Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (3): 691-702.doi: 10.13481/j.1671-587X.20250314
• Research in clinical medicine • Previous Articles
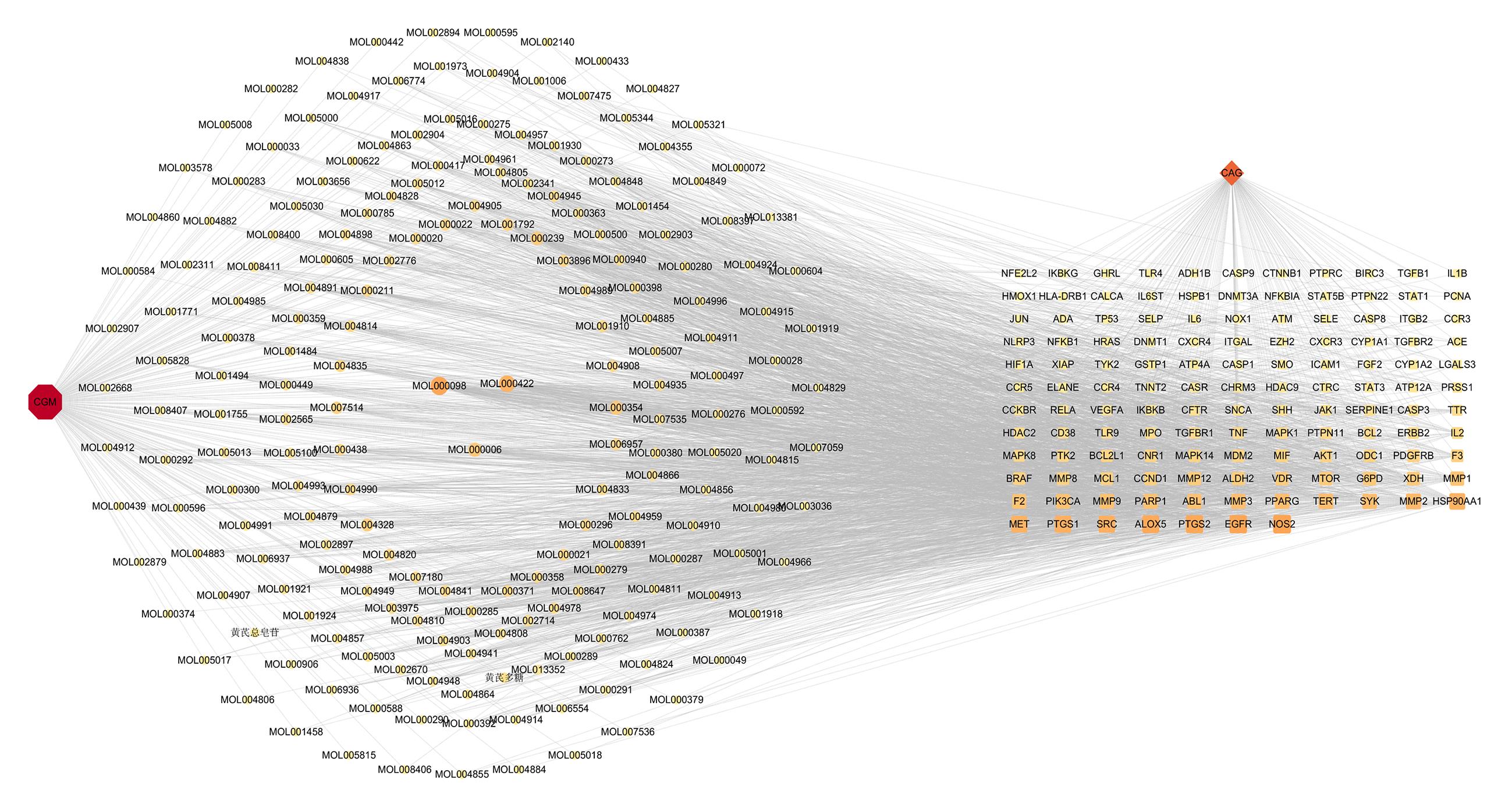
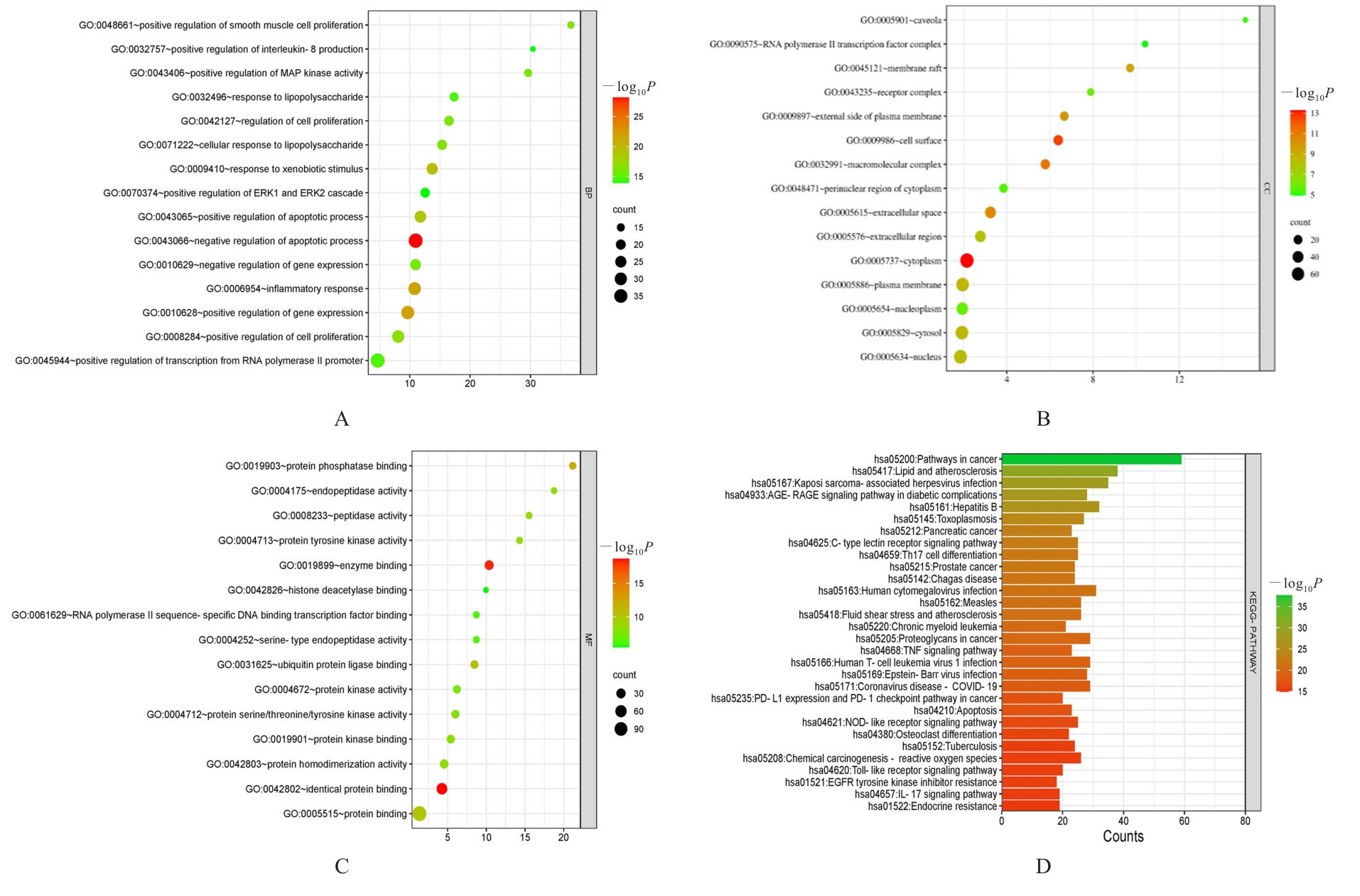
Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of Compound Gastritis Mixture in treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis
Qiuyue WANG,Zhengning YANG,Xiaofeng HUANG,Minghan HUANG( ),Wenrong WANG(
),Wenrong WANG( )
)
- Department of Spleen and Gastroenterology,Second Affiliated People’s Hospital,Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Fuzhou 350003,China
-
Received:2024-06-04Accepted:2024-08-26Online:2025-05-28Published:2025-07-18 -
Contact:Minghan HUANG,Wenrong WANG E-mail:huangminghan2010@163.com;wangwenrong88@sina.com
CLC Number:
- R285.5
Cite this article
Qiuyue WANG,Zhengning YANG,Xiaofeng HUANG,Minghan HUANG,Wenrong WANG. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of Compound Gastritis Mixture in treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis[J].Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2025, 51(3): 691-702.
