吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (12): 3404-3414.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20220094
• 交通运输工程·土木工程 • 上一篇
基于冗余工序编码的高速列车节能驾驶智能算法
应沛然1( ),曾小清1(
),曾小清1( ),沈拓2,3,袁腾飞4,5,宋海峰6,王奕曾7
),沈拓2,3,袁腾飞4,5,宋海峰6,王奕曾7
- 1.同济大学 道路与交通工程教育部重点实验室,上海 201804
2.上海理工大学 光电与计算机工程学院,上海 200093
3.上海市轨道交通结构耐久与系统安全重点实验室,上海 201804
4.上海大学 悉尼工商学院,上海 201800
5.上海城市基础设施更新工程技术研究中心,上海 200032
6.北京航空航天大学 电子信息工程学院,北京 100191
7.香港城市大学 计算机科学系,香港 999077
Redundant operation code-based intelligent algorithm for energy⁃efficient driving of high-speed train
Pei-ran YING1( ),Xiao-qing ZENG1(
),Xiao-qing ZENG1( ),Tuo SHEN2,3,Teng-fei YUAN4,5,Hai-feng SONG6,Yi-zeng WANG7
),Tuo SHEN2,3,Teng-fei YUAN4,5,Hai-feng SONG6,Yi-zeng WANG7
- 1.Key Laboratory of Road and Traffic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Tongji University,Shanghai 201804,China
2.School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering,University of Shanghai for Science and Technology,Shanghai 200093,China
3.Shanghai Key Laboratory of Rail Infrastructure Durability and System Safety,Shanghai 201804,China
