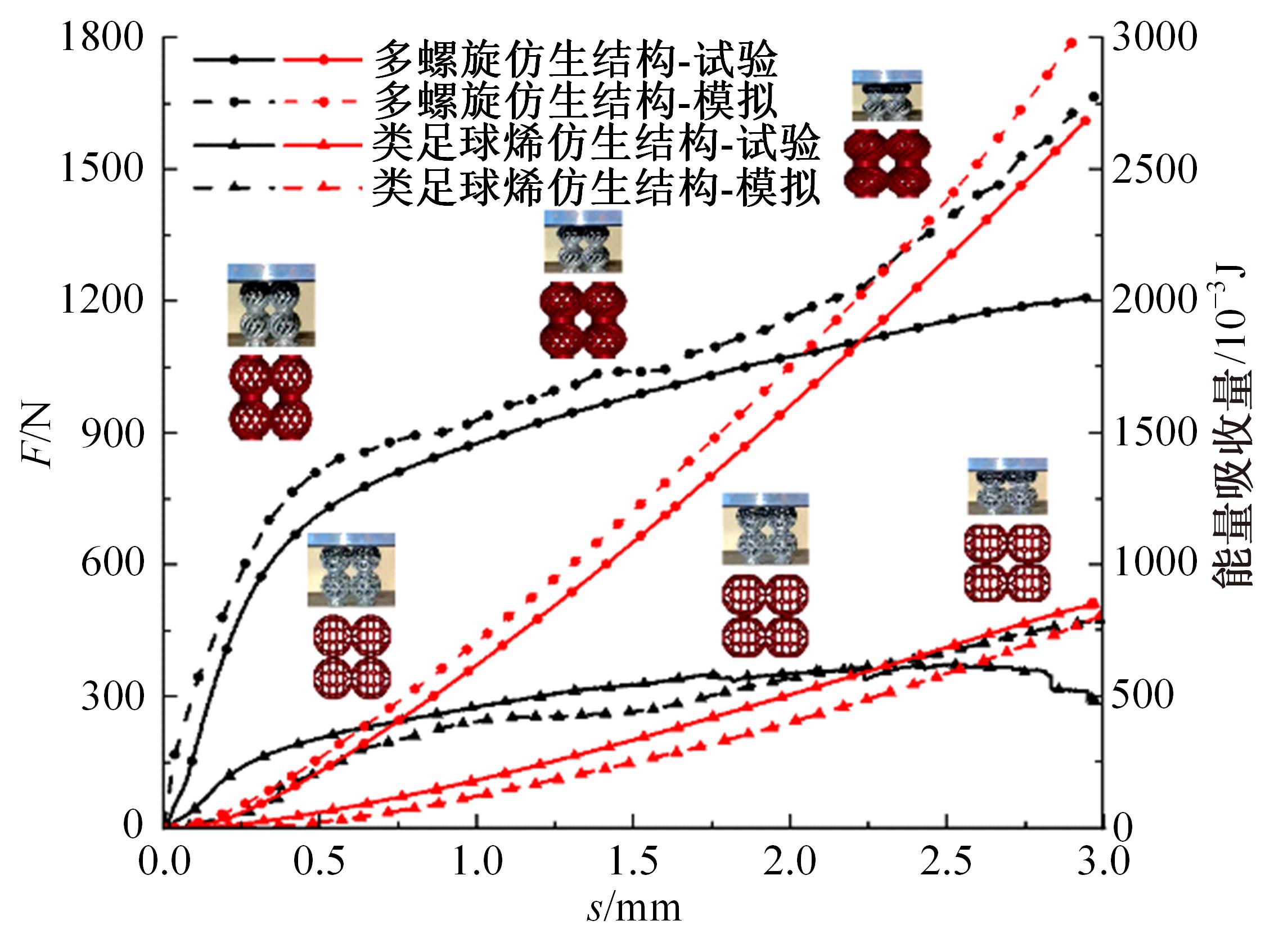
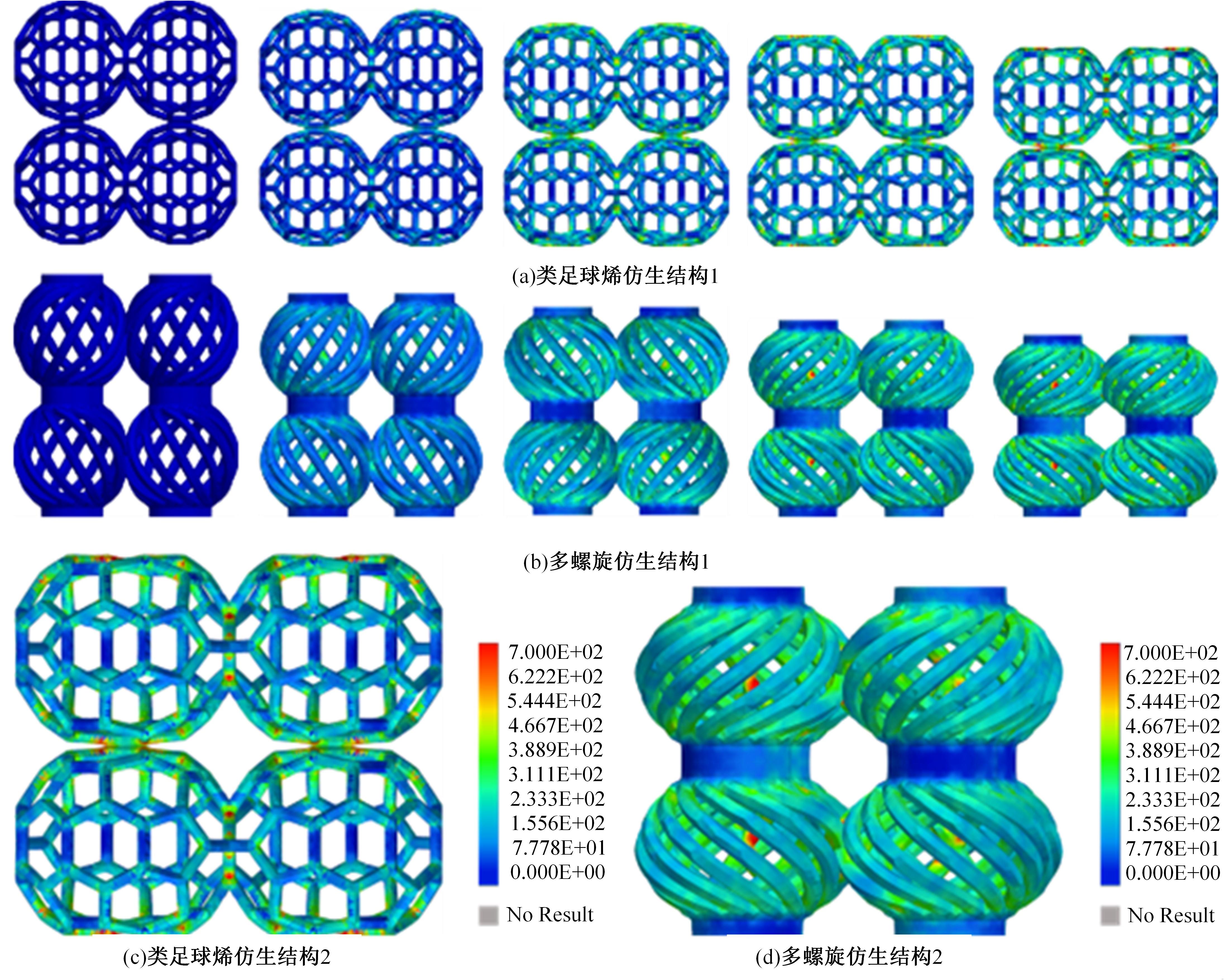
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 54 ›› Issue (10): 3077-3084.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20221595
Mechanical properties of a bionic buffer structure of a lander based on additive manufacturing
Zheng-lei YU1( ),Qing CAO1,Jun-dong ZAHNG1,Peng-wei SHA1,Jing-fu JIN2(
),Qing CAO1,Jun-dong ZAHNG1,Peng-wei SHA1,Jing-fu JIN2( ),Wan-zhen WEI1,Ping LIANG1,Zhi-hui ZHANG1
),Wan-zhen WEI1,Ping LIANG1,Zhi-hui ZHANG1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
2.College of Biological and Agricultural Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TB17
| 1 | 吴宏宇, 王春洁, 丁宗茂, 等. 着陆姿态不确定下的着陆器缓冲机构优化设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(12): 1323-1331. |
| Wu Hong-yu, Wang Chun-jie, Ding Zong-mao, et al. Optimization design of a landing gear under uncertain landing attitude[J]. J of Astronautics, 2018, 39(12): 1323-1331. | |
| 2 | 王欣宇. 月球着陆器缓冲机构设计与姿态分析[J]. 电子制作, 2018(23): 95-97. |
| Wang Xin-yu. Buffer mechanism design and attitude analysis of lunar lander[J]. Electronic Production, 2018(23): 95-97. | |
| 3 | 王鹏, 李佳欣, 苏建波, 等. 月球探测器着陆缓冲机构精密装配技术[J]. 航天制造技术, 2022(3): 71-75. |
| Wang Peng, Li Jia-xin, Su Jian-bo, et al. Precision assembly technology of lunar probe landing buffer mechanism[J]. Aerospace Manufacturing Technology, 2022(3): 71-75. | |
| 4 | 罗敏, 杨建中, 韩福生, 等. “天问一号”着陆缓冲机构吸能材料设计分析与试验验证[J]. 深空探测学报:中英文, 2021, 8(5): 472-477. |
| Luo Min, Yang Jian-zhong, Han Fu-sheng, et al. Design analysis and experimental verification of energy-absorbing material for landing buffer mechanism of "Tianmen-1"[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration (Chinese and English) 2021, 8(5): 472-477. | |
| 5 | 董小闵, 李军礼, 于建强, 等. 月面低空飞行器着陆缓冲机构设计与仿真分析[J]. 载人航天, 2019, 25(6): 779-782, 798. |
| Dong Xiao-min, Li Jun-li, Yu Jian-qiang, et al. Design and simulation analysis of landing buffer mechanism for lunar low-altitude vehicle[J]. Manned spaceflight, 2019, 25(6): 779-782, 798. | |
