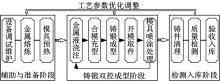
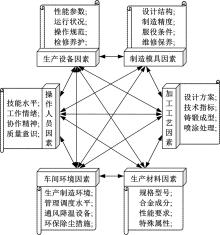
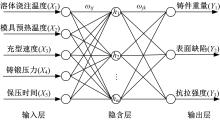
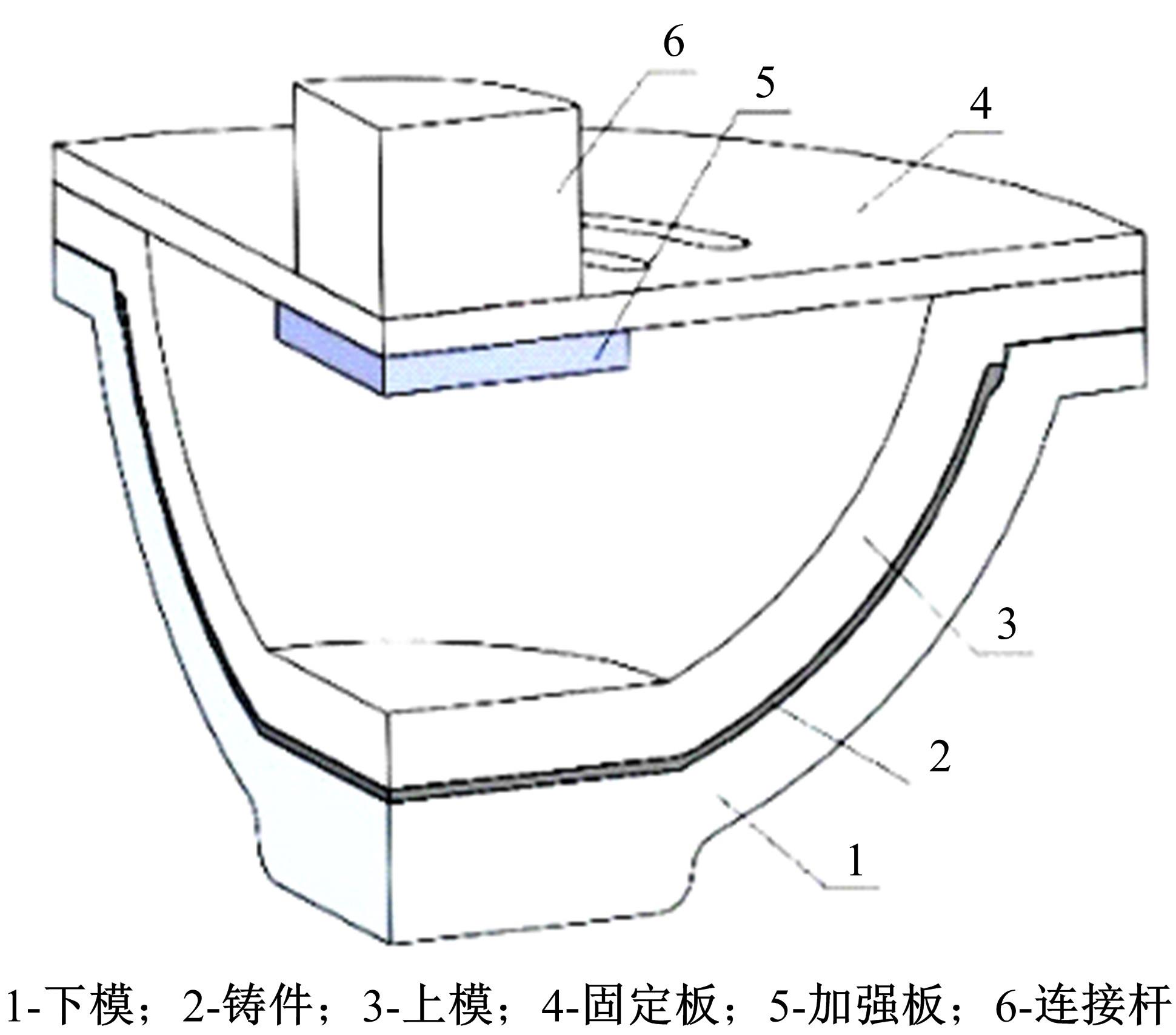
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1524-1533.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210108
Multi-objective optimization of casting-forging dynamic forming based on improved particle swarm neural network and finite element analysis
Zhao-ming CHEN1,2( ),Jin-song ZOU3,Wei WANG4,Ming-quan SHI3
),Jin-song ZOU3,Wei WANG4,Ming-quan SHI3
- 1.College of Mechanical Engineering,Chongqing University,Chongqing 400044,China
2.School of Artificial Intelligence,Chongqing School of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Chongqing 400714,China
3.Intelligent Manufacturing Technology Institute,Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Chongqing 400714,China
4.College of Computer Science and Engineering,Chongqing University of Technology,Chongqing 400054,China
CLC Number:
- TP183
| 1 | 吴月松, 张桂军. 铸造工艺特点分析[J]. 建筑工程技术与设计, 2017, 21:4498. |
| Wu Yue-song, Zhang Gui-jun. Analysis of casting process characteristics[J]. Architectural Engineering Technology and Design, 2017, 21:4498. | |
| 2 | 马敬仲. 铸造产品升级与高端铸件研制的关键问题论述[J]. 现代铸铁, 2016, 2:19-23. |
| Ma Jing-zhong. Key problems talk about up-grading of casting products and development of high-end castings[J]. Modern Cast Iron, 2016, 2:19-23. | |
| 3 | 卢杰. 我国铸造技术的发展趋势[C]∥第24届重庆市铸造年会论文集, 重庆,2014:16-18. |
| 4 | Zhou H T, Xu S X, Li W D, et al. A study of automobile brake bracket formed by casting-forging integrated forming technology[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 67(2):285-292. |
| 5 | Jiang J, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. A double control forming technology combining die casting and forging for the production of Mg alloy components with enhanced properties[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Tech, 2012, 212(5):1191-1199. |
| 6 | Zhang Wen-yu, Ju Dong-ying, Zhao Hong-yang, et al. Fuzzy controller optimized by genetic algorithm for the molten metal level in the twin roll strip casting process[J]. Materials Science Forum,2015, 833:197-200. |
| 7 | 周华民, 高煌, 张云, 等. 注塑成型工艺参数自动设置与优化技术[J]. 精密成形工程, 2016, 8(1):7-13, 26. |
| Zhou Hua-min, Gao Huang, Zhang Yun, et al. Automatic setting and optimization of injection molding process parameters[J]. Journal of Netshap Forming Engineering, 2016, 8(1):7-13, 26. | |
| 8 | Schmidt R, Pusch D, Voigt M, et al. Numerical and experimental sensitivity analysis for the determination of casting parameter-microstructure-property relations and mechanical properties of IN738LC in investment casting[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2015, 16(10):1217-1225. |
| 9 | 李瑞娟, 黄力. 基于BP神经网络的汽车内饰面板注塑成型工艺参数优化[J]. 塑料, 2016, 45(3):81-85. |
| Li Rui-juan, Huang Li. Optimization of injection molding process for automotive interior panel based on BP neural network[J]. Plastics, 2016, 45(3):81-85. | |
| 10 | Zarei J, Poshtan J. Optimization of process parameters for biological 3D printing forming based on BP neural network and genetic algorithm[J]. Tribology International, 2014, 42(2):213-219. |
| 11 | Darajeh N, Masoumi H R F, Kalantari K, et al. Optimization of process parameters for rapid adsorption of Pb(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) by magnetic/talc nanocomposite using wavelet neural network[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2015, 42(3):1977-1987. |
| 12 | Sreeraj P, Kannan T, Subhashis M. Optimization of GMAW process parameters using particle swarm optimization[J]. Isrn Metallurgy, 2015, 2013:1-10. |
