吉林大学学报(工学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 989-997.doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20210778
基于粒子群优化算法⁃长短时记忆模型的刀具磨损预测方法
- 武汉理工大学 机电工程学院,武汉 430070
Tool wear prediction method based on particle swarm optimizationlong and short time memory model
Fei WU( ),Hao-ye NONG,Chen-hao MA
),Hao-ye NONG,Chen-hao MA
- School of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering,Wuhan University of Technology,Wuhan 430070,China
摘要:
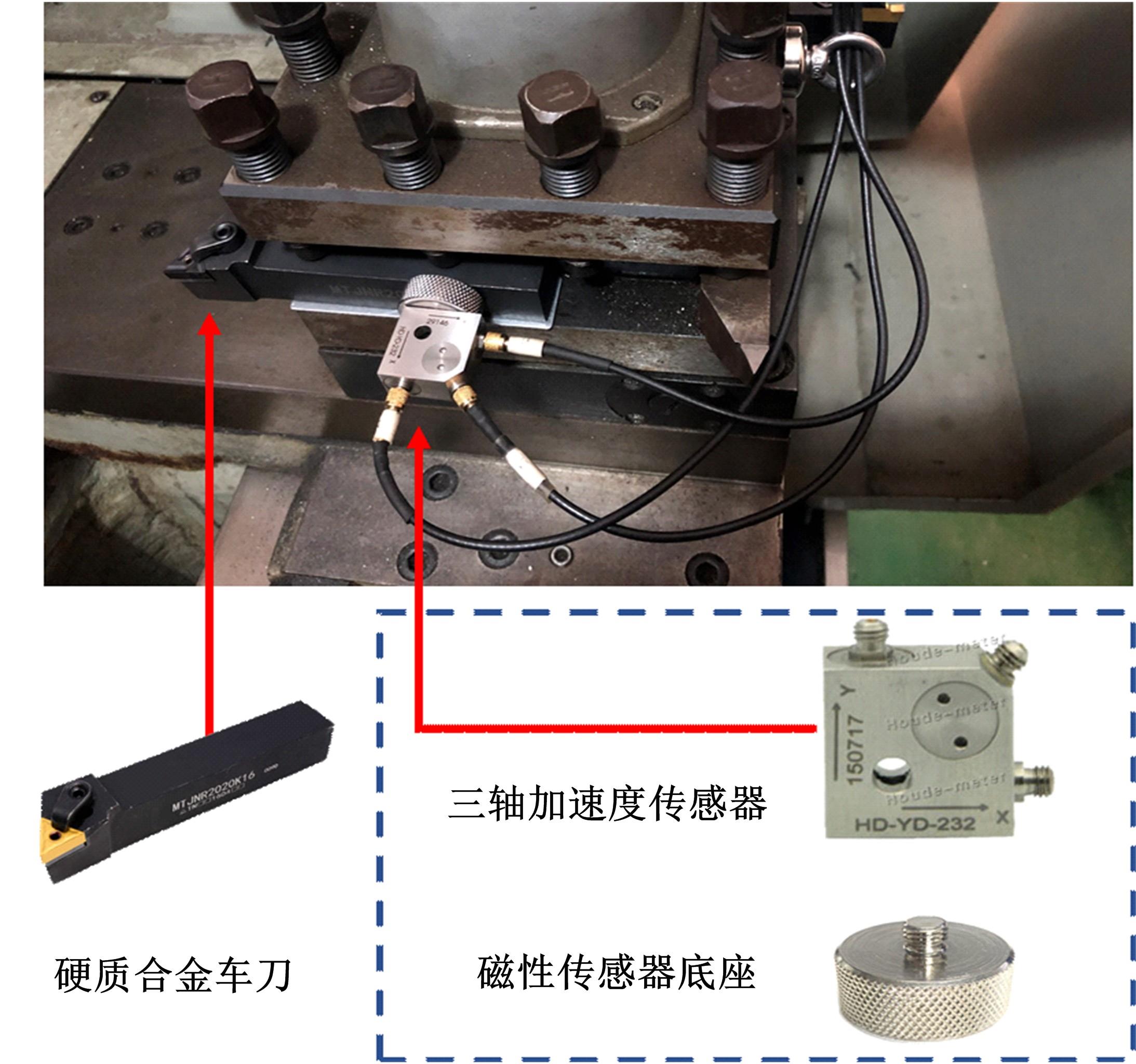
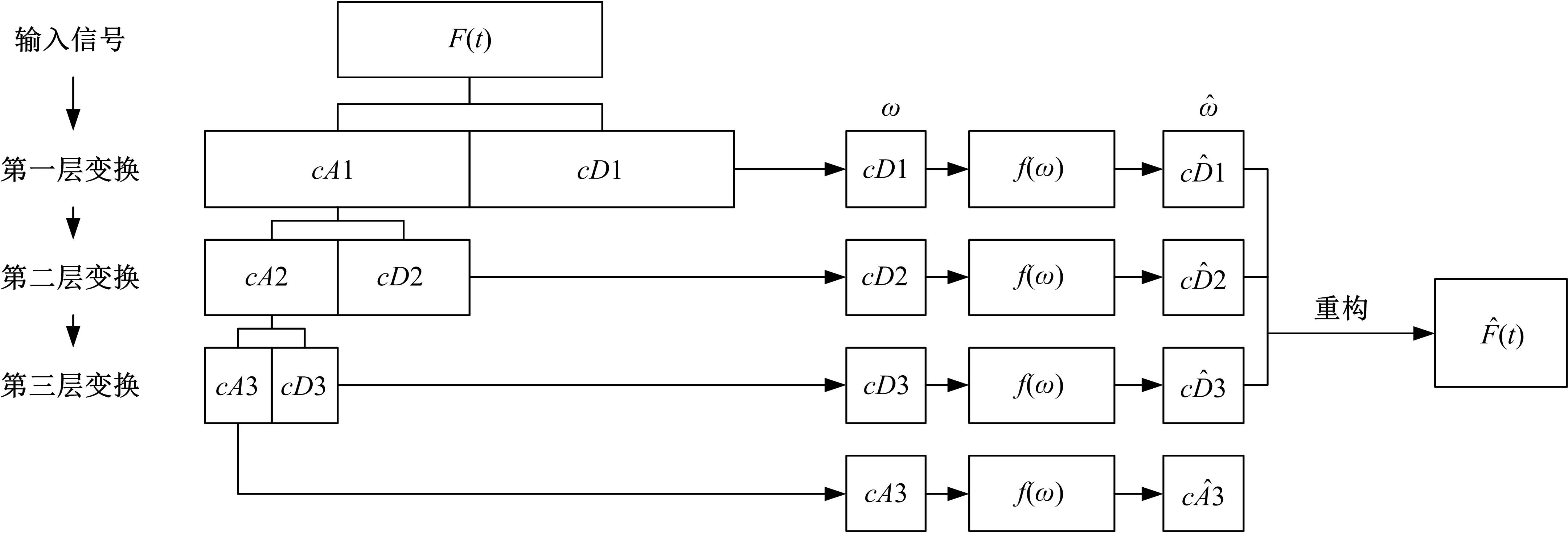
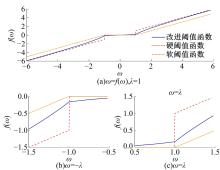
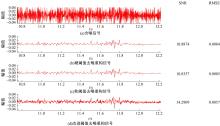
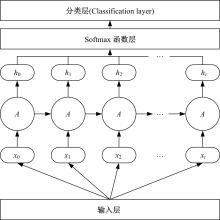
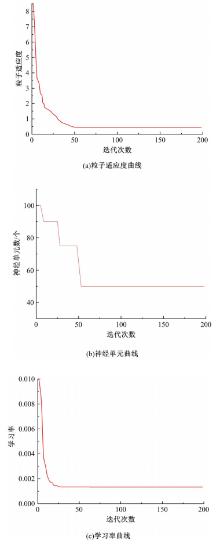
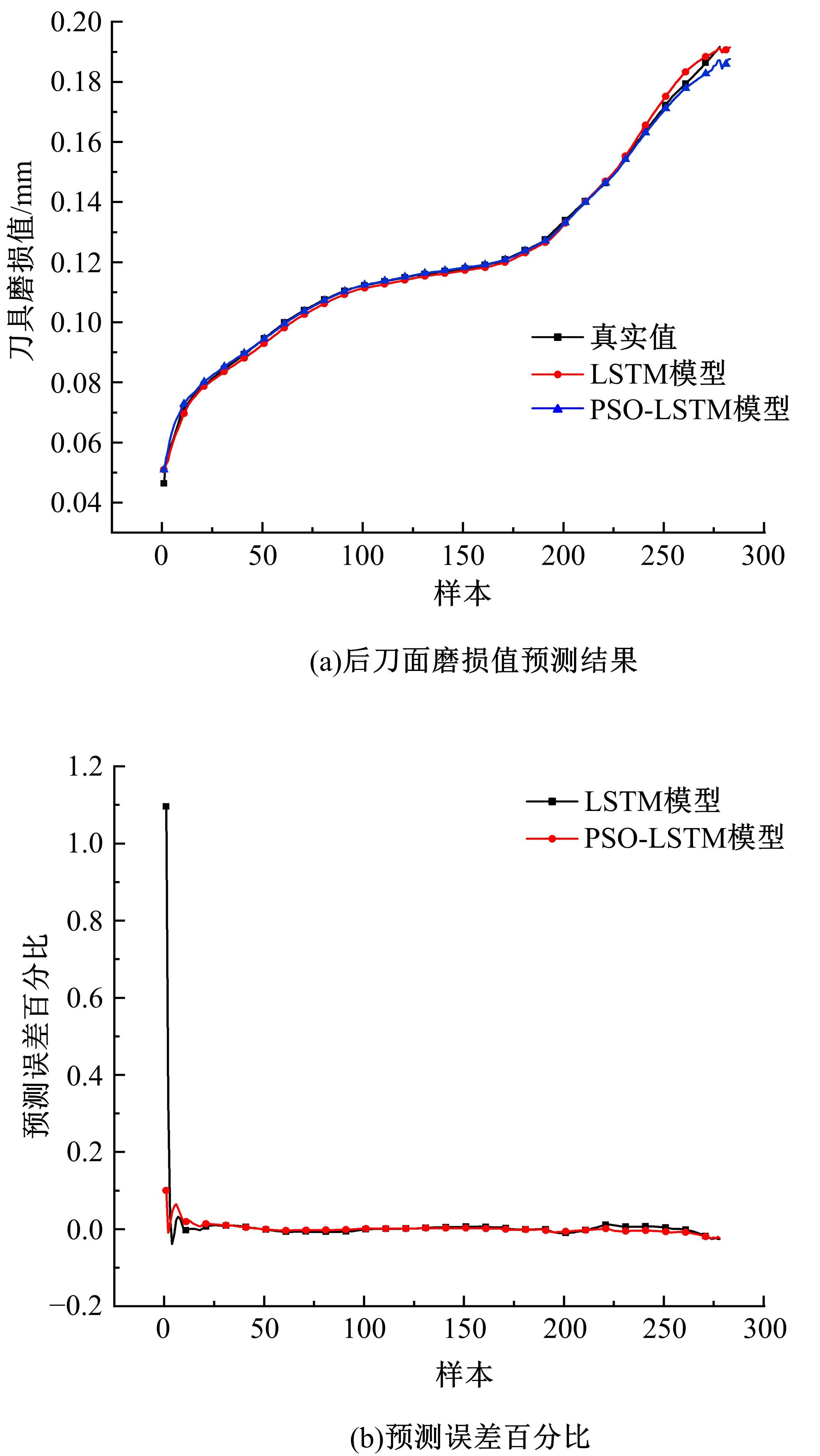
为确保车削加工的表面质量和加工稳定性,实现对车刀磨损状态的实时准确监控,提出了基于小波阈值去噪、长短时记忆(LSTM)网络和粒子群优化算法(PSO)的刀具磨损状态预测模型。采用改进多项式阈值函数对刀具加速度振动信号进行去噪,构建了优质的信号输入样本。训练长短时记忆网络对刀具后刀面磨损值进行预测和磨损状态分类。利用粒子群优化算法对网络进行参数寻优,结果表明,提出的PSO-LSTM模型在预测和分类精度方面均优于未优化的LSTM网络。
中图分类号:
- TP183
| 1 | Kurada S, Bradley C. A review of machine vision sensors for tool condition monitoring[J]. Computers in Industry, 1997, 34(1): 55-72. |
| 2 | Mobley R K. An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance [M]. New York: Elsevier, 2002. |
| 3 | Gao D, Liao Z R, Lv Z, et al. Multi-scale statistical signal processing of cutting force in cutting tool condition monitoring[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 80(9): 1843-1853. |
| 4 | Antić A, Šimunović G, Šarić T, et al. A model of tool wear monitoring system for turning[J]. Tehnicki vjesnik/Technical Gazette, 2013, 20(2): 247-254. |
