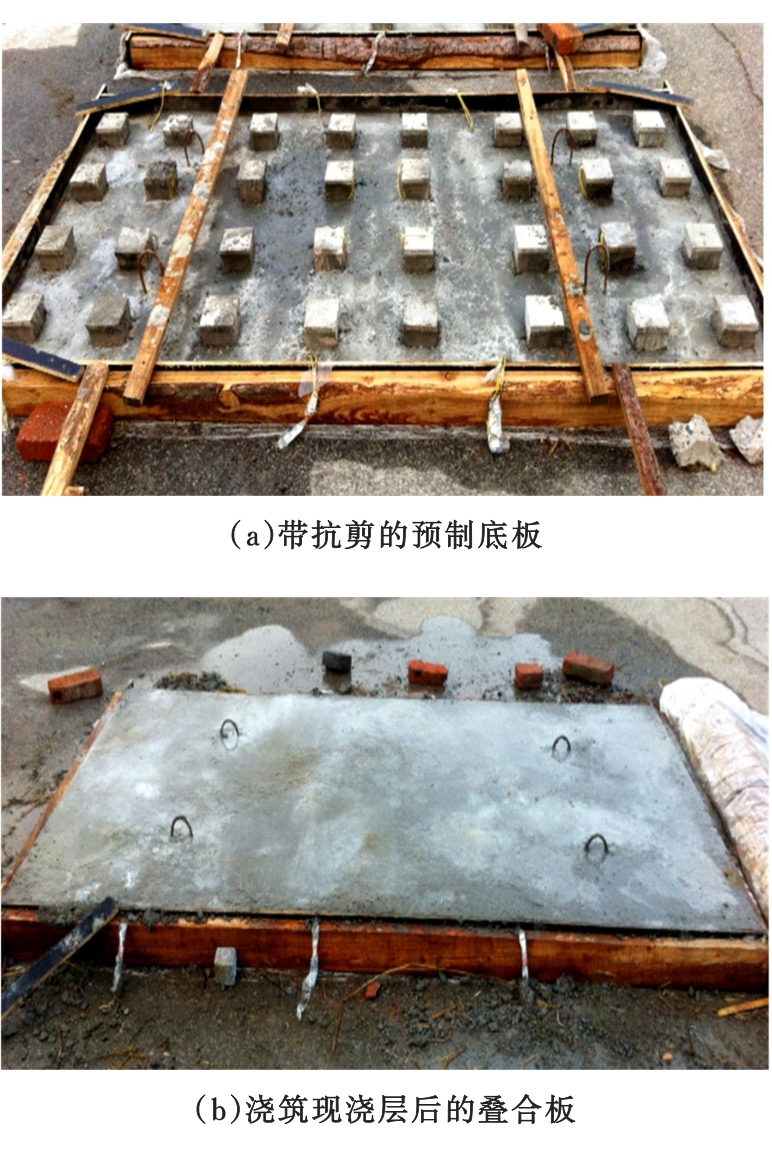
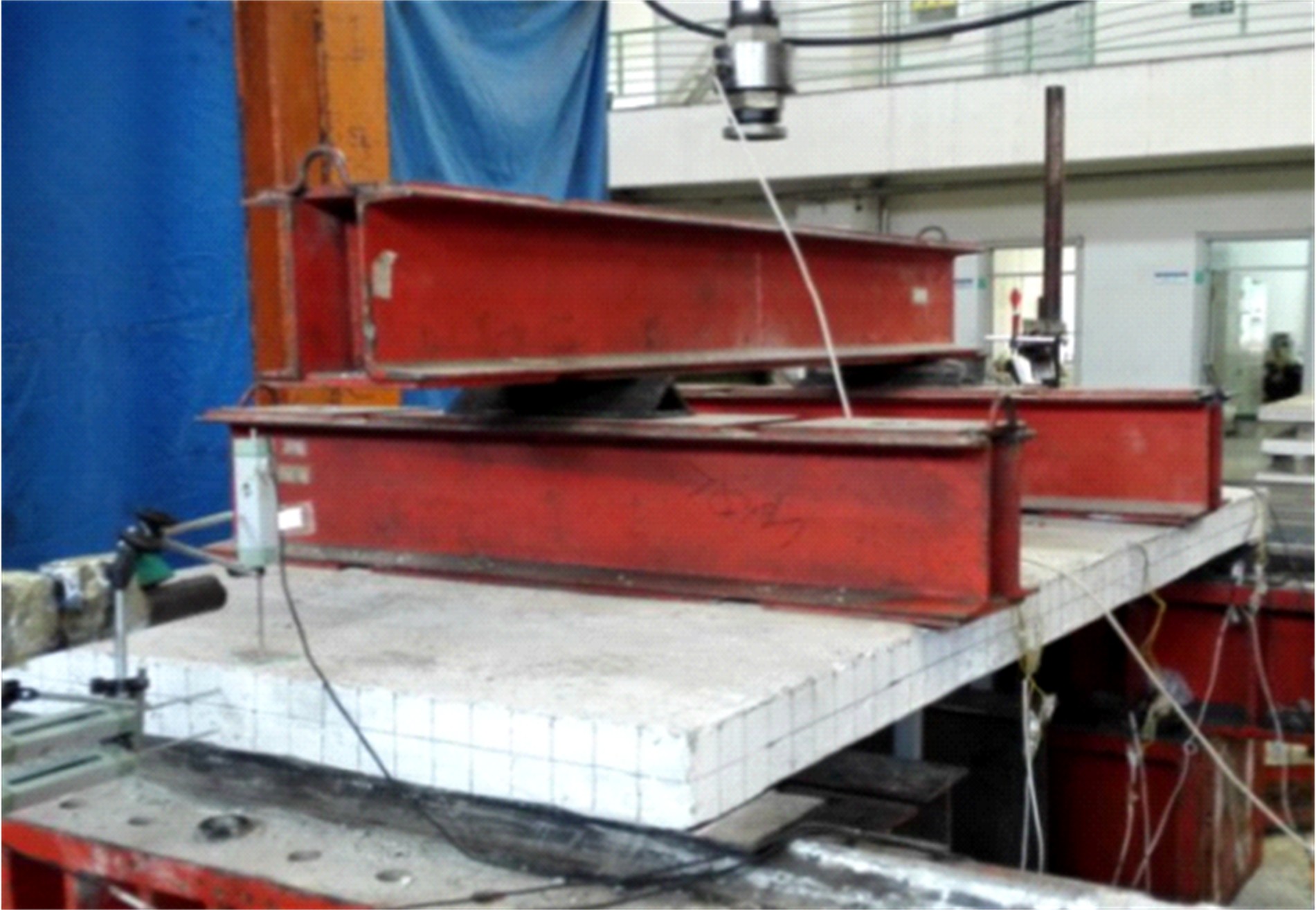
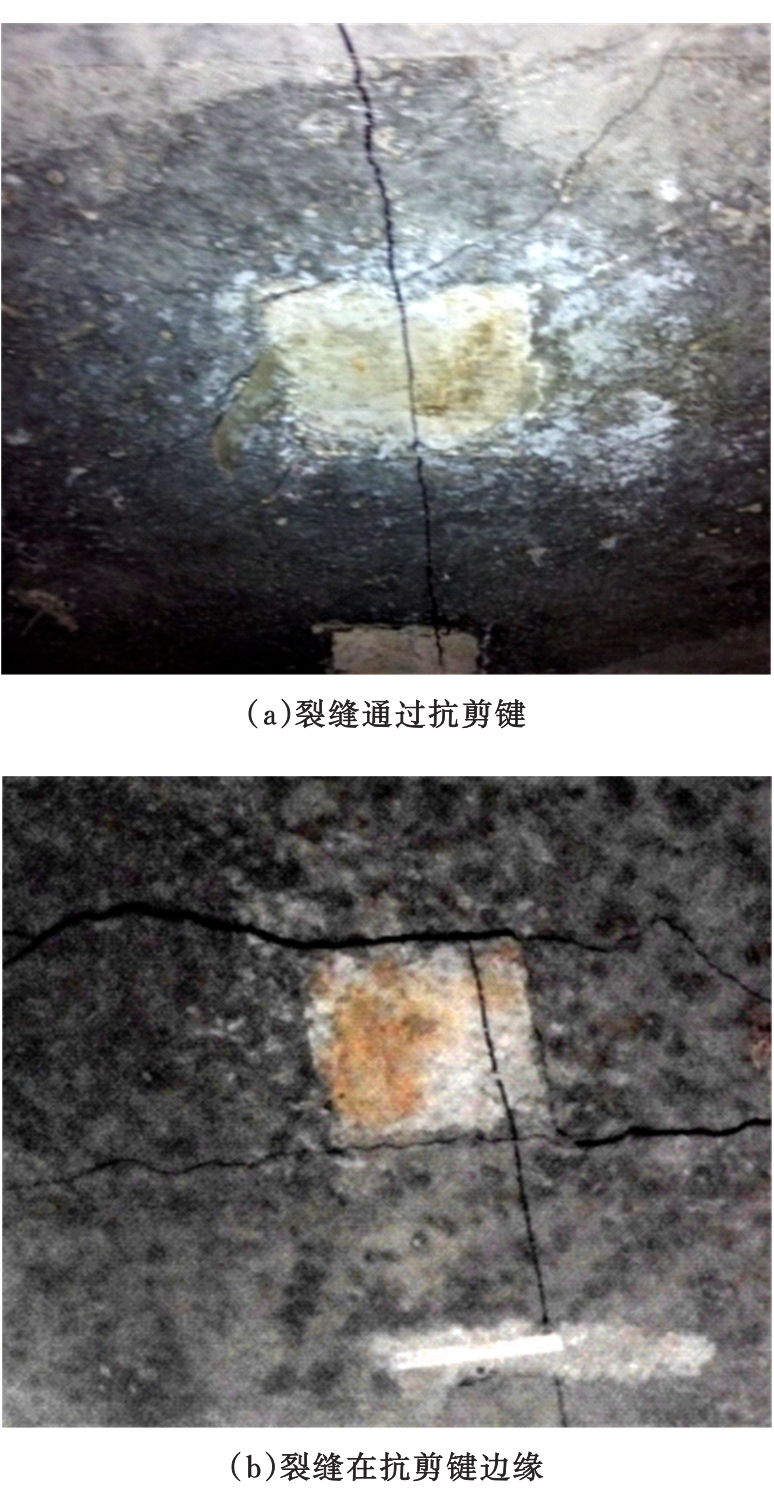
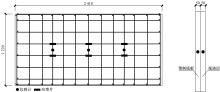
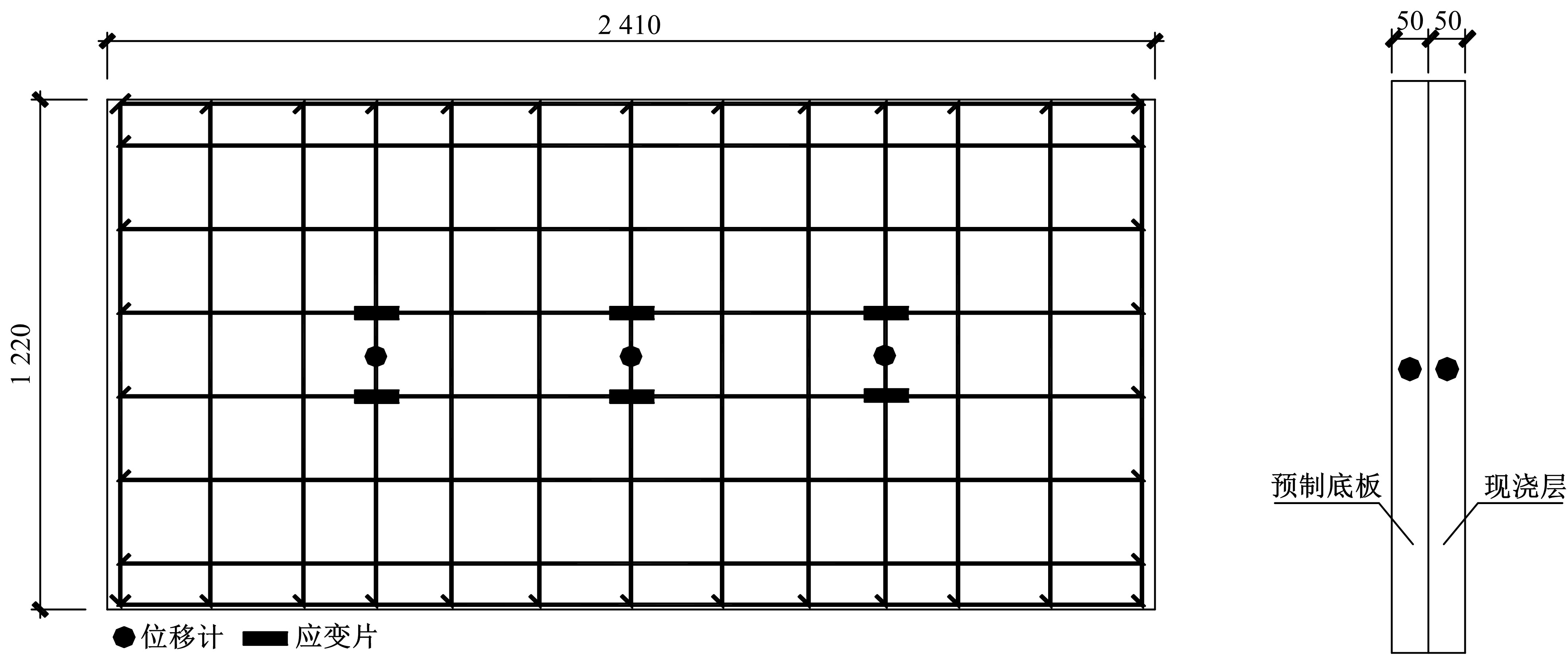
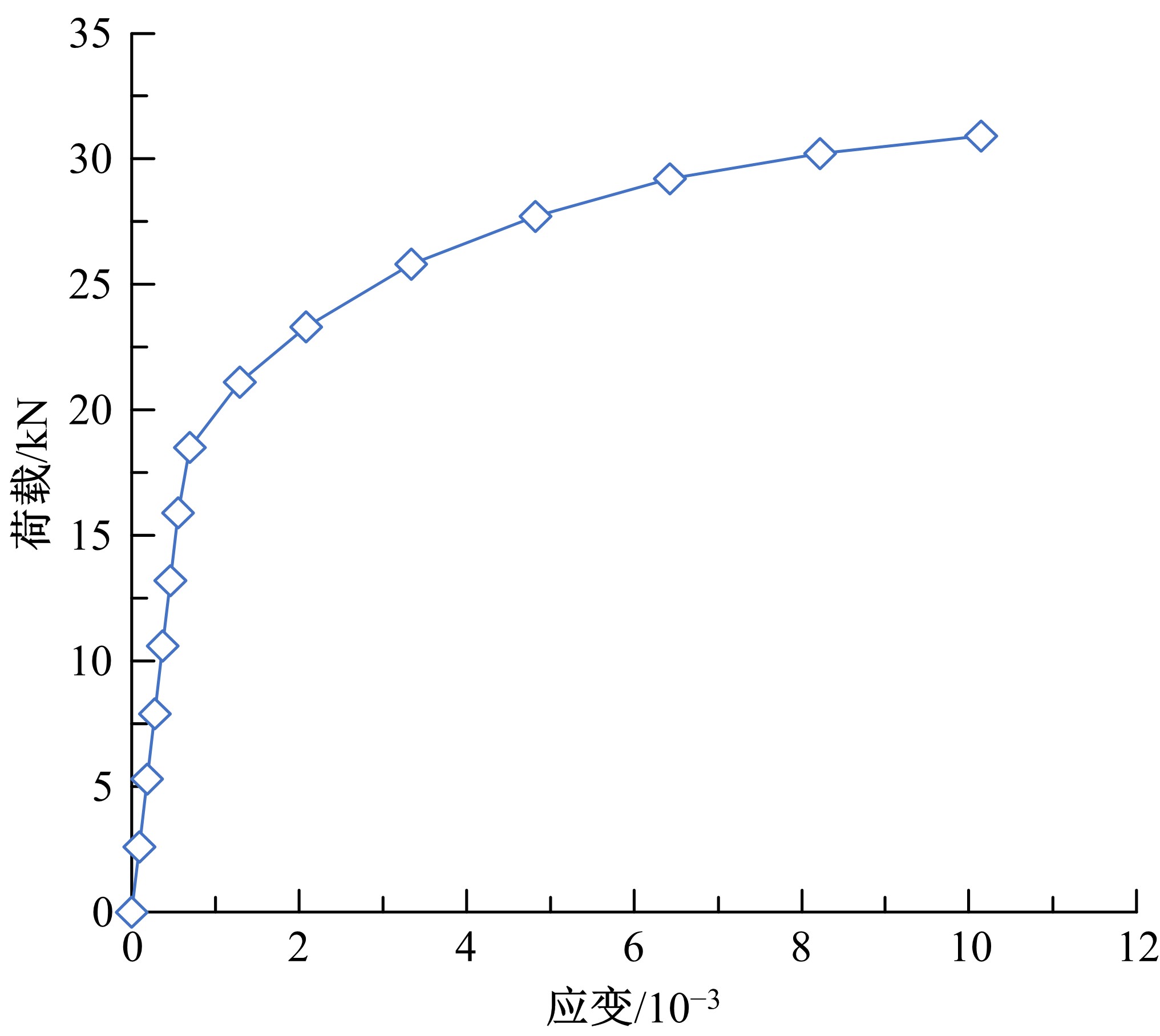
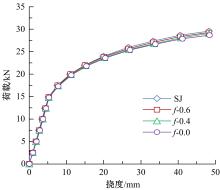
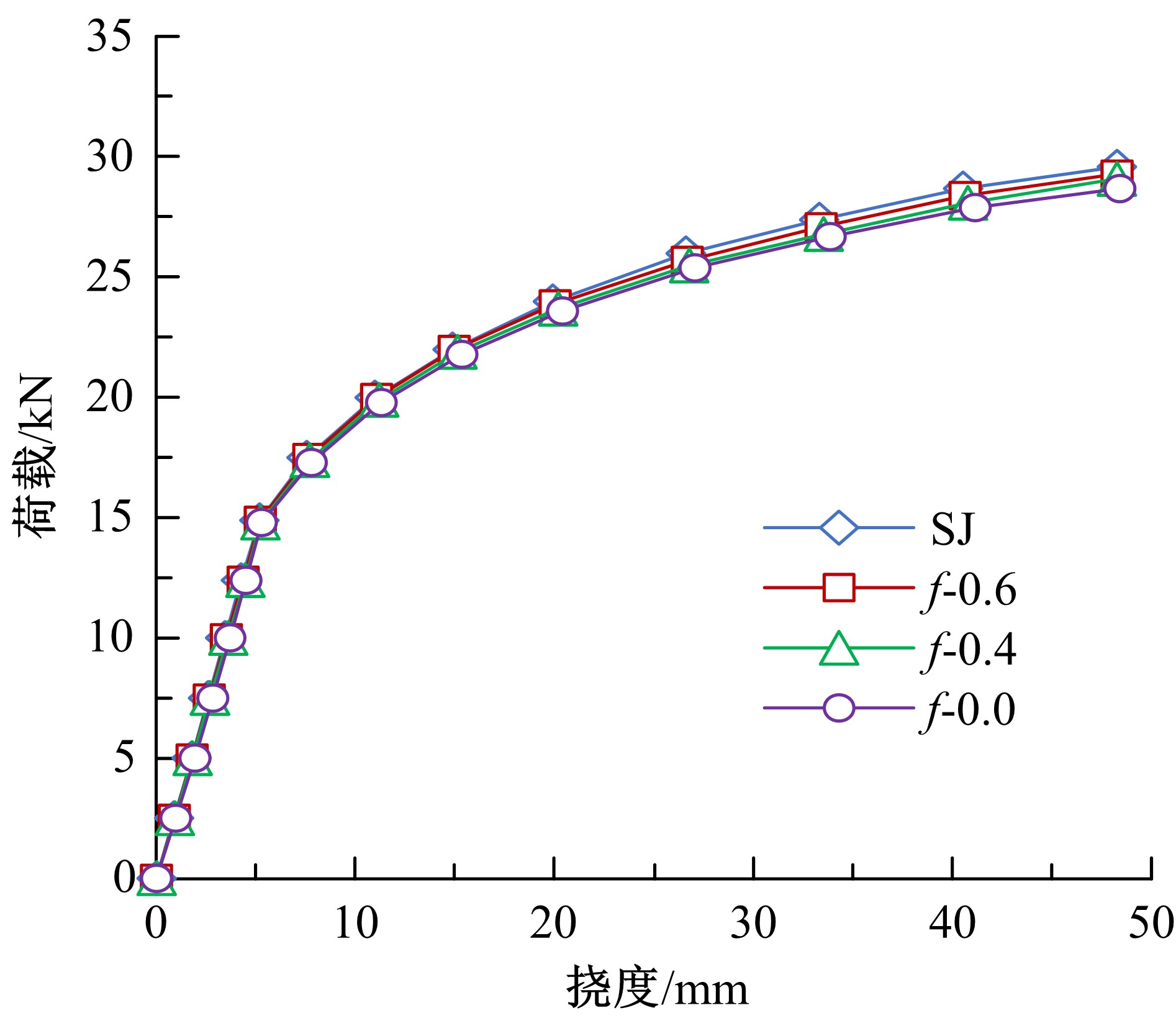
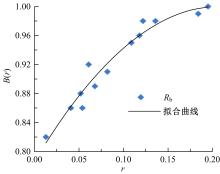
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2020, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (2): 654-667.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20181062
Experimental of loading-bearing capacity of one-way laminated slab with shear keys
Ming LI1( ),Hao-ran WANG1,Wei-jian ZHAO2
),Hao-ran WANG1,Wei-jian ZHAO2
- 1.School of Civil Engineering,Shenyang Jianzhu University,Shenyang 110168,China
2.College of Civil Engineering and Architecture,Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058,China
CLC Number:
- TU375.2
| 1 | 赵唯坚. 超高强材料与装配式结构[J]. 工程力学, 2012, 29(增刊2): 31-42. |
