吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2022, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 1524-1533.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb20210108
• 车辆工程·机械工程 • 上一篇
改进粒子群神经网络融合有限元分析的铸锻双控动态成型多目标优化
- 1.重庆大学 机械工程学院,重庆 400044
2.中国科学院大学重庆学院 人工智能学院,重庆 400714
3.中国科学院重庆绿色智能技术研究院 智能制造技术研究所,重庆 400714
4.重庆理工大学 计算机科学与工程学院,重庆 400054
Multi-objective optimization of casting-forging dynamic forming based on improved particle swarm neural network and finite element analysis
Zhao-ming CHEN1,2( ),Jin-song ZOU3,Wei WANG4,Ming-quan SHI3
),Jin-song ZOU3,Wei WANG4,Ming-quan SHI3
- 1.College of Mechanical Engineering,Chongqing University,Chongqing 400044,China
2.School of Artificial Intelligence,Chongqing School of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Chongqing 400714,China
3.Intelligent Manufacturing Technology Institute,Chongqing Institute of Green and Intelligent Technology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Chongqing 400714,China
4.College of Computer Science and Engineering,Chongqing University of Technology,Chongqing 400054,China
摘要:
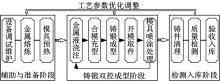
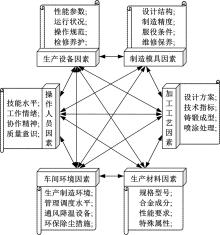
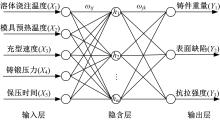
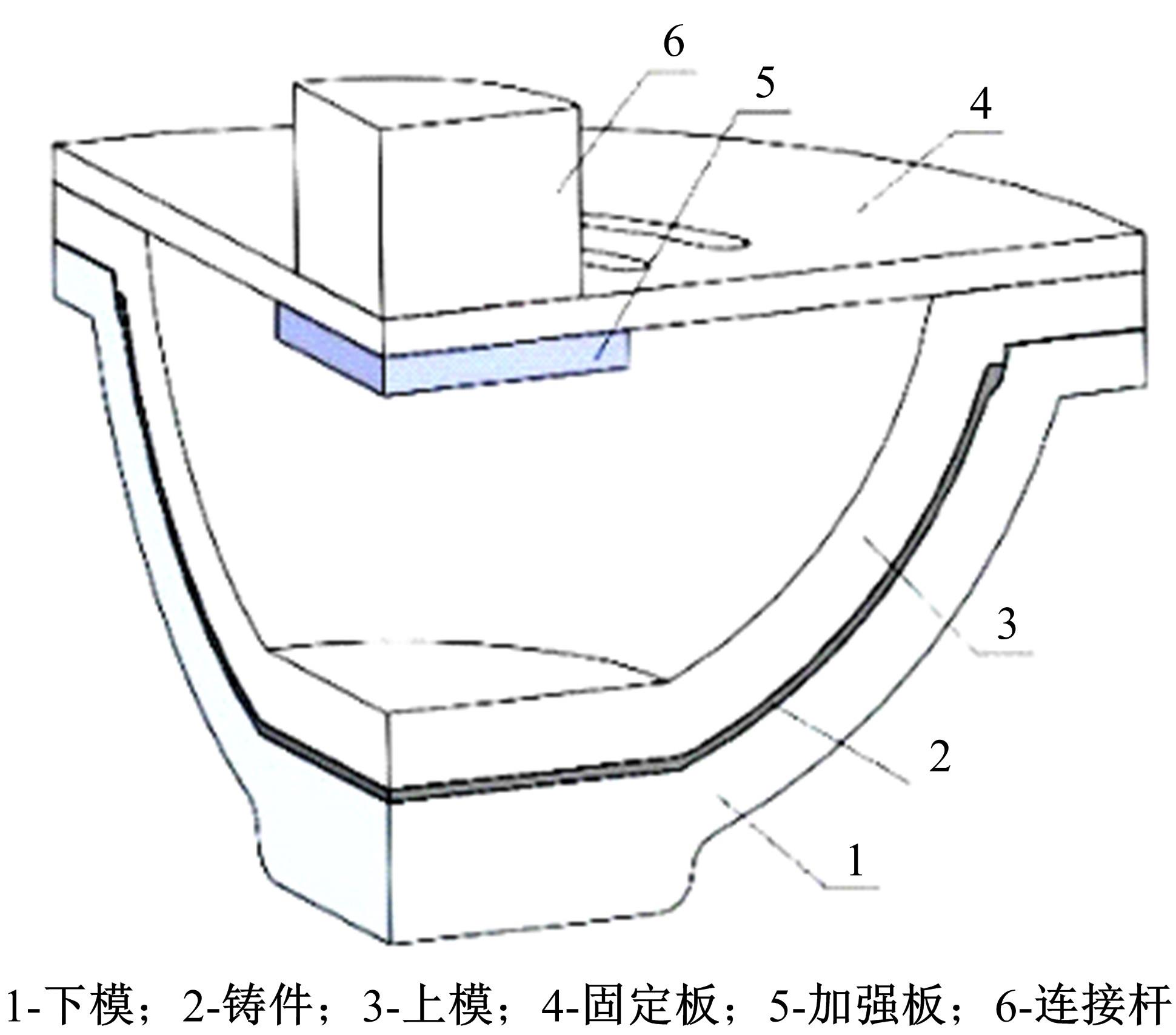
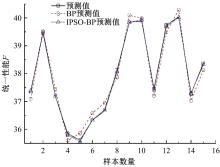
针对铸锻双控成型过程中多工艺参数的优选问题,提出一种改进粒子群算法优化神经网络融合有限元分析的成型工艺参数优选方法。首先根据成型工艺的特点,以金属液浇注温度、模具预热温度、充型速度、铸锻压力、保压时间5个工艺参数为输入因素,以铸件重量、表面缺陷、抗拉强度3个参数为输出指标,采用正交拉丁超立方设计进行试验,并将所得工艺参数作为训练样本,通过神经网络构建影响因素与优化目标间的非线性函数关系。再以神经网络的输出误差值作为粒子适应度,并采用改进粒子群算法优化BP神经网络的权值和阈值,构建工艺参数预测模型进行多参数寻优。通过CAE有限元仿真验证表明,该方法能够准确地获得成型过程中的最佳工艺参数组合。研究结果可为铸锻双控过程的工艺参数调整与优化提供参考。
中图分类号:
- TP183
| 1 | 吴月松, 张桂军. 铸造工艺特点分析[J]. 建筑工程技术与设计, 2017, 21:4498. |
| Wu Yue-song, Zhang Gui-jun. Analysis of casting process characteristics[J]. Architectural Engineering Technology and Design, 2017, 21:4498. | |
| 2 | 马敬仲. 铸造产品升级与高端铸件研制的关键问题论述[J]. 现代铸铁, 2016, 2:19-23. |
| Ma Jing-zhong. Key problems talk about up-grading of casting products and development of high-end castings[J]. Modern Cast Iron, 2016, 2:19-23. | |
| 3 | 卢杰. 我国铸造技术的发展趋势[C]∥第24届重庆市铸造年会论文集, 重庆,2014:16-18. |
| 4 | Zhou H T, Xu S X, Li W D, et al. A study of automobile brake bracket formed by casting-forging integrated forming technology[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 67(2):285-292. |
| 5 | Jiang J, Wang Y, Li Y, et al. A double control forming technology combining die casting and forging for the production of Mg alloy components with enhanced properties[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Tech, 2012, 212(5):1191-1199. |
