吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (10): 3014-3025.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211326
基于智能反射表面辅助和信息年龄度量的安全状态更新
- 1.华北电力大学(保定) 电子与通信工程系,河北 保定 071000
2.国网河北省电力有限公司,石家庄 050022
Security status updates based on intelligent reflecting surface assistance and age of information metrics
Bao-gang LI1( ),Yu WANG1,Fan-wei KONG2,Cheng-wei TIAN1
),Yu WANG1,Fan-wei KONG2,Cheng-wei TIAN1
- 1.Department of Electronic and Communication Engineering,North China Electric Power University(Baoding),Baoding 071000,China
2.State Grid Hebei Electric Power Co. Ltd. ,Shijiazhuang 050022,China
摘要:
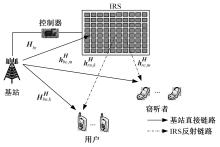
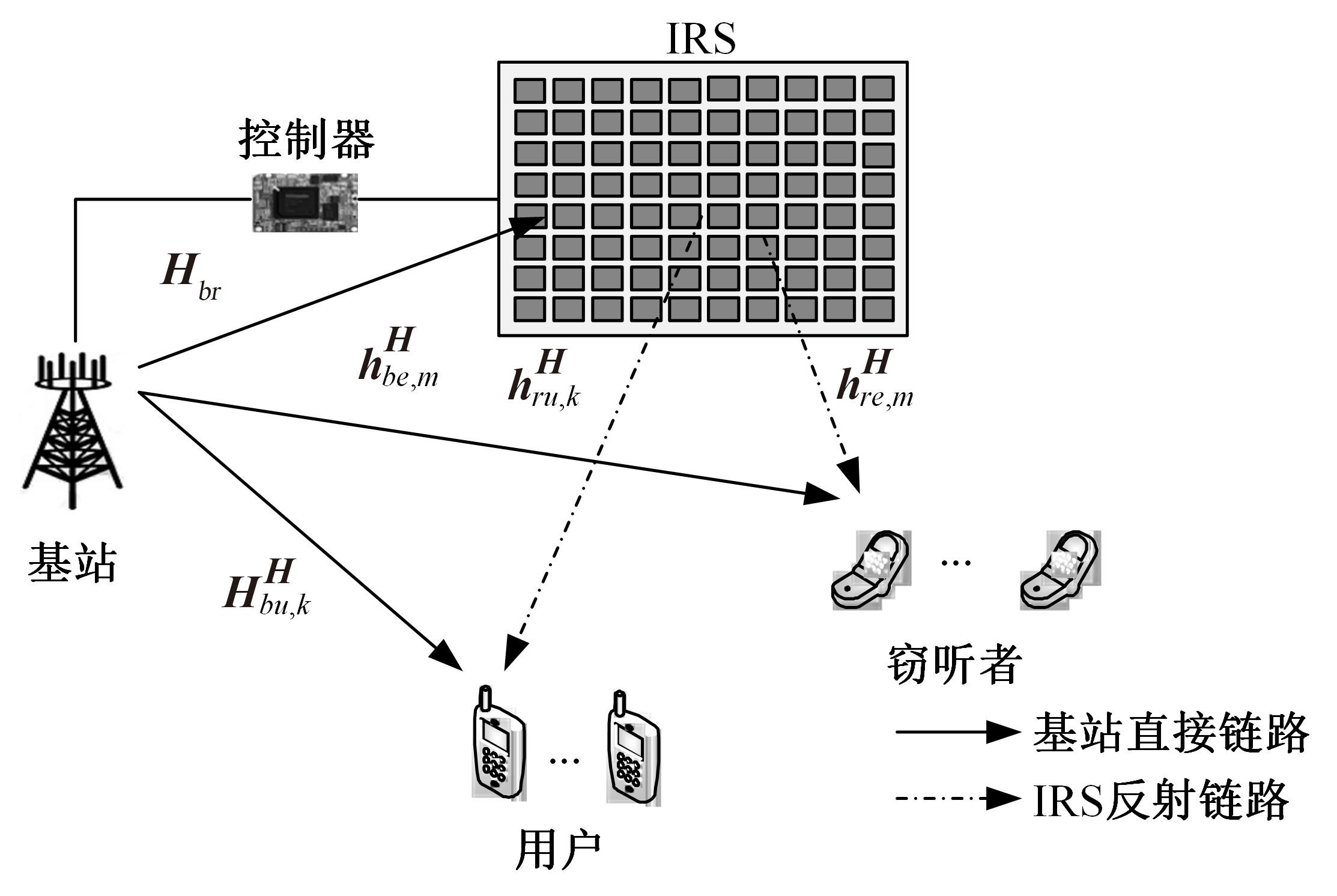
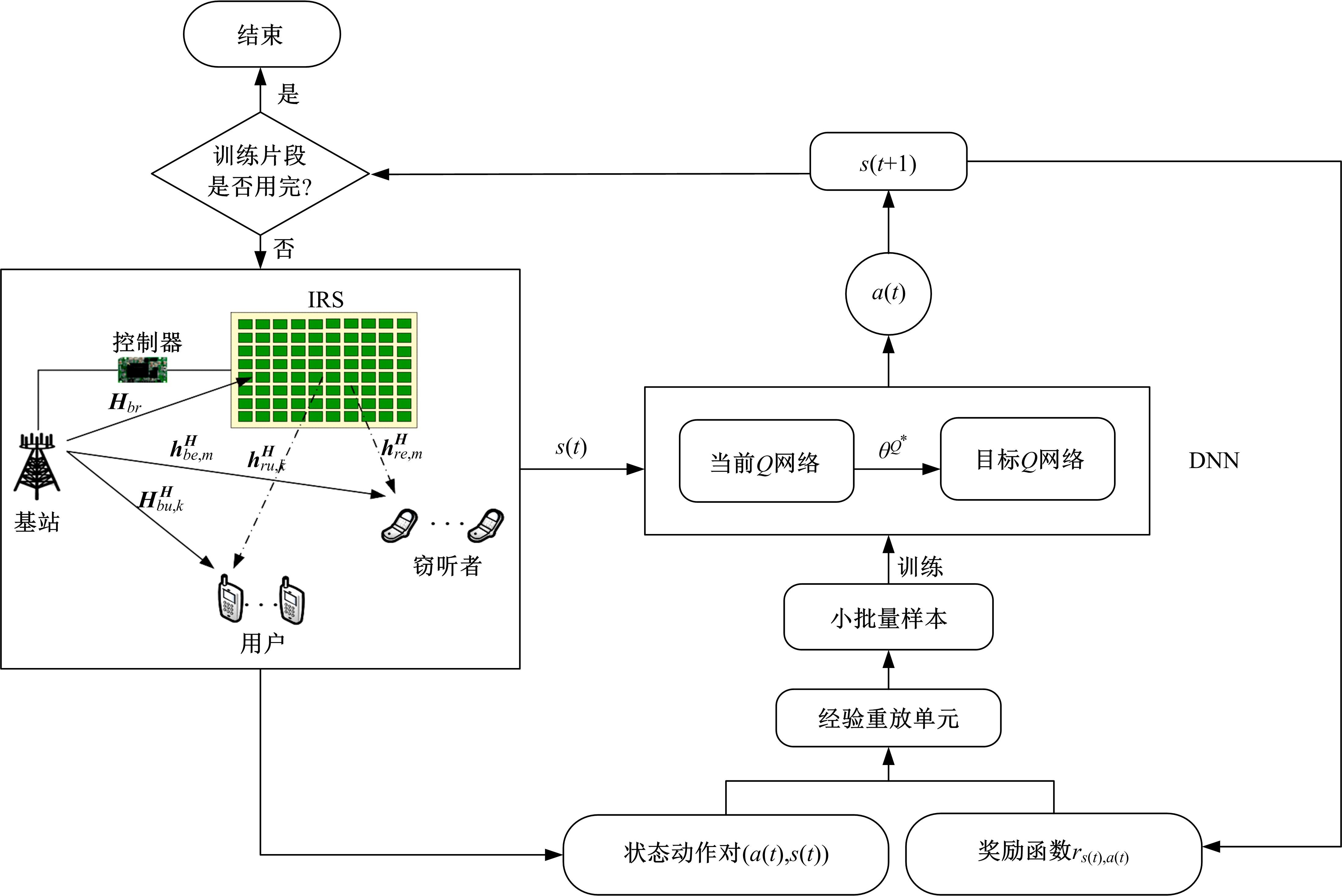
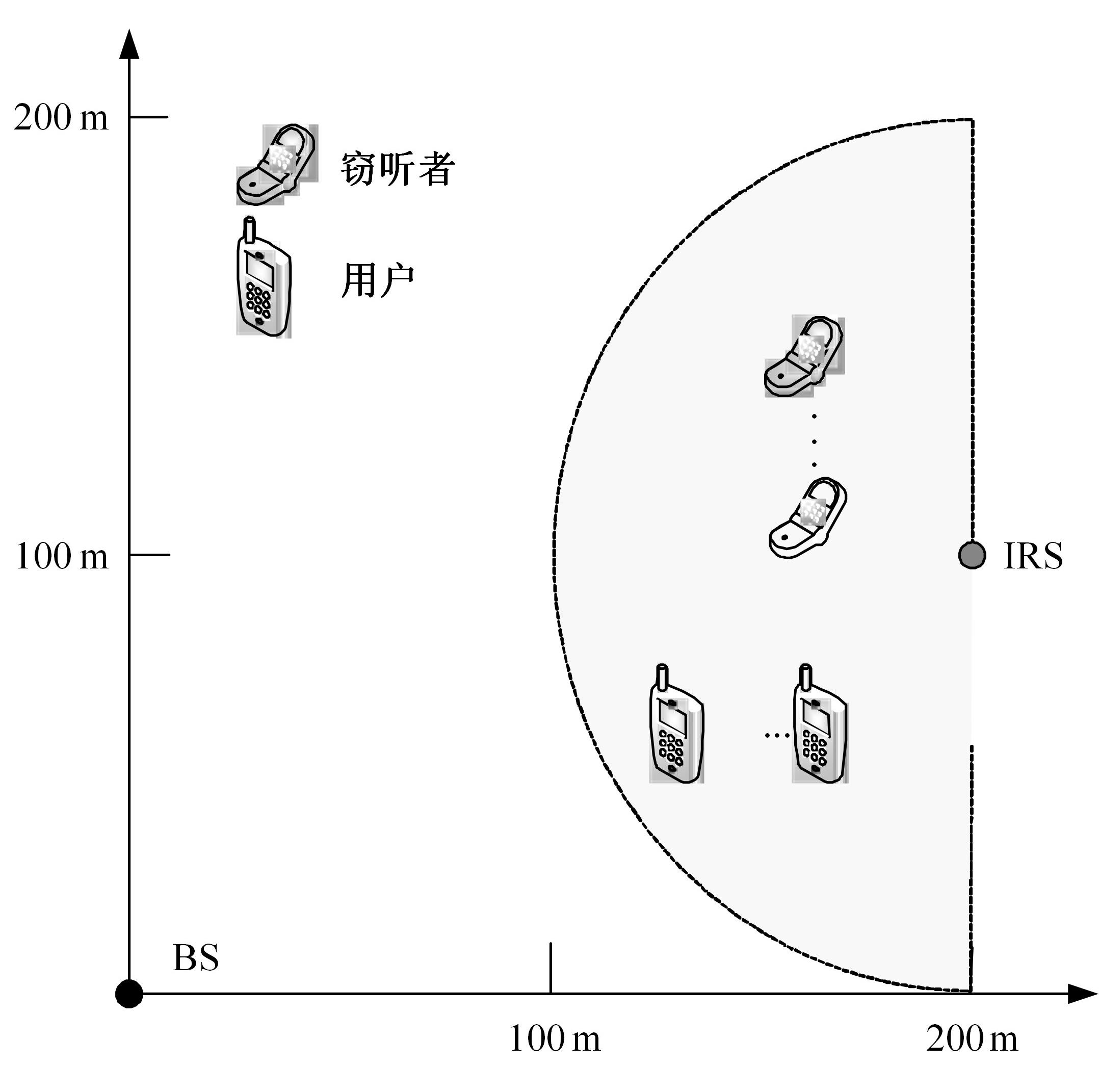
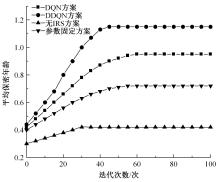
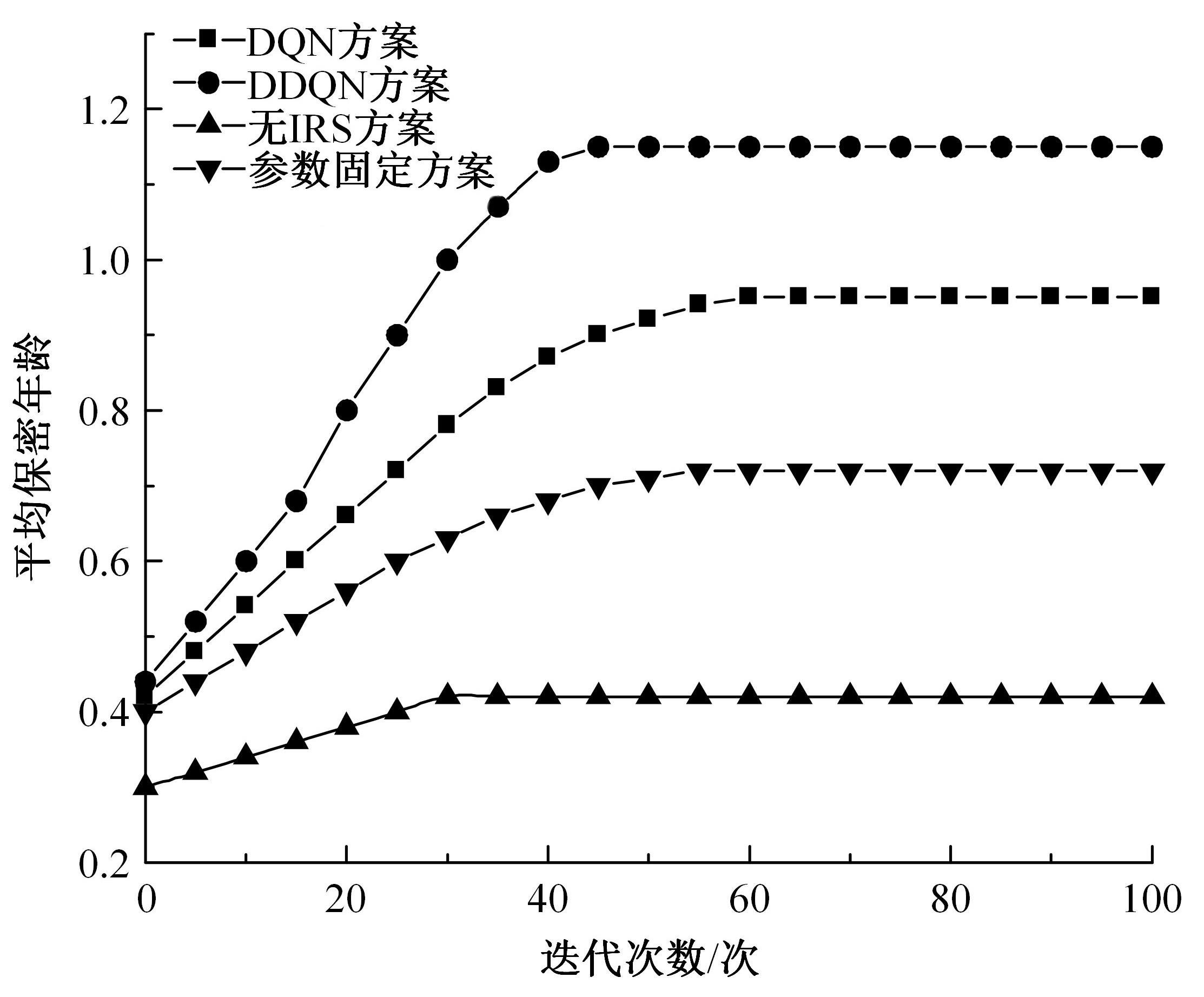
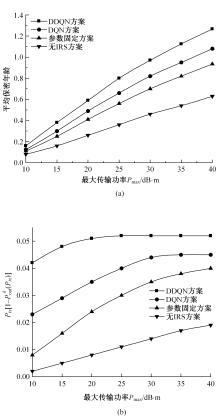
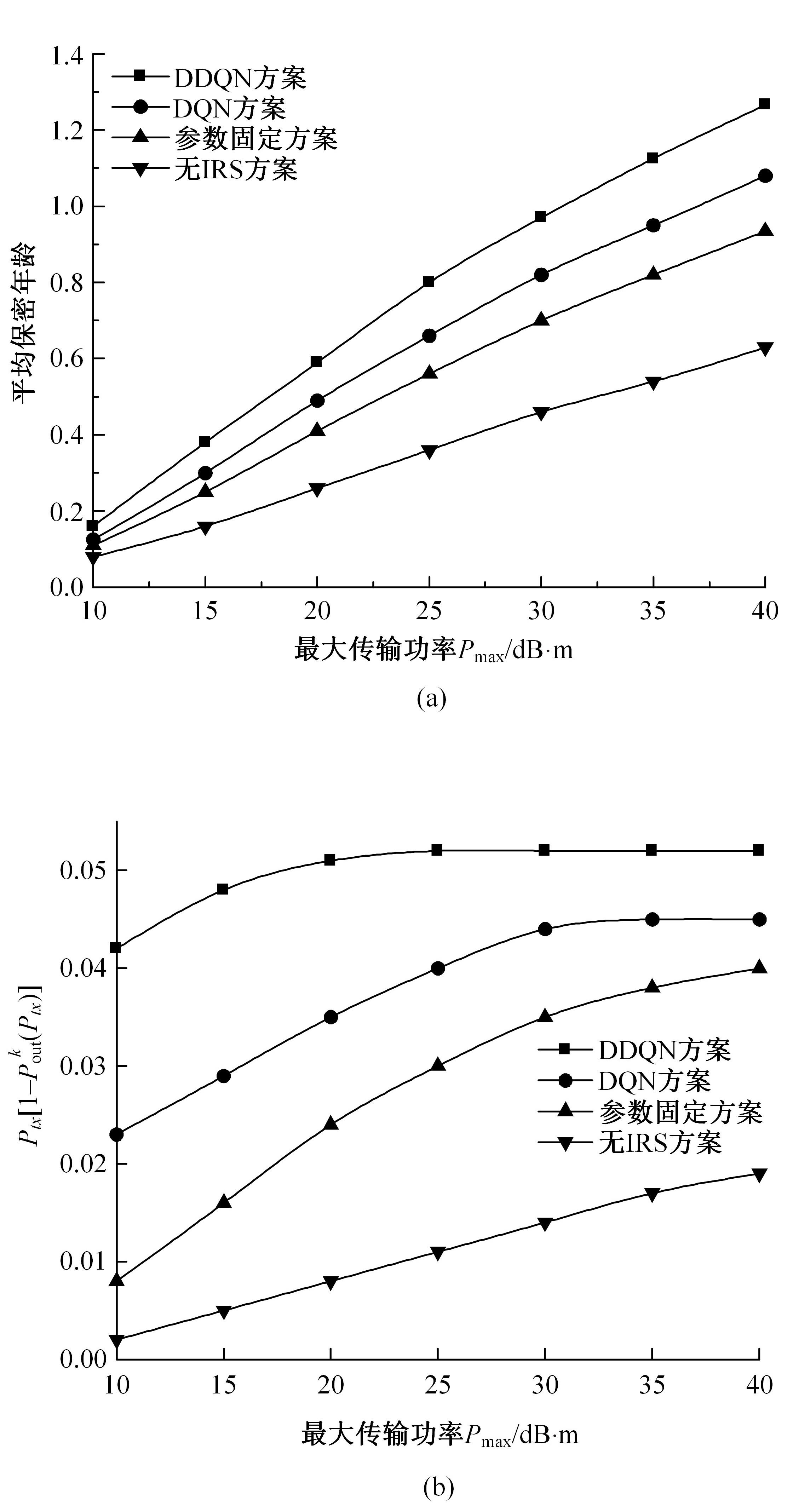
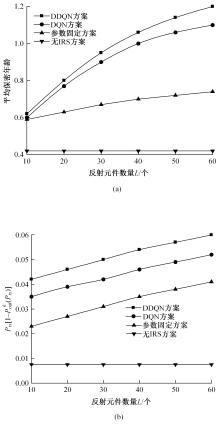
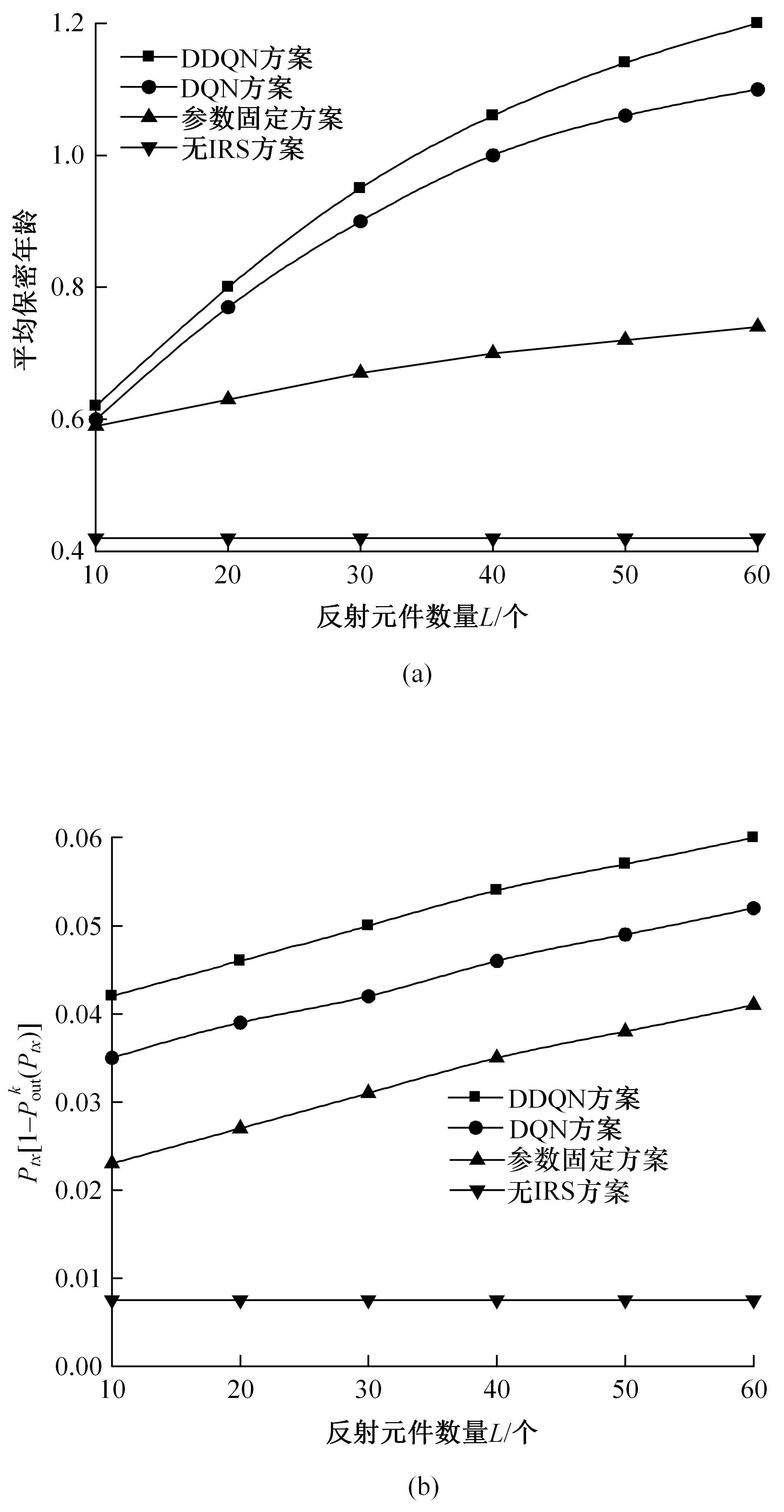
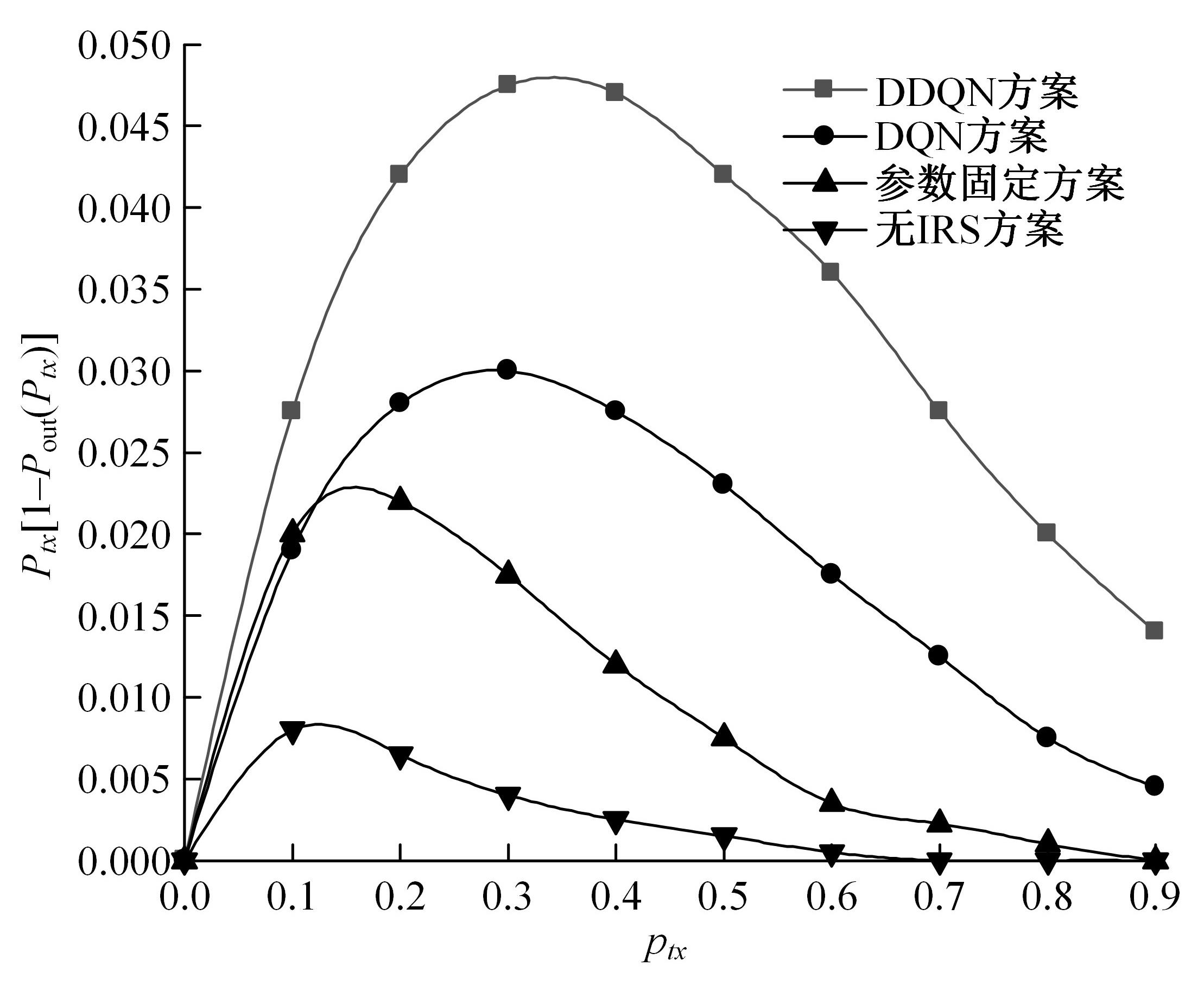
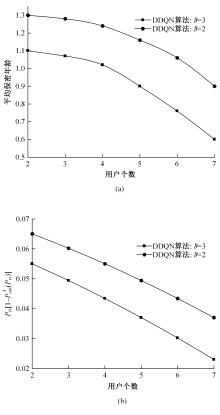
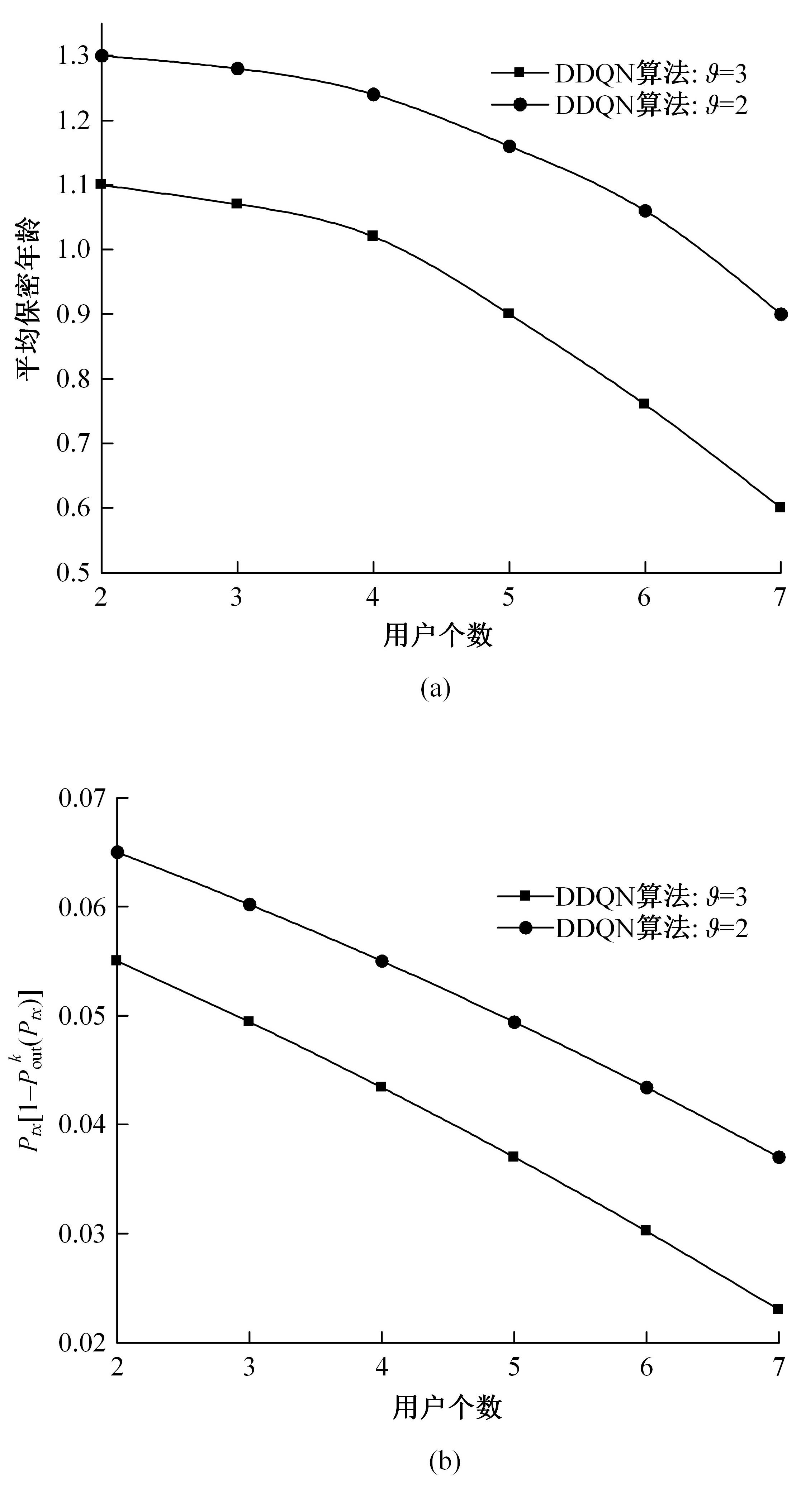
为满足万物互联和物理层安全的要求,针对存在多个窃听者和多个合法用户的状态更新系统的通信安全问题,提出了一种利用智能反射表面(IRS)辅助的安全波束成形设计方法实现主动防御。同时,考虑了状态更新场景下对于信息新鲜度的要求,引入平均保密年龄和保密年龄中断概率的信息年龄(AoI)性能指标,在发射功率、状态更新概率和IRS反射相移的约束下,联合优化基站发射波束成形矩阵、IRS相移和状态更新概率,从而保证状态更新的同时最大化系统安全性。针对系统的动态性和复杂性以及非凸优化问题的挑战性,提出了一种基于深度双Q网络(DDQN)算法的安全波束成形方法,以实现动态环境下针对窃听者的最优波束成形策略。仿真结果表明,本文提出的基于DDQN的安全波束成形方法可以显著提高IRS辅助状态更新系统的安全性。
