吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (5): 1705-1713.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230812
基于自选择架构网络的交通标志分类算法
- 1.三峡大学 电气与新能源学院,湖北 宜昌 443002
2.湖北省输电线路工程技术研究中心(三峡大学),湖北 宜昌 443002
3.电子科技大学 航空航天学院,成都 611731
Self-selected architecture network for traffic sign classification
Bin WEN1,2( ),Yi-fu DING1,Chao YANG1(
),Yi-fu DING1,Chao YANG1( ),Yan-jun SHEN1,Hui LI3
),Yan-jun SHEN1,Hui LI3
- 1.College of Electrical Engineering and New Energy,China Three Gorges University,Yichang 443002,China
2.Hubei Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center for Power Transmission Line,Yichang 443002,China
3.School of Aeronautics and Astronautics,University of Electronic Science and Technology of China,Chengdu 611731,China
摘要:
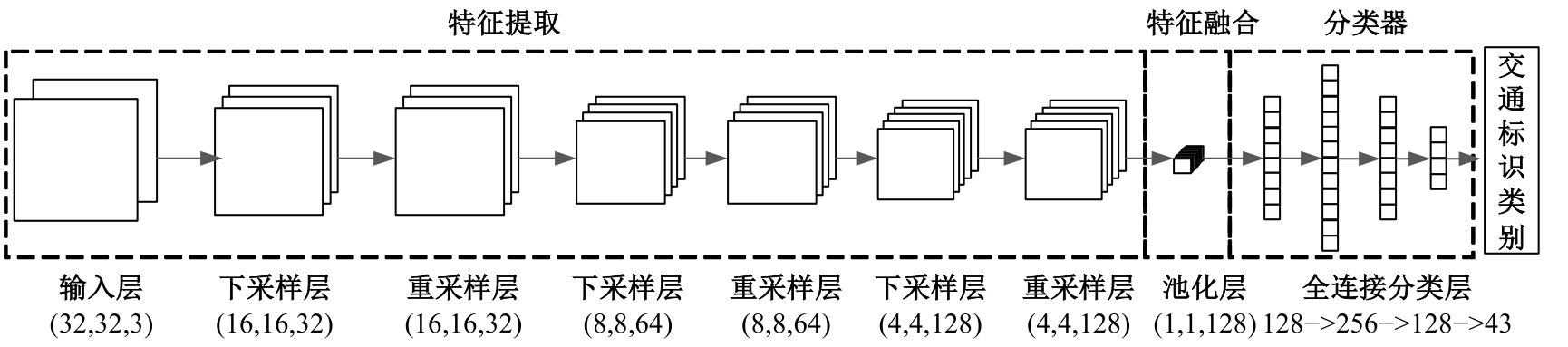
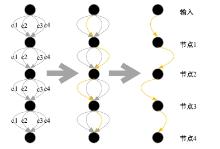
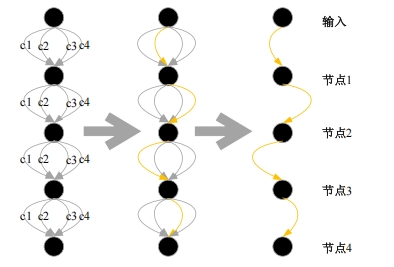
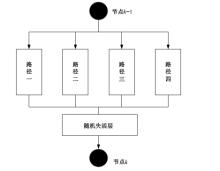
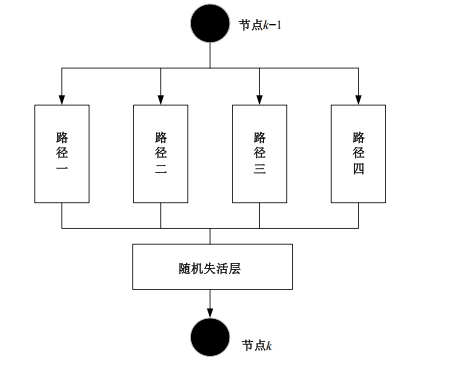
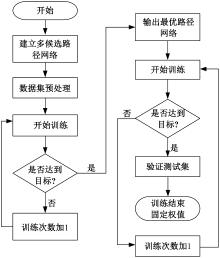
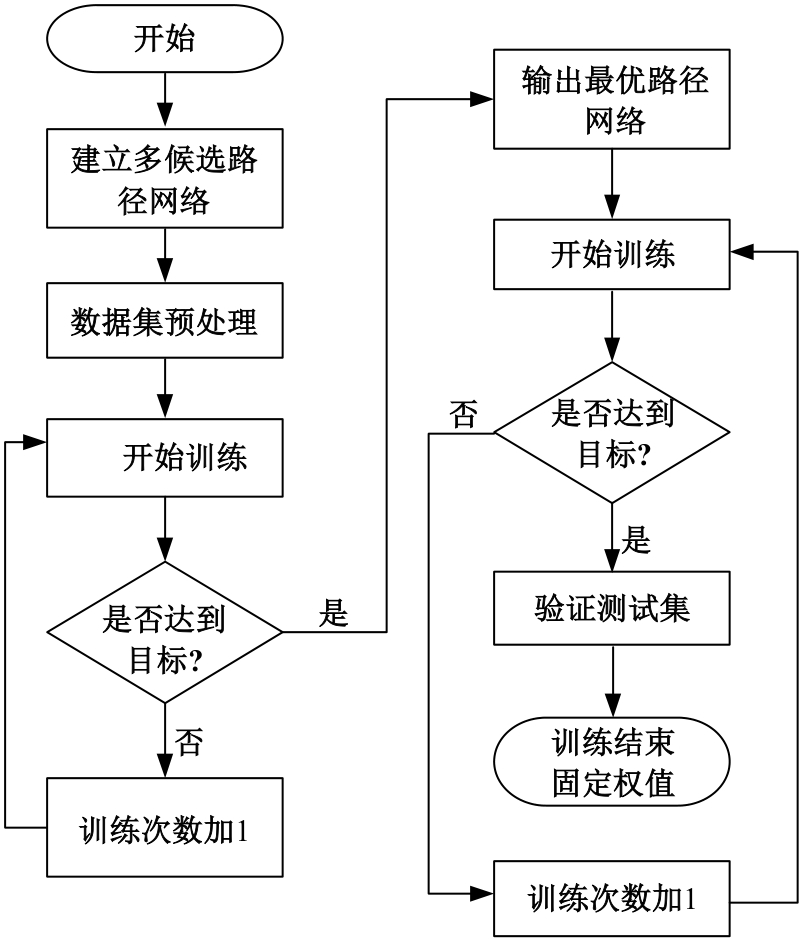
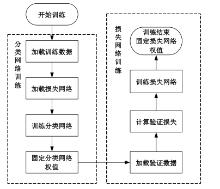
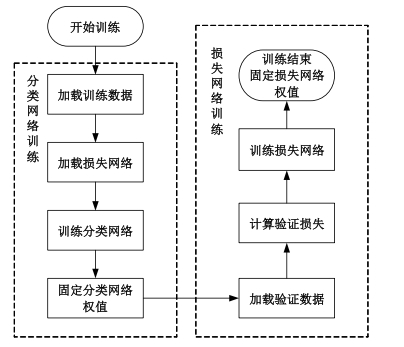
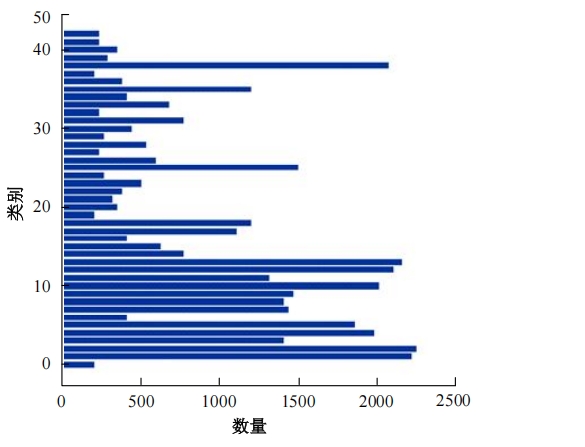
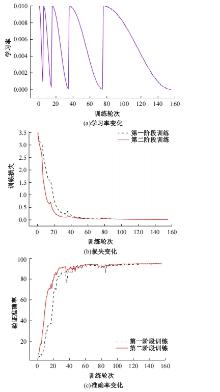
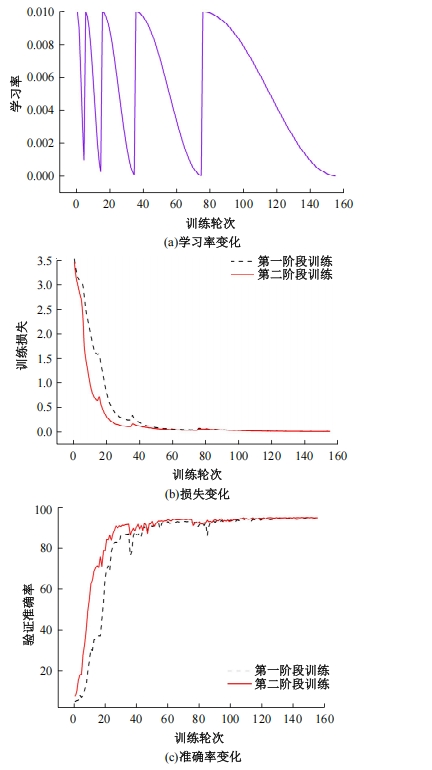
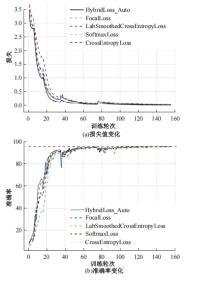
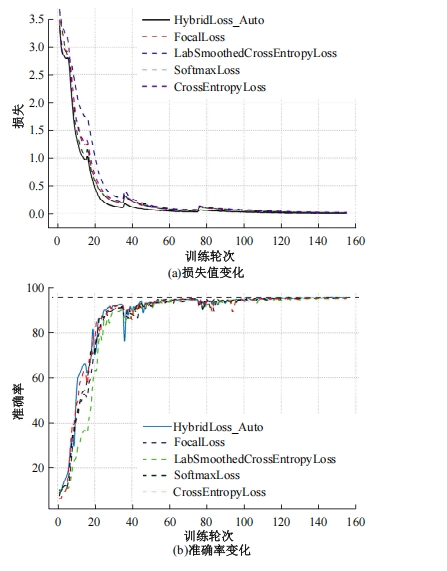
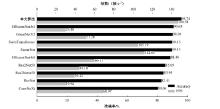
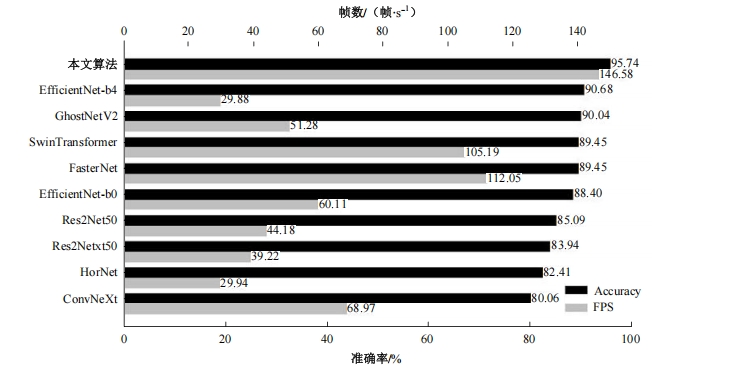
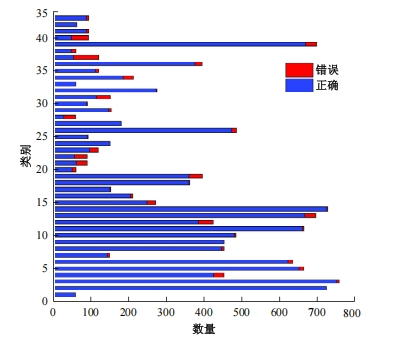
自动驾驶技术的实现需要对交通标识进行高精度的识别,但由于交通标识的相似度高、尺寸小且易受户外环境影响,实时精准检测变得具有挑战性。针对传统神经网络设计方式效率低下的问题,本文提出了自选择架构算法,可以自动调整网络结构以提高模型的性能和效率。该算法采用两阶段训练实现网络节点最优路径选择,同时对多损失函数权重超参数使用梯度传播进行训练,使用动态损失网络方案替代传统人工调参。实验结果表明,该算法在GTSRB数据集中实现了95.74%的准确率和146.58帧/s的检测速度,且模型参数量仅为0.46 Mb,可部署于移动设备。与传统手动设计静态网络相比,采用自学习架构模块可以降低实验成本,提高精度和性能,在不同环境下更容易实现更好的检测效果,其损失收敛速度也获得明显提升。
中图分类号:
- TP391.4
