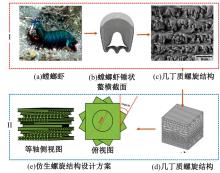
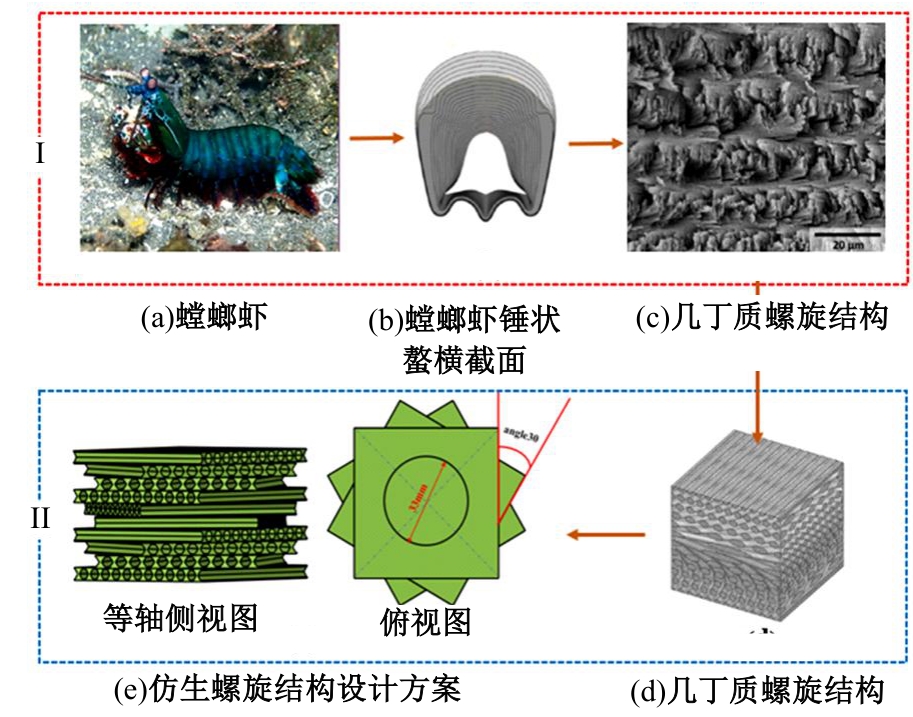
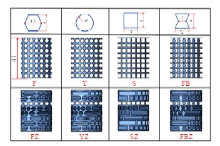
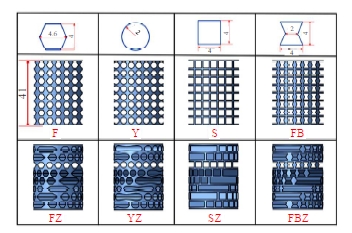
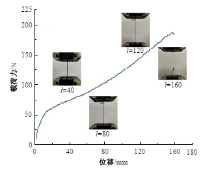
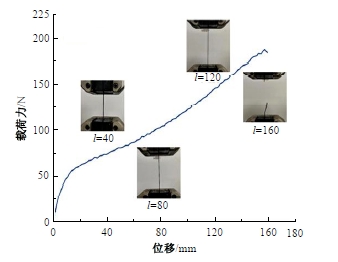
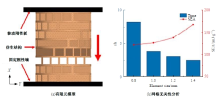
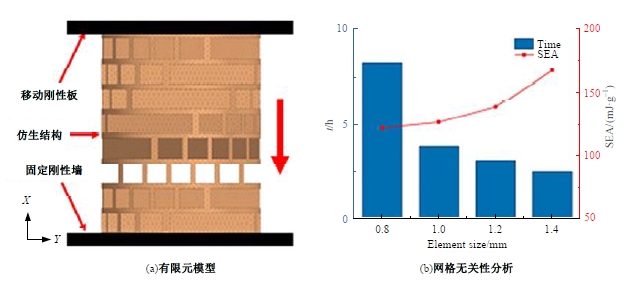
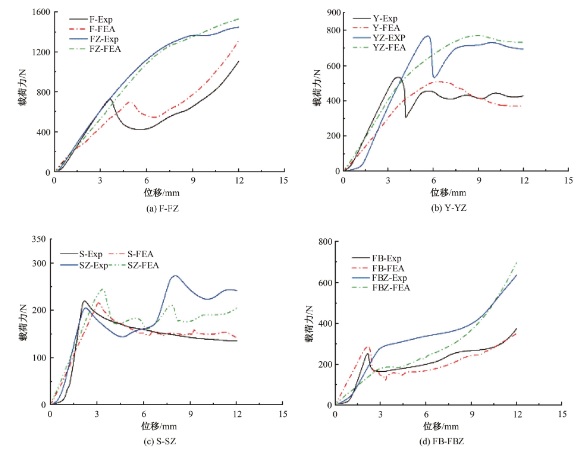
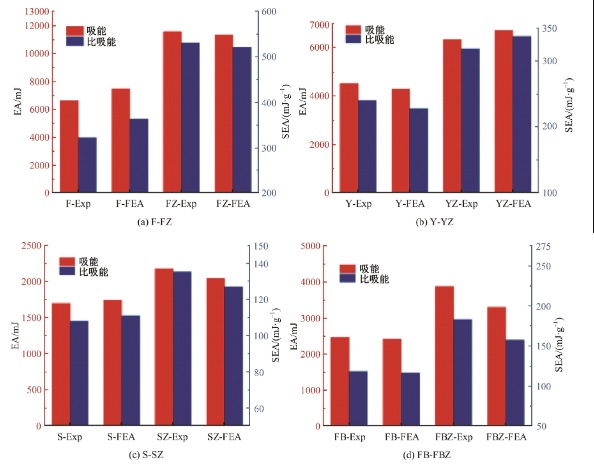
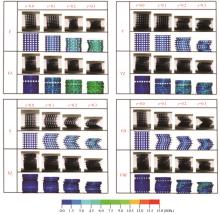
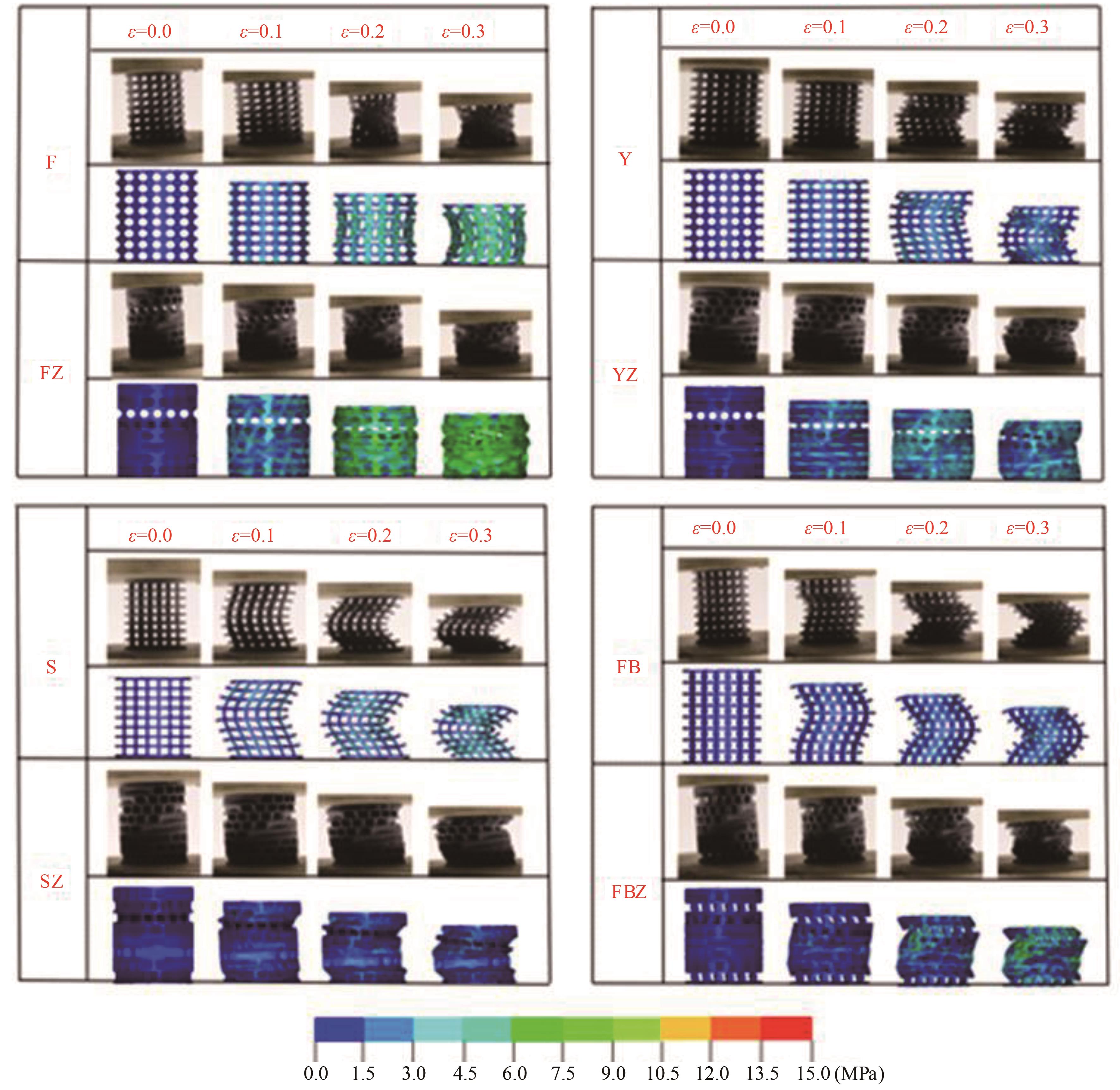
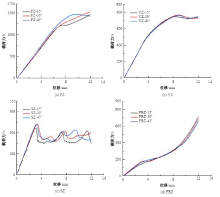
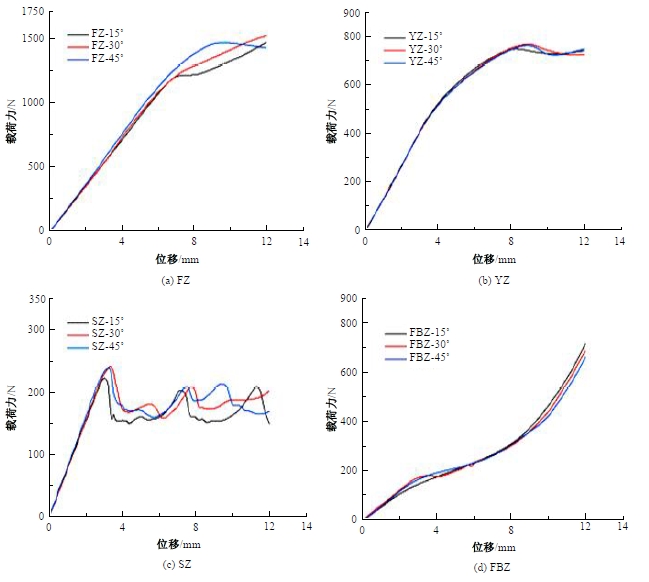
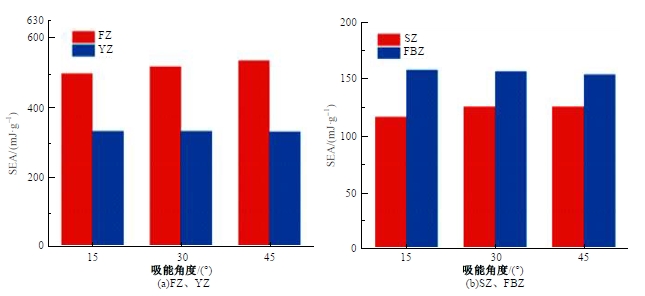
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (4): 1474-1482.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230636
Energy absorption characteristics of bionic helical structures inspired by mantis shrimp
Ying-chun QI( ),Zhao-hui ZHANG,Li-xin CHEN,Qing-yang WANG,Xue GUO,Zheng-lei YU(
),Zhao-hui ZHANG,Li-xin CHEN,Qing-yang WANG,Xue GUO,Zheng-lei YU( ),Zhi-hui ZHANG
),Zhi-hui ZHANG
- Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,China
CLC Number:
- TB17
| [1] | Tan H L, He Z C, Li K X, et al. In-plane crashworthiness of re-entrant hierarchical honeycombs with negative Poisson's ratio[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 229: No.111415. |
| [2] | 于征磊, 信仁龙, 陈立新, 等. 仿蜂窝防护结构的承载特性[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2021, 51(3): 1140-1145. |
| Yu Zheng-lei, Xin Ren-long, Chen Li-xin, et al. Load bearing characteristics of honeycomb protection structure[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1140-1145. | |
| [3] | Yang X F, Sun Y X, Yang J L, et al. Out-of-plane crashworthiness analysis of bio-inspired aluminum honeycomb patterned with horseshoe mesostructure[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2018, 125: 1-11. |