中图分类号:
- TN92
| 1 | Yang N, Wang L, Geraci G, et al. Safeguarding 5G wireless communication networks using physical layer security[J]. IEEE Commun, 2015, 53(4): 20-27. |
| 2 | Wyner A D. The wiretap channel[J]. Bell Syst Tech J, 1975, 54(8): 1355-1387. |
| 3 | Li Q, Yang L. Beamforming for cooperative secure transmission in cognitive two-way relay networks[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security, 2020, 15(4): 130-143. |
| 4 | Xiao L, Lu X, Xu D, et al. UAV relay in VANETs against smart jamming with reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2018, 67(5): 4087-4097. |
| 5 | Wang W, Teh K C, Li K H. Artificial noise aided physical layer security in multi-antenna small-cell networks[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security, 2017, 12(6): 1470-1482. |
| 6 | Wang H, Zheng T, Xia X. Secure MISO wiretap channels with multiantenna passive eavesdropper: artificial noise vs. artificial fast fading[J]. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2015, 14(1): 94-106. |
| 7 | Nakai R, Sugiura S. Physical layer security in buffer-state-based max-ratio relay selection exploiting broadcasting with cooperative beamforming and jamming[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security, 2019, 14(2): 431-444. |
| 8 | Mobini Z, Mohammadi M, Tellambura C. Wireless-powered full-duplex relay and friendly jamming for secure cooperative communications[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Security, 2019, 14(3): 621-634. |
| 9 | Wu Q, Zhang R. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Commun, 2020, 58(1): 106-112. |
| 10 | Zhao J. A survey of intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRSs): towards 6G wireless communication networks with massive MIMO 2.0[J]. Electrical Engineering and Systems Science, 2019(2): 180-188. |
| 11 | Han H, Zhao J, Niyato D, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface aided network: power control for physical-layer broadcasting[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Communications(ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1-7. |
| 12 | Huang C, Zappone A, Alexandropoulos G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2019, 18(8): 4517-4170. |
| 13 | Wu Q, Zhang R. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2019, 18(11): 5394-5409. |
| 14 | Liu Q, Yang J, Xu Y, et al.Energy-efficient Resource allocation for secure IRS networks with an active eavesdropper[C]∥IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China(ICCC), Shanghai,China, 2020: 1-5. |
| 15 | Tiong T. Robust secure SWIPT MISO[C]∥The 7th International Conference on Smart Computing & Communications(ICSCC), Sarawak, Malaysia, 2019: 1-5. |