| [1] | Babi D, Babi D, Fioli M, et al.Analysis of market-ready traffic sign recognition systems in cars: a test field study[J].Energies, 2021, 14: 14123697. |
| [2] | 冯润泽, 江昆, 于伟光, 等. 基于两阶段分类算法的中国交通标志牌识别 [J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(3): 434-441. |
| Feng Run-ze, Jiang Kun, Yu Wei-guang, et al. Chinese traffic sign recognition based on two-stage classification algorithm[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(3): 434-441. | |
| [3] | Wang M, Liu R, Yang J, et al.Traffic sign three-dimensional reconstruction based on point clouds and panoramic images[J].Photogrammetric Record, 2022, 37(177): 87-110. |
| [4] | Shen L, You L, Peng B, et al.Group multi-scale attention pyramid network for traffic sign detection[J].Neuro Computing, 2021, 452(6): 1-14. |
| [5] | Liu Y, Peng J, Xue J H, et al. TSingNet: scale-aware and context-rich feature learning for traffic sign detection and recognition in the wild[J].Neurocomputing, 2021, 447(4): 10-22. |
| [6] | Vashisht M, Kumar B. Effective implementation of machine learning algorithms using 3D colour texture feature for traffic sign detection for smart cities[J]. Expert Systems, 2021, 39(5): e12781. |
| [7] | Wan H, Gao L, Su M, et al. A novel neural network model for traffic sign detection and recognition under extreme conditions[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2021, 7: 9984787. |
| [8] | Yu L, Xia X, Zhou K. Traffic sign detection based on visual co-saliency in complex scenes [J]. Applied Intelligence, 2019, 49(2): 764-790. |
| [9] | Coţovanu D, Zet C, Foşalău C, et al. Detection of traffic signs based on support vector machine classification using HOG features[C]∥Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference and Exposition on Electrical And Power Engineering, Iasi, Romania, 2018: 8559784. |