| Zhao Wei-jian. Ultra-high strength materials and precast concrete structures[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2012, 29(Sup.2): 31-42. | |
| 2 | 杨联萍, 余少乐, 张其林, 等. 叠合剪力墙结构研究现状和关键问题[J]. 建筑结构, 2017, 47(12): 78-88. |
| Yang Lian-ping, Yu Shao-le, Zhang Qi-lin, et al. Research status quo and key issues in superimposed shear wall structure[J]. Building Structure, 2017, 47(12): 78-88. | |
| 3 | 赵广军. 预制装配式混凝土结构发展现状分析[J]. 工程质量, 2016, 34(7): 16-18. |
| Zhao Guang-jun. The development prospects of the prefabricated concrete structure[J]. Construction Quality, 2016, 34(7): 16-18. | |
| 4 | Vaquero S F, Correa D R, Wolkomirski S F. Precast concrete,steel-braced,hybrid pipe rack structures[J]. PCI Journal, 2013, 58(4): 55-67. |
| 5 | JGJ 1—2014. 装配式混凝土结构技术规程[S]. |
| 6 | 刘香, 倪东阳, 李娟. 预制带肋钢筋桁架叠合板的试验与有限元分析[J]. 沈阳建筑大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 34(1): 42-52. |
| Liu Xiang, Ni Dong-yang, Li Juan. Experimental study and finite element analysis of prefabricated ribbed steel truss laminated slabs[J]. Journal of Shenyang Jianzhu University (Natural Science), 2018, 34(1): 42-52. | |
| 7 | Chou C C,Chen J H. Development of floor slab for steel post-tensioned self-centering moment frames[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2011, 67(10): 1621-1635. |
| 8 | 李明, 赵唯坚, 孙哲哲. 带抗剪键的混凝土叠合楼板、预制构造和施工方法[P]. 中国: CN201210279952, 2014-09-24. |
| 9 | 肖景平. 预应力高强叠合结构叠合梁生产工艺[J]. 建筑技术, 2014, 45(1): 53-55. |
| Xiao Jing-ping. Production process of prestressed high-strength superimposed beam[J]. Architecture Technology, 2014, 45(1): 53-55. | |
| 10 | GB/T 50152—2012 混凝土结构试验方法标准[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. |
| 11 | GB 50010—2010. 混凝土结构设计规范[S]. |
| 12 | 徐国林, 徐倩, 王祥建, 等. 混凝土单轴弹塑性损伤本构模型及参数确定[J]. 广西大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 41(2): 332-338. |
| Xu Guo-lin, Xu Qian, Wang Xiang-jian, et al. Uniaxial elastic-plastic damage constitutive model and parameters of concrete[J]. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 41(2): 332-338. | |