| [4] | Liang H Y, Hao W Q, Xue G L, et al. Parametric design strategy of a novel self-similar hierarchical honeycomb for multi-stage energy absorption demand[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2022, 217:No. 107029. |
| [5] | Zhang Y, Wang J, Wang C H, et al. Crashworthiness of bionic fractal hierarchical structures[J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 158: 147-159. |
| [6] | Zhang W, Yu T X, Xu J. Uncover the underlying mechanisms of topology and structural hierarchy in energy absorption performances of bamboo-inspired tubular honeycomb[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2022, 52: No.101640. |
| [7] | Yang W, Chen Irene H, Bernd G, et al. Natural flexible dermal armor[J]. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(1): 31-48. |
| [8] | Quan H C, Yang W, Eric S, et al. Novel defense mechanisms in the armor of the scales of the "living fossil" coelacanth fish[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(46): No.1804237. |
| [9] | 韩铖. 仿生轻质抗冲击结构材料的设计、制备与性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学机电学院,2018. |
| Han Cheng. Research on bio-inspired lightweight anti-impact structure and its mechanical analysis[D]. Nanjing:College of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018. | |
| [10] | Meng Q H, Gao Y, Shi X H, et al. Three-dimensional crack bridging model of biological materials with twisted Bouligand structures[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2022, 159:No.104729. |
| [11] | Lian J, Wang J. Microstructure and mechanical anisotropy of crab cancer magister exoskeletons[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 2014, 54(2): 229-239. |
| [12] | Ma C L, Gu D D, Lin K J, et al. Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of cancer pagurus's claw inspired bionic structures with high strength and toughness[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 469: 647-656. |