| 16 | Xu D, Yu X, Sun Y, et al. Resource allocation for secure IRS-assisted multiuser MISO systems[C]∥IEEE Globecom Workshops(GC Wkshps), Waikoloa, USA, 2019: 1-6. |
| 17 | Zhou G, Pan C, Ren H, et al. Secure wireless communication in RIS-aided MISO system with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 10(6): 1309-1313. |
| 18 | Hong S, Pan C, Ren H, et al. Artificial-noise-aided secure MIMO wireless communications via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(12): 7851-7866. |
| 19 | Dong L, Wang H. Secure MIMO transmission via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(6): 787-790. |
| 20 | Dong L, Wang H M, Xiao H, et al. Secure intelligent reflecting surface assisted MIMO cognitive radio transmission[C]∥IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference(WCNC), Nanjing,China, 2021: 1-6. |
| 21 | Dong L, Wang H. Enhancing secure MIMO transmission via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7543-7556. |
| 22 | Zhang Z, Lv L, Wu Q, et al. Robust and secure communications in intelligent reflecting surface assisted NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(3): 739-743. |
| 23 | Xiu Y, Wu J, Gui G, et al. Artificial noise-aided secure SWIPT communication systems using intelligent reflecting surface[C]∥IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China(ICCC), Shanghai,China, 2020: 6-11. |