| 13 | 戴岩, 聂少锋, 周天华. 带环梁的方钢管约束钢骨混凝土柱-钢梁节点滞回性能有限元分析[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 48(5): 1426-1435. |
| Dai Yan, Nie Shao-feng, Zhou Tian-hua. Finite element analysis of hysteretic behavior of square steel tube confined steel reinforced concrete column steel frame ring beam joint[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(5): 1426-1435. | |
| 14 | 陈富强, 田唯, 刘占国, 等. 匹配浇筑混凝土接触面摩擦系数试验研究[J]. 中国港湾建设, 2014(12): 34-38. |
| Chen Fu-qiang, Tian Wei, Liu Zhan-guo, et al. Experiment study on friction coefficient of concrete with matching pouring surface[J]. China Harbor Engineering, 2014(12): 34-38. | |
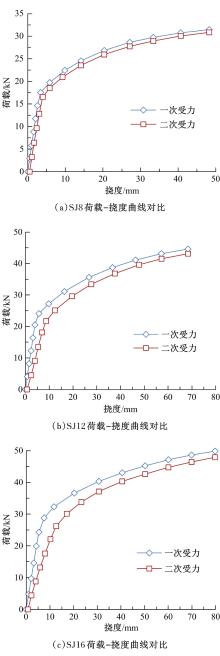
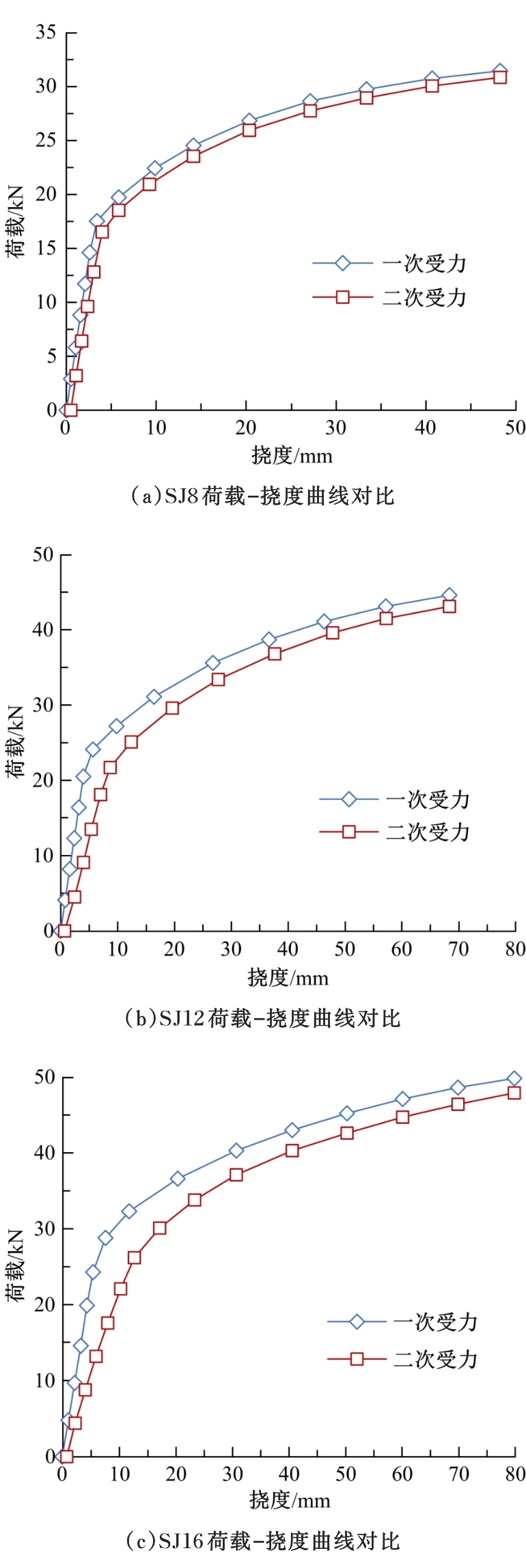
| 15 | 孙兵, 丁德鑫, 曾晟, 等. 钢筋混凝土叠合结构二次受力过程数值分析[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 城市科学版, 2008, 25(4): 260-263. |