| 6 | 刘志全, 黄传平. 月球探测器软着陆机构发展综述[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2006(1): 33-39. |
| Liu Zhi-quan, Huang Chuan-ping. A summary of the development of lunar probe soft landing mechanism[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2006(1): 33-39. | |
| 7 | 王永滨, 武士轻, 牟金岗, 等. 月球着陆器着陆缓冲展开锁定机构设计与分析[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2021, 42(1): 57-64. |
| Wang Yong-bin, Wu Shi-qing, Mou Jin-gang, et al. Design and analysis of landing buffer deployment locking mechanism for lunar lander[J]. Space Return and Remote Sensing, 2021, 42(1): 57-64. | |
| 8 | 党明珠, 向泓澔, 蔡超, 等. 4D打印形状记忆合金研究进展与展望[J]. 航空科学技术, 2022, 33(9): 94-108. |
| Dang Ming-zhu, Xiang Hong-hao, Cai Chao, et al. Research progress and prospect of 4D printed shape memory alloy[J]. Aviation Science and Technology, 2022, 33(9): 94-108. | |
| 9 | 徐汉权, 陈泽鑫, 路新, 等. 增材制造NiTi合金研究进展[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2022, 40(2): 159-171. |
| Xu Han-quan, Chen Ze-xin, Lu Xin, et al. Research progress in manufacturing NiTi alloy by adding materials[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2022, 40(2): 159-171. | |
| 10 | 余春风, 胡永俊, 卢冰文, 等. 扫描间距对激光选区熔化NiTi形状记忆合金相变行为及力学性能的影响[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(19): 265-274. |
| Yu Chun-feng, Hu Yong-jun, Lu Bing-wen, et al. Effect of scanning spacing on phase transformation behavior and mechanical properties of laser selective melting NiTi shape memory alloy[J]. Progress in Laser and Optoelectronics, 2021, 58(19): 265-274. | |
| 11 | 方嘉铖, 刘洋, 李治国, 等. 工艺参数对SLM成形NiTi合金组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2021, 41(12): 1553-1559. |
| Fang Jia-cheng, Liu Yang, Li Zhi-guo, et al. Effect of process parameters on microstructure and mechanical properties of NiTi alloy formed by SLM[J]. Special Casting and Non-Ferrous Alloys, 2021, 41(12): 1553-1559. | |
| 12 | 宋英杰, 张红梅, 顾冬冬, 等. 激光增材制造NiTi轻量化点阵结构变形与回复行为[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(14): 231-243. |