| [13] | Kellersztein I, Cohen S R, Bar-On B, et al. The exoskeleton of scorpions' pincers: structure and micro-mechanical properties[J]. Acta Biomaterialia, 2019, 94: 565-573. |
| [14] | Israel G, Israel K, Daniel W H. Nested helicoids in biological microstructures[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1):No.224. |
| [15] | Yang R G, Zaheri A, Gao W, et al. AFM identification of beetle exocuticle: bouligand structure and nanofiber anisotropic elastic properties[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(6): No.1603993. |
| [16] | Lee N, Berthelson P R, Nguyen V, et al. Microstructure and nanomechanical properties of the exoskeleton of an ironclad beetle[J]. Bioinspiration & Biomimetics, 2021, 16(3): No.036005. |
| [17] | Zimmermann E A, Gludovatz B, Schaible E, et al. Mechanical adaptability of the Bouligand-type structure in natural dermal armour[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: No.2634. |
| [18] | Chen S M, Wu K J, Gao H L, et al. Biomimetic discontinuous Bouligand structural design enables high-performance nanocomposites[J]. Matter, 2022, 5(5): 1563-1577. |
| [19] | Zhang X Y, Luan Y B, Li Y C, et al. Bioinspired design of lightweight laminated structural materials and the intralayer/interlayer strengthening and toughening mechanisms induced by the helical structure[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 276:No. 114575. |
| [20] | Yang F, Xie W H, Meng S H. Crack-driving force and toughening mechanism in crustacean-inspired helicoidal structures[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2021, 208: 107-118. |
| [21] | Cheng L, Thomas A, Glancey James L, et al. Mechanical behavior of bio-inspired laminated composites[J]. Composites Part A-Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2011, 42(2): 211-220. |
| [22] | 韩奇钢, 石绍迁, 徐凯强,等. 仿螳螂虾鳌结构/功能的玄武岩纤维增强复合材料碟簧研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2020, 10(27): 77-82. |