| Sun Bing, Ding De-xin, Zeng Sheng, et al. Numerical analysis of two-stage loading progresses on reinforcement concrete composite structures[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Urban Science Edition), 2008, 25(4): 260-263. | |
| 16 | 郭楠, 张平阳, 左熠, 等. 竹板增强胶合木梁受弯性能[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2017, 47(3): 778-788. |
| Guo Nan, Zhang Ping-yang, Zuo Yi, et al. Bending performance of glue-lumber beam reinforced by bamboo plyboard[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(3): 778-788. |
| [1] | Peng-hui WANG,Hong-xia QIAO,Qiong FENG,Hui CAO,Shao-yong WEN. Durability model of magnesium oxychloride-coated reinforced concrete under the two coupling factors [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 191-201. |
| [2] | Yong PENG,Hua GAO,Lei WAN,Gui-ying LIU. Numerical simulation of influence factors of splitting strength of asphalt mixtures [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1521-1530. |
| [3] | Xin TONG,Ya-jiao ZHANG,Yu-shan HUANG,Zheng-zheng HU,Qing WANG,Zhi-hui ZHANG. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 304L stainless steel processed by selective laser melting [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1615-1621. |
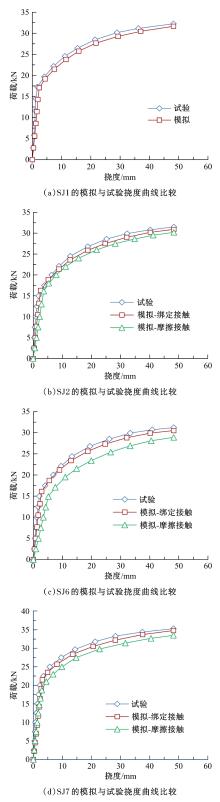
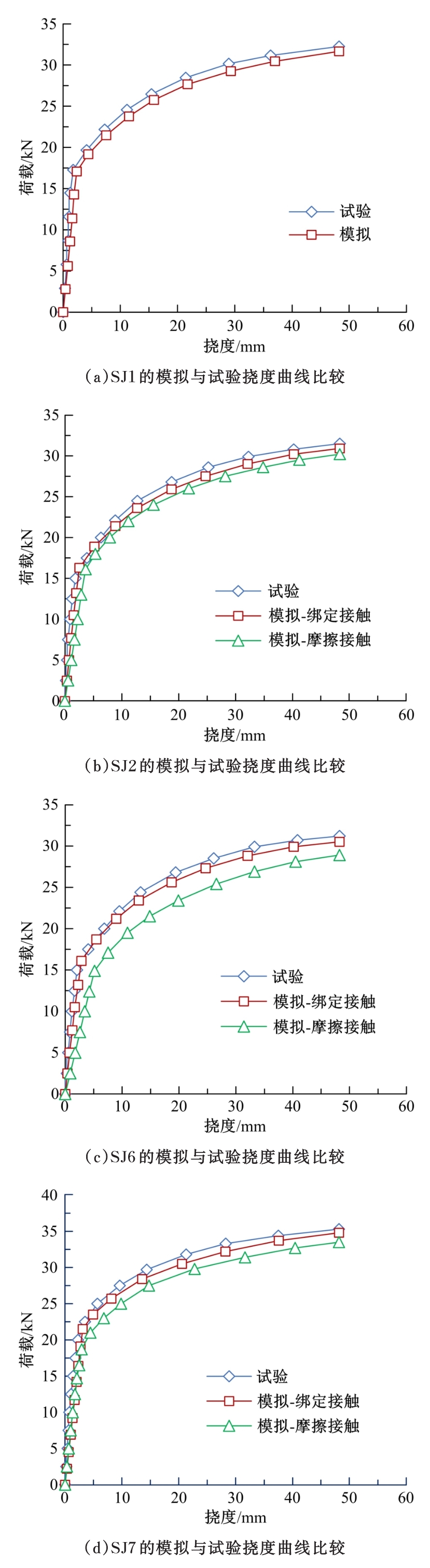
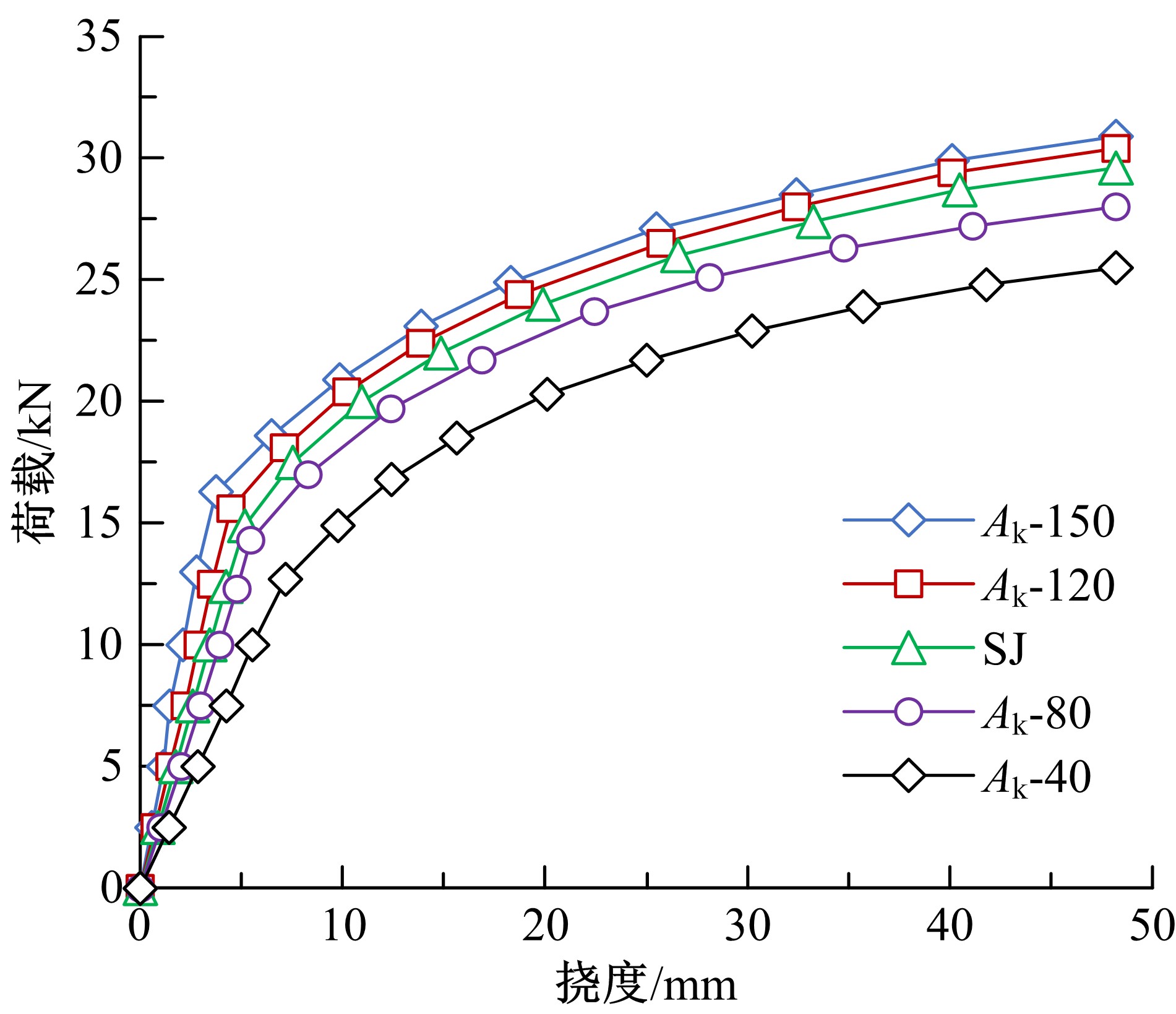
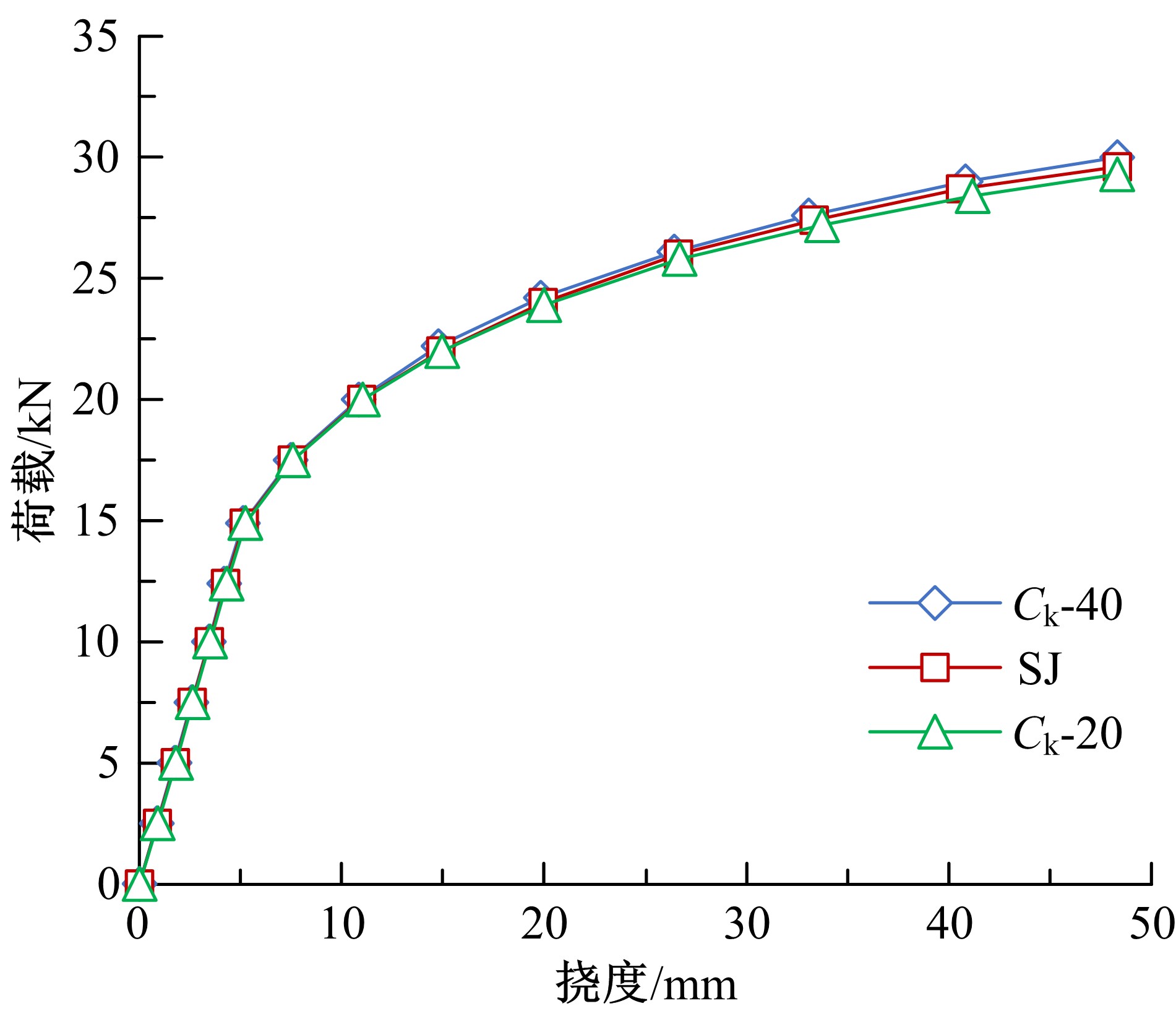
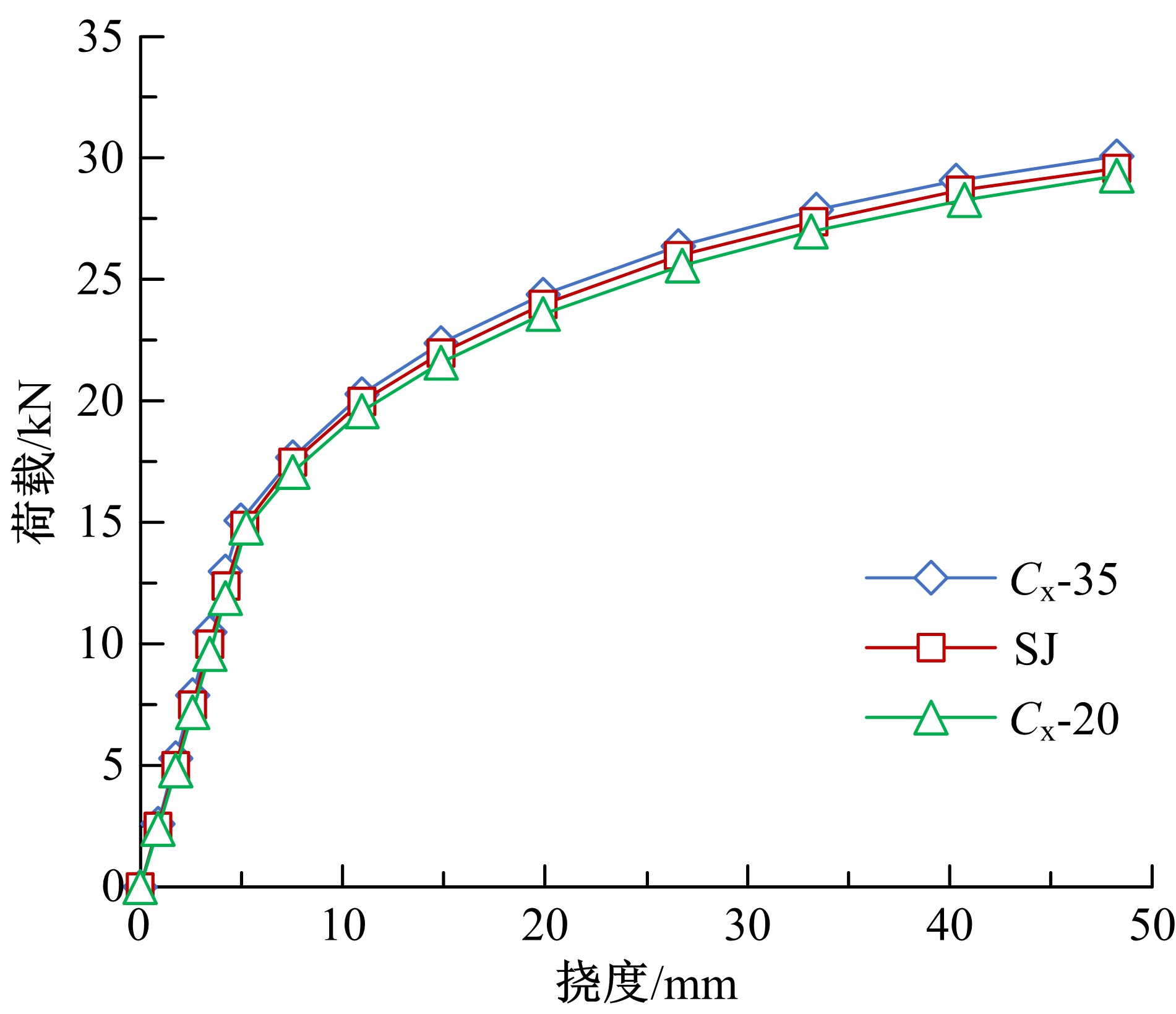
| [4] | Ming LI,Hao-ran WANG,Wei-jian ZHAO. Mechanical properties of laminated slab with shear keys [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1509-1520. |
| [5] | Jun ZHANG,Cheng QIAN,Chun⁃yan GUO,Yu⁃jun QIAN. Dynamic design of building livability based on multi⁃source spatiotemporal data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1169-1173. |
| [6] | Ning⁃hui LIANG,Qing⁃xu MIAO,Xin⁃rong LIU,Ji⁃fei DAI,Zu⁃liang ZHONG. Determination of fracture toughness and softening traction⁃separation law of polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1144-1152. |