| [10] | Lecun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition [J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. |
| [11] | Simonyan K, Zisserman A.Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition [J/OL].(2015-04-10)[2023-07-30]. |
| [12] | He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 7780459. |
| [13] | Chollet F. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 8099678. |
| [14] | Yu F, Koltun V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[J/OL].(2016-04-30)[2023-07-30]. |
| [15] | Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 8237586. |
| [16] | Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, et al. Swin transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]∥Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 10012-10022. |
| [17] | Real E, Liang C, So D R, et al. AutoML-Zero: evolving machine learning algorithms from scratch[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2020: 8007-8019. |
| [18] | Liu H, Simonyan K, Yang Y. DARTS: differentiable architecture search[J/OL].(2019-04-23)[2023-07-30]. |
| [19] | Gao S H, Cheng M M, Zhao K, et al. Res2Net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(2): 652-662. |
| [20] | Liu Z, Mao H, Wu C Y, et al. A convnet for the 2020s[C]∥Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, USA, 2022: 9879745. |
| [21] | Pham H, Guan M Y, Zoph B, et al.Efficient neural architecture search via parameter sharing [J/OL].(2018-02-12)[2023-07-30]. |
| [22] | Tang Y, Han K, Guo J, et al. GhostNetV2: enhance cheap operation with long-range attention [J/OL].(2022-11-23)[2023-07-30]. |
| [23] | Rao Y, Zhao W, Tang Y, et al.HorNet: efficient high-order spatial interactions with recursive gated convolutions [J/OL].(2022-10-11)[2023-07-30]. |