| 6 | Zhang Wen-yu, Ju Dong-ying, Zhao Hong-yang, et al. Fuzzy controller optimized by genetic algorithm for the molten metal level in the twin roll strip casting process[J]. Materials Science Forum,2015, 833:197-200. |
| 7 | 周华民, 高煌, 张云, 等. 注塑成型工艺参数自动设置与优化技术[J]. 精密成形工程, 2016, 8(1):7-13, 26. |
| Zhou Hua-min, Gao Huang, Zhang Yun, et al. Automatic setting and optimization of injection molding process parameters[J]. Journal of Netshap Forming Engineering, 2016, 8(1):7-13, 26. | |
| 8 | Schmidt R, Pusch D, Voigt M, et al. Numerical and experimental sensitivity analysis for the determination of casting parameter-microstructure-property relations and mechanical properties of IN738LC in investment casting[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2015, 16(10):1217-1225. |
| 9 | 李瑞娟, 黄力. 基于BP神经网络的汽车内饰面板注塑成型工艺参数优化[J]. 塑料, 2016, 45(3):81-85. |
| Li Rui-juan, Huang Li. Optimization of injection molding process for automotive interior panel based on BP neural network[J]. Plastics, 2016, 45(3):81-85. | |
| 10 | Zarei J, Poshtan J. Optimization of process parameters for biological 3D printing forming based on BP neural network and genetic algorithm[J]. Tribology International, 2014, 42(2):213-219. |
| 11 | Darajeh N, Masoumi H R F, Kalantari K, et al. Optimization of process parameters for rapid adsorption of Pb(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II) by magnetic/talc nanocomposite using wavelet neural network[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2015, 42(3):1977-1987. |
| 12 | Sreeraj P, Kannan T, Subhashis M. Optimization of GMAW process parameters using particle swarm optimization[J]. Isrn Metallurgy, 2015, 2013:1-10. |
| 13 | Zhang Jian-feng, Peng An-hua. Processing parameter optimization of FDM based on robust design[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2012, 29(1):62-67. |
| 14 | Equbal M I, Kumar R, Shamim M, et al. A grey-based taguchi method to optimize hot forging process[J]. Procedia Materials Science, 2014, 6:1495-1504. |
| 15 | 韩明兴. 挤压铸造充型过程的计算机数值模拟仿真研究[D]. 武汉:武汉理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 2012. |
| Han Ming-xin. Numerical computer simulation technology of squeeze casting filling process[D]. Wuhan:College of Materials and Engineering,Wuhan University of Technology, 2012. | |