| Han Qi-gang, Shi Shao-qian, Xu Kai-qiang, et al. Study on basalt fiber reinforced composite disc spring of bionic structure/function of dactyl club of mantis shrimp[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2020, 10(27): 77-82. |
| [1] | Peng XI,Qian CONG,Shao-bo YE,Hong-bo LI,Yan-qing ZHANG. Bionic design and adsorption performance analysis of vacuum sucker [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 382-391. |
| [2] | Xin YANG,Yang WANG,Jia-feng SONG,Yong ZHU,Bin-bing HUANG,Shu-cai XU. Design and numerical simulation of bionic sandwich panel based on a shrimp chela structure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(3): 842-851. |
| [3] | Zheng-lei YU,Qing CAO,Jun-dong ZAHNG,Peng-wei SHA,Jing-fu JIN,Wan-zhen WEI,Ping LIANG,Zhi-hui ZHANG. Mechanical properties of a bionic buffer structure of a lander based on additive manufacturing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 3077-3084. |
| [4] | Wei-min ZHUANG,En-ming WANG. Modeling and compression simulation of 3D solid aluminum foam with random cell wall thickness [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(8): 1777-1785. |
| [5] | Han HUANG,Qing-hao YAN,Zhi-xin XIANG,Xin-tao YANG,Jin-bao CHEN,Shu-cai XU. Crashworthiness investigation and optimization of bionic multi⁃cell tube based on shrimp chela [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 716-724. |
| [6] | Zheng-lei YU,Li-xin CHEN,Ze-zhou XU,Ren-long XIN,Long MA,Jing-fu JIN,Zhi-hui ZHANG,Shan JIANG. Analysis of mechanical characteristics and recovery characteristics of bionic protective structures based on additive manufacturing [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(4): 1540-1547. |
| [7] | Zheng-lei YU,Ren-long XIN,Li-xin CHEN,Yi-ning ZHU,Zhi-hui ZHANG,Qing CAO,Jing-fu JIN,Jie-liang ZHAO. Load bearing characteristics of honeycomb protection structure [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 1140-1145. |