share this article
Tab.1
Primer sequences"
| Gene | Forward primer(5'—3') | Reverse primer(5'—3') |
|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | TCCAGAACAGATTTGAGAGTAGTG | GCATTTGTGGTTGGGTCAGG |
| TNF | CGGGATCCGAAATTGACACAAGTGGACC | CGGAATTCCTCCCAAATAAATACATTCATCTG |
| AKT1 | CAACTTCTCTGTGGCGCAGTG | GACAGGTGGAAGAACAGCTCG |
| IL-1β | CCAGGGACAGGATATGGAGCA | TTCAACCGCAGGACAGGTACAG |
| EGFR | GGCACTTTTGAAGATCATTTTCTC | CTGTGTTGAGGGCAATGAG |
| GAPDH | TATCATGCGTTCTCCTCAGA | TTTGAAGGCAGTCTGTCGTA |
Tab.2
Common active ingredients of CGM herbs"
| MOLID | Common active ingredient | CGM herbs |
|---|---|---|
| MOL000296 | Hederagenin | Huangqi, Fulin, Ezhu |
| MOL000033 | (3S,8S,9S,10R,13R,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-17-[(2R,5S)-5-propan-2-yloctan-2-yl]-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-ol | Huangqi, Baizhu |
| MOL000449 | Stigmasterol | Dangshen,Peilan, Sharen, Banxia, Sanqi |
| MOL000006 | Luteolin | Dangshen, Peilan |
| MOL007514 | Methyl icosa-11,14-dienoate | Dangshen, Sharen |
| MOL001755 | 24-Ethylcholest-4-en-3-one | Banxia, Sharen |
| MOL000358 | Seta-sitosterol | Sanqi,Banxia, Sharen, Zhike, Baishao |
| MOL000359 | Sitosterol | Chenpi,Peilan,Baishao, Gancao |
| MOL002879 | Diop | Sanqi, Dangshen |
| MOL000098 | Quercetin | Huangqi,Sanqi, Huanglian, Gancao |
| MOL001792 | DFV | Sanqi, Gancao |
| MOL003896 | 7-Methoxy-2-methyl isoflavone | Dangshen, Gancao |
MOL004328 MOL005828 | Naringenin Nobiletin | Chenpi, Zhike |
MOL000239 MOL000354 MOL000417 | Jaranol Isorhamnetin Calycosin | Huangqi, Gancao |
MOL000211 MOL000422 | Mairin kaempferol | Huangqi, Baishao, Gancao |
Tab.3
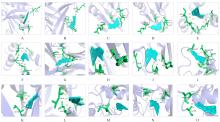
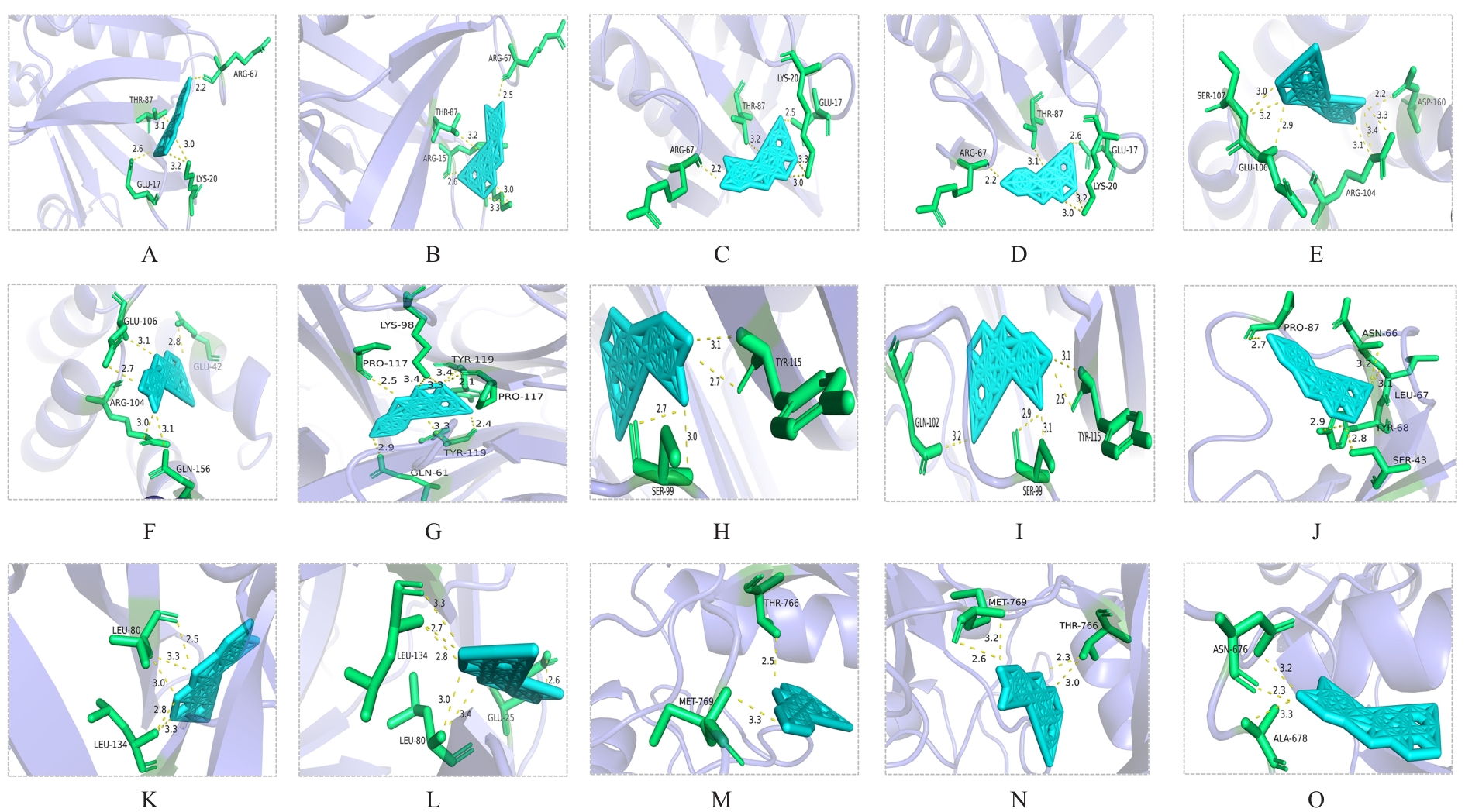
Molecular docking analysis on main herb ingredients and core targets"
| Target | Herb ingredient | Binding energy (kcal·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
IL-6 | Quercetin | -8.0 |
| Kaempferol | -7.7 | |
| Luteolin | -8.0 | |
TNF | Quercetin | -10.1 |
| Kaempferol | -10.9 | |
| Luteolin | -9.7 | |
AKT1 | Quercetin | -8.4 |
| Kaempferol | -8.1 | |
| Luteolin | -8.3 | |
IL-1β | Quercetin | -8.0 |
| Kaempferol | -8.1 | |
| Luteolin | -8.0 | |
EGFR | Quercetin | -7.9 |
| Kaempferol | -8.4 | |