| 16 | 李春龙, 郑伟刚, 阳鑫,等. 汽车发动机附件支架挤压铸造数值模拟研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2015, 44(1):63-65, 68. |
| Li Chun-long, Zheng Wei-gang, Yang Xin, et al. Numerical simulation research of squeeze casting for automotive engine accessories stent[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2015, 44(1):63-65, 68. | |
| 17 | 陈玖新, 代颖辉, 张川吉,等. 基于ProCAST的挤压铸造重载车轮铸件成形过程数值模拟[J]. 铸造, 2015, 64(7):639-642. |
| Chen Jiu-xin, Dai Ying-hui, Zhang Chuan-ji, et al. Numerical simulation of casting forming for squeeze casting heavy load wheel on ProCAST[J]. Foundry, 2015, 64(7):639-642. | |
| 18 | Wang Ru-jia, Wu Shi-ping, Chen Wei. Mechanism of burst feeding in ZL205A casting under mechanical vibration and low pressure [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(8):45-51. |
| 19 | 向青春, 张伟, 邱克强,等. 基于DOE的大型下架体铸钢件铸造工艺优化研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(6):88-93. |
| Xiang Qing-chun, Zhang Wei, Qiu Ke-qiang, et al. Casting process optimization for large lower frame body of heavy gyratory crusher based on DOE[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2017, 53(6):88-93. | |
| 20 | 兰鹏, 杜辰伟, 陈培莉,等. 微合金钢连铸表面横裂纹形成机理与控制技术研究现状[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2017, 29(1):1-12. |
| Lan Peng, Du Chen-wei, Chen Pei-li, et al. Research status of surface transverse cracking formation mechanism and control technique for continuously cast microalloyed steels[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017, 29(1):1-12. | |
| 21 | 黄璇, 郭立红, 李姜, 等. 改进粒子群优化BP神经网络的目标威胁估计[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(3):996-1002. |
| Huang Xuan, Guo Li-hong, Li Jiang, et al. Target threat assessment based on BP neural network optimized by modified particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2017, 47(3):996-1002. | |
| 22 | Wang B, Lin R, Liu D, et al. Investigation of the effect of humidity at both electrode on the performance of PEMFC using orthogonal test method[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44(26):13737-13743. |
| 23 | Dey A, Sarkar D. A note on the construction of orthogonal latin hypercube designs[J]. Journal of Combinatorial Designs, 2016, 24(3):105-111. |
| 24 | Ye K Q. Orthogonal column latin hypercubes and their application in computer experiments[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1998, 93(444): 1430-1439. |
| 25 | 杜常清, 曹锡良, 何彪, 等. 基于混合粒子群算法的双离合变速器参数优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2020, 50(5):1556-1564. |