| [8] | Chun-bao LIU,Shan-shi CHEN,Chuang SHENG,Zhi-hui QIAN,Lu-quan REN,Lei REN. Bionic hydraulic driving mechanism of spider and its bio⁃inspiration [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 375-381. |
| [9] | Xing-tian QU,Xue-xu WANG,Hui-chao SUN,Kun ZHANG,Long-wei YAN,Hong-yi WANG. Fuzzy self⁃adaptive PID control for fused deposition modeling 3D printer heating system [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 77-83. |
| [10] | Dong⁃liang CHEN,Rui ZANG,Peng DUAN,Wei⁃peng ZHAO,Xu⁃tao WENG,Yang SUN,Yi⁃peng TANG. Biomimetic design of multi⁃link fishbone based on crescent′s fishtail propulsion theory [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(4): 1246-1257. |
| [11] | Na WU,Jian ZHUANG,Ke⁃song ZHANG,Hui⁃xin WANG,Yun⁃hai MA. Compression mechanical properties and fracture mechanism of Scapharca Subcrenata shell [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(3): 897-902. |
| [12] | GUO Hao-tian,XU Tao,LIANG Xiao,YU Zheng-lei,LIU Huan,MA Long. Optimization on thermal surface with rib turbulator inspired by turbulence of alopias' gill in simplified gas turbine transition piece [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1793-1798. |
| [13] | XI Peng,CONG Qian,WANG Qing-bo,GUO Hua-xi. Wear test and anti-friction mechanism analysis of bionic stripe grinding roll [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2018, 48(6): 1787-1792. |
| [14] | QIAN Zhi-hui, ZHOU Liang, REN Lei, REN Lu-quan. Completely passive walking machine with bionic subtalar joint and matatarsal phalangeal joint [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(1): 205-211. |
| [15] | QU Xing-tian, YAN Long-wei, SUN Hui-chao, ZHOU Wei, LI Guang-hui. Structure analysis of 3D printer device of reversible working platform [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2017, 47(5): 1489-1497. |
|