| 24 | Xue J, Zhou X, Wang C, et al. Hybrid precoding for IRS-assisted secure mmwave communication system with SWIPT[C]∥International Conference on Space-Air-GroundComputing(SAGC), Beijing,China, 2020: 82-86. |
| 25 | Psomas C, Krikidis I. On the effect of correlation in IRS-aided SWIPT networks[C]∥IEEE Wireless Power Transfer Conference (WPTC), Seoul, Korea, 2020: 460-462. |
| 26 | Yang H, Xiong Z, Zhao J, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based intelligent reflecting surface for secure wireless communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 375-388. |
| 27 | Kaul S, Yates R, Gruteser M. Real-time status: How often should one update?[J]. Proc IEEE INFOCOM, 2012, 18(6): 2731-2735. |
| 28 | Soysal A, Ulukus S. Age of Information in G/G/1/1 systems: age expressions, bounds, special cases, and optimization, 2018[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2021, 67(11): 7477-7489. |
| 29 | Inoue Y, Masuyama H, Takine T,et al. A general formula for the stationary distribution of the age of information and its application to single-server queues[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2019, 65(12): 8305-8324. |
| 30 | Zheng X, Zhou S, Jiang Z, et al. Closed-form analysis of non-linear age of information in status updates with an energy harvesting transmitter[J]. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun, 2019, 18(8): 4129-4142. |