| Luteolin | -8.3 |
Tab.4
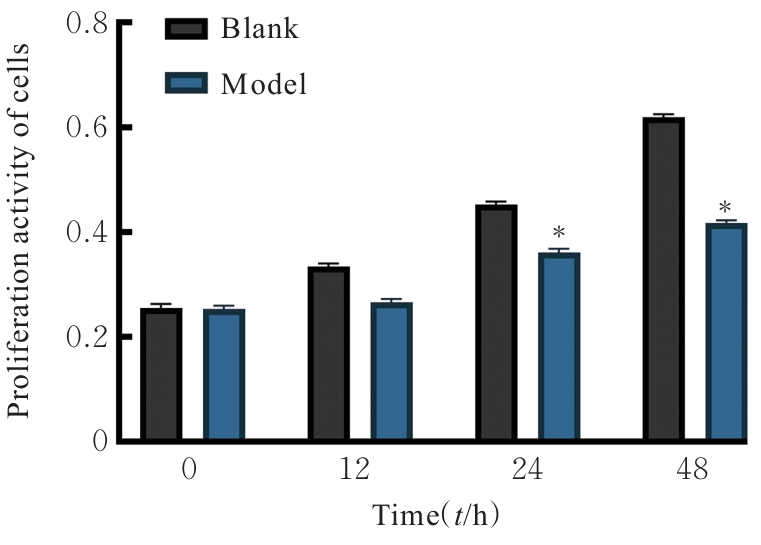
Expression levels of IL-6, TNF, IL-1β, AKT1, and EGFR mRNA in cells in various groups"
| Group | IL-6 mRNA | TNF mRNA | AKT1 mRNA | IL-1β mRNA | EGFR mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 1.00±0.14 | 1.00±0.23 | 1.00±0.18 | 1.00±0.21 | 1.00±0.21 |
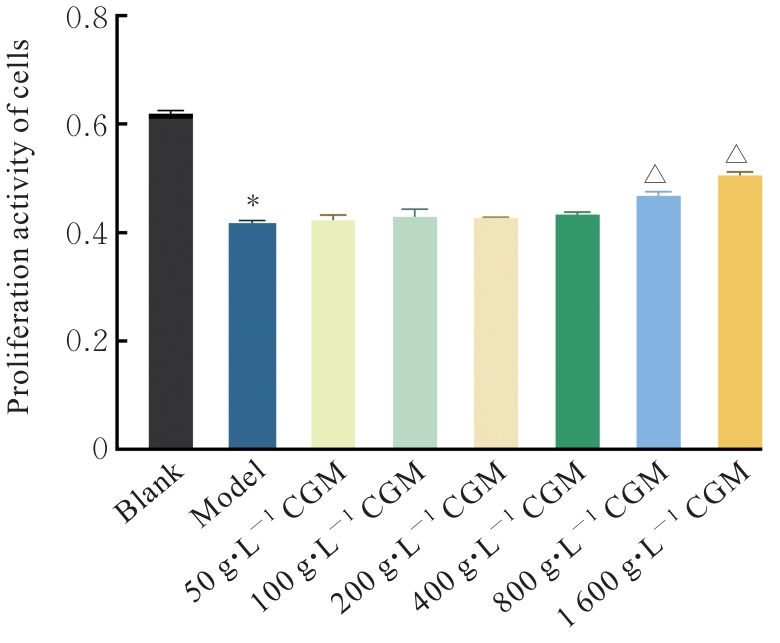
| Model | 3.64±0.75* | 2.19±0.26* | 3.78±0.67* | 5.72±0.66* | 5.72±0.66* |
| CGM | 1.94±0.57△ | 1.79±0.19 | 1.96±0.20△ | 1.84±0.63△ | 2.21±0.72△ |
| [1] | 国家消化系疾病临床医学研究中心(上海), 国家消化道早癌防治中心联盟, 中华医学会消化病学分会幽门螺杆菌学组 等. 中国胃黏膜癌前状态和癌前病变的处理策略专家共识(2020年)[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2020, 40(11): 731-741. |
| [2] | LAHNER E, ZAGARI R M, ZULLO A, et al. Chronic atrophic gastritis: natural history, diagnosis and therapeutic management. A position paper by the Italian Society of Hospital Gastroenterologists and Digestive Endoscopists[AIGO], the Italian Society of Digestive Endoscopy[SIED], the Italian Society of Gastroenterology[SIGE], and the Italian Society of Internal Medicine[SIMI][J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2019, 51(12): 1621-1632. |
| [3] | 王思慈, 李 园, 李 萍, 等. 中医药治疗慢性萎缩性胃炎的多途径作用机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2023, 29(19): 193-202. |
| [4] | 林 平, 黄小燕, 施婧瑶, 等. 慢性胃炎的证素特点[J]. 福建中医药大学学报, 2013, 23(2): 7-9. |
| [5] | 黄铭涵, 黄 健, 李思汉, 等. 复方胃炎合剂逆转胃癌前病变的临床研究[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志, 2016, 23(4): 20-23. |
| [6] | 田琳, 黄铭涵, 李思汉, 等. 从JAK1/STAT3信号通路探讨复方胃炎合剂抑制慢性萎缩性胃炎进展的分子机制[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2021, 35(9): 37-40. |
| [7] | 黄铭涵, 李思汉, 田琳, 等. 基于Sonic Hedgehog通路探讨复方胃炎合剂干预慢性萎缩性胃炎癌前病变的机制[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2021, 41(2): 230-235. |
| [8] | 王子怡, 王 鑫, 张岱岩, 等. 中医药网络药理学: 《指南》引领下的新时代发展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2022, 47(1): 7-17. |
| [9] | RU J L, LI P, WANG J N, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines[J]. J Cheminform, 2014, 6: 13. |
| [10] | KIM S, CHEN J, CHENG T J, et al. PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2021, 49(D1): D1388-D1395. |
| [11] | DAINA A, MICHIELIN O, ZOETE V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(W1): W357-W364. |