4.SHU-UTS SILC Business School,Shanghai University,Shanghai 201800,China
5.Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Urban Infrastructure Renewal,Shanghai 200032,China
6.School of Electronic Information Engineering,Beihang University,Beijing 100191,China
7.Department of Computer Science,City University of Hong Kong,Hongkong 999077,China
摘要:
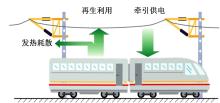
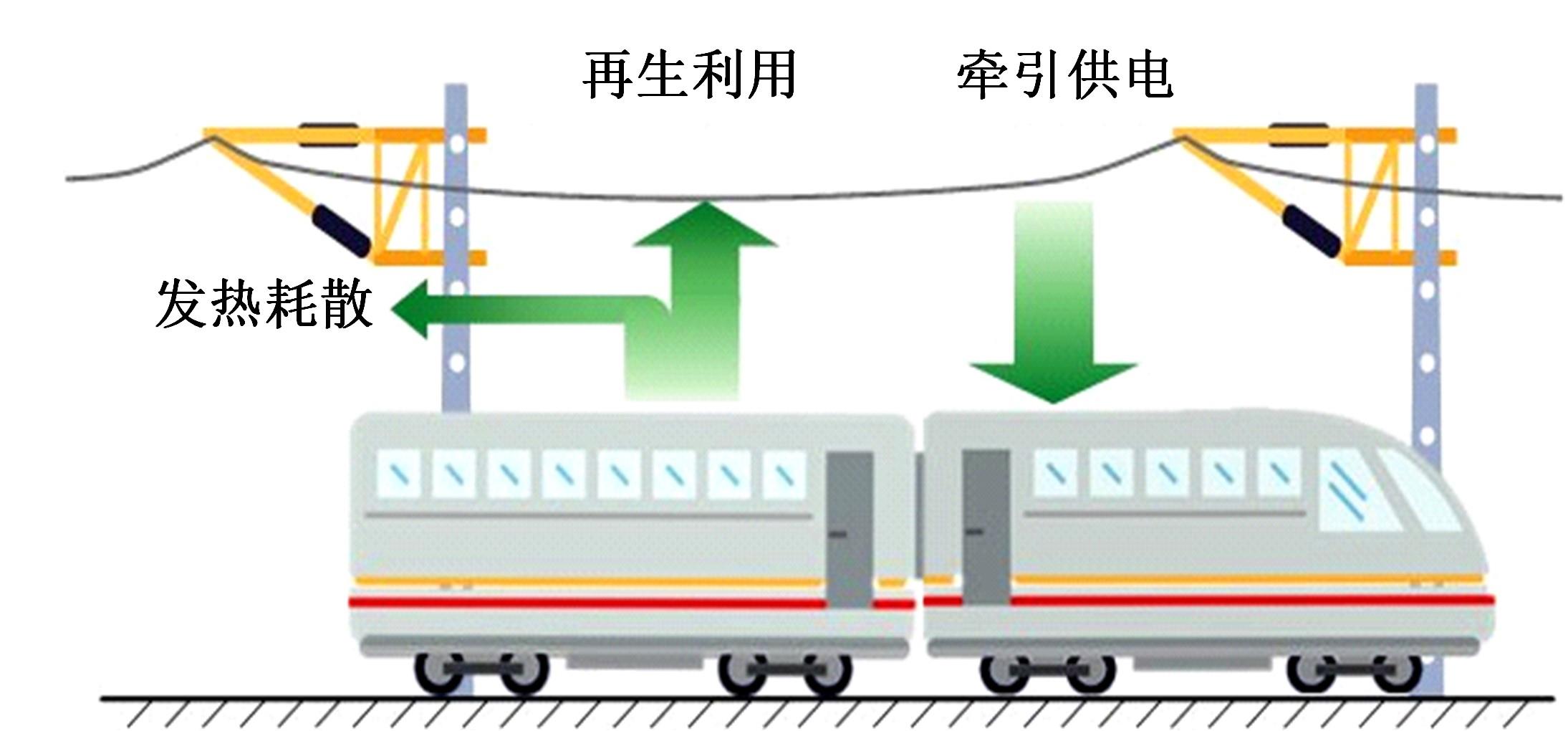
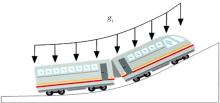
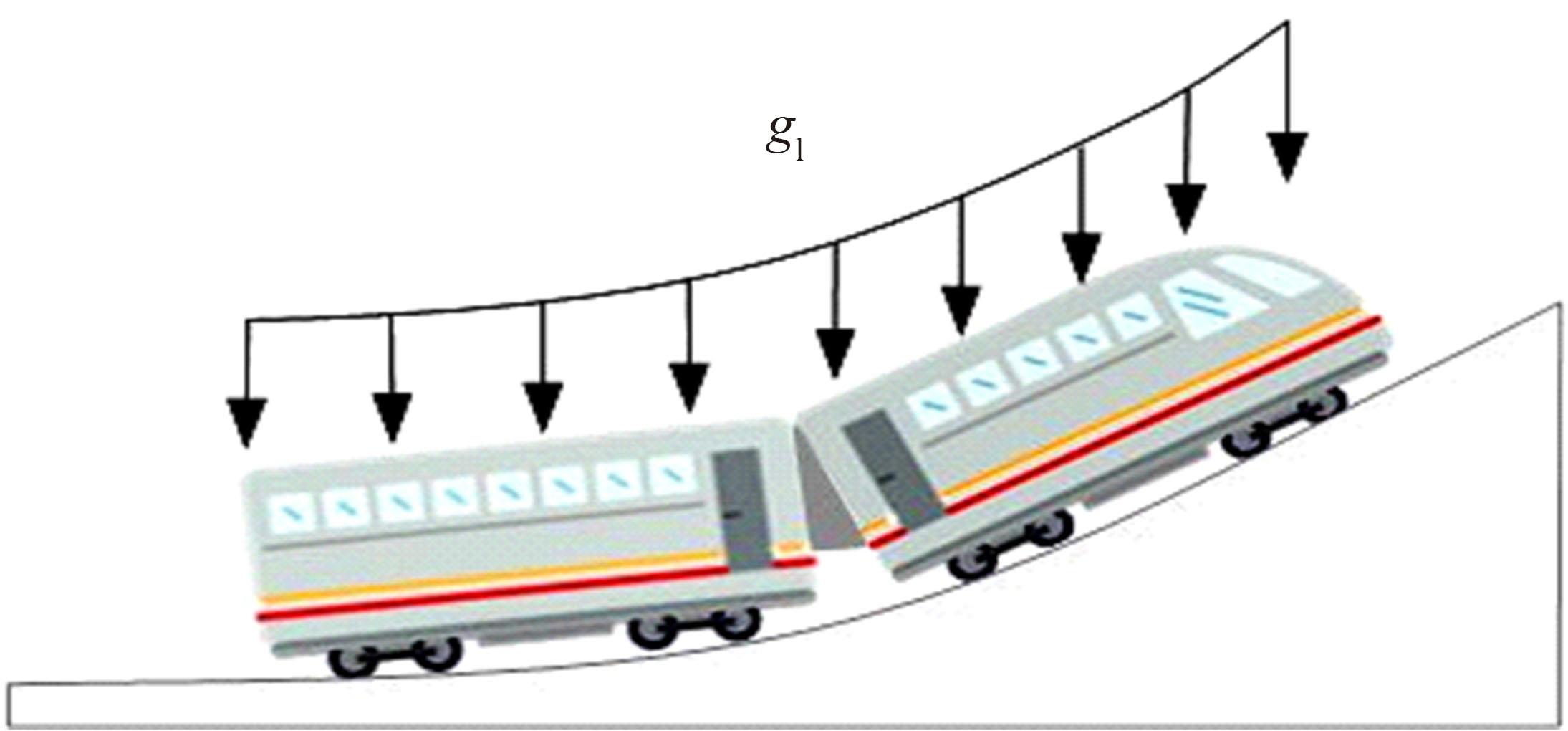
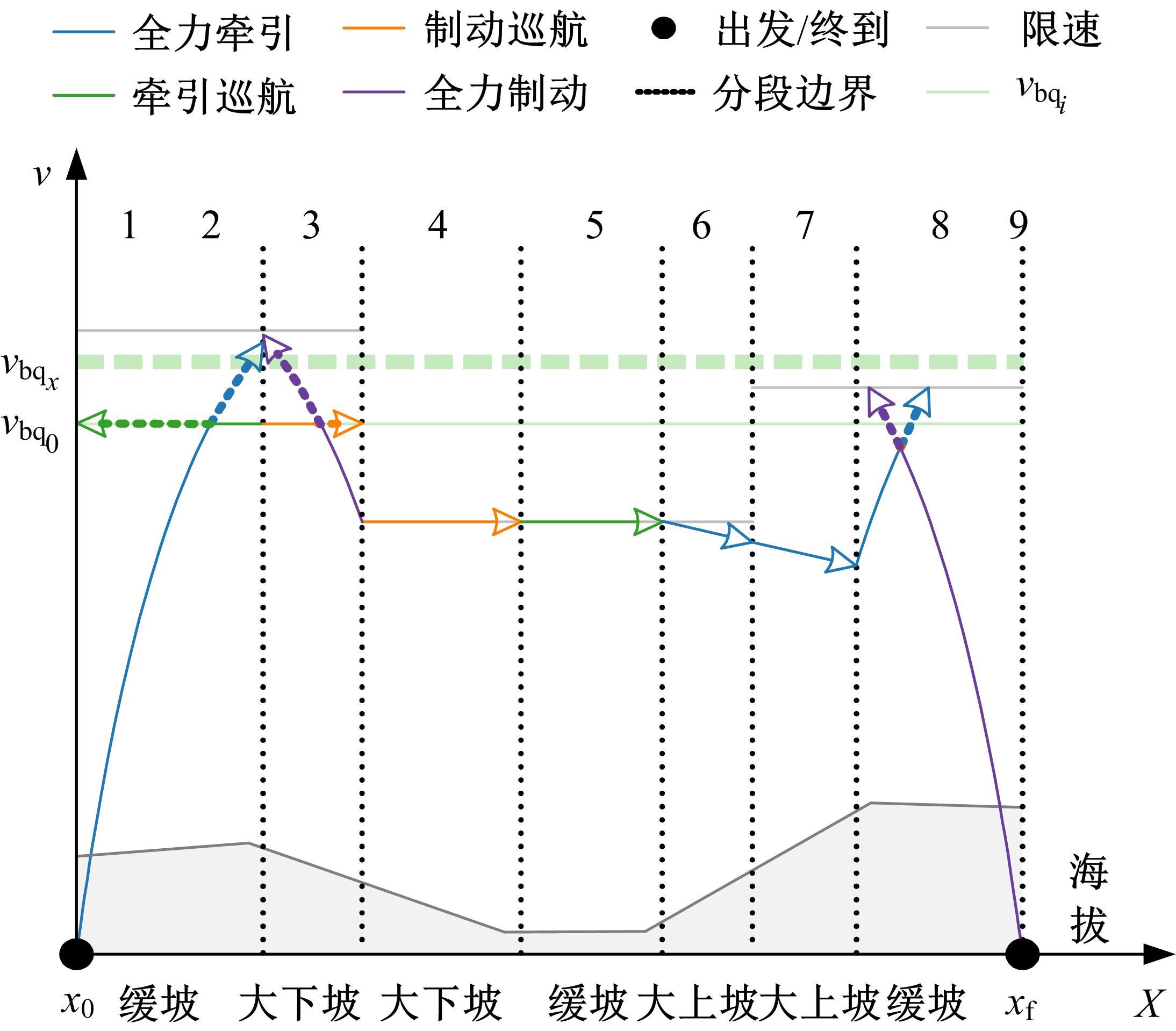
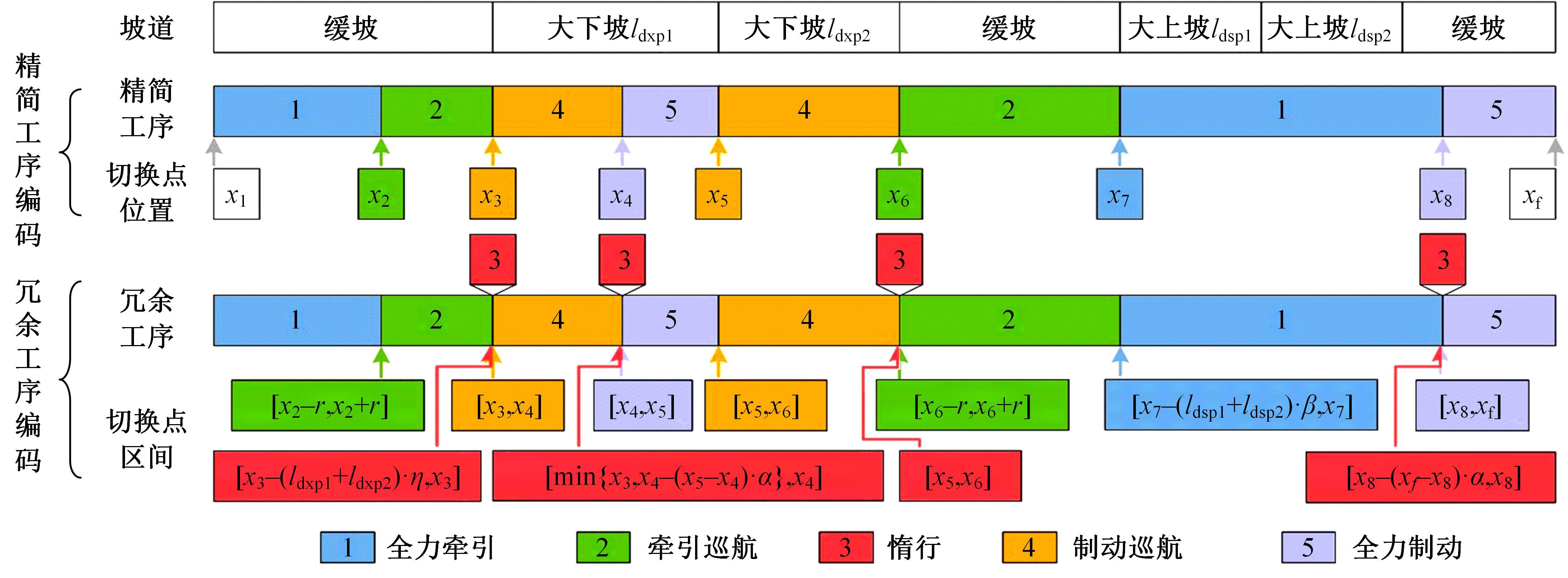
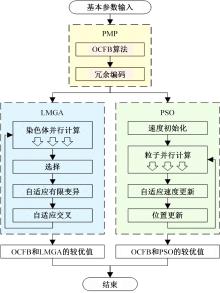
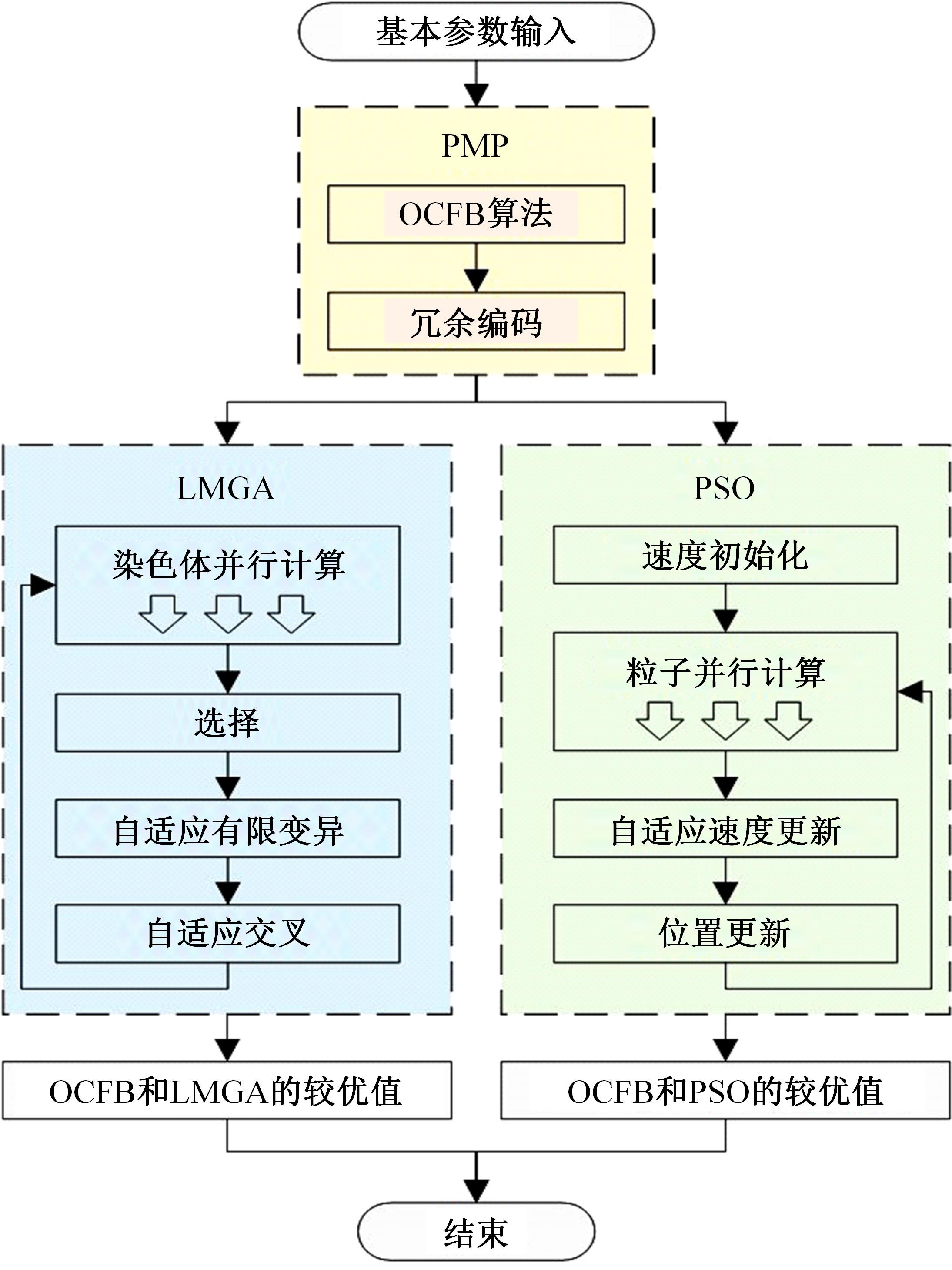
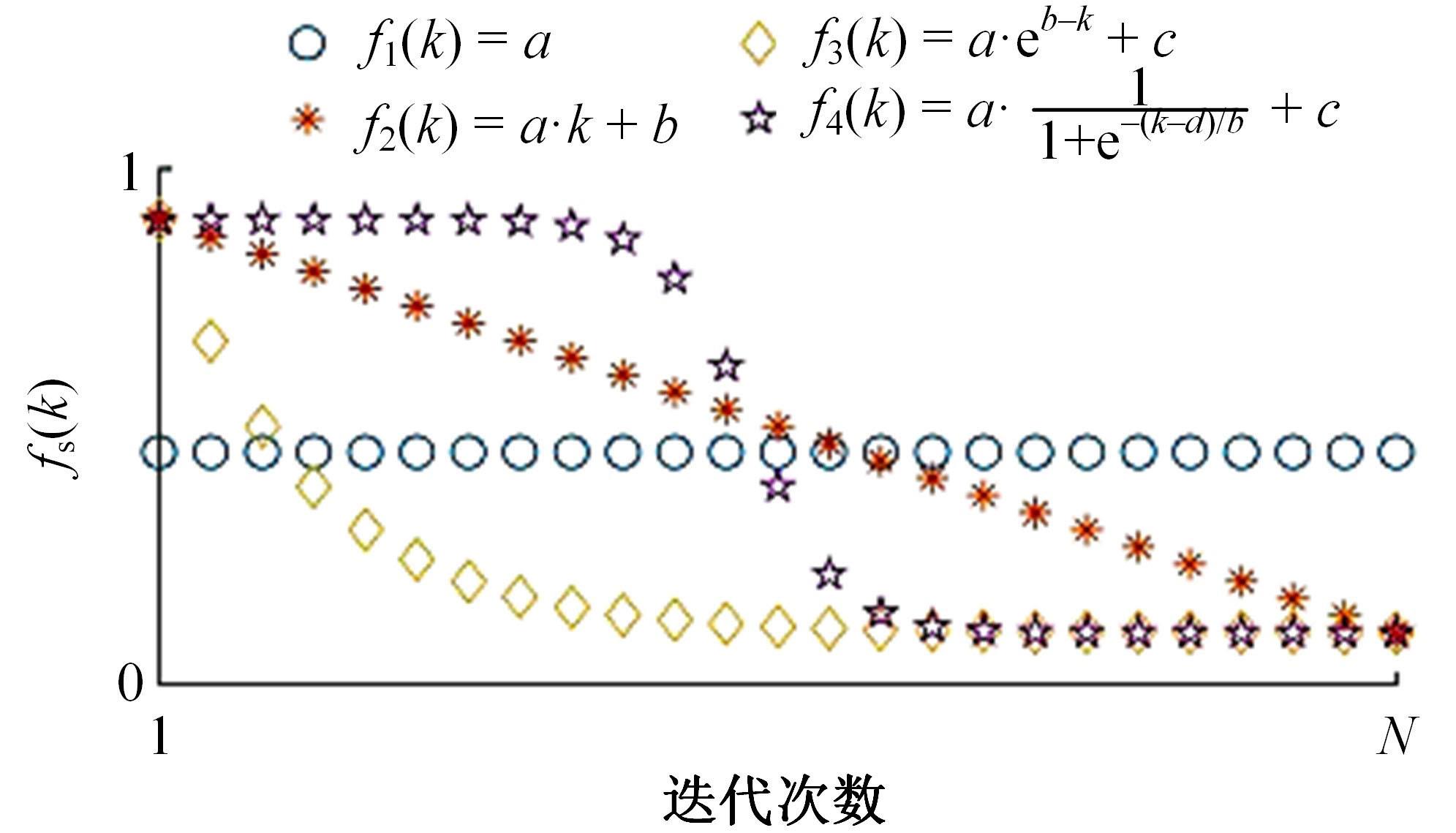
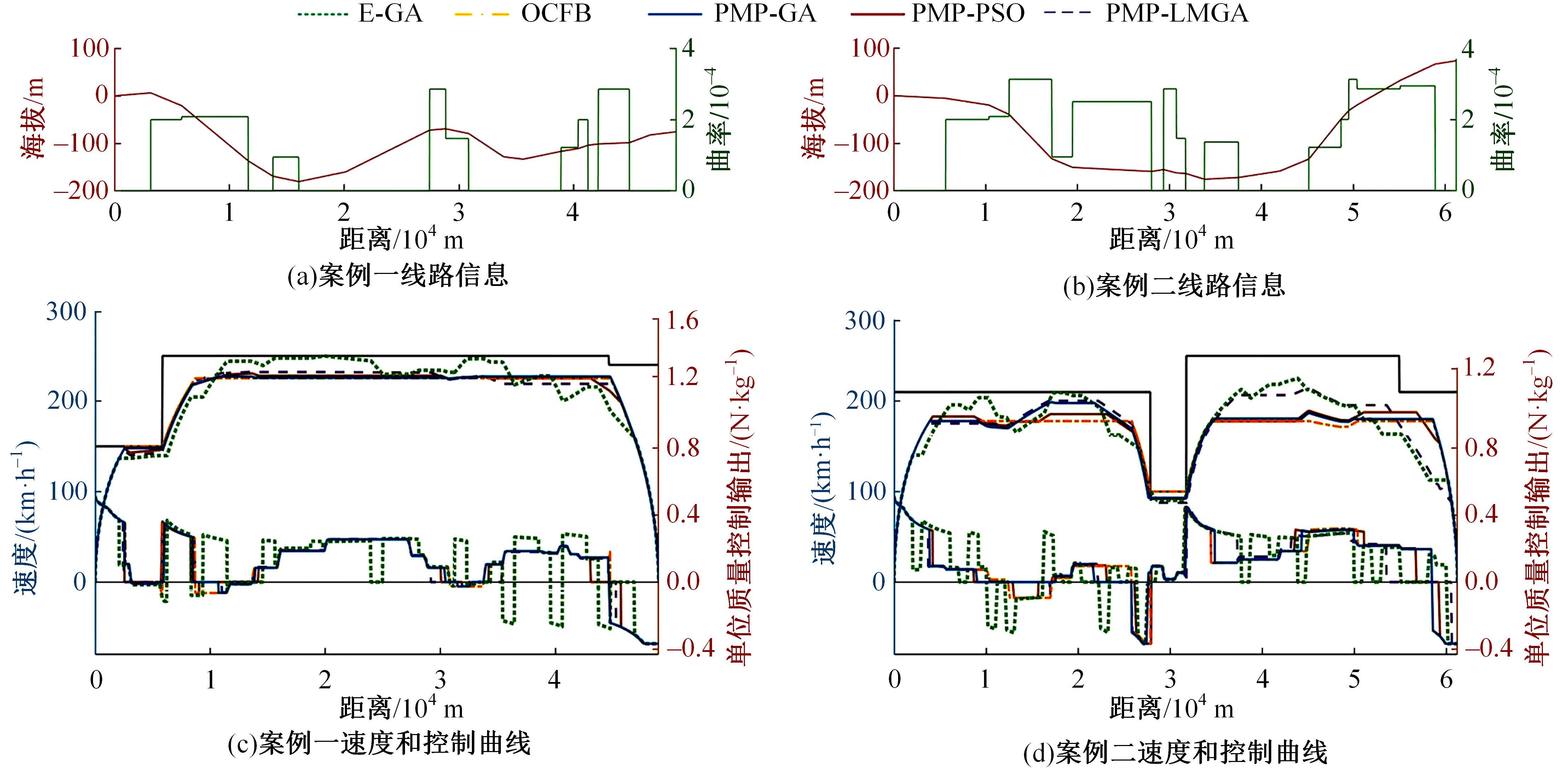
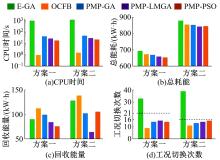
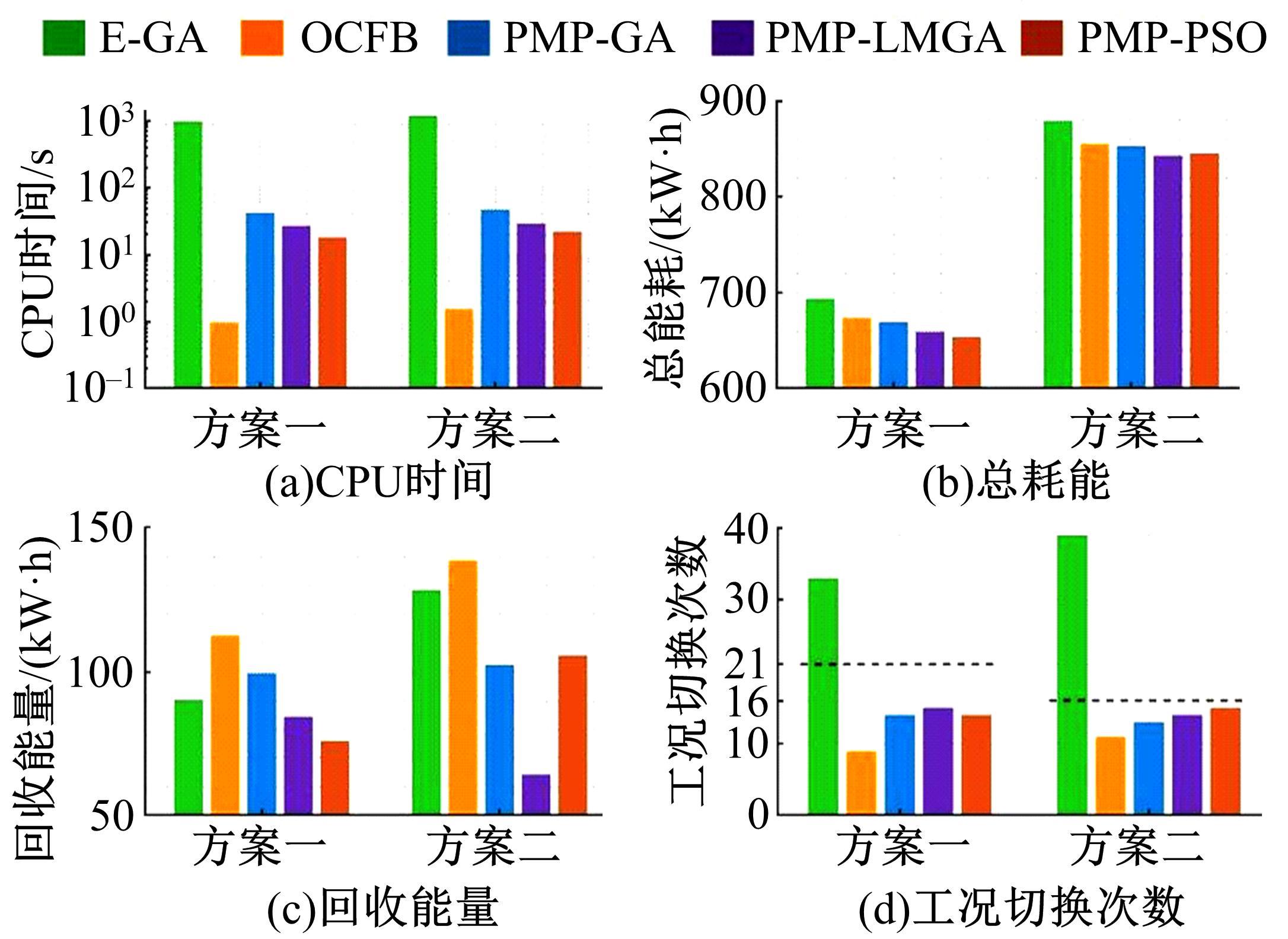
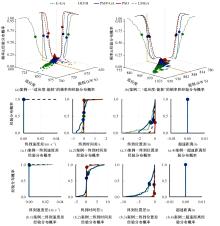
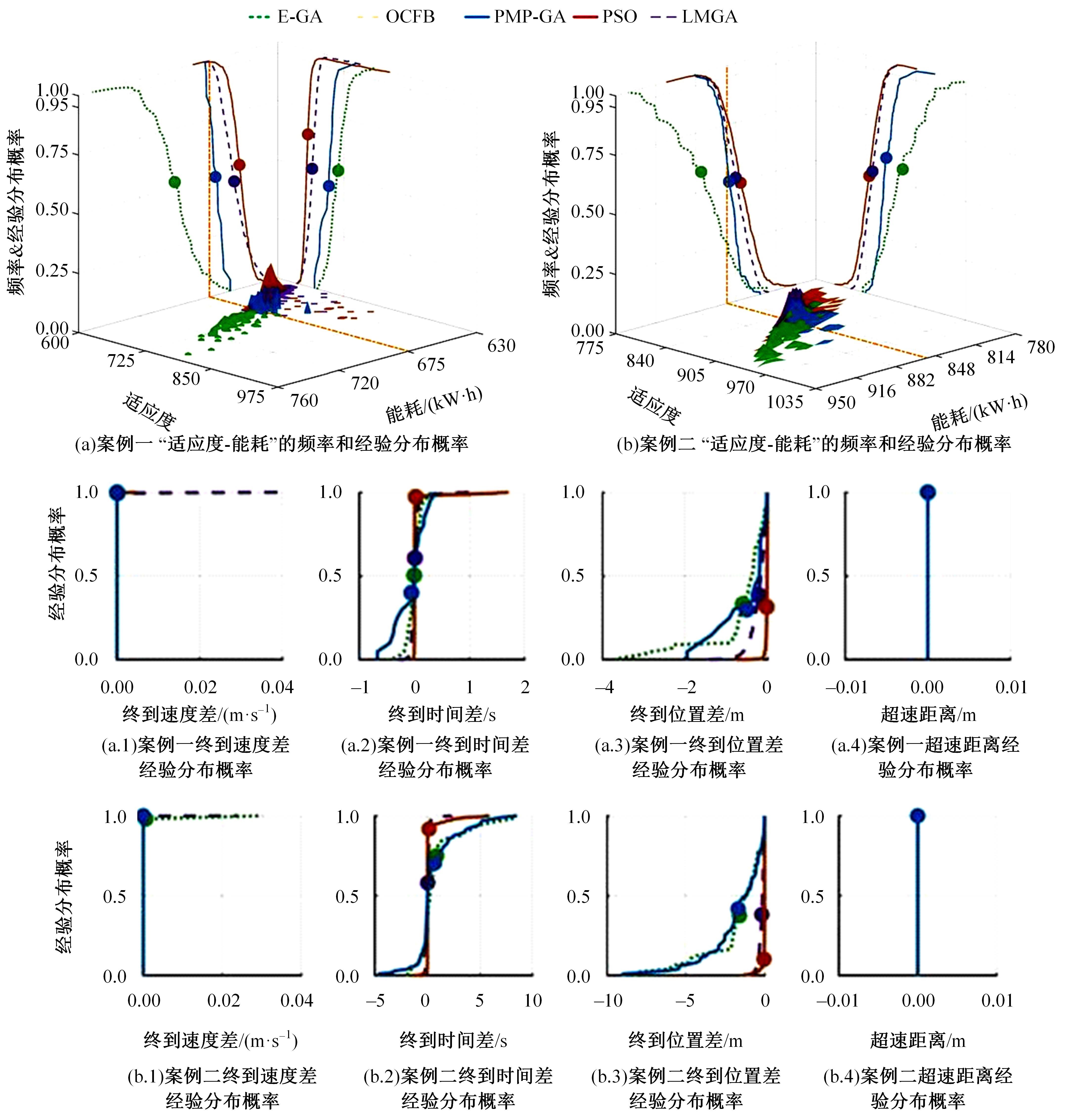
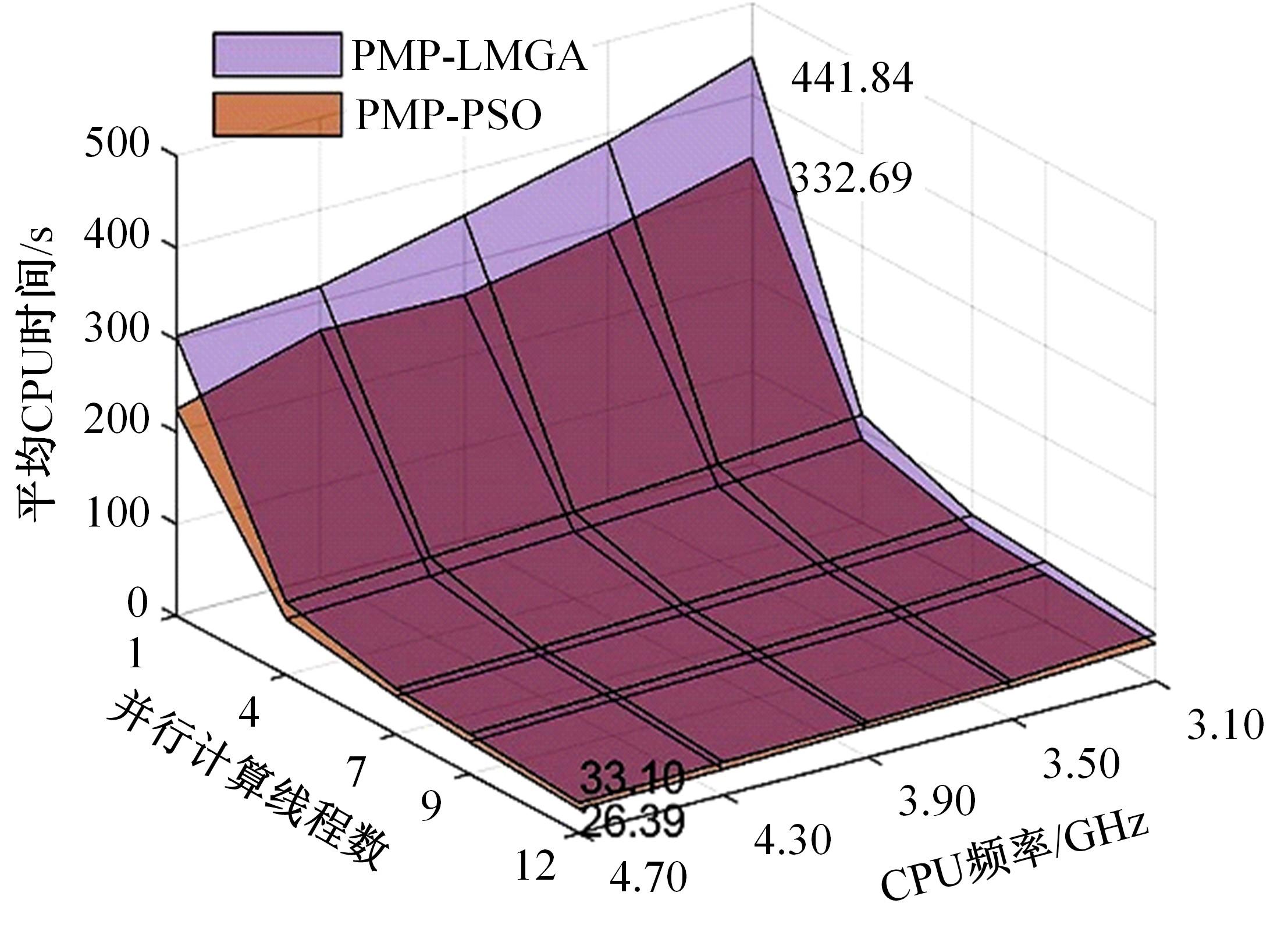
