吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 49 ›› Issue (6): 1437-1444.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20230605
川芎嗪对胶质瘤干细胞裸鼠皮下移植瘤生长、TGF-β信号通路和上皮-间质转化的影响
- 河南大学淮河医院神经外科, 河南 开封 475000
Influence of ligustrazine on growth of glioma stem cells subcutaneous xenografts in nude mice, TGF-β signaling pathway, and epithelial-mesenchymal transiton
Tao HE( ),Zhenjiang LI,Bingqian DING
),Zhenjiang LI,Bingqian DING
- Huaihe Hospital of Henan University Neurosurgery Department,Kaifeng 475000,China
摘要:
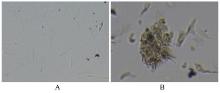
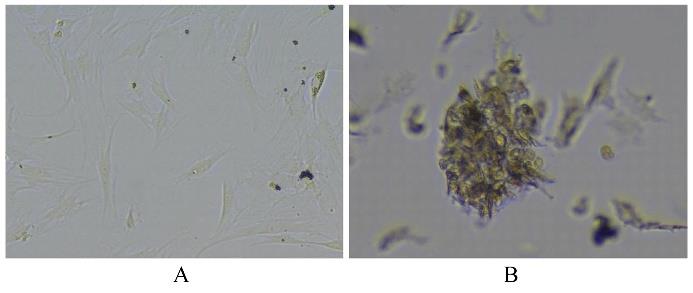
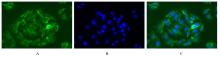
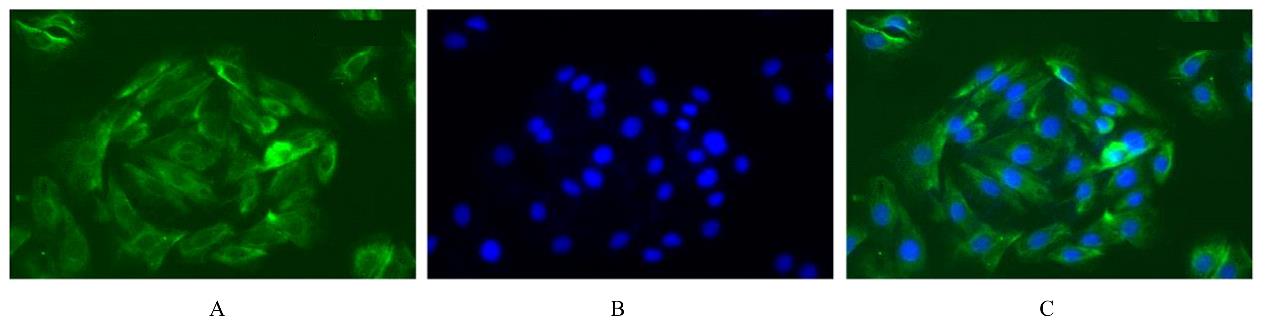
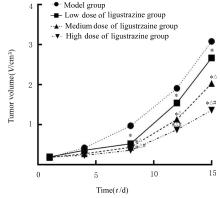