| [12] | STELZER G, ROSEN N, PLASCHKES I, et al. The GeneCards suite: from gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses[J]. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics, 2016, 54: 1.30.1-1.30.33. |
| [13] | HAMOSH A, AMBERGER J S, BOCCHINI C, et al. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®): victor McKusick’s magnum opus[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2021, 185(11): 3259-3265. |
| [14] | SZKLARCZYK D, KIRSCH R, KOUTROULI M, et al. The STRING database in 2023: protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2023, 51(D1): D638-D646. |
| [15] | MAJEED A, MUKHTAR S. Protein-protein interaction network exploration using cytoscape[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2023, 2690: 419-427. |
| [16] | SHERMAN B T, HAO M, QIU J, et al. DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021update)[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(W1): W216-W221. |
| [17] | EBERHARDT J, SANTOS-MARTINS D, TILLACK A F, et al. AutoDock vina 1.2.0: new docking methods, expanded force field, and python bindings[J]. J Chem Inf Model, 2021, 61(8): 3891-3898. |
| [18] | 黄铭涵, 何友成, 杨正宁, 等. 国医大师杨春波辨治脾胃湿热证胃肠病经验[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2024, 36(1): 40-45. |
| [19] | QI W D, QI W X, XIONG D W, et al. Quercetin: its antioxidant mechanism, antibacterial properties and potential application in prevention and control of toxipathy[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(19): 6545. |
| [20] | HSIEH H L, YU M C, CHENG L C, et al. Quercetin exerts anti-inflammatory effects via inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-α-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in normal human gastric epithelial cells[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28(11): 1139-1158. |
| [21] | CAMPOS-VIDAL Y, ZAMILPA A, JIMÉNEZ-FERRER E, et al. A mixture of kaempferol-3-O-sambubioside and kaempferol-3-O-sophoroside from Malvaviscus arboreus prevents ethanol-induced gastric inflammation, oxidative stress, and histologic changes[J]. Plants, 2022, 11(21): 2951. |
| [22] | IMRAN M, RAUF A, ABU-IZNEID T, et al. Luteolin, a flavonoid, as an anticancer agent: a review[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 112: 108612. |