针对任意类型坡道组合和限速环境下高速列车节能驾驶优化问题,依据极大值原理推导得到最优解必要性条件,提出了包括冗余工序及其切换点区间的冗余工序编码概念和生成规则,设计了冗余工序编码分别与粒子群算法和有限变异遗传算法相结合的PMP-PSO算法和PMP-LMGA算法,用以归并部分冗余工况并优化切换点位置。实验结果表明:在满足各项运行规则前提下,运用冗余工序编码可以显著加快复杂场景下的求解速度,稳定且有效降低总能耗,同时,应用多智能体并行计算可进一步提升求解效率。
中图分类号:
- U238
| 1 | Howlett P. The optimal control of a train[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2000, 98: 65-87. |
| 2 | Scheepmaker G M, Goverde R M P, Kroon L G. Review of energy-efficient train control and timetabling[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2017, 257(2): 355-376. |
| 3 | 陈功, 傅瑜, 郭继峰. 飞行器轨迹优化方法综述[J]. 飞行力学, 2011, 29(4): 1-5. |
| Chen Gong, Fu Yu, Guo Ji-feng. Survey of aircraft trajectory optimization methods[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2011, 29(4): 1-5. | |
| 4 | Albrecht A, Howlett P, Pudney P, et al. The key principles of optimal train control—Part 2: existence of an optimal strategy, the local energy minimization principle, uniqueness, computational techniques[J]. Transportation Research Part B—Methodological, 2016, 94: 509-538. |