| 5 | Moia D F G, Thomazella I H, Aguiar P R, et al. Tool condition monitoring of aluminum oxide grinding wheel in dressing operation using acoustic emission and neural networks[J]. Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering, 2015, 37(2): 627-640. |
| 6 | 吴雪峰, 刘亚辉, 毕淞泽. 基于卷积神经网络刀具磨损类型的智能识别[J]. 计算机集成制造系统, 2020, 26(10): 2762-2771. |
| Wu Xue-feng, Liu Ya-hui, Bi Song-ze. Intelligent recognition of tool wear type based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2020, 26(10): 2762-2771. | |
| 7 | Mohanraj T, Shankar S, Rajasekar R, et al. Tool condition monitoring techniques in milling process — a review[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(1): 1032-1042. |
| 8 | Cheng M H, Jiao L, Shi X C, et al. An intelligent prediction model of the tool wear based on machine learning in turning high strength steel[J]. Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 2020, 234(13): 1580-1597. |
| 9 | Kong D D, Chen Y J, Li N. Gaussian process regression for tool wear prediction[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 104: 556-574. |
| 10 | Du M H, Wang P X, Wang J H, et al. Intelligent turning tool monitoring with neural network adaptive learning[J]. Complexity, 2019(5A): 1-21. |
| 11 | Kong D D, Chen Y J, Li N, et al. Tool wear estimation in end milling of titanium alloy using NPE and a novel WOA-SVM model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(7): 5219-5232. |
| 12 | Yen C L, Lu M C, Chen J. Applying the self-organizing feature map (SOM) algorithm to AE-based tool wear monitoring in micro-cutting[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2013, 34(1/2): 353-366. |