| [23] | JAFAR M, SALAHUDDIN M, KHAN M S A, et al. Preparation and in vitro-In vivo evaluation of luteolin loaded gastroretentive microsponge for the eradication of Helicobacter pylori infections[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13(12): 2094. |
| [24] | TANIGUCHI K, KARIN M. IL-6 and related cytokines as the critical lynchpins between inflammation and cancer[J]. Semin Immunol, 2014, 26(1): 54-74. |
| [25] | 汤 淼, 赖运庆, 吴文朝. 细胞因子基因多态性及Hp感染与慢性萎缩性胃炎易感性的关系[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2021, 31(19): 2973-2977. |
| [26] | GONG H Y, HAN D, LUO Z C, et al. Xiangshao Decoction alleviates gastric mucosal injury through NRF2 signaling pathway and reduces neuroinflammation in gastric ulcer rats[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 118: 154954. |
| [27] | MA J J, WU D D, HU X, et al. Associations between cytokine gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to Helicobacter pylori infection and Helicobacter pylori related gastric cancer, peptic ulcer disease: a meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(4): e0176463. |
| [28] | 王杰, 杜朋丽, 董佳琪, 等. 黄连碱对慢性萎缩性胃炎大鼠PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2024, 30(18): 117-124. |
| [29] | CHATURVEDI R, ASIM M, PIAZUELO M B, et al. Activation of EGFR and ERBB2 by Helicobacter pylori results in survival of gastric epithelial cells with DNA damage[J]. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146(7): 1739-1751. |
| [30] | 杨玥玮, 程楠, 刘丽然, 等. 香连化浊方对慢性萎缩性胃炎模型大鼠胃黏膜EGFR/MAPK/ERK信号通路的影响[J]. 中医杂志, 2023, 64(14): 1483-1490. |
| [31] | 朱景茹, 黄婉仪, 洪银洁, 等. 基 于 EGFR/JAK1/STAT1信号通路探讨柴芍六君汤治疗慢性萎缩性胃炎肝郁脾虚证大鼠的机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(7): 3334-3338. |
| [32] | WU M L, HUANG Q R, XIE Y, et al. Improvement of the anticancer efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade via combination therapy and PD-L1 regulation[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2022, 15(1): 24. |
| [33] | 黄铭涵, 黄健, 陈琴, 等. 健脾清化中药复方对大鼠慢性萎缩性胃炎TLR4-MyD88依赖途径蛋白表达及TNF-α的影响[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2016, 32(9): 1321-1325. |
| [34] | 林翔英, 王鑫, 钟国栋, 等. 基于NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD信号通路探讨清化饮对慢性萎缩性胃炎大鼠胃上皮细胞焦亡的影响[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2024, 38(11): 32-35. |
