Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 48 ›› Issue (6): 1375-1381.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20220601
• Research in basic medicine • Next Articles
Effect of lateral parabrachial nucleus chemical lession on fever induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats
Wenmin GAO,Tianhui HE,Lan YAO,Hanghong WU,Zhenwei CHEN,Yupei LAI,Jianhui XU,Jie ZHANG( )
)
- Key Laboratory of Thermoregulation and Inflammation of Sichuan Higher Education Institutes,Chengdu Medical College,Chengdu 610500,China
-
Received:2022-03-04Online:2022-11-28Published:2022-12-07 -
Contact:Jie ZHANG E-mail:zhangjiefa8888@126.com
CLC Number:
- R364.6
Cite this article
Wenmin GAO,Tianhui HE,Lan YAO,Hanghong WU,Zhenwei CHEN,Yupei LAI,Jianhui XU,Jie ZHANG. Effect of lateral parabrachial nucleus chemical lession on fever induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1375-1381.
share this article
Tab.1
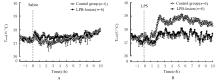
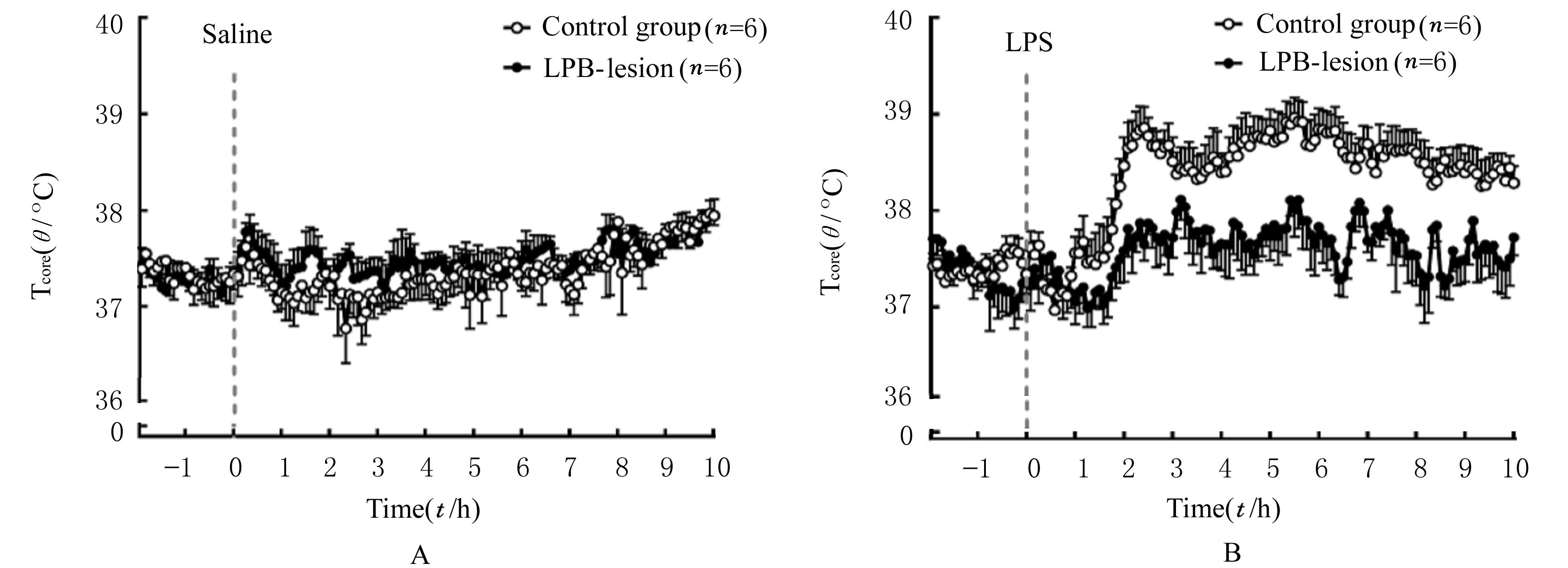
Tcore of rats in and control group and LPB-lesion group at different time points after intraperitoneal injection of saline and LPS (n=6,x±s,T/°C)"
| Group | Tcore | Tcore | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 2.5 h after treated with saline | 5.5 h after treated with saline | Baseline | 2.5 h after treated with LPS | 5.5 h after treated with LPS | |
| Control | 37.34±0.17 | 37.22±0.10 | 37.40±0.10 | 37.34±0.08 | 38.78±0.16△ | 38.97±0.21△ |
| LPB-lesion | 37.28±0.18 | 37.29±0.15 | 37.35±0.20 | 37.27±0.16 | 37.75±0.11* | 38.23±0.24*△ |
Tab. 2
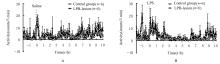
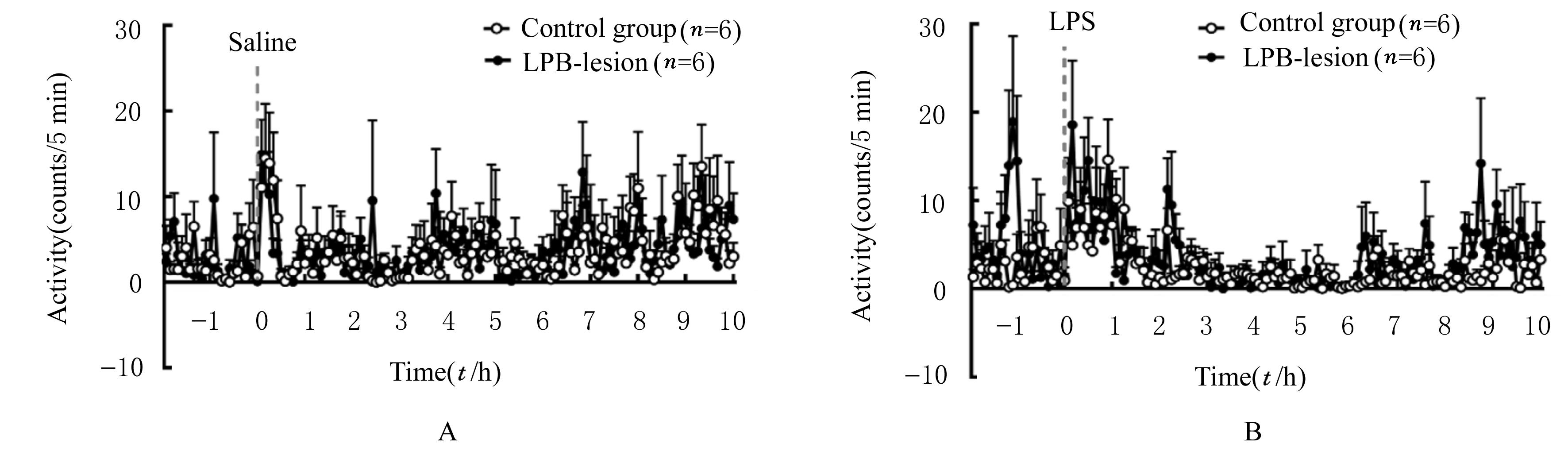
Activities of rats in control group and LPB-lesion group at different time points after intraperitoneal injection of saline and LPS (n=6,x±s)"
| Group | Activity | Activity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 2.5 h after treated with saline | 5.5 h after treated with saline | Baseline | 2.5 h after treated with LPS | 5.5 h after treated with LPS | |
| Control | 0.67±0.52 | 0.00±0.00 | 2.80±1.23 | 0.93±0.72 | 1.73±0.91 | 1.70±1.13 |
| LPB-lesion | 0.10±0.07 | 1.17±0.52 | 0.80±0.55 | 1.37±1.06 | 1.47±0.66 | 1.30±0.71 |
| 1 | NAKAMURA K. Afferent pathways for autonomic and shivering thermoeffectors[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2018, 156: 263-279. |
| 2 | MORRISON S F, NAKAMURA K. Central mechanisms for thermoregulation[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2019, 81: 285-308. |