| 5 | Albrecht A, Howlett P, Pudney P, et al. The key principles of optimal train control—Part 1: formulation of the model, strategies of optimal type, evolutionary lines, location of optimal switching points[J]. Transportation Research Part B—Methodological, 2016, 94: 482-508. |
| 6 | Khmelnitsky E. On an optimal control problem of train operation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(7): 1257-1266. |
| 7 | 梁志成, 王青元, 何坤, 等. 基于极大值原理的电动车组节能操纵[J]. 铁道学报, 2015, 37(10): 16-25. |
| Liang Zhi-cheng, Wang Qing-yuan, He Kun, et al. Energy saving control of electric multiple unit train based on maximum principle[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2015, 37(10): 16-25. | |
| 8 | 王青元, 冯晓云, 朱金陵, 等. 考虑再生制动能量利用的高速列车节能最优控制仿真研究 [J]. 中国铁道科学, 2015, 36(1): 96-103. |
| Wang Qing-yuan, Feng Xiao-yun, Zhu Jin-ling, et al. Simulation study on optimal energy-efficient control of high speed train considering regenerative brake energy[J]. China Railway Science, 2015, 36(1): 96-103. | |
| 9 | 杨杰. 货运列车节能运行优化与智能控制方法[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2017. |
| Yang Jie. Methodology of energy-efficient freight train optimization and intelligent control[D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2017. | |
| 10 | Wang W, Zeng X, Shen T, et al. Energy-efficient speed profile optimization for urban rail transit with considerations on train length[C]∥21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Maui, HI, USA, 2018: 1585-1591. |
| 11 | Zhu Q, Su S, Tang T, et al. An eco-driving algorithm for trains through distributing energy: a Q-Learning approach[J]. ISA transactions, 2022, 122: 24-37. |
| 12 | Yang L, Li K, Gao Z, et al. Optimizing trains movement on a railway network[J]. Omega, 2012, 40(5): 619-633. |
| 13 | Wong K, Ho T. Coast control for mass rapid transit railways with searching methods[J]. IEE Proceedings-Electric Power Applications, 2004, 151(3): 365-376. |
| 14 | Kang M-H. A GA-based algorithm for creating an energy-optimum train speed trajectory[J]. Journal of International Council on Electrical Engineering, 2014, 1(2): 123-128. |