| Song Ying-jie, Zhang Hong-mei, Gu Dong-dong, et al. Deformation and recovery behavior of NiTi lightweight lattice structure fabricated by laser augmentation[J]. China Laser, 2022, 49(14): 231-243. | |
| 13 | Andani M T, Haberland C, Walker J M, et al. Achieving biocompatible stiffness in NiTi through additive manufacturing[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2016, 27(19): 2661-2671. |
| 14 | Andani M T, Saedi S, Turabi A S, et al. Mechanical and shape memory properties of porous Ni50.1Ti49.9 alloys manufactured by selective laser melting[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2017, 68: 224-231. |
| 15 | Hu D Y, Wang Y Z, Song B, et al. Energy-absorption characteristics of a bionic honeycomb tubular nested structure inspired by bamboo under axial crushing[J]. Composites Part B, 2019, 162:21-32. |
| 16 | Sherman J, Zhang W, Xu J. Energy Absorption performance of bioinspired honeycombs: numerical and theoretical analysis[J]. Acta Mech Solida Sin, 2021,34:884-894. |
| 17 | Niu X Q, Xu F X, Zou Z, et al. In-plane dynamic crashing behavior and energy absorption of novel bionic honeycomb structures[J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 299: No.116064. |
| 18 | Ma C L, Gu D D, Dai D H, et al. Tailored pore canal characteristics and compressive deformation behavior of bionic porous NiTi shape memory alloy prepared by selective laser melting[J]. Smart Materials and Structures,2020, 29(9): No.95001. |
| 19 | Sun J F, Gu D D, Lin K J, et al. Laser powder bed fusion of diatom frustule inspired bionic NiTi lattice structures: compressive behavior and shape memory effect[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2022, 31(7): No.74003. |
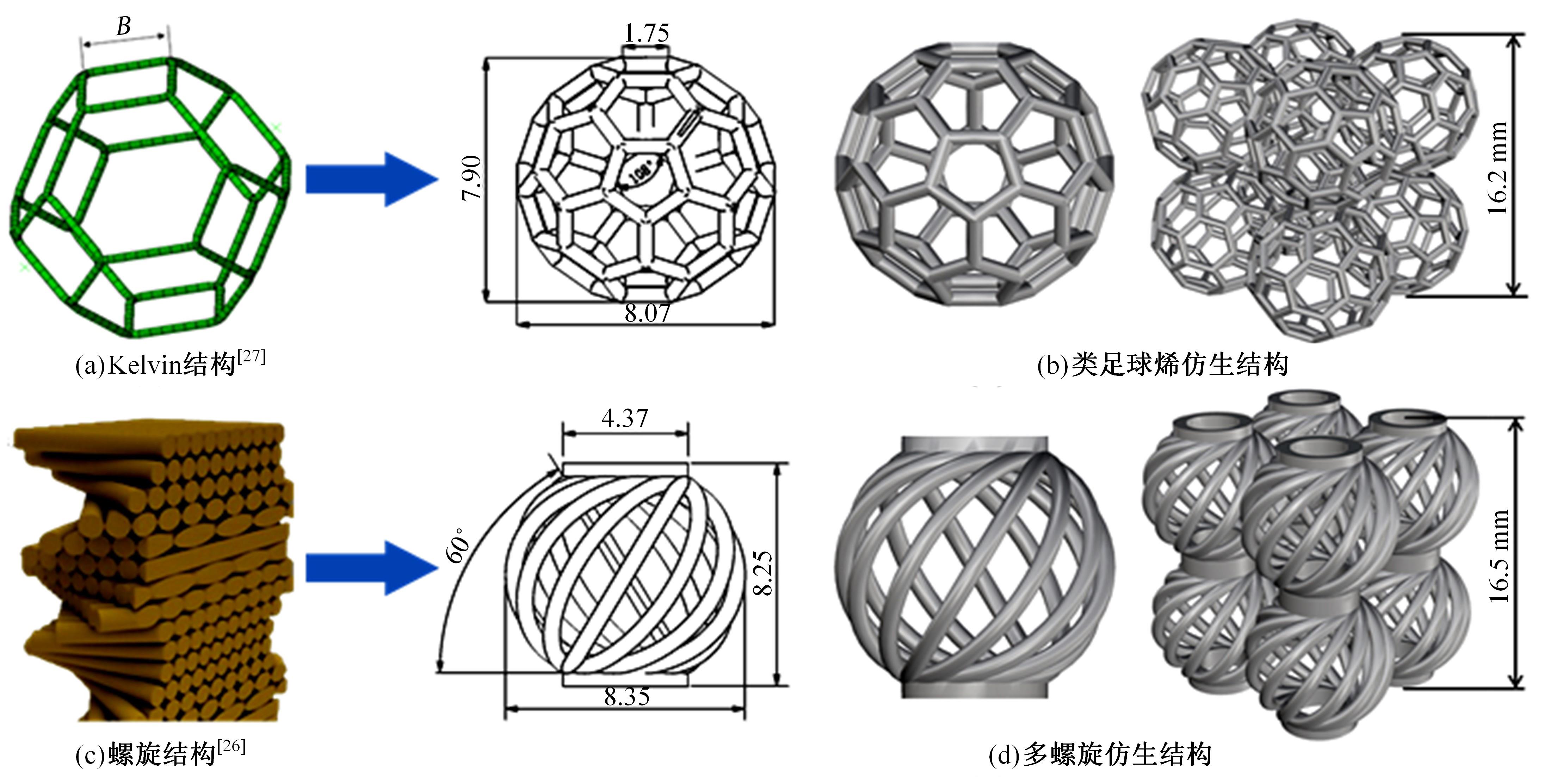
| 20 | 鲁埝坤. 开尔文结构缓冲力学性能分析[D]. 广州:暨南大学力学与建筑工程学院, 2017. |
| Lu Nian-kun. Analysis of cushioning mechanical properties of Kelvin structure[D].Guangzhou:School of Mechanics and Construction Engineering, Jinan University, 2017. | |