| 3 | NAKAMURA K, NAKAMURA Y, KATAOKA N. A hypothalamomedullary network for physiological responses to environmental stresses[J]. Nat Rev Neurosci, 2022, 23(1): 35-52. |
| 4 | YANG W Z, DU X S, ZHANG W, et al. Parabrachial neuron types categorically encode thermoregulation variables during heat defense[J]. Sci Adv,2020, 6(36): eabb9414. |
| 5 | NORRIS A J, SHAKER J R, CONE A L, et al. Parabrachial opioidergic projections to preoptic hypothalamus mediate behavioral and physiological thermal defenses[J]. eLife, 2021, 10: e60779. |
| 6 | MU D, DENG J, LIU K F, et al. A central neural circuit for itch sensation[J]. Science, 2017, 357(6352): 695-699. |
| 7 | SUN L, LIU R, GUO F, et al. Parabrachial nucleus circuit governs neuropathic pain-like behavior[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 5974. |
| 8 | 张 洁, 林友胜. 臂旁外侧核神经元电生理特性及其在体温调节中的作用[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2013, 42(3): 13-17. |
| 9 | CHENG Y J, XU J H, ZENG R X, et al. The role of prostaglandin E2 synthesized in rat lateral parabrachial nucleus in LPS-induced fever[J]. Neuroendocrinology, 2022, 112(4): 399-416. |
| 10 | SKIBICKA K P, ALHADEFF A L, LEICHNER T M, et al. Neural controls of prostaglandin 2 pyrogenic, tachycardic, and anorexic actions are anatomically distributed[J]. Endocrinology,2011,152(6):2400-2408. |
| 11 | ENGBLOM D,EK M, ERICSSON-DAHLSTRAND A,et al. EP3 and EP4 receptor mRNA expression in peptidergic cell groups of the rat parabrachial nucleus[J]. Neuroscience, 2004, 126(4): 989-999. |
| 12 | 纪晓方, 李伟阳, 杨 琳, 等. 脂多糖通过TLR4参与小鼠脂肪性肝损伤模型炎症反应观察[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2019,54(3):390-394. |
| 13 | REN S C, WANG Y L, YUE F G, et al. The paraventricular thalamus is a critical thalamic area for wakefulness[J]. Science, 2018, 362(6413): 429-434. |
| 14 | ROTH J, BLATTEIS C M. Mechanisms of fever production and lysis: lessons from experimental LPS fever[J]. Compr Physiol, 2014, 4(4): 1563-1604. |
| 15 | 李 军, 刘嘉利, 李尧锋, 等. 鼠妇及其提取物对LPS发热模型大鼠解热作用的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2020, 31(10): 2361-2362. |
| 16 | BLOMQVIST A, ENGBLOM D. Neural mechanisms of inflammation-induced fever[J]. Neuroscientist, 2018, 24(4): 381-399. |
| 17 | MACHADO N L S, BANDARU S S, ABBOTT S B G,et al. EP3R-expressing glutamatergic preoptic neurons mediate inflammatory fever[J].J Neurosci,2020,40(12): 2573-2588. |