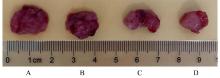
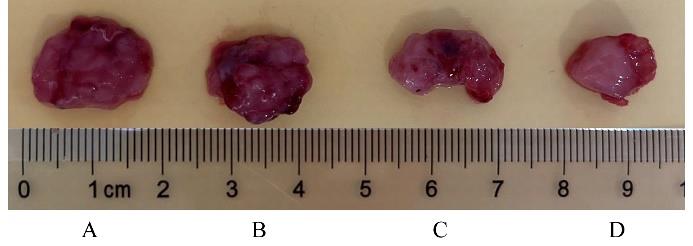
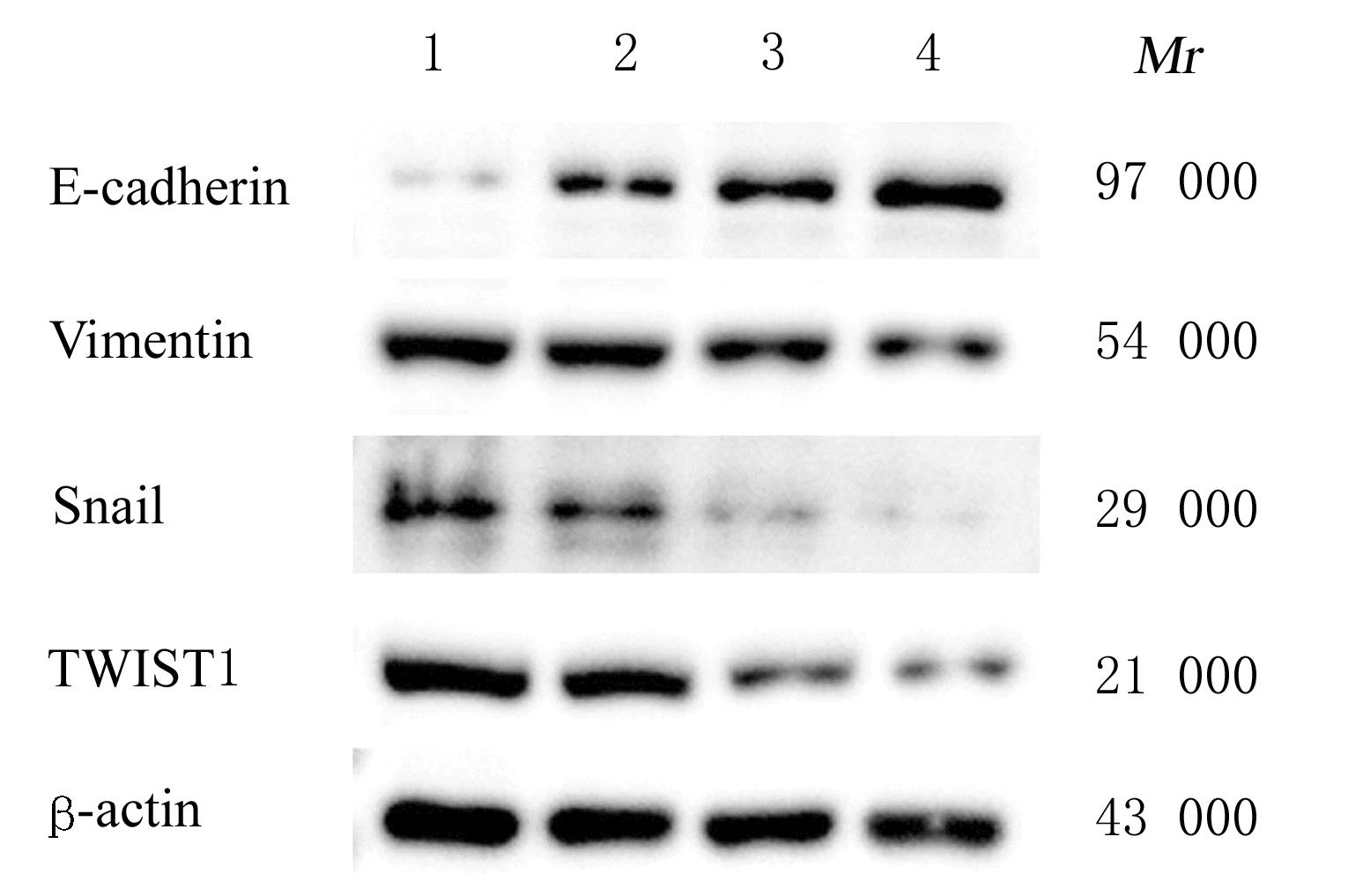
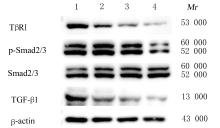
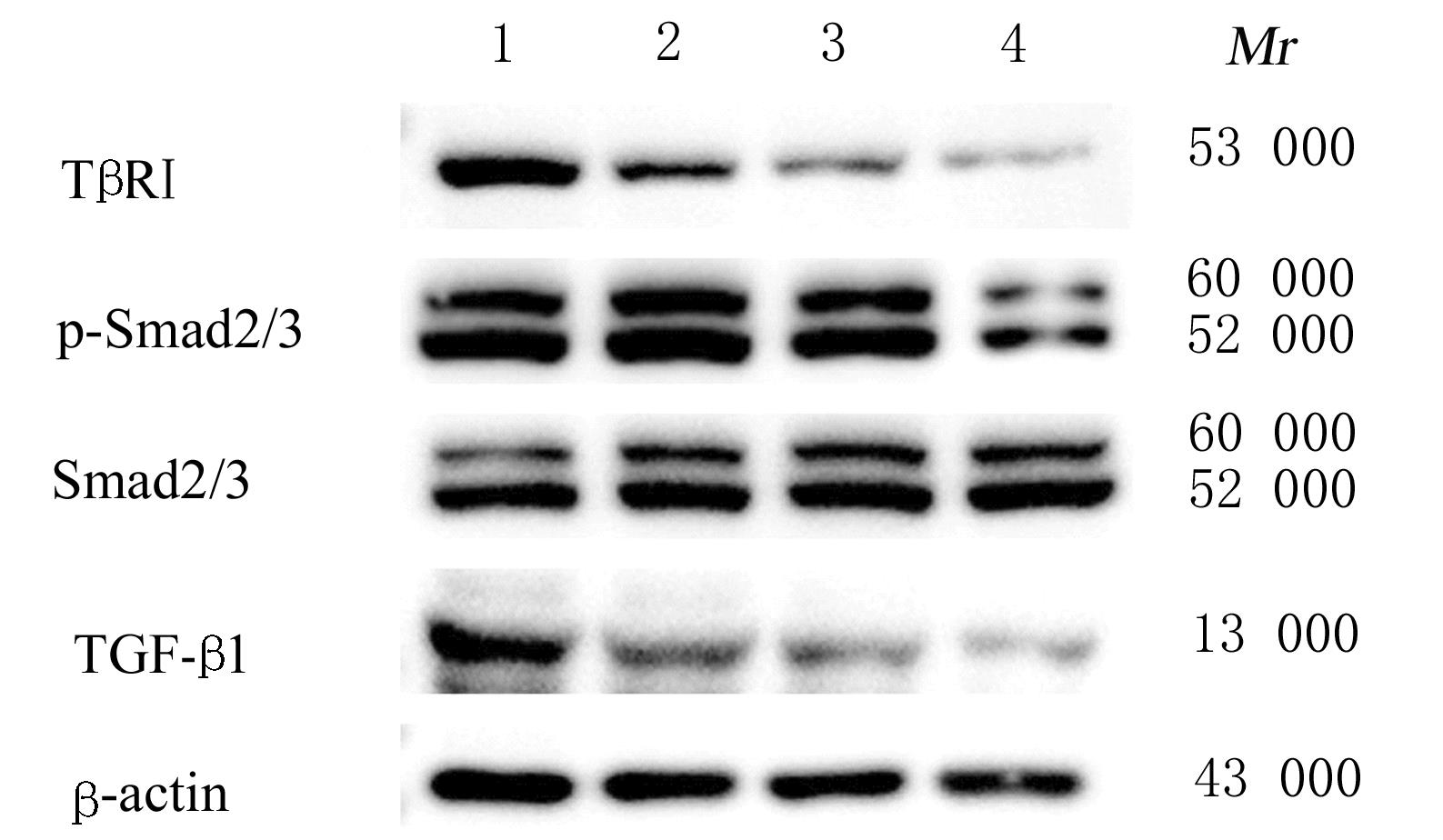
目的 探讨川芎嗪对胶质瘤干细胞(GSCs)裸鼠皮下移植瘤生长、转化生长因子β(TGF-β)信号通路和上皮-间质转化(EMT)的影响,为胶质瘤临床治疗药物的选择提供参考。 方法 收集人脑胶质瘤细胞系U87细胞,培养、分离、富集并鉴定GSCs。40只雌性BALB/c裸鼠,建立GSCs裸鼠皮下移植瘤模型,成模后随机分为模型组和低、中及高剂量川芎嗪组,每组10只。低、中和高剂量川芎嗪组裸鼠每3 d腹腔注射给药1次,给药剂量分别为1.5、3.0和6.0 mg·kg-1,模型组裸鼠仅腹腔注射等量生理盐水,连续15 d。测量各组裸鼠移植瘤体积,称瘤质量,计算瘤质量抑制率,绘制肿瘤生长曲线。HE染色观察各组裸鼠肿瘤组织病理形态表现,实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测各组裸鼠肿瘤组织中TGF-β1和TGF-β受体Ⅰ(TβRⅠ) mRNA表达水平,Western blotting法检测各组裸鼠肿瘤组织中TGF-β1、TβRⅠ、母亲DPP同源物2/3(Smad2/3)、磷酸化Smad2/3(p-Smad2/3)、E-钙黏蛋白(E-cadherin)、TWIST家族bHLH转录因子1(TWIST1)、波形蛋白(Vimentin)及锌指蛋白(Snail)表达水平。 