| 21 | Cheng L, Wang L Y, Karlsson A M. Image analyses of two crustacean exoskeletons and implications of the exoskeletal microstructure on the mechanical behavior[J].Journal of Materials Research, 2008,23(11): 2854-2872. |
| 22 | Cheng L, Wang L Y, Karlsson A M. Mechanics-based analysis of selected features of the exoskeletal microstructure of Popillia japonica[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2009, 24(11): 3253-3267. |
| 23 | Neville A C. Biology of the arthropod cuticle[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Springer Verlag, 1975. |
| 24 | Vincent J F V. Arthropod cuticle: a natural composite shell system[J].Composites, Part A. Applied Science and Manufacturing,2002, 33A(10): 1311-1315. |
| 25 | Barbakadze N, Enders S, Gorb S,et al.Local mechanical properties of the head articulation cuticle in the beetle Pachnoda marginata (Coleoptera, Scarabaeidae)[J].The Journal of Experimental Biology, 2006,209(4): 722-730. |
| 26 | Song Z, Ni Y, Cai S. Fracture modes and hybrid toughening mechanisms in oscillated/twisted plywood structure[J]. Acta Biomater,2019, 91: 284-293. |
| 27 | Schäfer I, Mlikota M, Schmauder S, et al. Modelling the damping response of biomimetic foams based on pomelo fruit[J].Computational Materials Science, 2020, 183: No.109801. |
| 28 | Suksangpanya N, Yaraghi N A, Pipes R B, et al. Crack twisting and toughening strategies in Bouligand architectures[J]. Int J Solids Struct, 2018, 150: 83-106. |
| 29 | Wang X B, Yu J Y, Liu J W, et al. Effect of process parameters on the phase transformation behavior and tensile properties of NiTi shape memory alloys fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 36: No.101545. |
| 30 | Sa Edi S, Moghaddam N S, Amerinatanzi A, et al.On the effects of selective laser melting process parameters on microstructure and thermomechanical response of Ni-rich NiTi[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 144: 552-560. |
