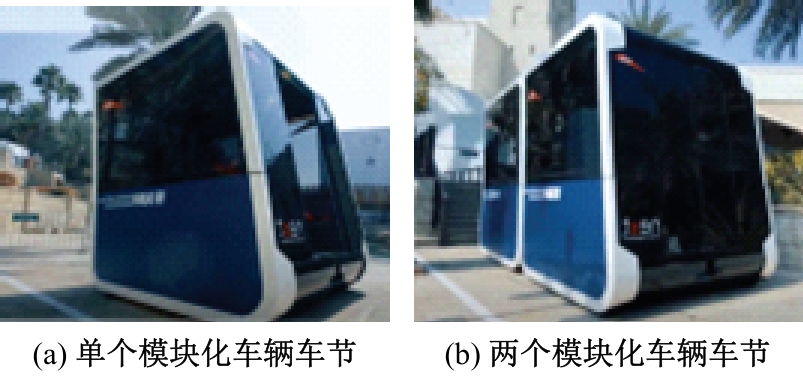
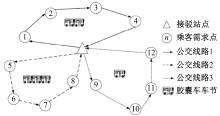
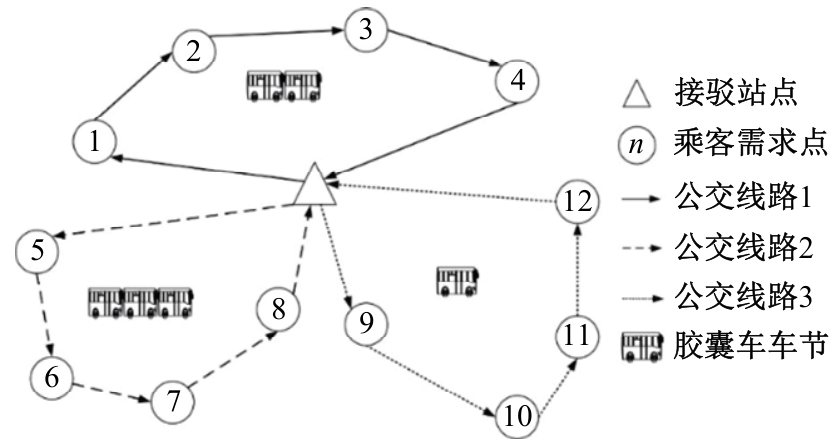
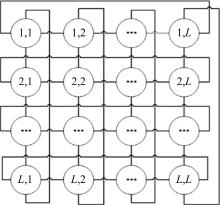
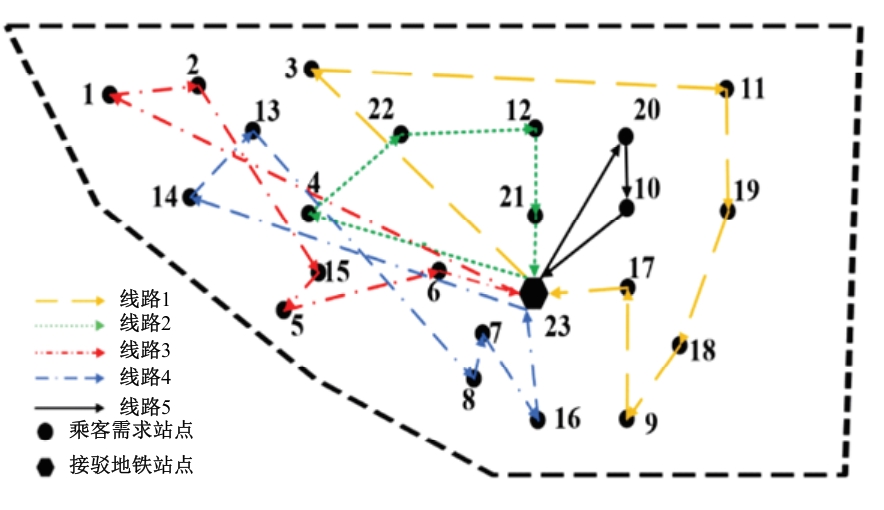
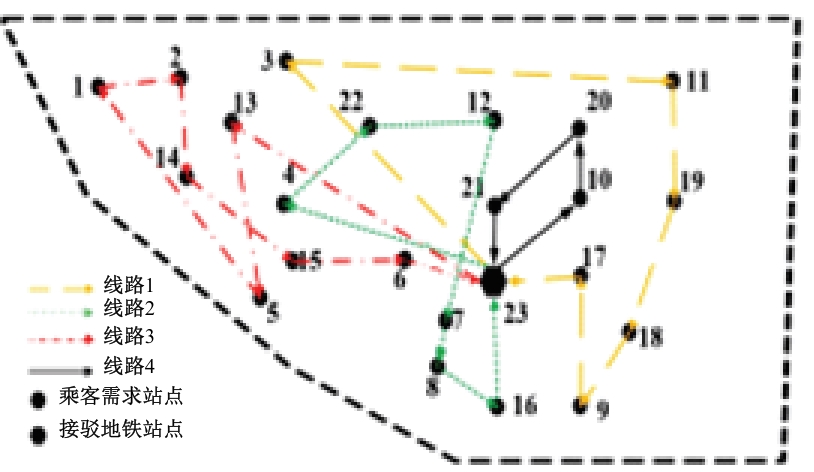
Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 55 ›› Issue (2): 537-545.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20230515
Optimization study of zonal-based flexible feeder bus routes based on modular vehicle system
Tian-yang GAO( ),Da-wei HU(
),Da-wei HU( ),Rui-sen JIANG,Xue WU,Hui-tian LIU
),Rui-sen JIANG,Xue WU,Hui-tian LIU
- College of Transportation Engineering,Chang'an University,Xi'an 710064,China
CLC Number:
- U491
| 1 | 苗一迪. 柔性路径公交车服务区域的决策模型研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学经济管理学院, 2011. |
| Miao Yi-di. A decision-making model for determining the service area of a flexible-route bus[D]. Dalian: Economics and Management School, Dalian University of Technology, 2011. | |
| 2 | 靳文舟, 胡为洋, 邓嘉怡, 等. 基于混合算法的需求响应公交灵活调度模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 49(1): 123-133. |
| Jin Wen-zhou, Hu Wei-yang, Deng Jia-yi, et al. Flexible scheduling model of demand responsive transit based on hybrid algorithm[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(1): 123-133. | |
| 3 | Huang A L, Dou Z Q, Qi L Z, et al. Flexible route optimization for demand-responsive public transit service[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering, Part A: Systems, 2020, 146(12): 1-15. |
| 4 | Melis L, Sörensen K. The static on-demand bus routing problem: large neighborhood search for a dial-a-ride problem with bus station assignment[J]. International Transactions in Operational Research, 2022, 29(3): 1417-1453. |
| 5 | 孙继洋, 黄建玲, 陈艳艳, 等. 面向多目标站的灵活型公交路径优化调度模型[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2019, 19(6): 105-111. |
| Sun Ji-yang, Huang Jian-ling, Chen Yan-yan, et al. Flexible bus route optimization scheduling model for multi-target stations[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2019, 19(6): 105-111. | |
| 6 | 孙继洋, 黄建玲, 陈艳艳, 等. 响应动态需求的灵活型公交路径优化调度模型[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2021, 47(3): 269-279. |
| Sun Ji-yang, Huang Jian-ling, Chen Yan-yan, et al. Flexible bus route optimal scheduling model in response to dynamic demand[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2021, 47(3): 269–279. | |
| 7 | Sun Q, Chien S, Hu D W, et al. Optimizing multi-terminal customized bus service with mixed fleet[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 156456-156469. |
| 8 | 汪怡然, 陈景旭, 王岳平, 等. 考虑服务公平性的定制公交动态响应方案[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2022, 52(11): 2574-2581. |
| Wang Yi-ran, Chen Jing-xu, Wang Yue-ping, et al. Instant demand-responsive scheme for customized bus considering service fairness[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022, 52(11): 2574-2581. | |