| 13 | Zhang Jian-feng, Peng An-hua. Processing parameter optimization of FDM based on robust design[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2012, 29(1):62-67. |
| 14 | Equbal M I, Kumar R, Shamim M, et al. A grey-based taguchi method to optimize hot forging process[J]. Procedia Materials Science, 2014, 6:1495-1504. |
| 15 | 韩明兴. 挤压铸造充型过程的计算机数值模拟仿真研究[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2012. |
| Han Ming-xin. Numerical computer simulation technology of squeeze casting filling process[D]. Wuhan:College of Materials and Engineering,Wuhan University of Technology, 2012. | |
| 16 | 李春龙, 郑伟刚, 阳鑫,等. 汽车发动机附件支架挤压铸造数值模拟研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2015, 44(1):63-65, 68. |
| Li Chun-long, Zheng Wei-gang, Yang Xin, et al. Numerical simulation research of squeeze casting for automotive engine accessories stent[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2015, 44(1):63-65, 68. | |
| 17 | 陈玖新, 代颖辉, 张川吉,等. 基于ProCAST的挤压铸造重载车轮铸件成形过程数值模拟[J]. 铸造, 2015, 64(7):639-642. |
| Chen Jiu-xin, Dai Ying-hui, Zhang Chuan-ji, et al. Numerical simulation of casting forming for squeeze casting heavy load wheel on ProCAST[J]. Foundry, 2015, 64(7):639-642. | |
| 18 | Wang Ru-jia, Wu Shi-ping, Chen Wei. Mechanism of burst feeding in ZL205A casting under mechanical vibration and low pressure [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(8):45-51. |
| 19 | 向青春, 张伟, 邱克强,等. 基于DOE的大型下架体铸钢件铸造工艺优化研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(6):88-93. |
| Xiang Qing-chun, Zhang Wei, Qiu Ke-qiang, et al. Casting process optimization for large lower frame body of heavy gyratory crusher based on DOE[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(6):88-93. | |
| 20 | 兰鹏, 杜辰伟, 陈培莉,等. 微合金钢连铸表面横裂纹形成机理与控制技术研究现状[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2017, 29(1):1-12. |
| Lan Peng, Du Chen-wei, Chen Pei-li, et al. Research status of surface transverse cracking formation mechanism and control technique for continuously cast microalloyed steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017, 29(1):1-12. | |
| 21 | 黄璇, 郭立红, 李姜, 等. 改进粒子群优化BP神经网络的目标威胁估计[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(3):996-1002. |
| Huang Xuan, Guo Li-hong, Li Jiang, et al. Target threat assessment based on BP neural network optimized by modified particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(3):996-1002. | |
| 22 | Wang B, Lin R, Liu D, et al. Investigation of the effect of humidity at both electrode on the performance of PEMFC using orthogonal test method[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(26):13737-13743. |
| 23 | Dey A, Sarkar D. A note on the construction of orthogonal latin hypercube designs[J]. Journal of Combinatorial Designs, 2016, 24(3):105-111. |
| 24 | Ye K Q. Orthogonal column latin hypercubes and their application in computer experiments[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1998, 93(444): 1430-1439. |
| 25 | 杜常清, 曹锡良, 何彪, 等. 基于混合粒子群算法的双离合变速器参数优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(5):1556-1564. |
| Du Chang-qing, Cao Xi-liang, He Biao, et al. Parameters optimization of dual clutch transmission based on hybrid particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5):1556-1564. | |
| 26 | 杨东民, 陈敏, 吴庆朝. 基于KPCA与MPSO–BP注射成型工艺参数优化[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2015, 43(12):42-47. |
| Yang Dong-min, Chen Min, Wu Qing-chao. Study on parameters optimization of injection molding based on KPCA and modified particle swarm optimized back propagation neural network[J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2015, 43(12):42-47. | |