| [7] | Na WU,Jian ZHUANG,Ke⁃song ZHANG,Hui⁃xin WANG,Yun⁃hai MA. Compression mechanical properties and fracture mechanism of Scapharca Subcrenata shell [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 897-902. |
| [8] | Lei ZHANG,Bao⁃guo LIU,Zhao⁃fei CHU. Model test of the influence on shield shaft owing to water loss settlement of deep sandstone aquifer layer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 788-797. |
| [9] | JIANG Qiu-yue,YANG Hai-feng,TAN Cai-wang. Strengthening properties of welded joints of 22MnB5 super high strength steel [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1806-1810. |
| [10] | ZHENG Yi-feng, ZHAO Qun, BAO Wei, LI Zhuang, YU Xiao-fei. Wind resistance performance of long-span continuous rigid-frame bridge in cantilever construction stage [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(2): 466-472. |
| [11] | NI Ying-sheng, SUN Qi-xin, MA Ye, XU Dong. Calculation of capacity reinforcement about composite box girder with corrugated steel webs based on tensile stress region theory [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 148-158. |
| [12] | WANG Teng, ZHOU Ming-ru, MA Lian-sheng, QIAO Hong-xia. Fracture grouting crack growth of collapsible loess based on fracture theory [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1472-1481. |
| [13] | ZHENG Yi-feng, MAO Jian, LIANG Shi-zhong, ZHENG Chuan-feng. Negative skin friction of pile foundation considering soil consolidation in high fill site [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(4): 1075-1081. |
| [14] | LI Jing, WANG Zhe. Mechanical characteristics of concrete under true triaxial loading condition [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 771-777. |
| [15] | GUO Nan, ZHANG Ping-yang, ZUO Yu, ZUO Hong-liang. Bending performance of glue-lumber beam reinforced by bamboo plyboard [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(3): 778-788. |
|
||