| 13 | Ertunc H M, Loparo K A, Ocak H. Tool wear condition monitoring in drilling operations using hidden Markov models (HMMs)[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2001, 41(9): 1363-1384. |
| 14 | 郭亮, 高宏力, 张一文, 等. 基于深度学习理论的轴承状态识别研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(12): 166-170, 195. |
| Guo Liang, Gao Hong-li, Zhang Yi-wen, et al. Research on bearing condition monitoring based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(12): 166-170, 195. | |
| 15 | Huang Z, Zhu J, Lei J, et al. Tool wear predicting based on multi-domain feature fusion by deep convolutional neural network in milling operations[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020, 31(4): 953-966. |
| 16 | Ma J, Luo D, Liao X, et al. Tool wear mechanism and prediction in milling TC18 titanium alloy using deep learning[J]. Measurement, 2021, 173: No. 108554. |
| 17 | Kong D, Chen Y, Li N. Monitoring tool wear using wavelet package decomposition and a novel gravitational search algorithm⁃least square support vector machine model[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2019, 234(3): No. 095440621988731. |
| 18 | Xie Y, Zhang C, Liu Q. Tool wear status recognition and prediction model of milling cutter based on deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2020(9): 1616-1625. |
| 19 | Cheng M H, Jiao L, Shi X C, et al. An intelligent prediction model of the tool wear based on machine learning in turning high strength steel[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part B Journal of Engineering Manufacture, 2020, 234(13): 1580-1597. |
| 20 | EN 10084-2008. Case hardening steels⁃technical delivery conditions [S]. |
| 21 | . Tool-life testing with single-point turning tools [S]. |