| 9 | 孙倩, 胡大伟, 钱一之, 等. 考虑车辆随机到站时间的动态需求响应型接驳公交线路优化[J]. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2022, 22(5): 196-204. |
| Sun Qian, Hu Da-wei, Qian Yi-zhi, et al. Dynamic bus routing optimization for demand-responsive feeder transit considering stochastic bus arrival time[J]. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(5): 196-204. | |
| 10 | 杨明, 黄乐. 面向早高峰通勤客流的多车型定制公交线网优化[J]. 长沙理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 17(3): 71-78. |
| Yang Ming, Huang Le. Network optimization of multi-vehicle-type customized bus for commuting demand during morning peak hour[J]. Journal of Changsha University of Science & Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 17(3): 71-78. | |
| 11 | 裴明阳. 灵活公共交通系统营运调度模型与方法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学交通学院, 2020. |
| Pei Ming-yang. Operational design models for flexible transit systems[D]. Guangzhou: School of Transportation, South China University of Technology, 2020. | |
| 12 | Ji Y X, Liu B, Shen Y, et al. Scheduling strategy for transit routes with modular autonomous vehicles[J]. International Journal of Transportation Science and Technology, 2021, 10: 121-135. |
| 13 | 范文博, 陈香, 刘涛. 模块化自动驾驶穿梭公交服务频率优化及时刻表设计[J]. 交通运输工程与信息学报, 2023, 21(2): 160-176. |
| Fan Wen-bo, Chen Xiang, Liu Tao. Modular autonomous shuttle transit service: frequency setting and timetabling[J]. Journal of Transportation Engineering and Information, 2023, 21(2): 160-176. | |
| 14 | Dai Z, Liu X Y, Chen X, et al. Joint optimization of scheduling and capacity for mixed traffic with autonomous and human-driven buses: a dynamic programming approach[J]. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2020, 114: 598-619. |
| 15 | Pei M Y, Lin P Q, Du J, et al. Vehicle dispatching in modular transit networks: a mixed-integer nonlinear programming model[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2021, 147: 102240. |
| 16 | Liu X H, Qu X B, Ma X L. Improving flex-route transit services with modular autonomous vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2021, 149: 102331. |
| 17 | 吴典文, 彭宇, 田奇, 等. 基于停靠站选址的响应型接驳公交调度优化[J]. 公路工程, 2021, 46(5): 176-182. |
| Wu Dian-wen, Peng Yu, Tian Qi, et al. Scheduling optimization for responsive feeder transit based on the stop location[J]. Highway Engineering, 2021, 46(5): 176-182. |
| [1] | Yi-yong PAN,Yi-wen YOU,Jing-ting WU. Analysis of heterogeneity and transferability of factors influencing severity of lane change accidents [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 520-528. |
| [2] | Yao SUN,Bao-zhen YAO,Zi-jian BAI. Evaluate the validity of traffic congestion dispersion based on random forest method [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 512-519. |