| [24] | Chen J, Kao S H, He H, et al. Run, don't walk: chasing higher flops for faster neural networks [J/OL].(2023-05-21)[2023-07-30]. |
| [1] | 李健,刘欢,李艳秋,王海瑞,关路,廖昌义. 基于THGS算法优化ResNet-18模型的图像识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1629-1637. |
| [2] | 张汝波,常世淇,张天一. 基于深度学习的图像信息隐藏方法综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(5): 1497-1515. |
| [3] | 李振江,万利,周世睿,陶楚青,魏巍. 基于时空Transformer网络的隧道交通运行风险动态辨识方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(4): 1336-1345. |
| [4] | 赵孟雪,车翔玖,徐欢,刘全乐. 基于先验知识优化的医学图像候选区域生成方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(2): 722-730. |
| [5] | 刘元宁,臧子楠,张浩,刘震. 基于深度学习的核糖核酸二级结构预测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 297-306. |
| [6] | 徐慧智,蒋时森,王秀青,陈爽. 基于深度学习的车载图像车辆目标检测和测距[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2025, 55(1): 185-197. |
| [7] | 李路,宋均琦,朱明,谭鹤群,周玉凡,孙超奇,周铖钰. 基于RGHS图像增强和改进YOLOv5网络的黄颡鱼目标提取[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2638-2645. |
| [8] | 张磊,焦晶,李勃昕,周延杰. 融合机器学习和深度学习的大容量半结构化数据抽取算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(9): 2631-2637. |
| [9] | 乔百友,武彤,杨璐,蒋有文. 一种基于BiGRU和胶囊网络的文本情感分析方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2026-2037. |
| [10] | 郭昕刚,何颖晨,程超. 抗噪声的分步式图像超分辨率重构算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(7): 2063-2071. |
| [11] | 张丽平,刘斌毓,李松,郝忠孝. 基于稀疏多头自注意力的轨迹kNN查询方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1756-1766. |
| [12] | 孙铭会,薛浩,金玉波,曲卫东,秦贵和. 联合时空注意力的视频显著性预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(6): 1767-1776. |
| [13] | 陆玉凯,袁帅科,熊树生,朱绍鹏,张宁. 汽车漆面缺陷高精度检测系统[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(5): 1205-1213. |
| [14] | 李雄飞,宋紫萱,朱芮,张小利. 基于多尺度融合的遥感图像变化检测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 516-523. |
| [15] | 杨国俊,齐亚辉,石秀名. 基于数字图像技术的桥梁裂缝检测综述[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 313-332. |
|