| [35] | BIE Q L, SONG H, CHEN X K, et al. IL-17B/IL-17RB signaling cascade contributes to self-renewal and tumorigenesis of cancer stem cells by regulating Beclin-1 ubiquitination[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(12): 2200-2216. |
| [1] | Shan CAO,Yijia ZHANG,Yang BAI,Fang CHEN,Sha XIE,Qianqian HAN. Network pharmacological analysis and in vitro experimental verification based on anti-atherosclerosis mechanism of Xiaoban Tongmai Formula [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 925-938. |
| [2] | Xinchen ZHOU,Shuhan DONG,Zhuo ZHANG,Mingmei SHEN,Xiangjun WANG,Ying LI,Limei LIU. Network pharmacology analysis based on potential mechanism of dandelion-mulberry leaf in treatment of acute myeloid leukemia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(4): 1087-1097. |
| [3] | Zijia ZHU,Xia CHEN,Man CUI,Jihong WEN,Ping WANG,Dong SONG. Bioinformatics and molecular docking technology analysis on mechanism of salidroside on key differential genes of triple negative breast cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(3): 759-769. |
| [4] | Li LIU,Linsheng HUANG,Yongheng ZHAO,Wenjie CAO,Yongshuai QIAN,Huifan YU,Fei LI. Network pharmacological analysis on Balanophora involucrataHook.f. in treatment of hyperuricemia and its therapeutic effect on hyperuricemia cell model and hyperuricemia model mouse [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 58-70. |
| [5] | Aiying CHEN,Jinwen JIANG,Hui ZHANG. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of Huangqin Tang in treatment of colorectal cancer [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 208-220. |
| [6] | Yang YU,Dan TIAN,Donghe NI,Duo ZHANG. Network pharmacologry and molecular docking analysis based on mechanism of monk fruit in treatment of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2024, 50(1): 161-167. |
| [7] | Chunling WANG,Sinuo WU,Xiaoyan YU,Weidong ZHANG. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on effective chemical components and action targets of epimedium in treatment of hypothalamus-pituitary- adrenal gland/ gonad / thyroid gland axis function damage [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(5): 1296-1303. |
