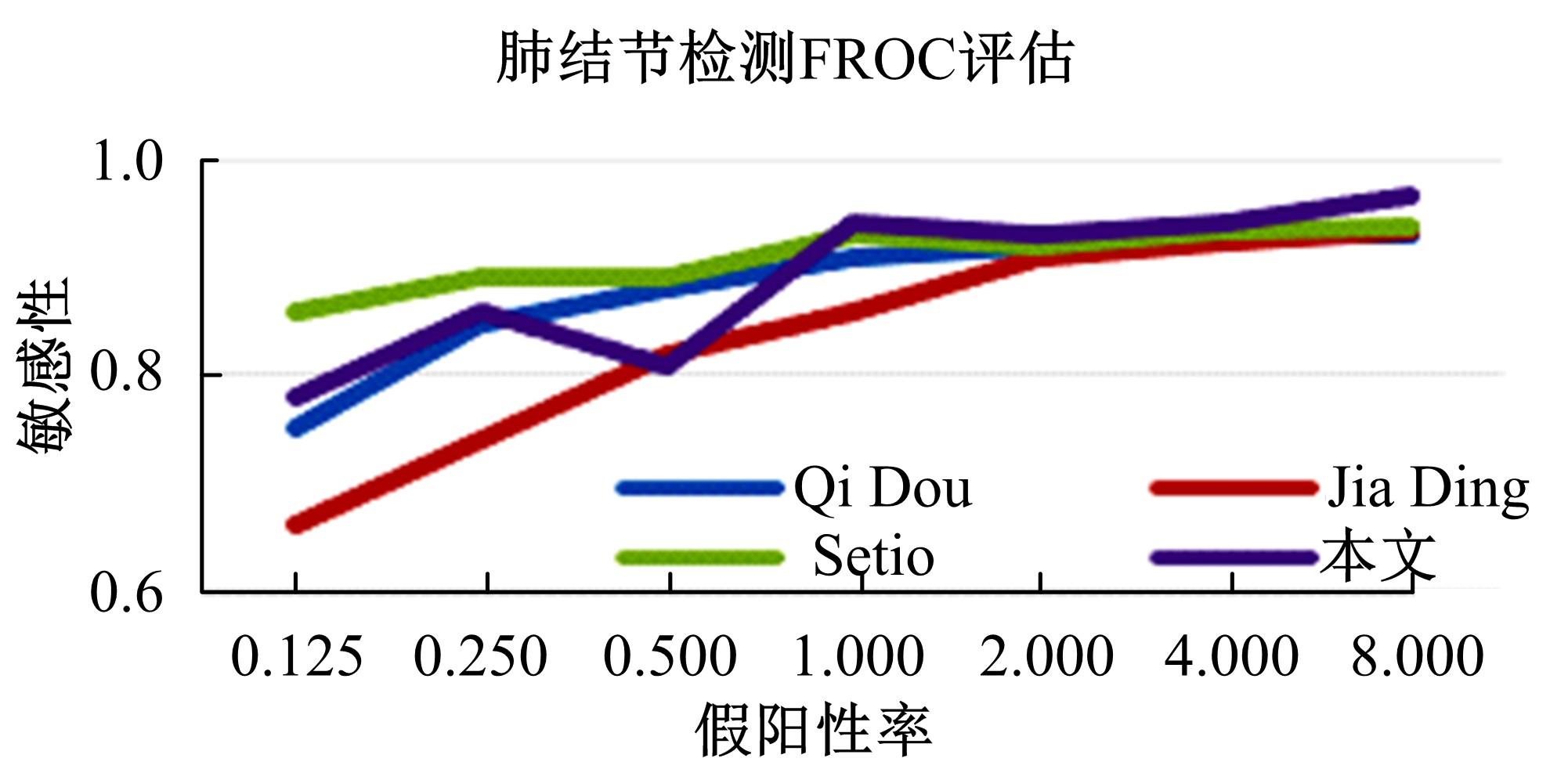
为了提高肺癌的早期诊断效果,提出了一种基于深度学习架构的肺结节检测算法,设计了基于V-Net和R-CNN混合的Mask R-CNN肺结节检测模块和基于多尺度与上下文的肺结节假阳性衰减网络。该算法首先使用V-Net进行肺结节定位,再使用3D R-CNN进行假阳性衰减,判断候选区域是否为真实肺结节。算法中引入Inception网络设计了V-Net多尺度模块,实现肺结节定位;设计3D R-CNN肺结节检测模型,融合肺结节定位结果,确定假阳性肺结节候选区域;设计的假阳性衰减网络分类模型,实现了对肺结节进行去假阳性判断,提升检测有效性。实验结果显示,本算法取得了0.97的FROC值,较已有算法提升了5%,表明本算法对肺癌早期检测和诊断具有较好的临床意义。
中图分类号:
- TP391
| 1 | 邹小农. 中国肺癌流行病学[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2007, 14(12): 881-883. |
| Zou Xiao-nong. Epidemiology of lung cancer in China[J]. China cancer Prev Trea, 2007, 14(12): 881-883. | |
| 2 | 杨德昌, 杨拴盈. 肺癌诊断水平的现状与进展[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2001, 24(8): 450-460. |
| Yang De-chang, Yang Shuan-ying. Current status and progress of diagnosis of lung cancer[J]. Chinese Journal of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Disease, 2001, 24(8): 450-460. | |
| 3 | 范雪丽, 时高峰, 杜煜, 等. 多层螺旋 CT 扫描在早期肺癌鉴别诊断中的应用[J]. 临床合理用药, 2017, 10(34): 114-116. |
| Fan Xue-li, Shi Gao-feng, Du-yu, et al. Application of multislice spiral CT scan in differential diagnosis of early lung cancer[J]. Rational Clinical Drug Use, 2017, 10(34): 114-116. | |
| 4 | 曹捍波, 王梅, 王和平. MSCT 对孤立性肺结节 (≤ 2cm) 胸膜凹陷征的诊断及鉴别诊断价值[J]. 医学影像学, 2017, 27(8): 1471-1474. |
| Cao Han-bo, Wang Mei, Wang He-ping. Value of MSCT in the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules (≤ 2 cm) with pleural depression[J]. Medical Radioglaciology, 2017, 27(8): 1471-1474. | |
| 5 | Ozdemir O, Woodward B, Berlin A A. Propagating uncertainty in multi-stage Bayesian convolutional neural networks with application to pulmonary nodule detection[EB/OL]. [2021-02-26]. arXiv preprint:1712.00497,2017. |
| 6 | Tan M, Deklerck R, Jansen B, et al. A novel computer‐aided lung nodule detection system for CT images [J]. Medical Physics, 2011, 38(10): 5630-5645. |
| 7 | Setio A A A, Ciompi F, Litjens G, et al. Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(5): 1160-1169. |
| 8 | Wang B, Qi G J, Tang S, et al. Automated pulmonary nodule detection: High sensitivity with few candidates[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Cham: Springer, 2018: 759-767. |
| 9 | 王伟胜. 基于 CT 影像的肺癌计算机辅助诊断关键技术研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学计算机学院, 2016. |
| Wang Wei-sheng. Research on key techniques of computer-aided diagnosis of lung cancer based on CT images[D]. Changsha: Department of Computer Science, Hunan University, 2016. | |
| 10 | Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, et al. Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]∥ Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, USA, 2017: 4278-4284. |
| 11 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation [C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, Cham: Springer, 2015: 234-241. |
