吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (4): 1109-1115.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240425
lncRNA H19和IGF2基因在乳腺癌组织中的表达水平及印记状态
- 1.吉林大学第一医院普外科中心乳腺外科,吉林 长春 130021
2.吉林大学第一医院肿瘤中心 器官再生与移植教育部重点实验室,吉林 长春 130061
Expression levels and imprinting status of lncRNA H19 and IGF2 genes in breast cancer tissue
Xue WEI1,Xue WEN2,Xiao XIE1,Yueyuan WANG1,Dan HUANG1,Ming YANG1( )
)
- 1.Department of Breast Surgery,General Surgery Center,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2.Key Laboratory of Organ Regeneration and Transplantation,Ministry of Education,Cancer Center,First Hospital,Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China
摘要:
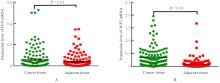
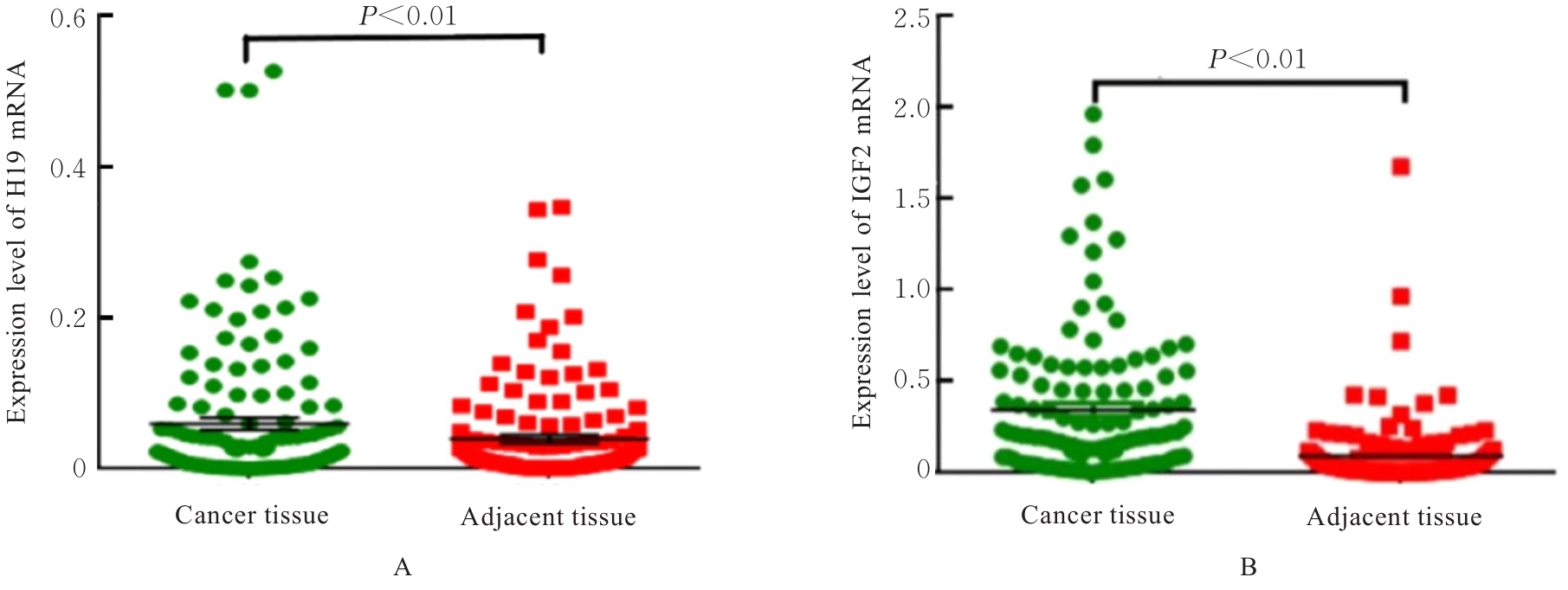
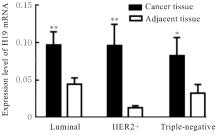
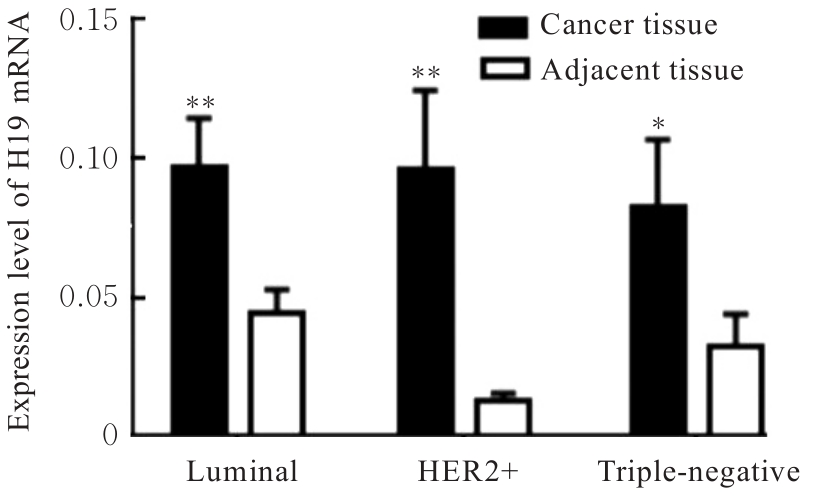