| [8] | Yumeng LIU,Song LENG, SARENGAOWA,Daijie LIN,Linsheng XIE,Mengrui LI,Xiao XU,Wannan LI. Network pharmacology analysis based on therapeutic effect of Sanghuang on pneumonia and its mechanism [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 923-930. |
| [9] | Sihan LAI,Juntong LIU,Luying TAN,Jinping LIU,Pingya LI. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on anti-ischemic stroke mechanism of Panax quinquefolium triolsaponins [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(4): 913-922. |
| [10] | Zhouquan LI,Hui LI,Ying TANG,Lijun YANG,Yinghong JIANG,Lipin YIN. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on mechanism of Tongluo Tangtai Power in treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 341-350. |
| [11] | Yushuang GONG,Yefan FU,Huijing XU,Jian GUO,Lin XIANG,Rui HU,Rui FAN,Jie WANG,Miao LI,Meiyan SUN. Network pharmacology analysis on mechanism of Tonifying Slpeen and Kidney Empirical Prescription in treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(2): 261-271. |
| [12] | Minghui WANG,Moyi LIU,Helin WANG,Ying LI,Xiangjun WANG,Hetong HUI,Xinyuan FAN,Tianqi WANG,Limei LIU. Bioinformatics analysis of network pharmacology and molecular docking technology based on mechanism of Physalis Calyx seu Fructus on leukemia [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2023, 49(1): 74-83. |
| [13] | Shaojie FU,Sensen SU,Yiying CHEN,Zhonggao XU. Analysis on network pharmacology and molecular docking technique based on mechanism of Shenqi Dihuang Decoction in treatment of membranous nephropathy [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(6): 1518-1527. |
| [14] | Yan LI,Yue HOU,Xingwei MU,Bingqing LIU,Hong WAN,Chang LIU,Wei XIA. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on mechanism of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus in occurrence and development of thoracic aortic aneurysm [J]. Journal of Jilin University(Medicine Edition), 2022, 48(2): 414-425. |
| [15] | ZHI Dingming, SUI Dianjun, QI Rui, MIAO Yongdi, HAN Dong, LOU Shilei, QIU Yue, SUN Cong. Potential targets of pueraria in treatment of hyperlipoproteinemia based on network pharmacology [J]. Journal of Jilin University Medicine Edition, 2018, 44(04): 724-730. |
|
||