| 18 | ESKILSSON A, SHIONOYA K, ENGBLOM D,et al. Fever during localized inflammation in mice is elicited by a humoral pathway and depends on brain endothelial interleukin-1 and interleukin-6 signaling and central EP 3 receptors[J]. J Neurosci, 2021, 41(24): 5206-5218. |
| 19 | ESKILSSON A, MATSUWAKI T, SHIONOYA K, et al. Immune-induced fever is dependent on local but not generalized prostaglandin E 2 synthesis in the brain[J]. J Neurosci, 2017, 37(19): 5035-5044. |
| 20 | ALMEIDA M C, STEINER A A, BRANCO L G S, et al. Neural substrate of cold-seeking behavior in endotoxin shock[J]. PLoS One, 2006, 1(1): e1. |
| 21 | XUE Y W, YANG Y L, TANG Y, et al. In vitro thermosensitivity of rat lateral parabrachial neurons[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2016, 619: 15-20. |
| 22 | XU J H, TANG Y, QI H P, et al. Electrophysiological properties of thermosensitive neurons in slices of rat lateral parabrachial nucleus[J]. J Therm Biol, 2019, 83: 87-94. |
| 23 | 叶梦萍, 綦黄鹏, 薛雅文, 等. 温度对臂旁外侧核神经元胞外放电活动的影响[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2017,46(9): 84-87. |
| [1] | Xuechun DU,Baosheng LI,Shuwei QIAO,Yanzhen OU,Zhen LI,Weiyan MENG. Effect of Porphyromonas gingivalis-LPS on expression levels of ferroptosis-related factors in macrophages [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(5): 1148-1155. |
| [2] | Shuwei QIAO,Baosheng LI,Xiaoyu LI,Zixuan WANG,Birong LI,Bo DONG,Weiyan MENG. Expression levels of SLC7A11 and GPX4 in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts under inflammation and their significance [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(4): 922-928. |
| [3] | Kangning LI,Zhiling SONG,Lilong JIA,Miao CHU,Chaohui XIONG. Anti-inflammatory effect of honeysuckle extract on acute anterior uveitis mice induced by LPS and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(4): 978-983. |
| [4] | Xue BAI,Lu YU,Wenqiang YANG,Xin HE,Xinsheng YANG,Jing YANG. Inhibitory effect of carnosine on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine release in astrocytes and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2021, 47(2): 330-337. |
| [5] | YANG Jiping, FEI Lin, CHAI Xuejun, GOU Xingchun. Inhibitory effect of MyD88 inhibitory peptide on polarization of BV2 microglial cells induced by LPS and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(05): 899-904. |