结果 在U87细胞中成功富集并分离获得GSCs,免疫荧光染色可见干细胞标志物CD133阳性表达。与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量川芎嗪组裸鼠移植瘤体积均减小(P<0.05),且呈剂量依赖性;移植瘤质量均降低(P<0.05),且呈剂量依赖性;低、中和高剂量川芎嗪组瘤质量抑制率逐渐增大,分别为12.72%、39.90%和55.36%。HE染色观察,模型组裸鼠肿瘤组织细胞形态良好,连接紧密,生长密度高,核异型性明显;低、中和高剂量川芎嗪组裸鼠肿瘤组织结构紊乱,细胞密度逐渐降低,核固缩和核裂解逐渐明显,组织坏死区逐渐增大,且随着川芎嗪剂量的增加,上述改善逐渐明显。RT-qRCR法检测,与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量川芎嗪组裸鼠移植瘤组织中TGF-β1和TβRⅠ mRNA表达水平均降低(P<0.05),且呈剂量依赖性。Western blotting法检测,与模型组比较,低、中和高剂量川芎嗪组裸鼠皮下移植瘤组织中E-cadherin蛋白表达水平均升高(P<0.05),TWIST1、Vimentin、Snail、TGF-β1、TβRⅠ和p-Smad2/3蛋白表达水平均降低(P<0.05),且呈剂量依赖性。 结论 川芎嗪可发挥对GSCs裸鼠皮下移植瘤生长的抑制作用,同时可干扰TGF-β1/Smad2/3信号激活和EMT诱导。
中图分类号:
- R285.5