吉林大学学报(医学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (6): 1565-1571.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20240610
• 基础研究 • 上一篇
人参皂苷Rh1通过激活Nrf2/HO-1信号通路对糖尿病小鼠肾脏损伤的改善作用
曲萌1,黄睿2,鞠欣达2,刘雨昕2,夏吉辰3,黄佳欣2,于春艳2,董志恒2( )
)
- 1.北华大学基础医学院生物化学与分子生物学教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
2.北华大学基础医学院病理学教研室,吉林 吉林 132013
3.吉林省吉林市中心医院骨科,吉林 吉林 132011
Ameliorative effect of ginsenoside Rh1 on kidney injury in diabetic mice through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
Meng QU1,Rui HUANG2,Xinda JU2,Yuxin LIU2,Jichen XIA3,Jiaxin HUANG2,Chunyan YU2,Zhiheng DONG2( )
)
- 1.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
2.Department of Pathology,School of Basic Medical Sciences,Beihua University,Jilin 132013,China
3.Department of Orthopaedics,Central Hospital,Jilin City,Jilin Province,Jilin 132011,China
摘要:
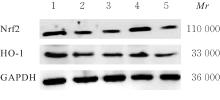
目的 探讨人参皂苷Rh1对糖尿病(DM)小鼠肾损伤的保护作用,并阐明其作用机制。 方法 应用高脂高糖饲养佐以腹腔注射链脲佐菌素(STZ)法制备糖尿病肾脏疾病(DKD)模型。将48只C57/BL6成模小鼠随机分为模型组、核因子红细胞2相关因子2(Nrf2)抑制剂ML385组(ML385组)(30 mg·kg-1 ML385)、人参皂苷Rh1组(G-Rh1组)(30 mg·kg-1人参皂苷Rh1)和G-Rh1+ML385组(30 mg·kg-1 人参皂苷Rh1+30 mg·kg-1 ML385),每组12只,另外12只C57/BL6小鼠作为对照组。作用8周后,全自动分析仪检测各组小鼠血清中空腹血糖(FBG)、尿素氮(BUN)和血肌酐(Scr)水平及尿液中24 h尿蛋白(24 h UP)水平,并计算肾脏指数。试剂盒检测各组小鼠肾组织中超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)活性及丙二醛(MDA)水平,Western blotting法检测各组小鼠肾组织中Nrf2和血红素加氧酶1(HO-1)蛋白表达水平。 结果 与对照组比较,模型组、ML385组和G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠血清中FBG水平和肾脏指数均明显升高(P<0.01),G-Rh1组小鼠血清中FBG水平明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,ML385组小鼠肾脏指数明显升高(P<0.05),G-Rh1组小鼠FBG水平和肾脏指数均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与G-Rh1组比较,G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠FBG水平和肾脏指数均明显升高(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,模型组、ML385组、G-Rh1组和G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠血清中BUN和Scr水平及尿液中24 h UP水平均明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,ML385组小鼠血清中BUN水平及尿液中24 h UP水平均明显升高(P<0.05),G-Rh1组小鼠血清中BUN和Scr水平及尿液中24 h UP水平均明显降低(P<0.01);与G-Rh1组比较,G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠血清中BUN和Scr水平及尿液中24 h UP水平均明显升高(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,模型组、ML385组、G-Rh1组和G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠肾组织中SOD活性均明显降低(P<0.01),MDA水平和LDH活性均明显升高(P<0.01);与模型组比较,ML385组小鼠肾组织中SOD活性明显降低(P<0.05),MDA水平明显升高(P<0.05),G-Rh1组小鼠肾组织中SOD活性明显升高(P<0.01),MDA水平和LDH活性均明显降低(P<0.01);与G-Rh1组比较,G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠肾组织中SOD活性明显降低(P<0.01),MDA水平和LDH活性均明显升高(P<0.01)。与对照组比较,模型组、ML385组、G-Rh1组和G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠肾组织中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05或P<0.01);与模型组比较,ML385组和G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠肾组织中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.05),G-Rh1组小鼠肾组织中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平均明显升高(P<0.01);与G-Rh1组比较,G-Rh1+ML385组小鼠肾组织中Nrf2和HO-1蛋白表达水平均明显降低(P<0.01)。 结论 人参皂苷Rh1可降低氧化应激,改善肾功能,对DM小鼠肾脏损伤具有保护作用,其作用机制可能与激活Nrf2/HO-1信号通路有关。
中图分类号:
- R285.5