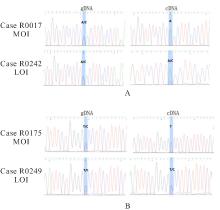
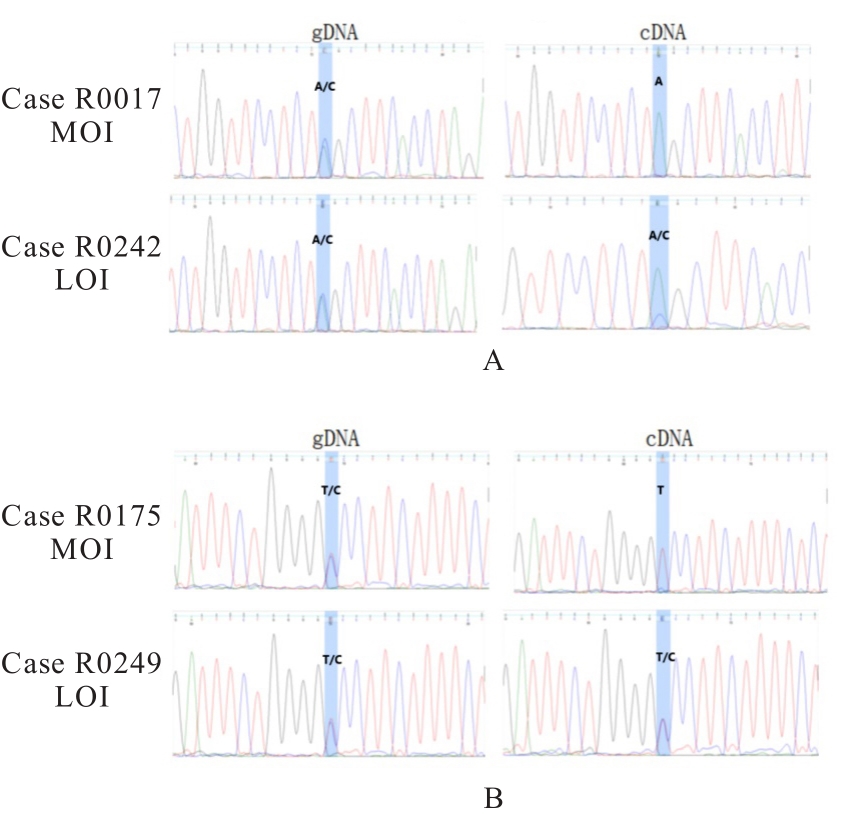
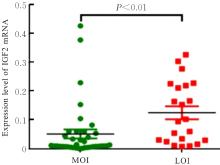
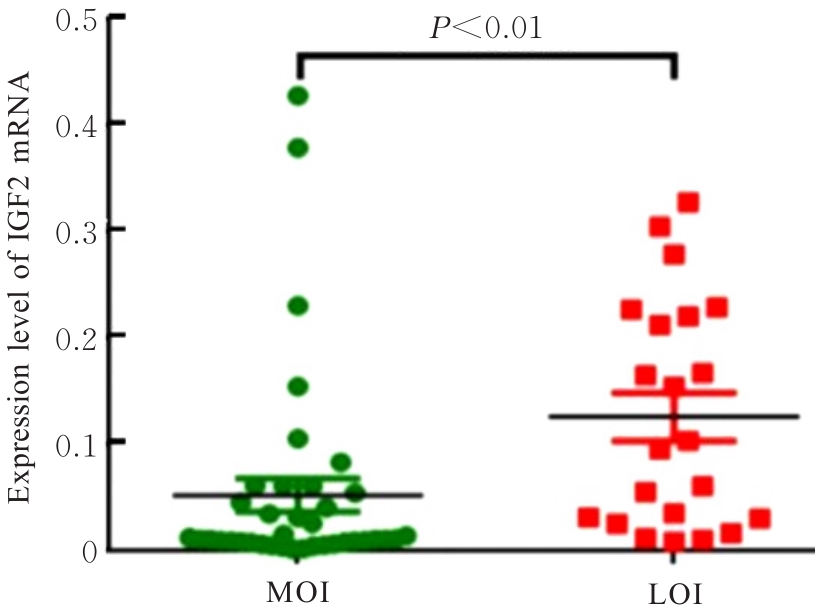
目的 研究长链非编码RNA(lncRNA) H19和胰岛素样生长因子2(IGF2)基因在乳腺癌组织中的表达水平,分析其印记状态。 方法 采用实时荧光定量PCR(RT-qPCR)法检测乳腺癌组织及癌旁组织中H19和IGF2 mRNA表达水平,分析H19和IGF2 mRNA在乳腺癌组织及癌旁组织中的表达差异,利用单核苷酸多态性(SNP)区分等位基因表达情况(纯合或杂合),基因组DNA中IGF2(ApaⅠ位点)或H19(AluⅠ位点)为杂合则进行印记分析,确定H19和IGF2在乳腺癌组织中的印记状态,即印记保持(MOI)或印记丢失(LOI)。分析乳腺癌组织中H19和IGF2表达与分子分型的关系。 结果 RT-qPCR法检测,乳腺癌组织中H19和IGF2 mRNA表达水平高于癌旁组织(P<0.01),H19 mRNA表达水平与IGF2 mRNA表达水平呈正相关关系(r=0.567,P<0.01)。不同分子分型乳腺癌患者癌组织中H19 mRNA表达水平均高于癌旁组织(P<0.05或P<0.01)。H19和IGF2在乳腺癌组织中均存在LOI,IGF2 的LOI发生率为36.7%,高于H19的LOI发生率(4.3%)。RT-qPCR法检测,IGF2 LOI组乳腺癌组织中IGF2 mRNA表达水平明显高于IGF2 MOI组(P<0.01)。 结论 乳腺癌组织中H19和IGF2 mRNA表达水平明显高于癌旁组织,IGF2的LOI发生率高于H19的LOI发生率,IGF2的LOI可能是乳腺癌发病的关键因素之一。
中图分类号:
- R737.9