| 31 | Arafa A, Yang J, Ulukus S, et al. Age-minimal transmission for energy harvesting sensors with finite batteries:online policies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2020, 66(1): 534-556. |
| 32 | Kam C, Kompella S, Nguyen G D, et al. Effect of message transmission path diversity on status age[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2016, 62(3): 1360-1374. |
| 33 | Costa M, Codreanu M, Ephremides A. On the age of informationin status update systems with packet management[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2016, 62(4): 1897-1910. |
| 34 | Guo X, Singh R, Kumar P R, et al. A risk-sensitive approach for packet inter-delivery time optimization in networked cyber-physical systems[J]. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw, 2018, 26(4): 1976-1989. |
| 35 | Bacinoglu B T, Ceran E T, Uysal-Biyikoglu E. Age of information under energy replenishment constraints[C]// Proc Inf Theory Appl Workshop(ITA),San Diego, USA, 2015;25-31. |
| 36 | Sun Y, Uysal-Biyikoglu E, Yates R D, et al. Update or wait: how to keep your data fresh[J]. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2017, 63(11): 7492-7508. |
| 37 | Xiao Y, Sun Y. A dynamic jamming game for real-time status updates[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops(INFOCOM WKSHPS), Honolulu, USA, 2018: 354-360. |
| 38 | Garnaev A, Zhang W, Zhong J, et al. Maintaining information freshness under jamming[C]∥IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, Paris, France, 2019: 90-95. |
| 39 | Chen H, Wang Q, Mohapatra P, et al. Secure status updates under eavesdropping: age of information-based physical layer security metrics[J/OL]. [2020-12-20].. |
| 40 | Chu Z, Xiao P, Shojafar M D,et al. Intelligent reflecting surface assisted mobile edge computing for Internet of Things[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(3): 619-623. |
| 41 | Huang C, Chen G, Gong Y, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based relay selection in intelligent reflecting surface assisted cooperative networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(5): 1036-1040. |
| 42 | Cui M, Zhang G, Zhang R. Secure wireless communication via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Wireless Commun Letter, 2019, 8(5): 1410-1414. |
| [1] | 张健,李青扬,李丹,姜夏,雷艳红,季亚平. 基于深度强化学习的自动驾驶车辆专用道汇入引导[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(9): 2508-2518. |
| [2] | 田彦涛,季言实,唱寰,谢波. 深度强化学习智能驾驶汽车增广决策模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 682-692. |
| [3] | 庄伟超,丁昊楠,董昊轩,殷国栋,王茜,周朝宾,徐利伟. 信号交叉口网联电动汽车自适应学习生态驾驶策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(1): 82-93. |