| 15 | Lu S, Wang M Q, Weston P, et al. Partial train speed trajectory optimization using mixed-integer linear programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2016, 17(10): 2911-2920. |
| 16 | Yin J, Tang T, Yang L, et al. Research and development of automatic train operation for railway transportation systems: a survey[J]. Transportation Research Part C-Emerging Technologies, 2017, 85: 548-572. |
| 17 | Hartl R F, Sethi S P, Vickson R G. A survey of the maximum-principles for optimal-control problems with state constraints[J]. Siam Review, 1995, 37(2): 181-218. |
| 18 | Liu R, Golovitcher I M. Energy-efficient operation of rail vehicles[J]. Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 2003, 37(10): 917-932. |
| 19 | Ying P, Zeng X, Song H, et al. Energy-efficient train operation with steep track and speed limits: a novel Pontryagin's maximum principle-based approach for adjoint variable discontinuity cases[J]. IET Intelligent Transport Systems, 2021, 15(9): 1183-1202. |
| 20 | Brenna M, Foiadelli F, Longo M. Application of genetic algorithms for driverless subway train energy optimization[J]. International Journal of Vehicular Technology, 2016(2): 1-14. |
| 21 | 李卓玥. 群智能算法在列车运行速度曲线节能优化中的研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学交通运输学院, 2016. |
| Li Zhuo-yue. Research on energy-saving optimization of train speed trajectories based on swarm intelligence algorithms[D]. Beijing: School of Traffic and Transportation, Beijing Jiaotong University, 2016. |
| [1] | 李岩,张久鹏,陈子璇,黄果敬,王培. 基于PCA-PSO-SVM的沥青路面使用性能评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(6): 1729-1735. |
| [2] | 刘洋,刘吉成. 基于大数据与粒子群的清洁能源协同优化调度方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(5): 1443-1448. |
| [3] | 吴剑,许斌. 基于CEEMDAN理论的堆积层滑坡位移区间预测模型及仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(2): 562-568. |
| [4] | 李杰,贾长旺,赵旗. 车辆转向非线性平衡状态求解及其稳定性确定[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(12): 3326-3334. |
| [5] | 陈永刚,许继业,王海涌,熊文祥. 基于自适应神经模糊网络的转辙机故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(11): 3274-3280. |
| [6] | 管仁初,贺宝润,梁艳春,时小虎. 基于亲缘关系选择的粒子群优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1842-1849. |