| [6] | CHEN Zhouhua, GONG Hui, FENG Lei, XIAO Yujie, HUANG Lizhong. Induction of LPS on epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and its effect on β-catenin expression [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2020, 46(02): 309-315. |
| [7] | LIANG Xiaobo, WU Dehong, WANG Xing, ZHANG Yun, WANG Xiaoyun, LI Guoping. Evaluation on mouse models of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease induced by intranasal instillation of cigarette smoke extract and lipopolysaccharide [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1454-1458. |
| [8] | ZHANG Chenhao, LI Yao, LI Zhengyi, LUO Xiaofeng. Protective effect of procyanidine B1 on LPS-induced injury of mouse macrophages RAW264.7 and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2019, 45(06): 1243-1247. |
| [9] | CHI Ming, GAO Ling, WU Weiwei, ZHANG Boru, WANG Lei. Improvement effect of berberine on acute lung injury and inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2018, 44(06): 1194-1199. |
| [10] | CHEN Guobing, WU Jinzhun, LIAN Zhulan, ZHAN Zhuqin, BAI Haitao. Effects of lipopolysaccharide on lung injury and expressions of AQP1 and AQP5 in lung tissue of rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2016, 42(02): 250-254. |
| [11] | YANG Kun, TIAN Zhenzhen, WANG Shuhua, XIU Ming, GUO Xiangling, QI Lina, LI Min, SUN Li, GAO Runping. Effect of LPS-TLR4 pathway in hepatic fibrogenesis of rats with chronic alcohol intake [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(04): 751-755. |
| [12] | ZHANG Min, LIU Lixing, HU Jianzhang. Role of TLR subunits 2 and 4 in pathogenesis of allergic rhinitis in rats [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2015, 41(01): 10-15. |
| [13] | WANG Xin-lei,HU Jie,ZHANG Xiao-tian,DUAN Zi-peng,WANG Huai-dong,LIU Chuan-gui,ZHENG Jing-tong,WANG Fang. Anti-lipopolysaccharide effect of antibacterial traditional Chinese medicine Yinhuamiyanling Tablet in vivo and in vitro [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2014, 40(02): 276-280. |
| [14] | YUAN Ming-zhen,GAO Guang-yuan,LI Bo,DONG Chun-ling,WANG Si-yi, LIANG Hao-jun,LIU Xiang-liang,SUN Xiao-fei. Role of instilled air in establishment of lipopolysaccharide-induced mouse model of acute lung injury [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2013, 39(6): 1089-1093. |
| [15] | YAO Li-yan|HUANG Mei-xiang|ZHONG Quan|ZHENG Yu-qian|LI Da-lan,LUO Kai,YAN Fu-hua. Effects of cyclosporine A and porphyromonas gingivalis-lipopolysaccharide on morphology of |periodontal tissues of rats [J]. J4, 2012, 38(5): 918-922. |
|