| 27 | Liu P, Zhang W. A fault diagnosis intelligent algorithm based on improved BP neural network[J]. International Journal of Pattern Recognition & Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(9):50-56. |
| [1] | Yong-jie MA,Min CHEN. Dynamic multi⁃objective optimization algorithm based on Kalman filter prediction strategy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(6): 1442-1458. |
| [2] | Han HUANG,Qing-hao YAN,Zhi-xin XIANG,Xin-tao YANG,Jin-bao CHEN,Shu-cai XU. Crashworthiness investigation and optimization of bionic multi⁃cell tube based on shrimp chela [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 716-724. |
| [3] | Bin-xiang JIANG,Tong-tong JIANG,Yong-lei WANG. Optimization of consensus algorithm for drug detection block chain based on cultural genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(3): 684-692. |
| [4] | Li-jie ZHANG,Xi-ta A,Xiao TIAN,Wen LI. Multi⁃objective optimization design of accelerated degradation test based on Gamma process [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(2): 361-367. |
| [5] | Bao-feng SUN,Xin-xin REN,Zai-si ZHENG,Guo-yi Li. Multi⁃objective flow shop optimal scheduling considering worker's load [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 900-909. |
| [6] | Bing-hai ZHOU,Zhao-xu HE. Static semi⁃kitting strategy⁃based multi⁃objective just⁃in⁃time material distribution scheduling [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(3): 910-916. |
| [7] | Ji-cheng HUANG,Cheng SHEN,Ai-min JI,Xian-wang LI,Bin ZHANG,Kun-peng TIAN,Hao-lu LIU. Optimization of cutting⁃conveying key working parameters of hemp harvester [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 772-780. |
| [8] | Bing-hai ZHOU,Qiong WU. Balancing and bi⁃objective optimization of robotic assemble lines [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [9] | Fang-wu MA,Li HAN,Liang WU,Jin-hang LI,Long-fan YANG. Damping optimization of heavy⁃loaded anti⁃vibration platform based on genetic algorithm and particle swarm algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1608-1616. |
| [10] | Xue-shen CHEN,Tao CHEN,Tao WU,Xu MA,Ling-chao ZENG,Lin-tao CHEN. Design and experiment on harvester for winter planting potato of straw coverage [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 749-757. |
| [11] | Yin-ping LI,Tian-xu JIN,Li LIU. Design and dynamic characteristic simulation of pantograph⁃catenary continuous energy system for pure electric LHD [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(2): 454-463. |
| [12] | Fang-wu MA,Hong-yu LIANG,Ying ZHAO,Meng YANG,Yong-feng PU. Multi⁃objective crashworthiness optimization design of concave triangles cell structure with negative Poisson′s ratio [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 29-35. |
| [13] | Zhong-yi CAI,Fan-xiang MENG,Qing-min CHEN,Xuan ZHAO. Preform optimization for near-net-shape forming process of complex knuckle forging [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(1): 84-90. |
| [14] | Fu-chun JIA,Xian-jie MENG,Yu-long LEI. Optimal design of two degrees of freedom dynamic vibration absorber based on multi-objective genetic algorithm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1969-1976. |
| [15] | QIU Xiao-ming, WANG Yin-xue, YAO Han-wei, FANG Xue-qing, XING Fei. Multi-objective optimization of resistance spot welding parameters for DP1180/DP590 using grey relational analysis based Taguchi [J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1147-1152. |
|
||