| [7] | 陈昭明,邹劲松,王伟,石明全. 改进粒子群神经网络融合有限元分析的铸锻双控动态成型多目标优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(7): 1524-1533. |
| [8] | 邢海燕,刘超,徐成,陈玉环,王松弘泽. 基于粒子群优化模糊C焊缝等级磁记忆定量识别模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 525-532. |
| [9] | 罗巍,卢博,陈菲,马腾. 基于PSO-SVM及时序环节的数控刀架故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 392-399. |
| [10] | 李翠玉,胡雅梦,康亚伟,张德良. 应用自适应遗传算法的电动汽车充放电协同调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(11): 2508-2513. |
| [11] | 杜常清,曹锡良,何彪,任卫群. 基于混合粒子群算法的双离合变速器参数优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1556-1564. |
| [12] | 马芳武,韩丽,吴量,李金杭,杨龙帆. 基于遗传与粒子群算法的隔振平台减振性能优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1608-1616. |
| [13] | 刘玉梅,乔宁国,庄娇娇,刘鹏程,胡婷,陈立军. 基于多传感器数据融合的轨道车辆齿轮箱异常检测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1465-1470. |
| [14] | 赖晴鹰,刘军,赵若愚,骆泳吉,孟令云,徐亚之. 基于变间距动态规划的中高速磁悬浮列车 速度曲线优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(3): 749-756. |
| [15] | 臧国帅, 孙立军. 基于惰性弯沉点的刚性下卧层深度设置方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2018, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
|
||