| [3] | Fa-cheng CHEN,Guang-quan LU,Qing-feng LIN,Hao-dong ZHANG,She-qiang MA,De-zhi LIU,Hui-jun SONG. Review of drivers' takeover behavior in conditional automated driving [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(2): 419-433. |
| [4] | Rong-han YAO,Wen-yan QI,Hong-yu HU,Xiao-jing DU,Yan-feng QIAO,Li-bing WANG. Multi-lane cellular automata model considering bus-high occupancy vehicle lane [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2025, 55(1): 162-174. |
| [5] | De-lin LI,Jun-xian CHEN,Yong-gang WANG,Lu WANG,Zhao-qing SHEN. Identification of driving behavior on steep sharp curves based on latent class model [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(12): 3526-3533. |
| [6] | Yi-yong PAN,Jing-ting WU,Xuan-ye Miao. Temporal instability analysis of factors affecting injury severities of elderly drivers [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2819-2826. |
| [7] | Jin XU,Zheng-huan CHEN,Qi-shuo LIAO,Zhan-ji ZHENG,He-shan ZHANG. Mental workload of drivers at high-density interchanges of freeways based on ECG data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2807-2818. |
| [8] | Hui-ying WEN,Zi-qi HE,Qiu-ling LI,Sheng ZHAO. Traffic conflict prediction and influencing factors analysis of truck lane change on expressway [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(10): 2827-2836. |
| [9] | Chun-jiao DONG,Yu-xiao LU,She-qiang MA,Peng-hui LI. Identification of E⁃bike violation behaviors by considering waiting tolerance time [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2540-2546. |
| [10] | Chang-jiang ZHENG,Tong-tong TAO,Zhi-chao CHEN. Cascading failure model based on adjustable redistribution of traffic flow [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2441-2450. |
| [11] | Xi-zhen ZHOU,He GONG,Dun-dun LI,Yan-jie JI,Jie YAN. Nonlinear model for impact of built environment on curb parking spaces occupancy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2520-2530. |
| [12] | Li-xin YAN,Tao ZENG,Yi HE,Jun-hua GUO,Xin-hui HU. Man-machine takeover behavior sequence coding and analysis of shared driving intelligent vehicle [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2547-2556. |
| [13] | Na ZHANG,Feng CHEN,Jian-po WANG,Ya-di ZHU. Recognition of travel patterns for urban rail transit passengers based on spatiotemporal sequence similarity [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2588-2599. |
| [14] | Rong-gui ZHOU,Pei GAO,Yu-xuan LI,Jian ZHOU. Abnormal driving behavior thresholds of highway minibuses based on trajectory data [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(9): 2581-2587. |
| [15] | Da-yi QU,Hao-min LIU,Zi-yi YANG,Shou-chen DAI. Dynamic allocation mechanism and model of traffic flow in bottleneck section based on vehicle infrastructure cooperation [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(8): 2187-2196. |
|
||