| [1] | 刘嫣然,孟庆瑜,郭洪艳,李嘉霖. 图注意力模式下融合高精地图的周车轨迹预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 792-801. |
| [2] | 何科,丁海涛,赖宣淇,许男,郭孔辉. 基于Transformer的轮式里程计误差预测模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 653-662. |
| [3] | 高金武,贾志桓,王向阳,邢浩. 基于PSO-LSTM的质子交换膜燃料电池退化趋势预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(9): 2192-2202. |
| [4] | 李晓英,杨名,全睿,谭保华. 基于深度学习的不均衡文本分类方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1889-1895. |
| [5] | 申铉京,张雪峰,王玉,金玉波. 像素级卷积神经网络多聚焦图像融合算法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1857-1864. |
| [6] | 胡丹,孟新. 基于时变网格的对地观测卫星搜索海上船舶方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(8): 1896-1903. |
| [7] | 高明华,杨璨. 基于改进卷积神经网络的交通目标检测方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(6): 1353-1361. |
| [8] | 欧阳继红,郭泽琪,刘思光. 糖尿病视网膜病变分期双分支混合注意力决策网络[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(3): 648-656. |
| [9] | 宋林,王立平,吴军,关立文,刘知贵. 基于信息物理融合和数字孪生的可靠性分析[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 439-449. |
| [10] | 曹洁,马佳林,黄黛麟,余萍. 一种基于多通道马尔可夫变迁场的故障诊断方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 491-496. |
| [11] | 蒋仁言,熊彬彬. 基于等效加工时间模型的机床退化过程建模[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(2): 483-490. |
| [12] | 燕杨,尤紫如,姚远,黄文博. 基于注意力U-Net的视网膜血管分类识别[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2933-2940. |
| [13] | 杨军,高志明. 基于无监督变形网络的三维模型稠密对应关系计算[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2971-2983. |
| [14] | 侯春萍,杨庆元,黄美艳,王致芃. 基于语义耦合和身份一致性的跨模态行人重识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2954-2963. |
| [15] | 刘元宁,朱琳,朱晓冬,刘震,吴浩萌. 基于生成模型提升训练的深度学习虹膜识别方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2022, 52(12): 2924-2932. |
|
||