| [4] | 刘勇,徐雷,张楚晗. 面向文本游戏的深度强化学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 666-674. |
| [5] | 王忠立,王浩,申艳,蔡伯根. 一种多感知多约束奖励机制的驾驶策略学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2718-2727. |
| [6] | 鲜斌,张诗婧,韩晓薇,蔡佳明,王岭. 基于强化学习的无人机吊挂负载系统轨迹规划[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(6): 2259-2267. |
| [7] | 赵亚慧,杨飞扬,张振国,崔荣一. 基于强化学习和注意力机制的朝鲜语文本结构发现[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1387-1395. |
| [8] | 吕帅,刘京. 基于深度强化学习的随机局部搜索启发式方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(4): 1420-1426. |
| [9] | 李丽娜,魏晓辉,郝琳琳,王兴旺,王储. 大规模流数据处理中代价有效的弹性资源分配策略[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1832-1843. |
| [10] | 杨顺,蒋渊德,吴坚,刘海贞. 基于多类型传感数据的自动驾驶深度强化学习方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(4): 1026-1033. |
| [11] | 雷维嘉, 左莉杰, 谢显中. 部分信道状态信息下抗窃听协作中继传输方案[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2015, 45(5): 1658-1664. |
| [12] | 董博, 刘克平, 李元春. 动态约束下可重构模块机器人分散强化学习最优控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(5): 1375-1384. |
| [13] | 叶锦华,李迪,叶峰. 轮式移动机器人的双强化学习自适应模糊控制[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2014, 44(3): 742-749. |
| [14] | 刘全, 杨旭东, 荆玲, 肖飞. 基于多Agent并行采样和学习经验复用的E3算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2013, 43(01): 135-140. |
| [15] | 付燕宁, 张家臣, 刘磊. 面向预定义过程的强化学习WS组合[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2010, 40(05): 1313-1317. |
|
||