| 31 | Yu Z L, Xu Z Z, Guo Y T, et al.Study on properties of SLM-NiTi shape memory alloy under the same energy density[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 13: 241-250. |
| 32 | 于征磊, 陈立新, 徐泽洲, 等. 基于增材制造的仿生防护结构力学及回复特性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2021, 51(4): 1540-1547. |
| Yu Zheng-lei, Chen Li-xin, Xu Ze-zhou, et al. Analysis of mechanical characteristics and recovery characteristics of bionic protective structures based on additive manufacturing[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1540-1547. |
| [1] | Jin-xing WU,Yu-xiang MA,Jia-bang XIAO,Yao XU,Song-ge LI. Numerical simulation of erosion characteristics of H-type finned elliptical tubes [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2495-2501. |
| [2] | Hua-fei HE,Zhao-ping LI,Rui-an FU,Shao-lin MA,Ming-li HUANG. Experiment on seismic performance of prefabricated sidewall joints considering strata restraint effect [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(6): 1601-1611. |
| [3] | Shu-mei LOU,Yi-ming LI,Xin LI,Peng CHEN,Xue-feng BAI,Bao-jia CHENG. Thermal deformation behavior of graphene nanosheets reinforced 7075Al based on BP neural network and Arrhenius constitutive equation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(5): 1237-1245. |
| [4] | Qiu ZHAO,Peng CHEN,Yu-wei ZHAO,Ao YU. Overall mechanical performance of jointless bridges with arch structure behind abutment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(4): 1016-1027. |
| [5] | Xin YANG,Yang WANG,Jia-feng SONG,Yong ZHU,Bin-bing HUANG,Shu-cai XU. Design and numerical simulation of bionic sandwich panel based on a shrimp chela structure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 842-851. |
| [6] | Yi-gang WANG,Yu-peng WANG,Hao ZHANG,Si-an ZHAO. Identification and analysis of aerodynamic noise sources in the bogie area of high⁃speed trains [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 346-355. |
| [7] | Wei-hua ZHANG,Jia-ming LIU,Li-peng XIE,Heng DING. Lane⁃changing model of autonomous vehicle in weaving area of expressway in intelligent and connected mixed environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 469-477. |