| Du Chang-qing, Cao Xi-liang, He Biao, et al. Parameters optimization of dual clutch transmission based on hybrid particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5):1556-1564. | |
| 26 | 杨东民, 陈敏, 吴庆朝. 基于KPCA与MPSO–BP注射成型工艺参数优化[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2015, 43(12):42-47. |
| Yang Dong-min, Chen Min, Wu Qing-chao. Study on parameters optimization of injection molding based on KPCA and modified particle swarm optimized back propagation neural network[J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2015, 43(12):42-47. | |
| 27 | Liu P, Zhang W. A fault diagnosis intelligent algorithm based on improved BP neural network[J]. International Journal of Pattern Recognition & Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(9):50-56. |
| [1] | 马永杰,陈敏. 基于卡尔曼滤波预测策略的动态多目标优化算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1442-1458. |
| [2] | 黄晗,闫庆昊,向枳昕,杨鑫涛,陈金宝,许述财. 基于虾螯的仿生多胞薄壁管耐撞性分析及优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 716-724. |
| [3] | 姜斌祥,姜彤彤,王永雷. 基于文化遗传算法的毒品检验区块链共识算法优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 684-692. |
| [4] | 张立杰,阿喜塔,田笑,李稳. 基于Gamma过程的加速退化试验多目标优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 361-367. |
| [5] | 孙宝凤,任欣欣,郑再思,李国一. 考虑工人负荷的多目标流水车间优化调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 900-909. |
| [6] | 周炳海,何朝旭. 基于静态半成套策略的多目标准时化物料配送调度[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(3): 910-916. |
| [7] | 黄继承,沈成,纪爱敏,李显旺,张彬,田昆鹏,刘浩鲁. 工业大麻收割机切割⁃输送关键部件作业参数优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 772-780. |
| [8] | 张刘,郑潇逸,张帆,赵宇,赵书阳. 大容差多柔性透镜组结构优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 478-485. |
| [9] | 周炳海,吴琼. 基于多目标的机器人装配线平衡算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2021, 51(2): 720-727. |
| [10] | 马芳武,韩丽,吴量,李金杭,杨龙帆. 基于遗传与粒子群算法的隔振平台减振性能优化[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1608-1616. |
| [11] | 陈学深,陈涛,武涛,马旭,曾令超,陈林涛. 覆草冬种马铃薯收获机稻草分离机构设计与试验[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 749-757. |
| [12] | 李银平,靳添絮,刘立. 纯电动铲运机弓网续能系统设计与动态特性仿真[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(2): 454-463. |
| [13] | 马芳武,梁鸿宇,赵颖,杨猛,蒲永锋. 内凹三角形负泊松比结构耐撞性多目标优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 29-35. |
| [14] | 庄蔚敏,施宏达,解东旋,杨冠男. 钢铝异质无铆钉粘铆复合连接胶层厚度分布[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 100-106. |
| [15] | 蔡中义,孟凡响,陈庆敏,赵轩. 复杂钩舌锻件近净成形的预锻形状优化设计[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(1): 84-90. |
|
||