| 12 | Cheng J Z, Ni D, Chou Y H, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis with deep learning architecture: applications to breast lesions in US images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: No. 24454. |
| 13 | Buty M, Xu Z Y, Gao M C, et al. Characterization of lung nodule malignancy using hybrid shape and appearance features[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Cham: Springer, 2016: 662-670. |
| 14 | Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 448-456. |
| 15 | Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, et al. Dropout: a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 1929-1958. |
| 16 | Ding J, Li A, Hu Z, et al. Accurate pulmonary nodule detection in computed tomography images using deep convolutional neural networks[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Cham: Springer, 2017: 559-567. |
| 17 | Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA,2013: 580-587. |
| 18 | Uijlings J R R, van de Sande K E, Gevers T, et al. Selective search for object recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154-171. |
| 19 | Dou Q, Chen H, Jin Y, et al. Automated pulmonary nodule detection via 3d convnets with online sample filtering and hybrid-loss residual learning[C]∥International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Cham: Springer, 2017: 630-638. |
| 20 | Bandos A I, Rockette H E, Song T, et al. Area under the free-response ROC curve (FROC) and a related summary index[J]. Biometrics, 2009,65(1):247-256. |
| [1] | 周丰丰,朱海洋. 基于三段式特征选择策略的脑电情感识别算法SEE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1834-1841. |
| [2] | 白天,徐明蔚,刘思铭,张佶安,王喆. 基于深度神经网络的诉辩文本争议焦点识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1872-1880. |
| [3] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [4] | 曲福恒,丁天雨,陆洋,杨勇,胡雅婷. 基于邻域相似性的图像码字快速搜索算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1865-1871. |
| [5] | 赵宏伟,张健荣,朱隽平,李海. 基于对比自监督学习的图像分类框架[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1850-1856. |
| [6] | 秦贵和,黄俊锋,孙铭会. 基于双手键盘的虚拟现实文本输入[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1881-1888. |
| [7] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [8] | 王军,徐彦惠,李莉. 低能耗支持完整性验证的数据融合隐私保护方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1657-1665. |
| [9] | 周丰丰,张亦弛. 基于稀疏自编码器的无监督特征工程算法BioSAE[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1645-1656. |
| [10] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [11] | 杨怀江,王二帅,隋永新,闫丰,周跃. 简化型残差结构和快速深度残差网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1413-1421. |
| [12] | 康耀龙,冯丽露,张景安,陈富. 基于谱聚类的高维类别属性数据流离群点挖掘算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1422-1427. |
| [13] | 王文军,余银峰. 考虑数据稀疏的知识图谱缺失连接自动补全算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1428-1433. |
| [14] | 陈雪云,贝学宇,姚渠,金鑫. 基于G⁃UNet的多场景行人精确分割与检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 925-933. |
| [15] | 方世敏. 基于频繁模式树的多来源数据选择性集成算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(4): 885-890. |
|
||