| [8] | Xing WEI,Ya-jie GAO,Zhi-rui KANG,Yu-chen LIU,Jun-ming ZHAO,Lin XIAO. Numerical simulation of residual stress field of stud girth weld in low temperature environment [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 198-208. |
| [9] | Yong-zhong ZHANG,Yun-hai MA. New honeycomb multi-stage thin-walled structure with high efficiency energy absorption characteristics [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(1): 259-267. |
| [10] | Zhi ZHENG,Pei YUAN,Xuan-hui JIN,Si-si WEI,Bo GENG. Experimental on composite flexible anti⁃collision fender of bridge pier [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(9): 2581-2590. |
| [11] | Feng WANG,Shuang-rui LIU,Jia-ying WANG,Jia-ling SONG,Jun WANG,Jiu-peng ZHANG,Xiao-ming HUANG. Size and shape effects of wind drag coefficients for porous structures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1677-1685. |
| [12] | Chun-li WU,Shi-ming HUANG,Kui LI,Zheng-wei GU,Xiao-ming HUANG,Bing-tao ZHANG,Run-chao YANG. Analysis of pier action effect under flood based on numerical simulation and statistical analysis [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1612-1620. |
| [13] | Zheng-wei GU,Pan ZHANG,Dong-ye LYU,Chun-li WU,Zhong YANG,Guo-jin TAN,Xiao-ming HUANG. Earthquake⁃induced residual displacement analysis of simply supported beam bridge based on numerical simulation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(6): 1711-1718. |
| [14] | Hai-bin WEI,Shuan-ye HAN,Hai-peng BI,Qiong-hui LIU,Zi-peng MA. Intelligent sensing road active ice and snow removal system and experimental technology [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(5): 1411-1417. |
| [15] | Jing-fu JIN,Xin-ju DONG,Zhi-cheng JIA,Kang WANG,Lian-bin HE,Meng ZOU,Ying-chun QI. Optimization of the tread plate-spring structure of flexible metal wheel with plate-spring [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(4): 964-972. |
|
||